How 3D Printing Improves Visualization of Complex Intestinal Structures?
Enhanced Anatomical Accuracy
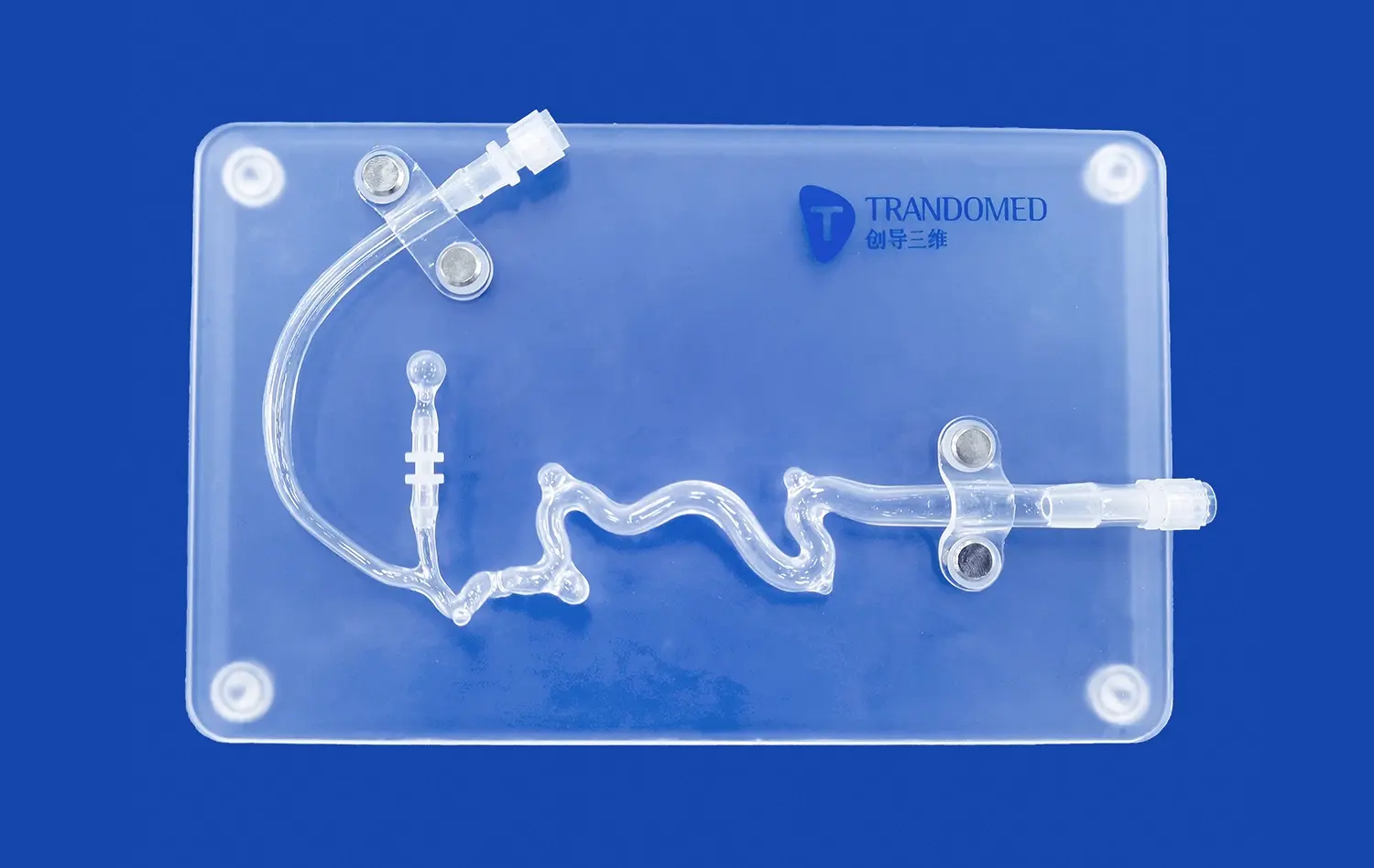
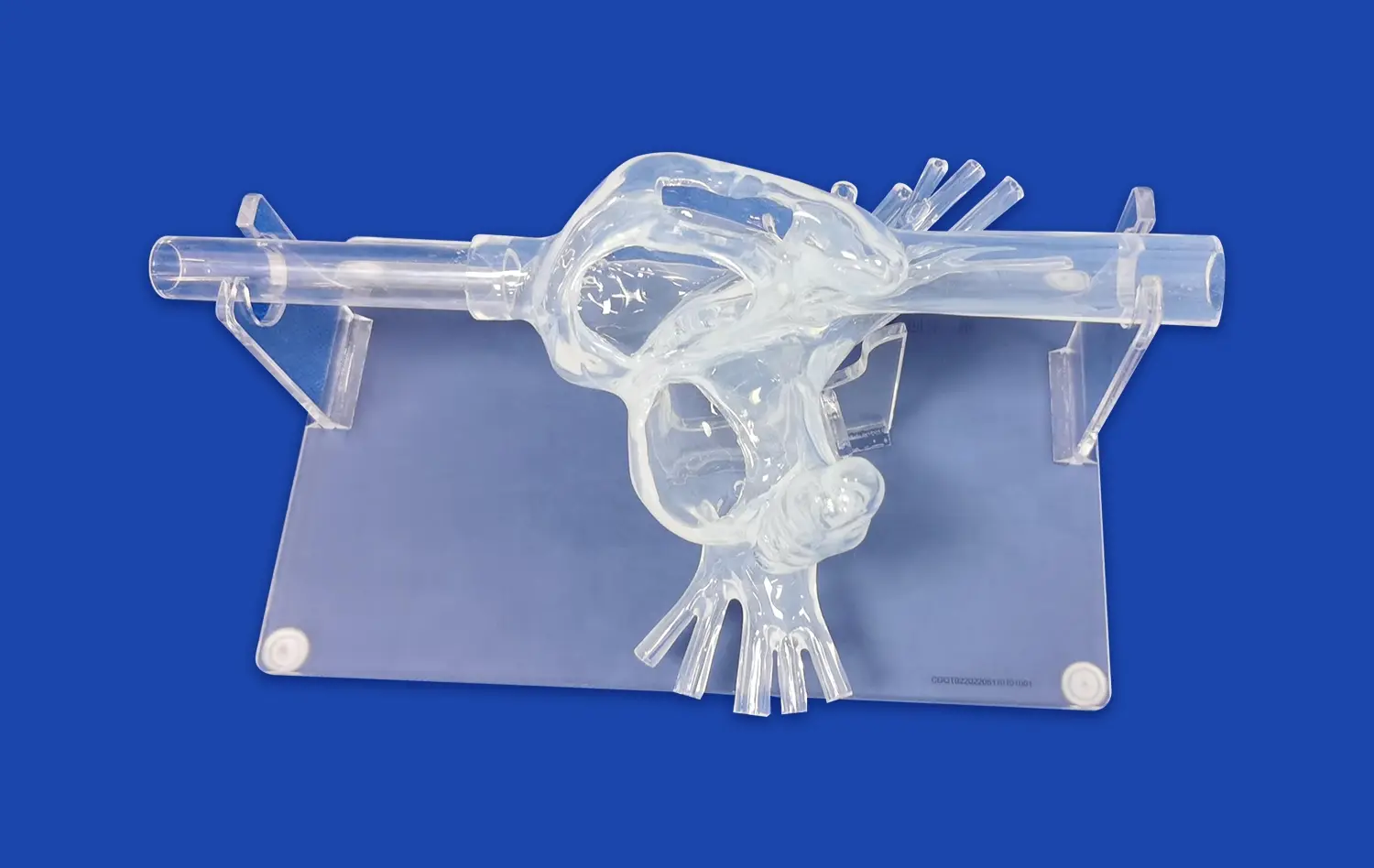
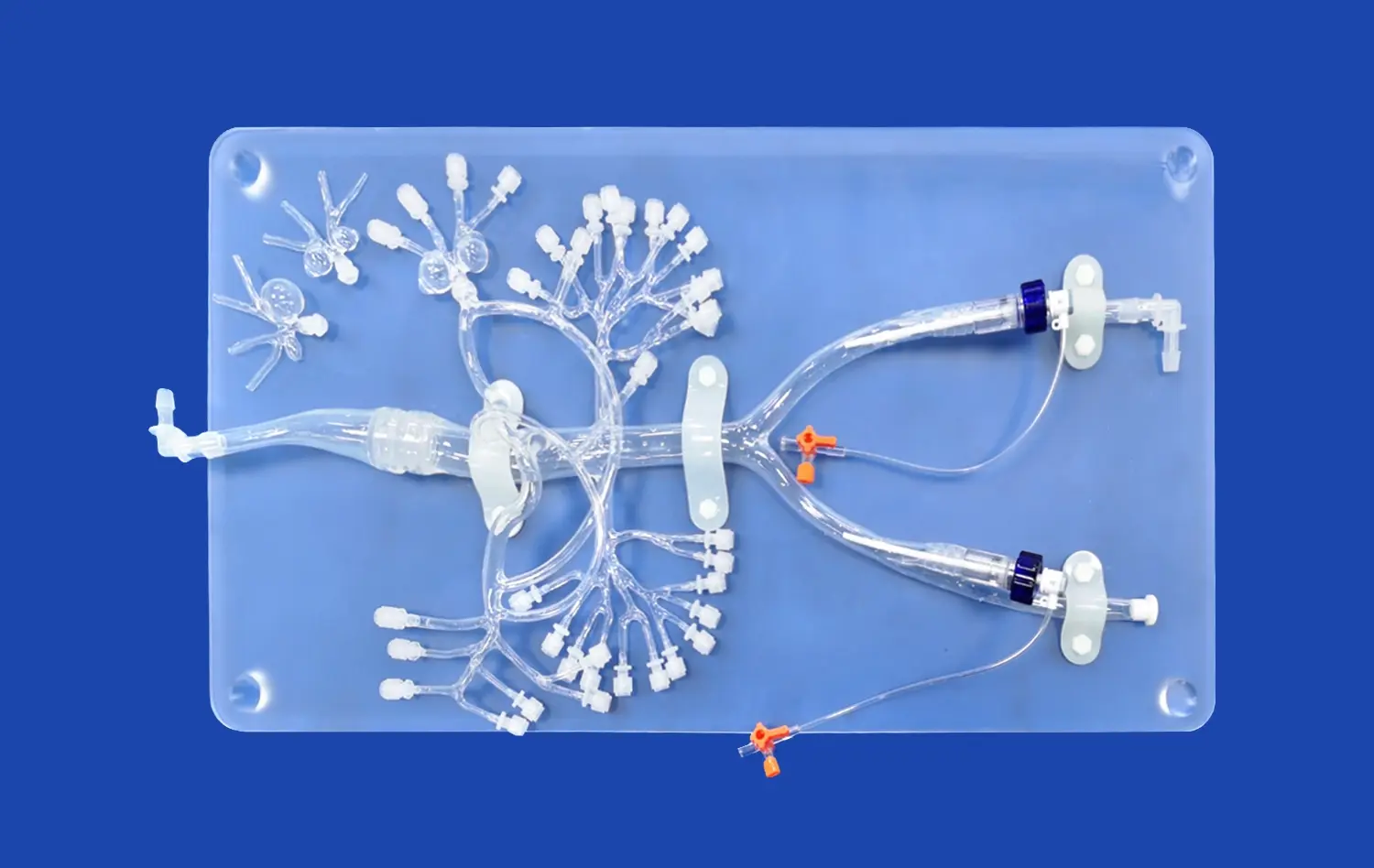
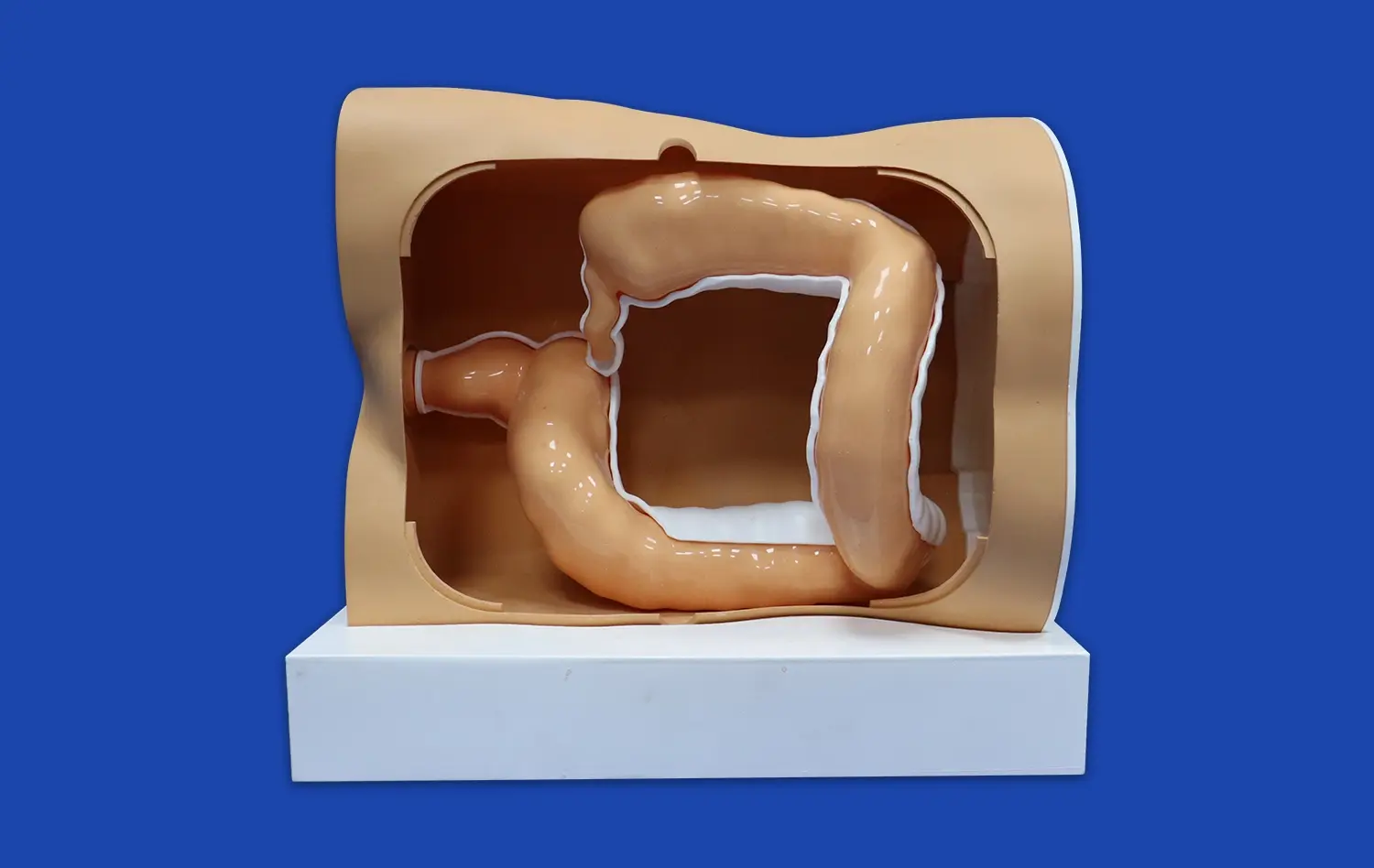
3D printed small intestine models offer unparalleled anatomical accuracy, capturing even the most minute details of the intestinal structure. By utilizing high-resolution imaging data from CT and MRI scans, these models faithfully reproduce the intricate folds, villi, and overall architecture of the small intestine. This level of precision allows learners to observe and understand the complex relationships between different anatomical features, providing a more comprehensive view of intestinal anatomy than traditional 2D images or textbook illustrations.
Realistic Texture and Tactile Feedback
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printed intestinal models is their ability to mimic the texture and feel of actual tissue. Advanced materials used in the printing process can replicate the softness and pliability of intestinal walls, giving students a realistic tactile experience. This haptic feedback is crucial for developing a true understanding of the organ's properties and how it might behave during surgical procedures or diagnostic examinations.
Customizable and Pathology-Specific Models
3D printing technology allows for the creation of customized small intestine models that can showcase specific pathologies or variations in anatomy. Educators can design models that illustrate common intestinal conditions such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or intestinal tumors. These pathology-specific models provide invaluable tools for teaching differential diagnosis and understanding the physical manifestations of various gastrointestinal disorders.
Interactive Learning Tools for Students and Trainees
Hands-on Exploration and Manipulation
3D printed small intestine models serve as interactive learning tools that encourage hands-on exploration. Students can physically manipulate the models, feeling the contours and examining the structures from various angles. This tactile interaction reinforces spatial relationships and helps learners develop a three-dimensional understanding of intestinal anatomy that is difficult to achieve through traditional learning methods.
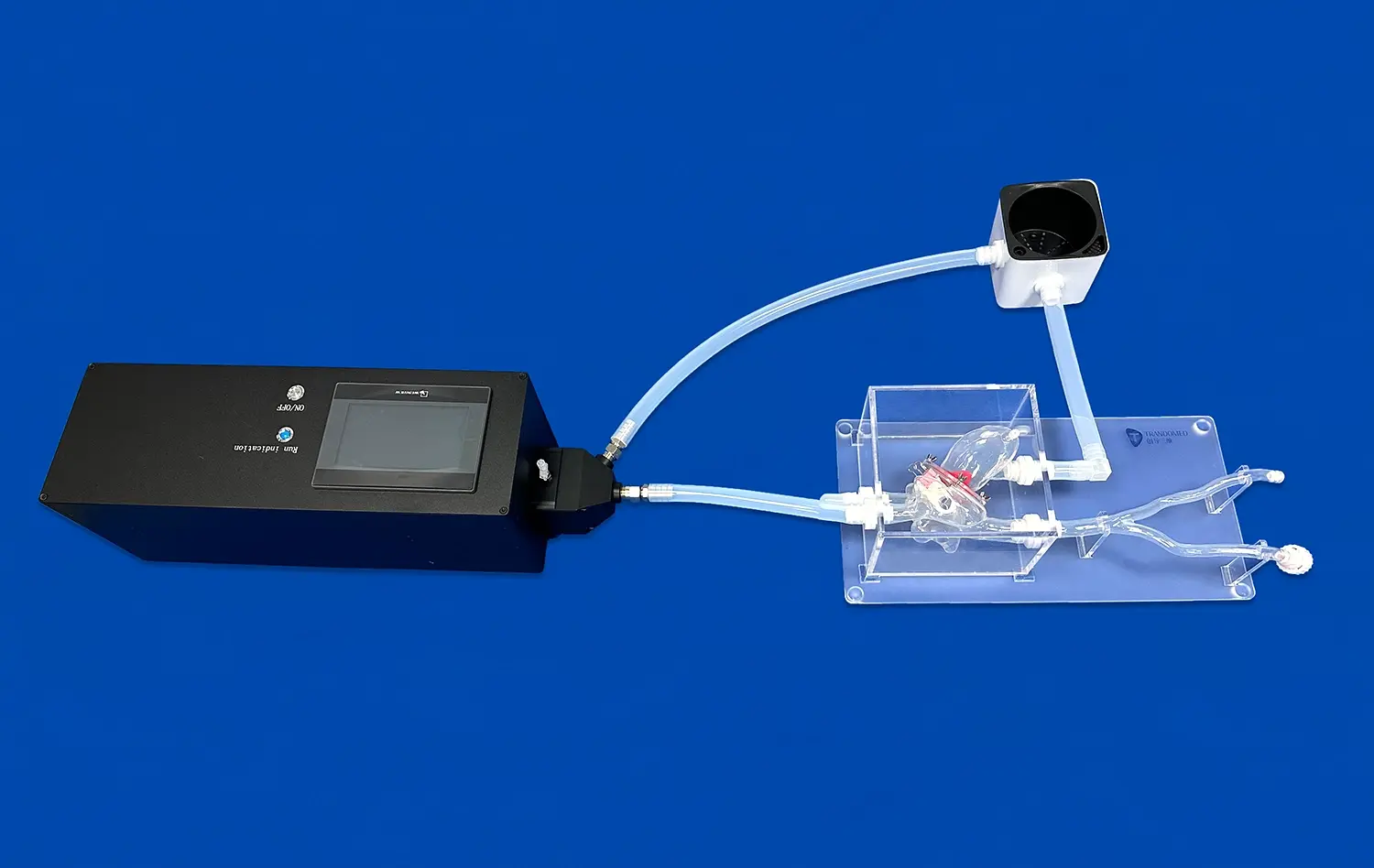
Simulation of Surgical Procedures
For medical trainees and surgical residents, 3D printed intestinal models offer a safe environment to practice surgical techniques. These models can be designed to simulate various surgical scenarios, allowing trainees to rehearse procedures such as intestinal resections, anastomoses, or endoscopic interventions. The ability to practice on realistic models enhances surgical skills and confidence before performing procedures on actual patients.
Collaborative Learning and Case Studies
3D printed small intestine models facilitate collaborative learning experiences. Groups of students can gather around a model to discuss case studies, pointing out anatomical features and debating diagnostic approaches. This interactive approach fosters teamwork and communication skills essential in medical practice. Additionally, instructors can use these models as focal points for problem-based learning exercises, challenging students to apply their knowledge to real-world clinical scenarios.
How Models Facilitate Mastery of Intestinal Anatomy and Physiology?
Visualization of Functional Anatomy
3D printed small intestine models excel in demonstrating the functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract. By incorporating features such as color-coded segments or removable layers, these models can illustrate the different functional zones of the small intestine, including the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. This visual representation helps learners understand how the structure of each segment relates to its specific physiological functions, such as nutrient absorption or hormone secretion.
Integration of Microscopic and Macroscopic Views
Advanced 3D printing techniques allow for the creation of models, such as the small intestine model, that seamlessly integrate microscopic and macroscopic views of intestinal anatomy. For instance, a model might feature a magnified section showing the structure of intestinal villi and microvilli alongside a full-scale representation of the organ. This multi-scale approach bridges the gap between histological understanding and gross anatomy, providing a comprehensive view of intestinal structure and function.
Dynamic Models for Physiological Processes
Innovative 3D printed small intestine models can incorporate dynamic elements to demonstrate physiological processes. For example, models with flexible components can simulate peristaltic movements, helping students visualize how food is propelled through the intestinal tract. Similarly, models with interchangeable parts can illustrate changes in the intestinal lining during different phases of digestion or in response to various stimuli, enhancing understanding of gastrointestinal physiology.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D printed small intestine models into anatomy education represents a significant leap forward in medical training. These innovative tools offer unparalleled realism, interactivity, and customization, enabling students and healthcare professionals to gain a deeper, more nuanced understanding of intestinal anatomy and physiology. By providing hands-on learning experiences and bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, these models are transforming how we approach gastrointestinal education and training. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and realistic models to emerge, further enhancing the quality of medical education and ultimately improving patient care.
Contact Us
Experience the future of medical education with Trandomed's cutting-edge 3D printed small intestine models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of advanced medical simulators, we offer customizable, high-fidelity anatomical models that meet the diverse needs of educational institutions, research facilities, and healthcare providers. Our state-of-the-art 3D printing technology and expert design team ensure unparalleled accuracy and realism in every model. Elevate your anatomy teaching and training programs with our innovative solutions. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about how our small intestine models and other medical simulators can transform your educational experience.