What Role Do Aneurysm Models Play in Neurosurgical Residency Programs?
Enhancing Anatomical Understanding
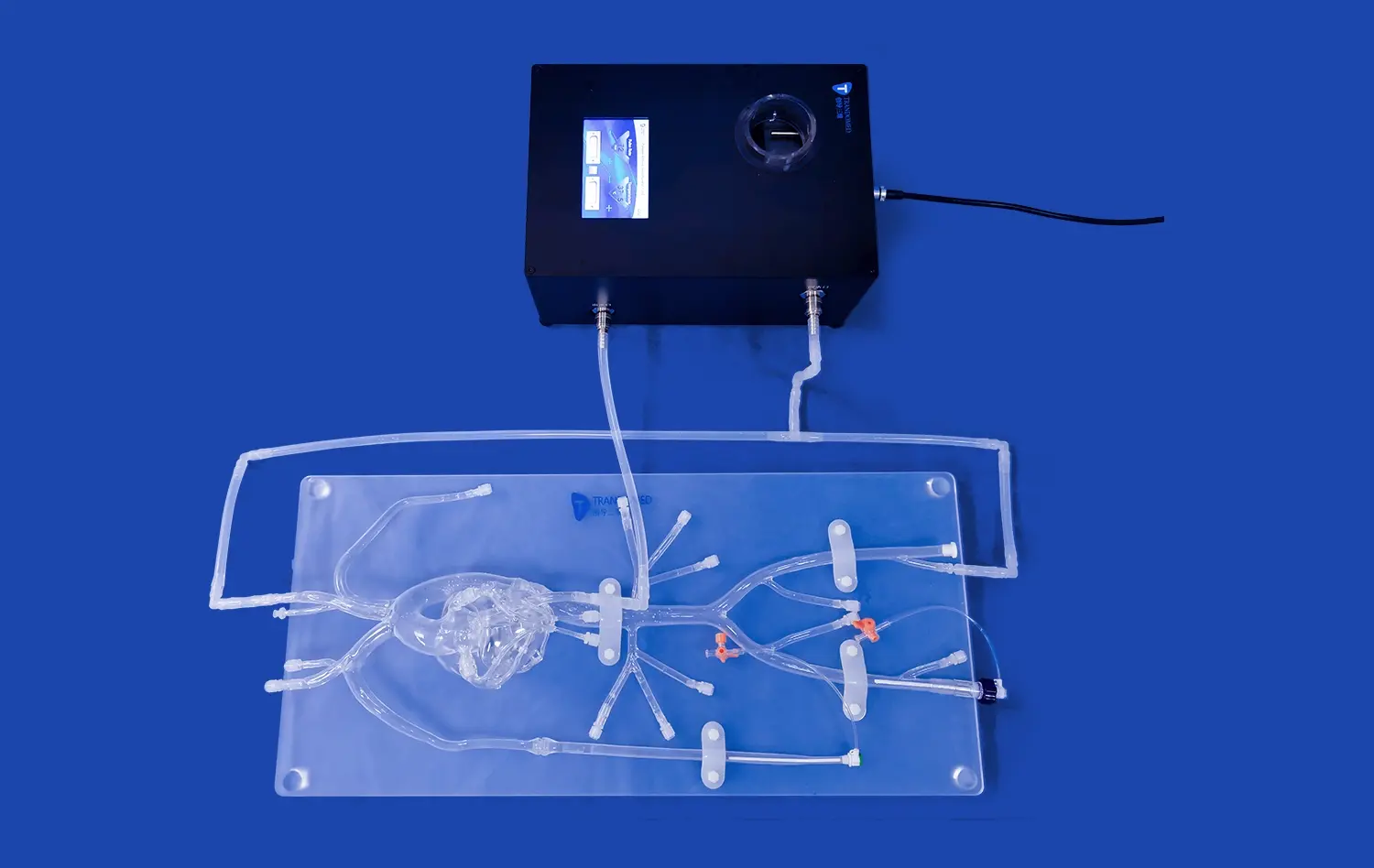
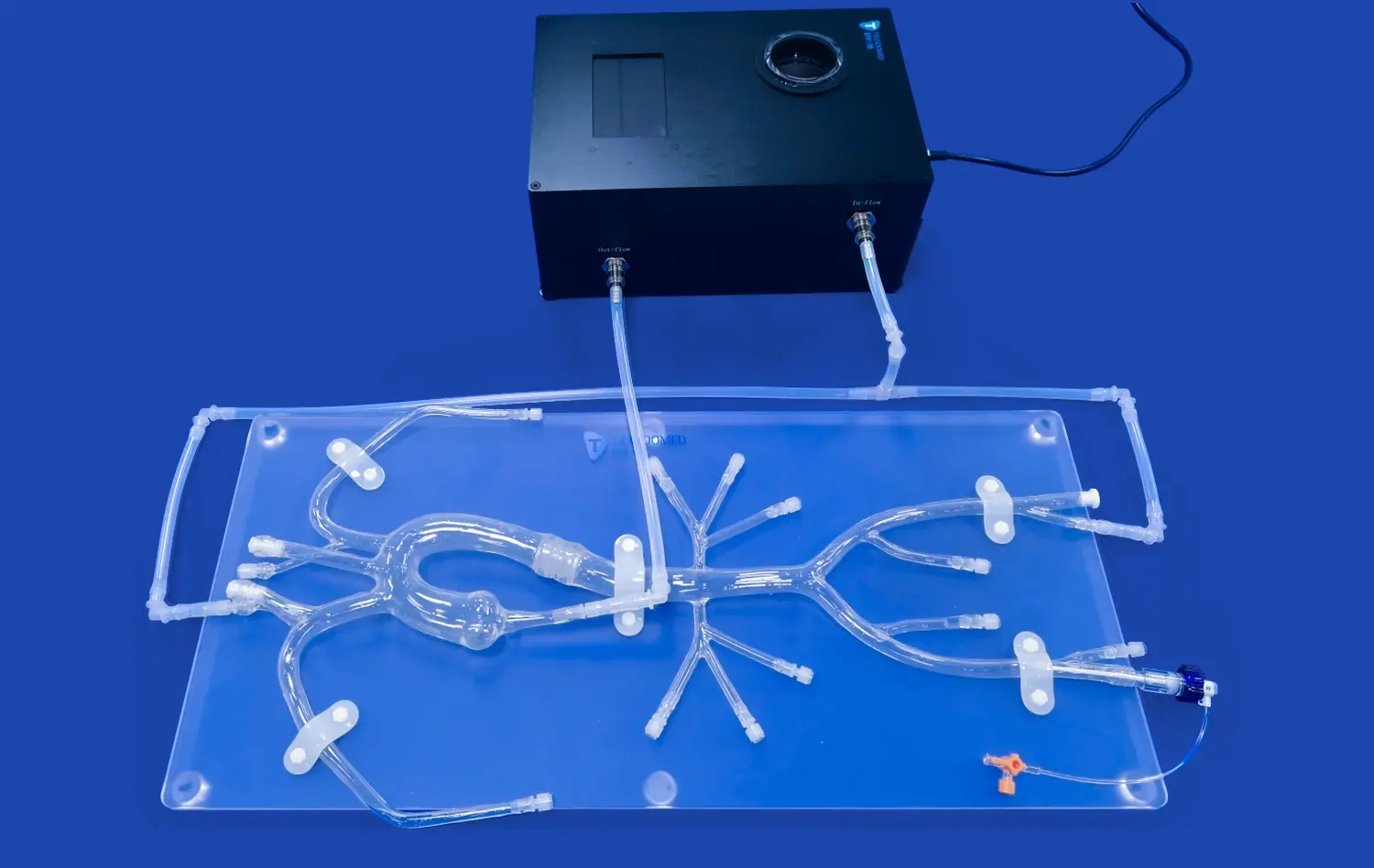
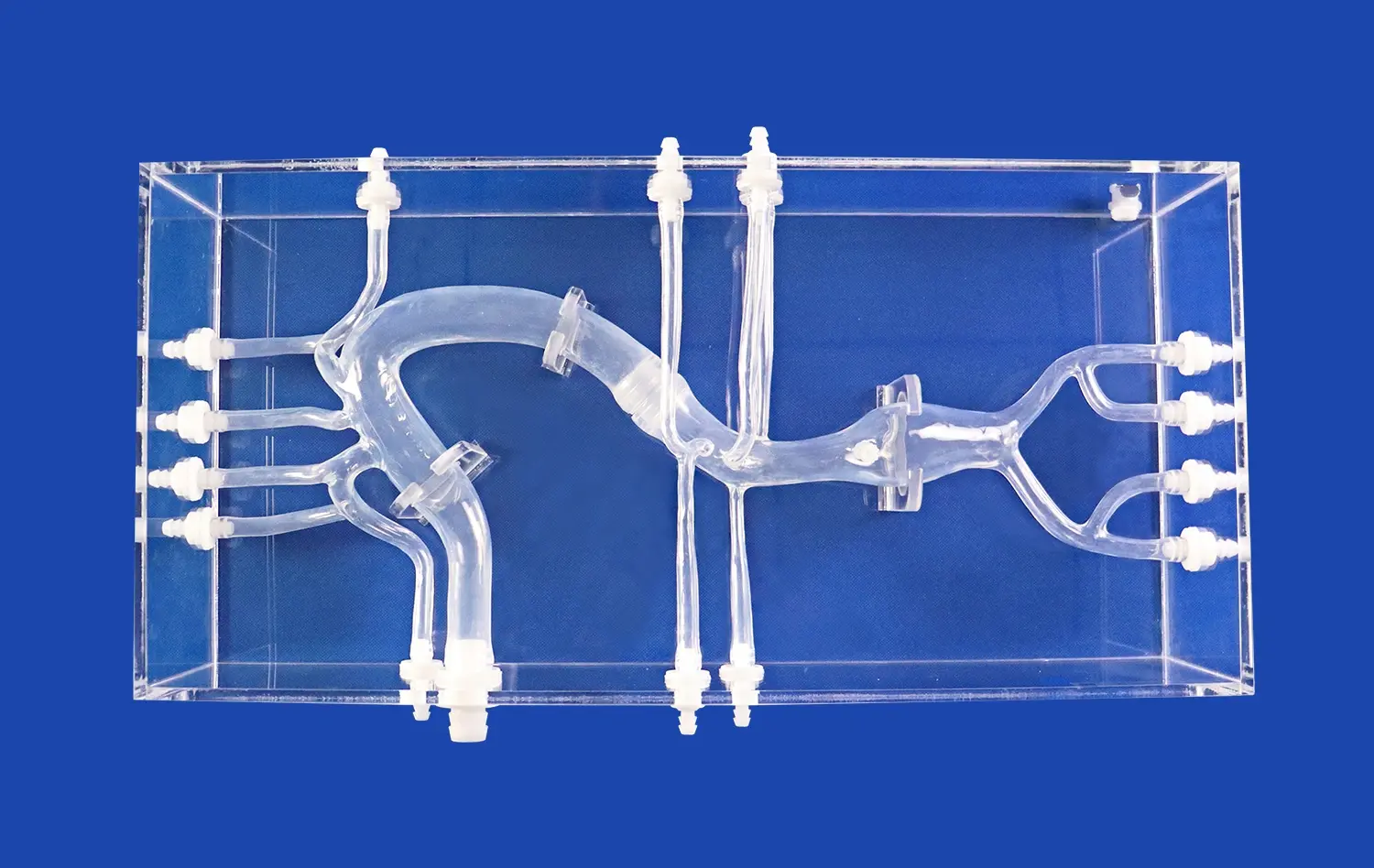
Aneurysm models serve as a cornerstone in neurosurgical residency programs, providing an unparalleled opportunity for residents to gain intimate knowledge of cerebrovascular anatomy. These models, such as the SJX011, meticulously recreate the complex network of arteries in the brain, including the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), middle cerebral artery (MCA), and the tortuous internal carotid artery. By interacting with these highly detailed representations, residents can develop a three-dimensional understanding of vascular structures that far surpasses what can be gleaned from textbooks or two-dimensional imaging alone.
Facilitating Procedural Familiarity
One of the primary advantages of incorporating aneurysm models into residency training is the ability to familiarize trainees with various neurosurgical procedures before they ever step into an operating room. The SJX011 model, for instance, is engineered to simulate the aneurysm tamponade operation, allowing residents to practice endovascular coiling, clipping, and other critical neurosurgical techniques. This hands-on experience is invaluable in building confidence and competence in performing these delicate procedures.
Promoting Patient Safety
By providing a risk-free environment for practice and experimentation, aneurysm models play a crucial role in promoting patient safety. Residents can make mistakes, learn from them, and refine their techniques without any danger to real patients. This safe learning environment is particularly important given the high-stakes nature of neurosurgical interventions, where even small errors can have significant consequences. The use of models like the SJX011 ensures that when residents do begin working with actual patients, they are well-prepared and have already overcome many of the initial learning hurdles.
Simulation-Based Skill Building for Complex Brain Aneurysm Procedures
Mastering Endovascular Techniques
Simulation-based training using aneurysm models is particularly effective for mastering endovascular techniques. The SJX011 model, with its realistic representation of cerebral vasculature and multiple aneurysms, provides an ideal platform for practicing catheter navigation through tortuous blood vessels. Residents can refine their skills in guidewire manipulation, catheter placement, and coil deployment, all crucial elements of successful endovascular procedures. The ability to repeat these techniques multiple times in a low-pressure environment allows for the development of muscle memory and procedural fluency.
Perfecting Microsurgical Clipping
For open surgical approaches, aneurysm models offer an unparalleled opportunity to perfect microsurgical clipping techniques. The SJX011 model's replaceable aneurysm lesions on the MCA allow for varied training scenarios, mimicking different aneurysm morphologies and locations. Residents can practice proper clip placement, ensuring complete aneurysm occlusion while preserving blood flow to vital brain regions. This hands-on experience is crucial for developing the fine motor skills and spatial awareness required for successful aneurysm clipping.
Adapting to Anatomical Variations
One of the challenges in neurosurgery is adapting to the wide range of anatomical variations encountered in patients. Advanced aneurysm models can be customized to reflect these variations, allowing residents to experience and prepare for diverse scenarios. The ability to adjust the tortuosity of the internal carotid artery or the radius of the MCA and ACA in models like the SJX011 ensures that trainees are exposed to a broad spectrum of anatomical challenges. This exposure is crucial for developing the adaptability and problem-solving skills essential for successful neurosurgical practice.
Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice in Neurosurgery Training
Integrating Theoretical Knowledge with Practical Skills
Aneurysm models serve as a critical bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application in neurosurgery training. While textbooks and lectures provide the foundational understanding of cerebrovascular pathology and treatment principles, these models offer the tangible experience necessary to truly internalize this knowledge. By working with the SJX011 model, residents can see firsthand how the principles of fluid dynamics affect aneurysm formation and how different intervention strategies impact blood flow. This hands-on experience reinforces theoretical concepts and helps trainees develop a more intuitive understanding of neurovascular anatomy and pathology.
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills
Beyond technical skills, aneurysm models play a crucial role in developing the decision-making abilities of future neurosurgeons. By presenting trainees with various aneurysm configurations and associated challenges, these models force residents to think critically about treatment strategies. Should an aneurysm be clipped or coiled? How should the approach be modified based on the aneurysm's location and morphology? The ability to practice these decision-making processes in a consequence-free environment is invaluable for building the confidence and judgment necessary for real-world patient care.
Facilitating Interdisciplinary Training
Aneurysm models like the SJX011 also facilitate interdisciplinary training, an increasingly important aspect of modern neurosurgery. These models can be used in collaborative sessions involving neurosurgeons, interventional neuroradiologists, and other specialists involved in the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders. By providing a common platform for discussion and practice, aneurysm models help foster better communication and understanding between different specialties, ultimately leading to more cohesive and effective patient care teams.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced aneurysm models into neurosurgical training programs represents a significant leap forward in preparing the next generation of neurosurgeons. These models, exemplified by the SJX011 Intracranial Vascular with aneurysm model, provide an unparalleled platform for skill development, anatomical understanding, and clinical decision-making. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, they ensure that future neurosurgeons are well-equipped to handle the complexities of cerebrovascular interventions, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and safer surgical practices.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we're committed to advancing neurosurgical education through innovative simulation technologies. Our range of customizable aneurysm models offers unparalleled realism and versatility for training programs worldwide. To learn more about how our products can enhance your neurosurgical training curriculum, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Let's work together to shape the future of neurosurgery education.
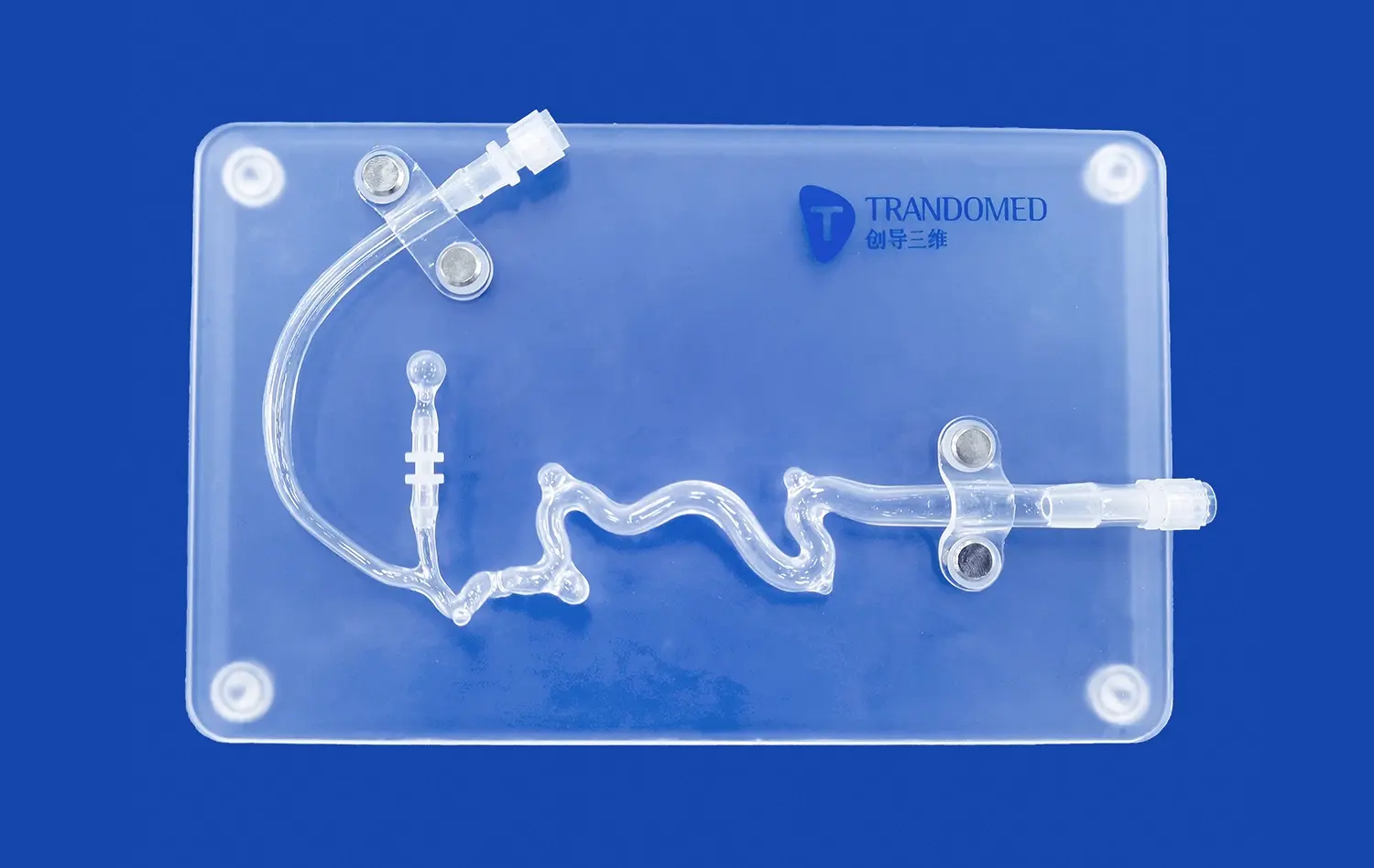

1_1732869849284.webp)
_1732866687283.webp)