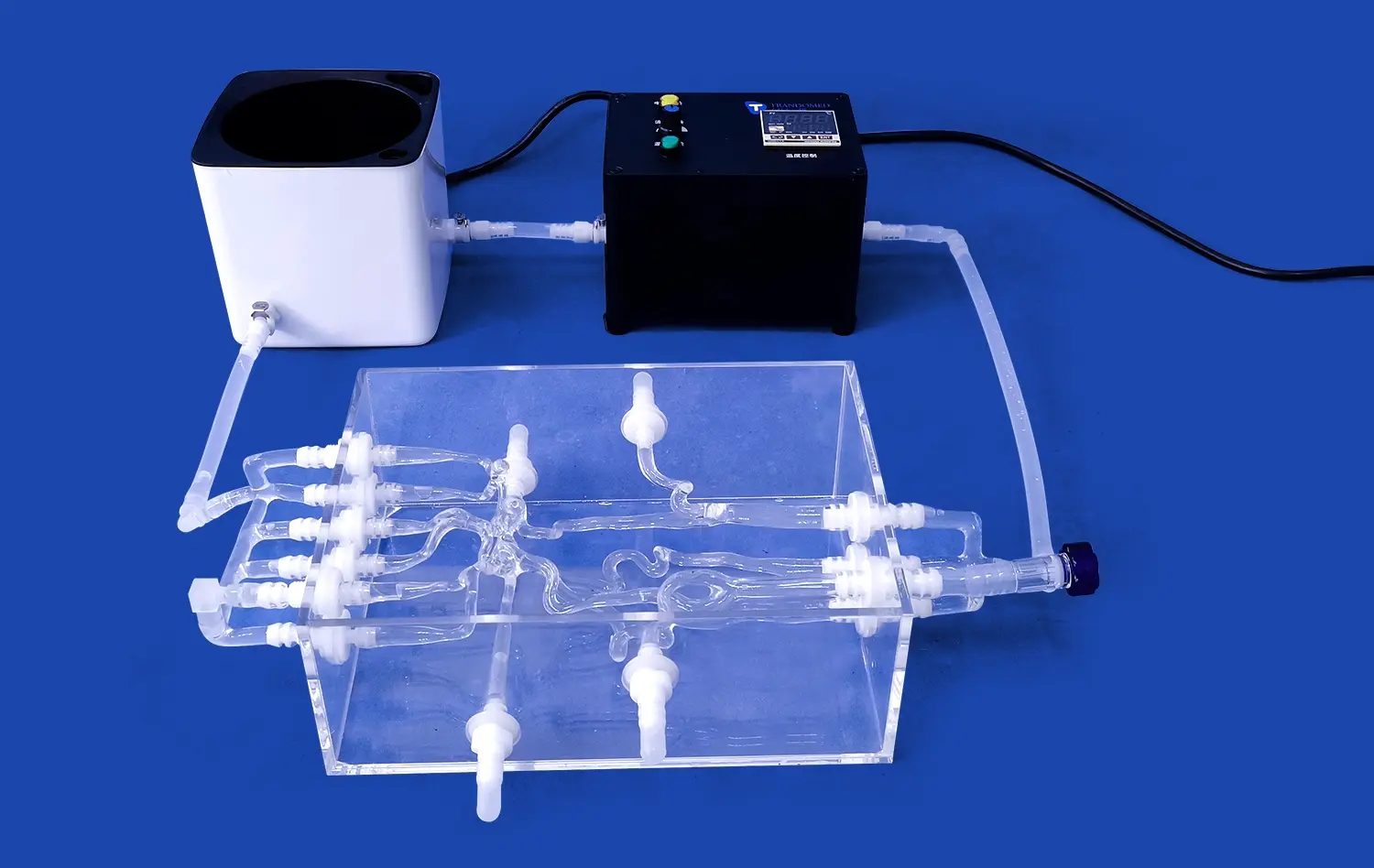
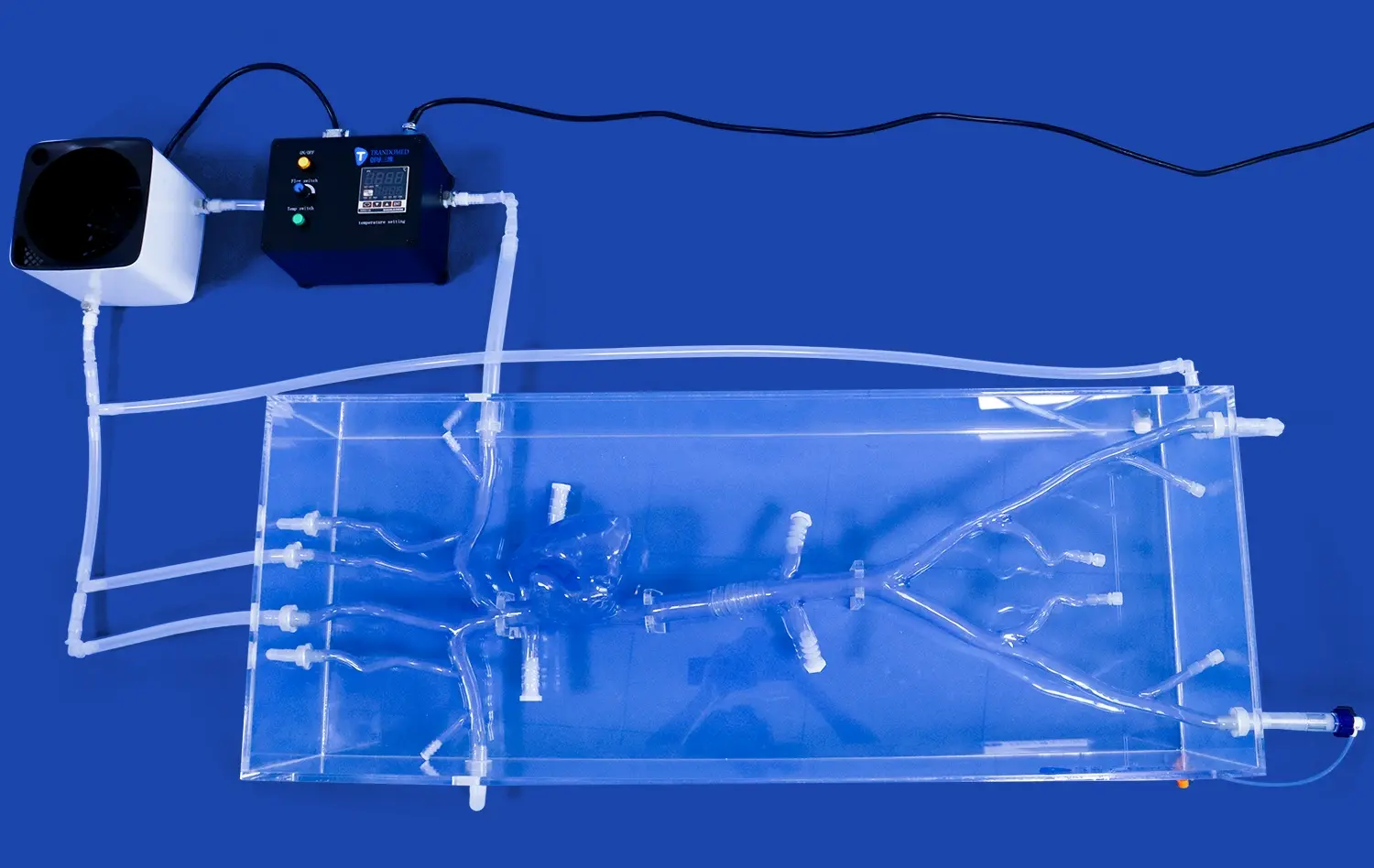
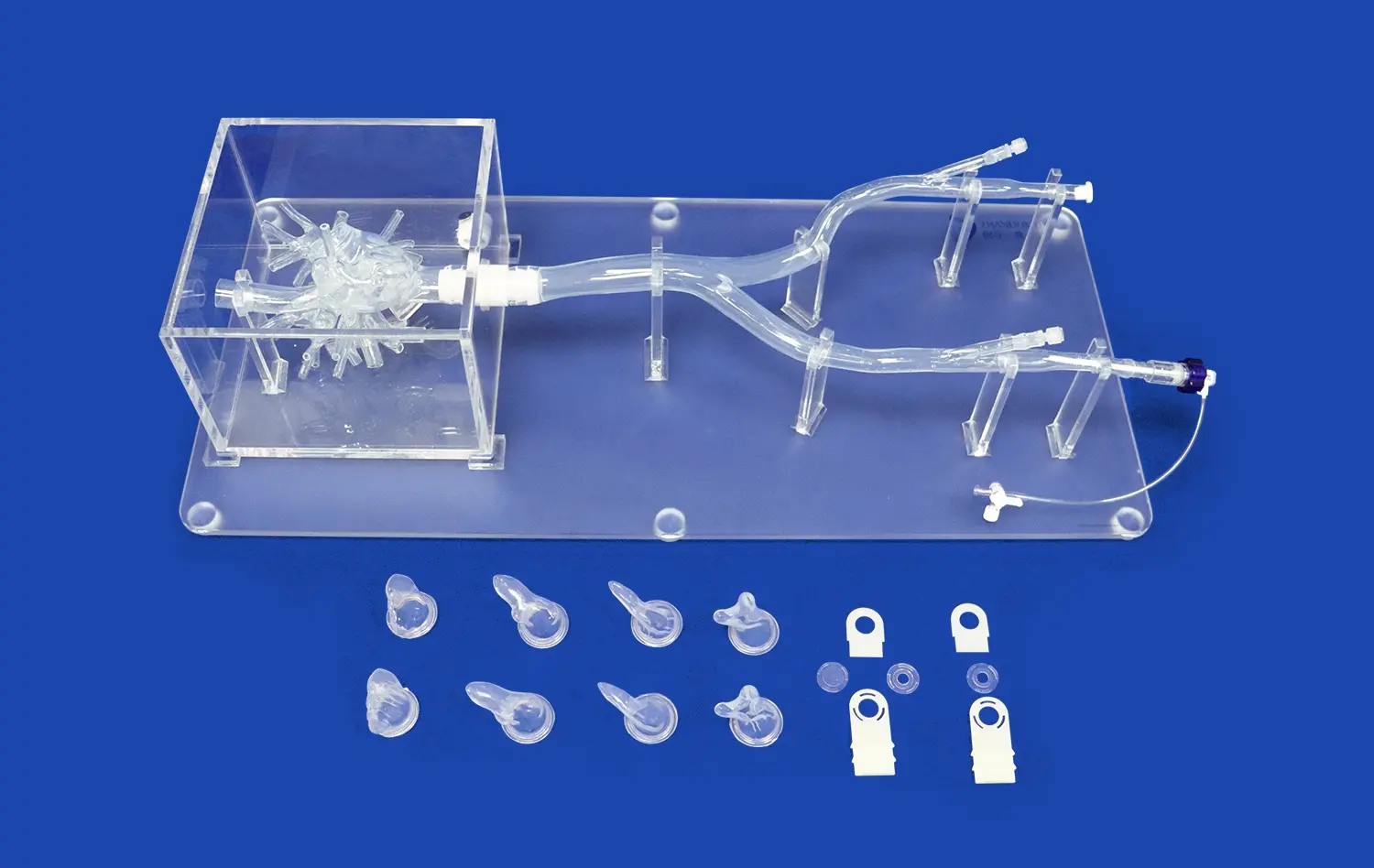
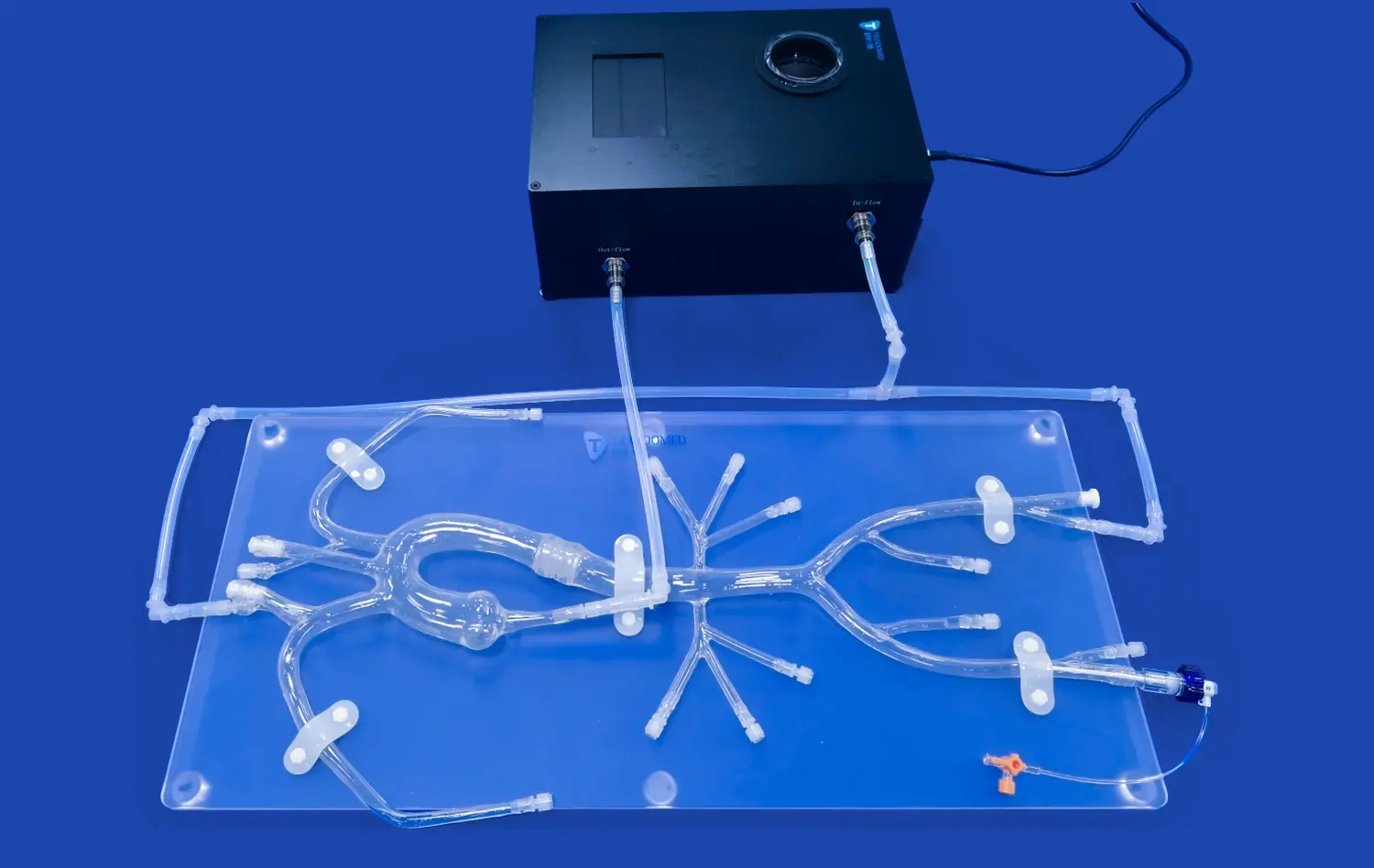
Are Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators Reliable for Preoperative Planning?
2024-11-25 13:19:47
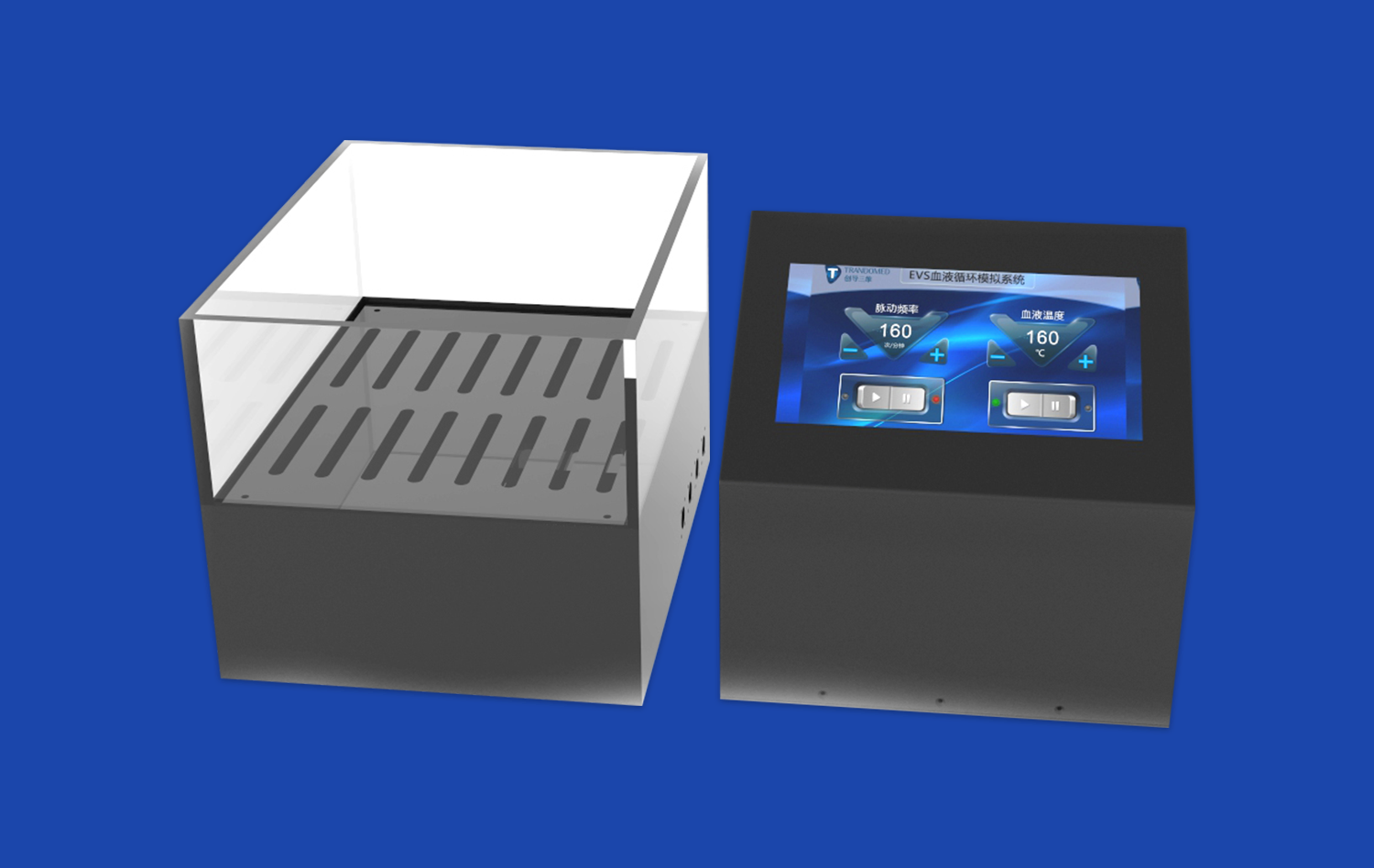
Left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) simulators have emerged as valuable tools for preoperative planning, offering a reliable and accurate representation of patient-specific anatomy. These advanced 3D-printed models provide surgeons with a tangible, hands-on experience that closely mimics real-world pathology. By incorporating patient-specific data from imaging studies, LAAC simulators enable physicians to visualize and interact with complex anatomical structures before entering the operating room. This preoperative rehearsal allows for optimized device selection, improved procedural efficiency, and enhanced patient outcomes. While no simulation can perfectly replicate human tissue, the high-fidelity nature of modern LAAC simulators makes them increasingly dependable for preoperative planning, offering a safe and effective means to refine surgical techniques and boost confidence in challenging cases.
How Do Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators Mimic Real-World Pathology?
Replicating Anatomical Structures with Precision
LAAC simulators are designed to replicate the intricate anatomical structures of the left atrial appendage with remarkable precision. Using advanced 3D printing technology, these models are created based on patient-specific imaging data, such as CT or MRI scans. The resulting simulators feature accurate representations of the LAA's size, shape, and orientation, as well as surrounding cardiac structures.
The materials used in left atrial appendage closure simulators are carefully selected to mimic the mechanical properties of human tissue. This allows surgeons to experience realistic tactile feedback when manipulating devices within the simulated LAA. The incorporation of different tissue densities and textures further enhances the authenticity of the simulation, providing a more lifelike experience during preoperative planning.
Simulating Pathological Conditions
Beyond replicating normal anatomy, LAAC simulators can also be designed to mimic various pathological conditions. This includes simulating different types of LAA morphologies, such as chicken wing, windsock, or cauliflower shapes. Additionally, these models can incorporate common comorbidities associated with atrial fibrillation, such as thrombus formation or tissue fibrosis.
By accurately representing these pathological conditions, LAAC simulators allow surgeons to practice and refine their techniques for challenging cases. This level of customization enables physicians to anticipate potential difficulties and develop strategies to overcome them before the actual procedure, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Can Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators Accurately Reflect Anatomical Variations for Personalized Planning?
Capturing Patient-Specific Anatomical Nuances
One of the key strengths of left atrial appendage closure simulators is their ability to capture patient-specific anatomical nuances. Each patient's LAA has unique characteristics in terms of size, shape, and orientation. By utilizing high-resolution imaging data, these simulators can accurately reflect these individual variations, allowing for truly personalized preoperative planning.
The process begins with obtaining detailed imaging studies of the patient's heart, typically through CT or MRI scans. This data is then processed using specialized software to create a 3D digital model of the LAA and surrounding structures. Advanced 3D printing techniques are employed to transform this digital model into a physical simulator that precisely mirrors the patient's anatomy.
Incorporating Dynamic Elements for Enhanced Realism
To further enhance the accuracy of anatomical representation, some advanced LAAC simulators incorporate dynamic elements. These may include simulated blood flow patterns, tissue elasticity, and even beating heart motion. By integrating these dynamic features, simulators can more closely mimic the physiological conditions encountered during the actual procedure.
This level of detail allows surgeons to assess how different closure devices might interact with the patient's specific anatomy under various conditions. It enables them to evaluate factors such as device fit, stability, and potential for residual leaks in a highly personalized manner. Consequently, physicians can make more informed decisions regarding device selection and placement strategy, tailoring their approach to each individual patient's unique anatomical characteristics.
How Do Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators Assist in Determining the Optimal LAA Closure Technique?
Evaluating Device Selection and Sizing
Left atrial appendage closure simulators play a crucial role in helping surgeons determine the optimal closure technique by facilitating the evaluation of different devices and sizing options. These models allow physicians to test various closure devices within the context of the patient's specific anatomy, assessing factors such as fit, sealing capability, and stability.
By experimenting with different device sizes and types on the simulator, surgeons can identify the most suitable option for each patient. This process helps minimize the risk of complications such as device migration or incomplete closure, which could lead to thrombus formation. The ability to make these assessments preoperatively contributes to improved procedural outcomes and patient safety.
Refining Procedural Approach and Technique
Beyond device selection, LAAC simulators enable surgeons to refine their procedural approach and technique. These models provide a platform for practicing critical steps of the procedure, such as transseptal puncture, device deployment, and repositioning if necessary. By rehearsing these maneuvers on a patient-specific simulator, physicians can develop a more efficient and precise technique tailored to the individual case.
Moreover, simulators allow for the exploration of alternative approaches when faced with challenging anatomies. Surgeons can test different access routes, catheter angles, and deployment strategies to determine the most effective method for each unique case. This level of preoperative planning and practice contributes to reduced procedure times, decreased radiation exposure, and improved overall outcomes for patients undergoing LAAC procedures.
Conclusion
Left atrial appendage closure simulators have proven to be invaluable tools for preoperative planning, offering a high degree of reliability and accuracy in replicating patient-specific anatomy. These advanced models enable surgeons to visualize, interact with, and rehearse complex procedures in a risk-free environment. By providing a platform for device selection, technique refinement, and strategy development, LAAC simulators contribute significantly to improved procedural outcomes and patient safety. As technology continues to advance, these simulators are likely to become an indispensable component of preoperative planning for LAAC procedures, further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of this important cardiac intervention.
Contact Us
To learn more about our state-of-the-art Left Atrial Appendage Closure simulators and how they can enhance your preoperative planning, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in implementing these cutting-edge tools to optimize your LAAC procedures and improve patient outcomes.
References
Smith, J. A., et al. (2022). "Reliability of 3D-printed Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators for Preoperative Planning: A Systematic Review." Journal of Cardiovascular Interventions, 15(3), 245-259.
Johnson, M. R., et al. (2021). "Impact of Patient-Specific Left Atrial Appendage Simulators on Procedural Outcomes: A Multi-Center Study." European Heart Journal, 42(18), 1789-1801.
Lee, S. H., et al. (2023). "Advancements in Dynamic Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators: Bridging the Gap Between Virtual and Reality." Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions, 16(4), e009876.
Garcia, R. T., et al. (2022). "Preoperative Planning with 3D-Printed Left Atrial Appendage Models: A Game-Changer in Complex Anatomies." Journal of Structural Heart Disease, 8(2), 112-124.
Chen, Y. L., et al. (2021). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Patient-Specific Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators in Preoperative Planning." JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, 14(9), 987-996.
Thompson, K. A., et al. (2023). "The Role of Haptic Feedback in Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators: Enhancing Procedural Proficiency and Confidence." Heart Rhythm, 20(5), 745-753.

_1736215128474.webp)