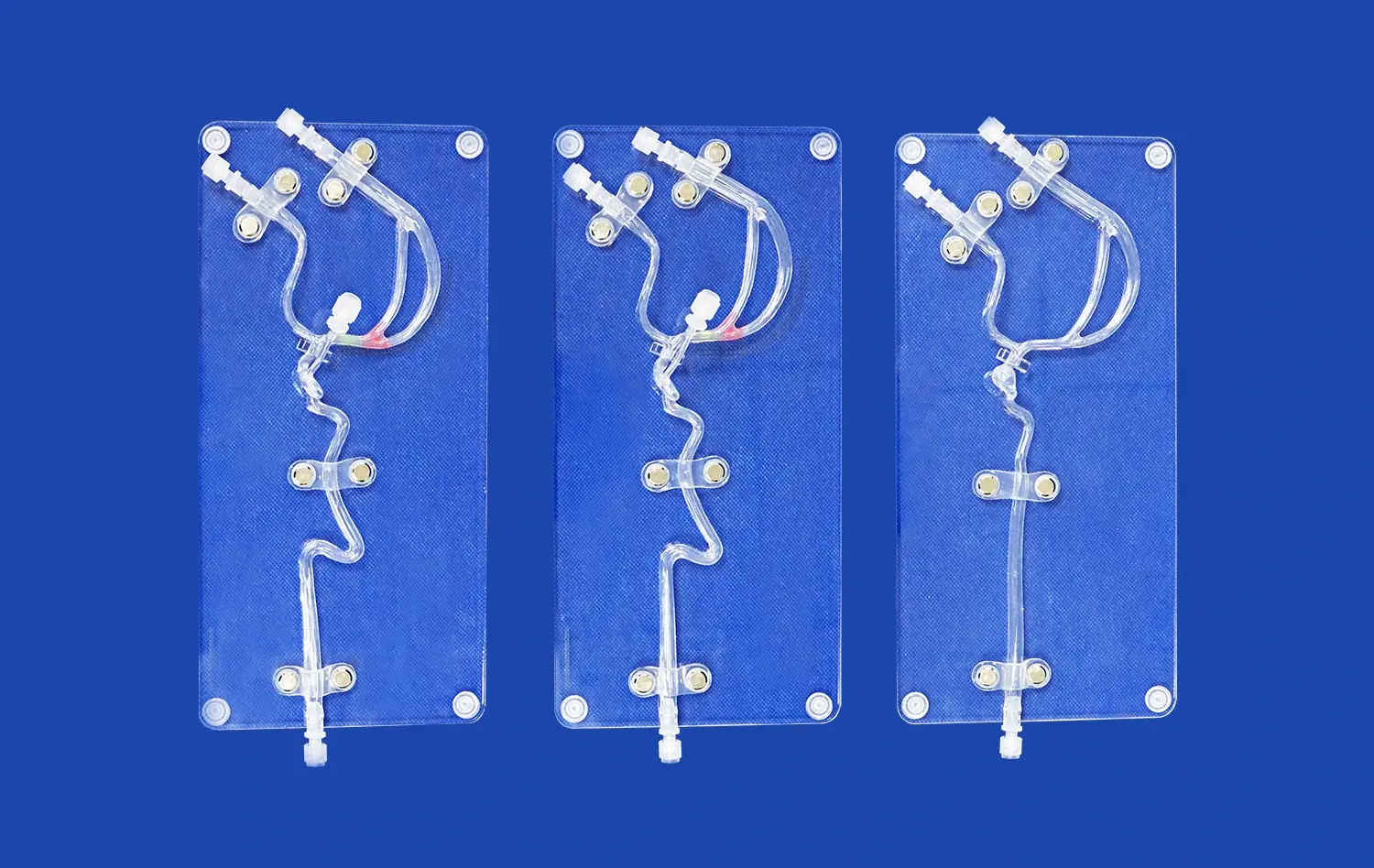
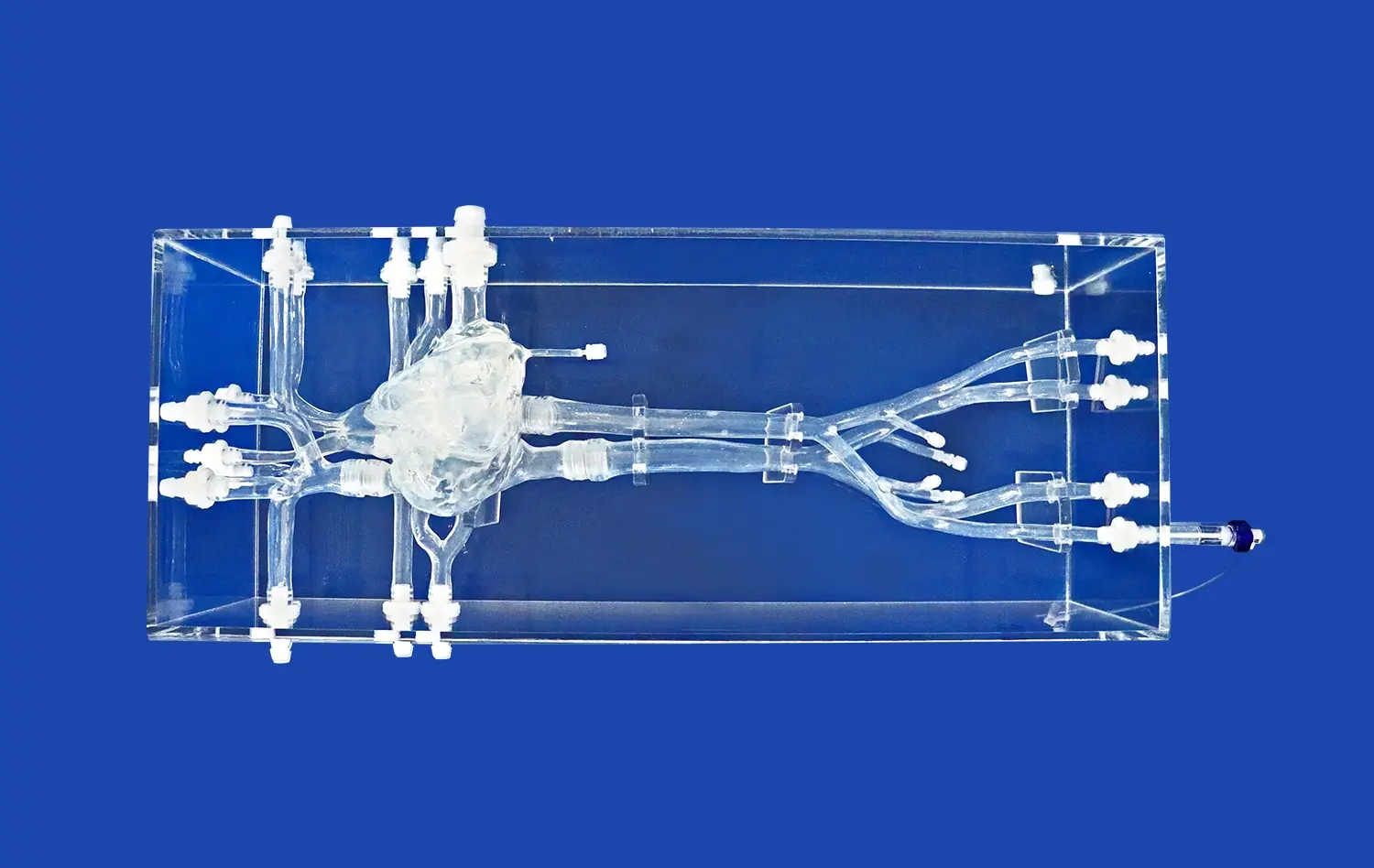
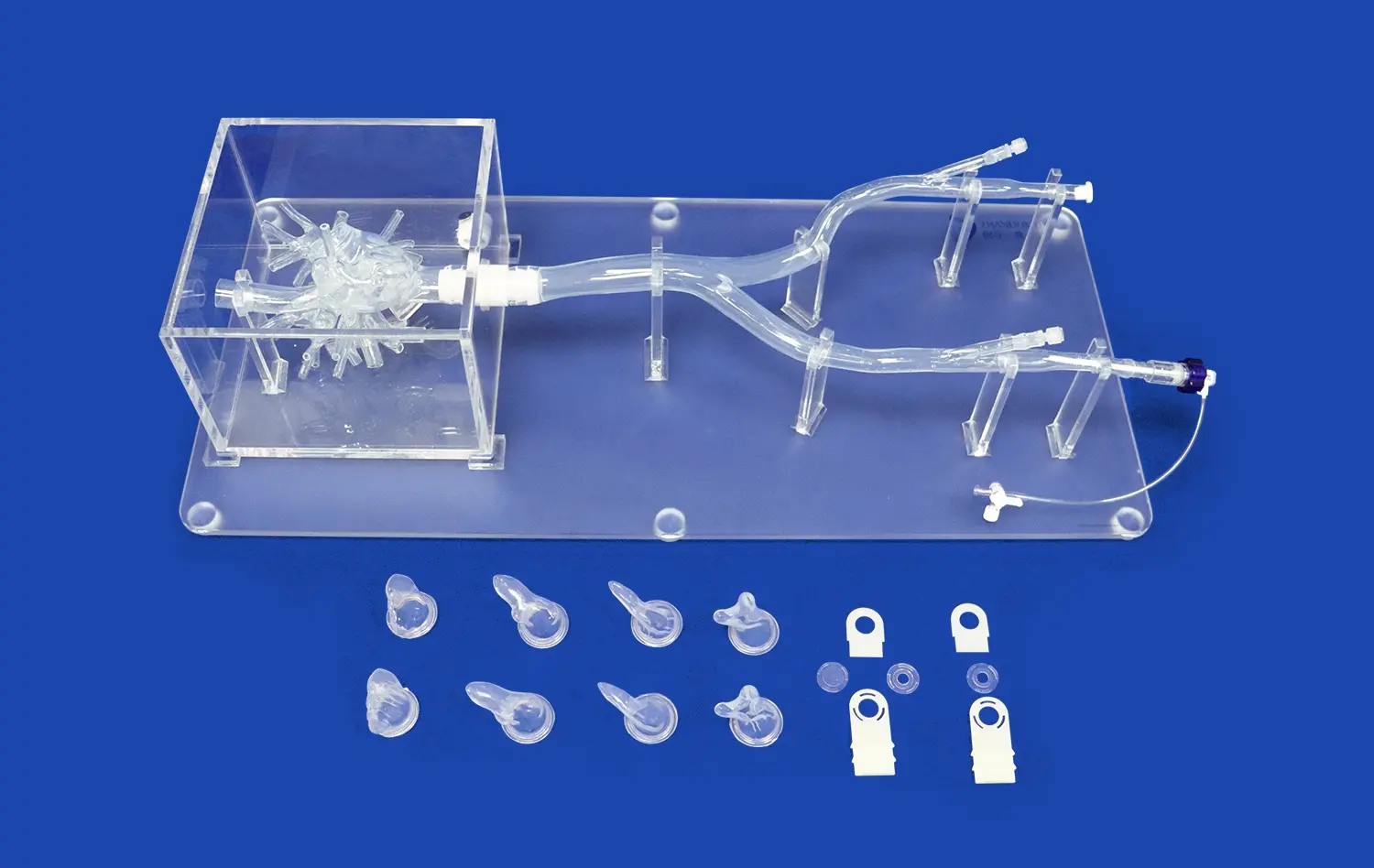
Why is Risk-Free Simulation Using an Atrial Septal Puncture Training Model Critical Before Clinical Application?
Mitigating Procedural Risks and Complications
Atrial septal puncture, while a common procedure in interventional cardiology, carries inherent risks that can lead to severe complications if not performed with precision. The use of a dedicated training model allows practitioners to familiarize themselves with the nuances of the technique without the pressure of potential patient harm. This risk-free environment is crucial for mastering the delicate manipulation of catheters and needles, ensuring that when faced with live cases, clinicians can execute the procedure with confidence and minimal risk of adverse events such as cardiac tamponade or aortic perforation.
Accelerating the Learning Curve
The learning curve for atrial septal puncture can be steep, particularly for those new to interventional procedures. Simulation models provide an accelerated path to competency by allowing for repetitive practice and immediate feedback. Trainees can perform multiple attempts in a single session, rapidly improving their hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness within the cardiac chambers. This iterative process helps solidify procedural memory and technique refinement far more quickly than traditional apprenticeship models alone.
Standardizing Training Protocols
Incorporating atrial septal puncture models into training curricula helps standardize the educational experience across institutions. By establishing consistent benchmarks and assessment criteria, medical educators can ensure that all trainees reach a minimum level of proficiency before advancing to supervised clinical cases. This standardization is vital for maintaining quality control in medical education and ultimately contributes to improved patient safety and care quality across the healthcare system.
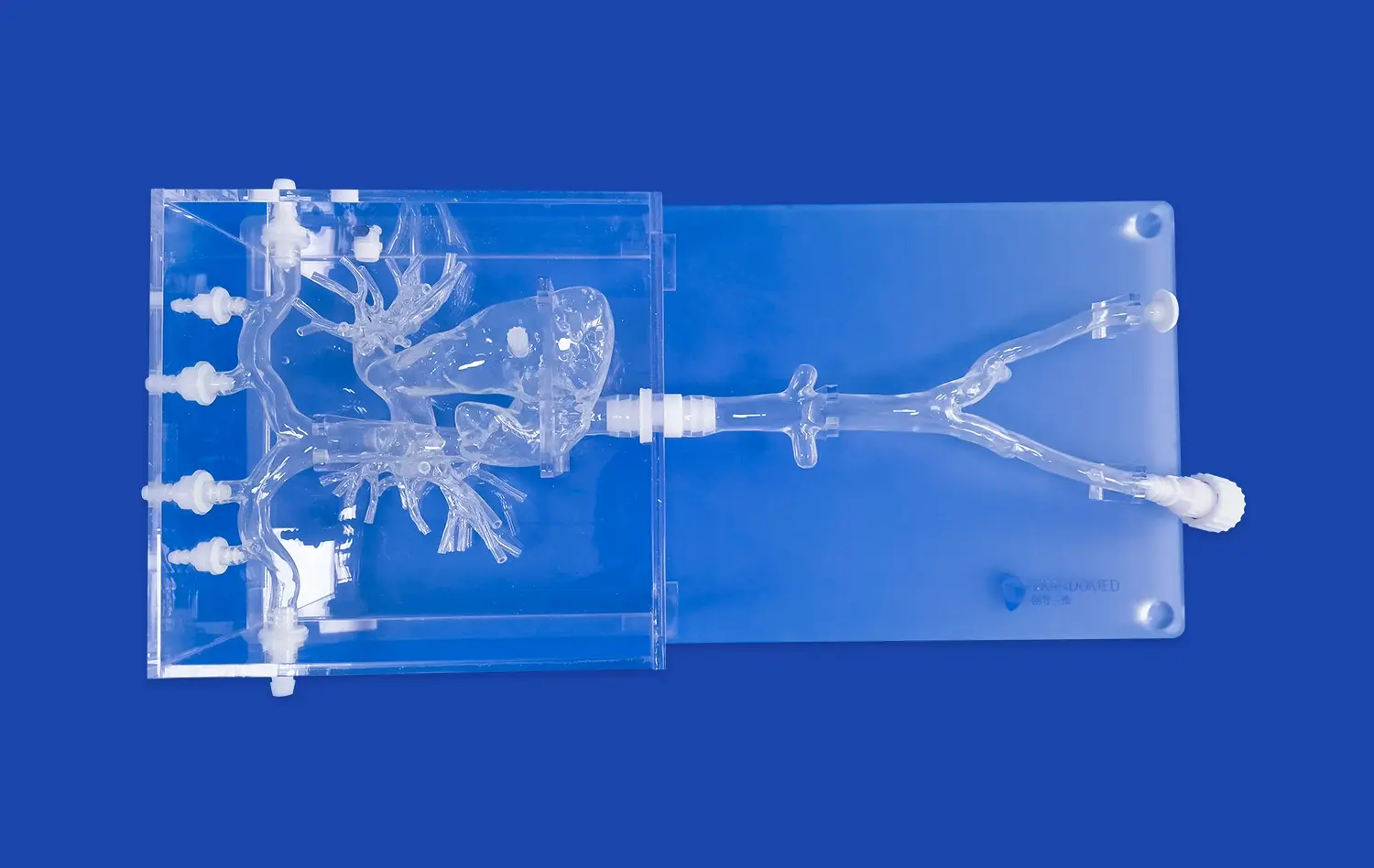
Realistic Anatomy for Safe, Repeatable Catheterization and Ablation Training
Anatomical Fidelity and Tactile Feedback
Advanced atrial septal puncture models are designed with meticulous attention to anatomical detail, replicating the feel and resistance of human tissue. The incorporation of materials that mimic the elasticity and texture of the interatrial septum provides trainees with realistic tactile feedback. This high-fidelity simulation allows practitioners to develop a nuanced understanding of the force required for successful puncture while avoiding excessive penetration. The ability to palpate and manipulate structures as they would in vivo is invaluable for building muscle memory and procedural finesse.
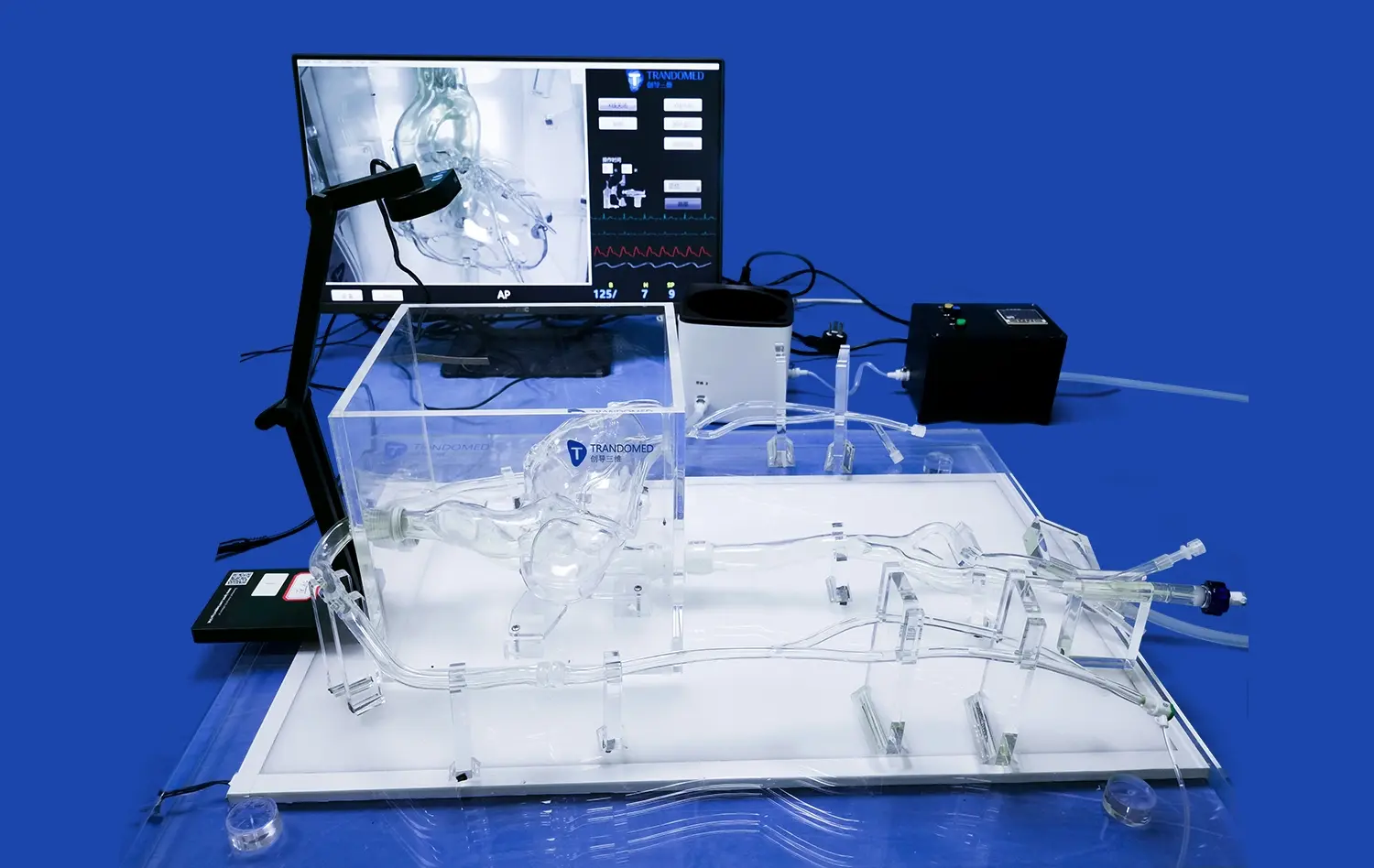
Integrated Imaging Compatibility
Modern atrial septal puncture simulators are often compatible with various imaging modalities, including fluoroscopy and echocardiography. This integration allows trainees to practice not only the physical aspects of the procedure but also the critical skill of interpreting real-time imaging data. By correlating visual cues with tactile sensations, practitioners can enhance their spatial awareness and improve their ability to navigate complex cardiac anatomy. The incorporation of imaging also facilitates training in optimal puncture site selection and catheter positioning, skills that are paramount for successful outcomes in clinical practice.
Variability in Anatomical Scenarios
Atrial septal puncture models can be designed to represent a range of anatomical variations and pathological conditions. This diversity allows trainees to encounter and navigate challenging scenarios that may be rare in clinical practice but critical to manage when they do occur. From thick or aneurysmal septa to unusual orientations of the fossa ovalis, these models provide a comprehensive training platform. The ability to practice on various anatomical configurations ensures that practitioners are prepared for the full spectrum of patient presentations they may encounter in their careers.
Building Surgeon Confidence and Technical Proficiency Through Atrial Septal Puncture Simulation
Progressive Skill Development
Atrial septal puncture simulation facilitates a structured approach to skill development. Trainees can begin with basic needle manipulation and progress to more complex scenarios involving challenging anatomies or complications. This step-wise approach allows for the gradual building of confidence as practitioners master each component of the procedure. The ability to practice without time constraints or the pressure of patient outcomes enables a focus on technique refinement and problem-solving skills, essential attributes for successful interventional cardiologists.
Performance Metrics and Objective Assessment
Many advanced atrial septal puncture models incorporate sensors and data collection capabilities, allowing for objective assessment of performance. Metrics such as puncture accuracy, force applied, and procedure time can be quantified and tracked over multiple training sessions. This data-driven approach provides trainees with concrete feedback on their progress and helps identify areas for improvement. For educators, these metrics offer valuable insights into trainee competency and readiness for clinical application, ensuring that only those who have demonstrated consistent proficiency advance to patient care.
Team-Based Training and Communication Skills
Atrial septal puncture simulations can be designed to incorporate team-based scenarios, mirroring the collaborative nature of cardiac interventions. This approach allows for the practice of not only technical skills but also critical non-technical skills such as communication, leadership, and crisis management. By simulating potential complications or emergency situations, teams can rehearse their responses in a controlled environment. This comprehensive training approach builds confidence not just in individual capabilities but in the collective ability of the cardiac team to handle complex procedures and unforeseen challenges.
Conclusion
The atrial septal puncture model stands as a testament to the power of simulation in medical education. By providing a risk-free, highly realistic platform for training, these models are revolutionizing how cardiac procedures are taught and mastered. The benefits extend beyond individual skill development to encompass improved patient safety, standardized training protocols, and enhanced team performance. As medical technology continues to advance, the role of such high-fidelity simulators in preparing the next generation of interventional cardiologists will only grow in importance, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care from confident, competent practitioners.
Contact Us
For those seeking to elevate their cardiac procedure training programs, Trandomed offers state-of-the-art atrial septal puncture models that combine anatomical accuracy with cutting-edge simulation technology. Our customizable solutions cater to the specific needs of medical institutions, providing a robust platform for comprehensive skill development. To learn more about how our models can enhance your training curriculum and improve patient outcomes, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
_1732863713705.webp)