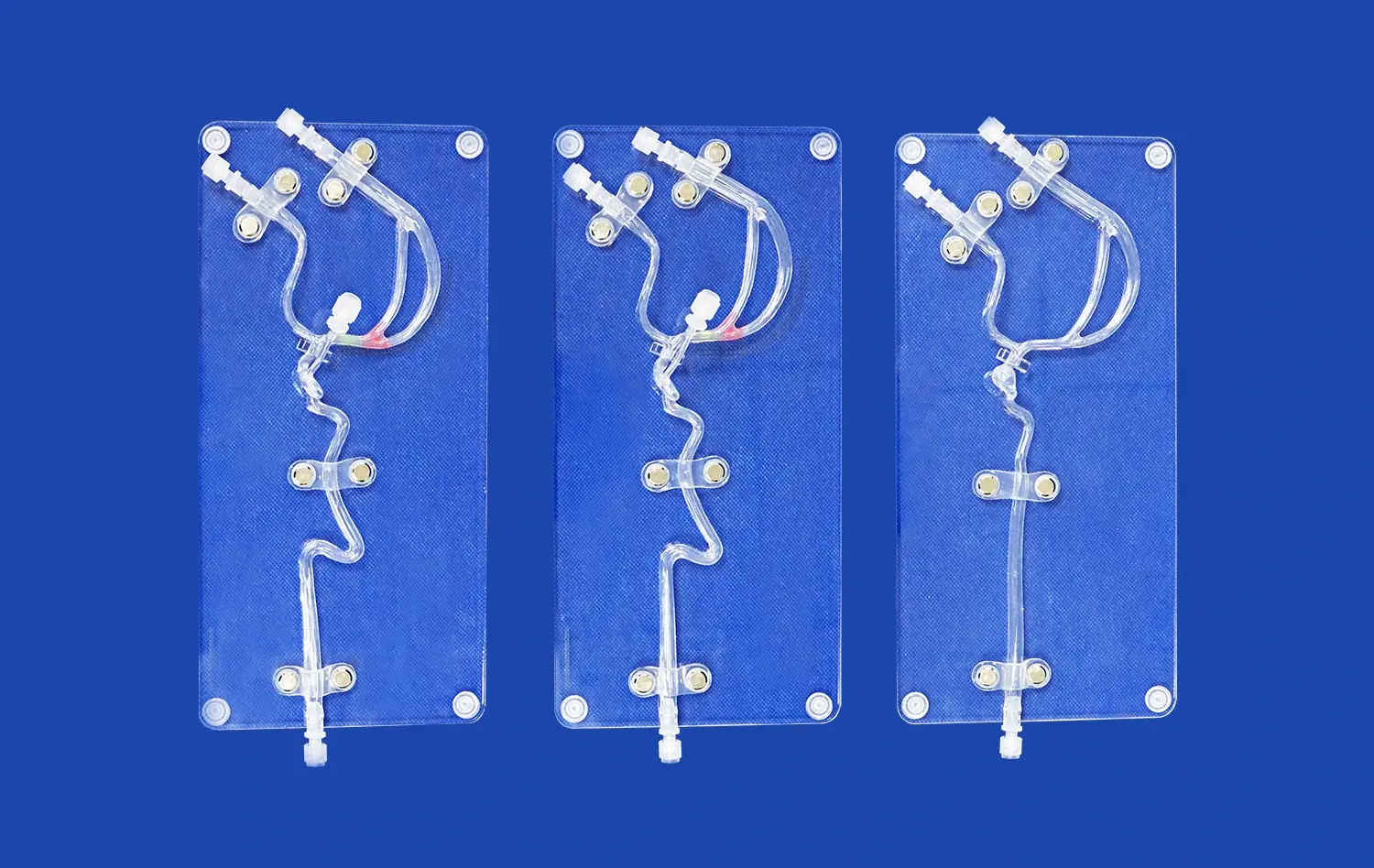
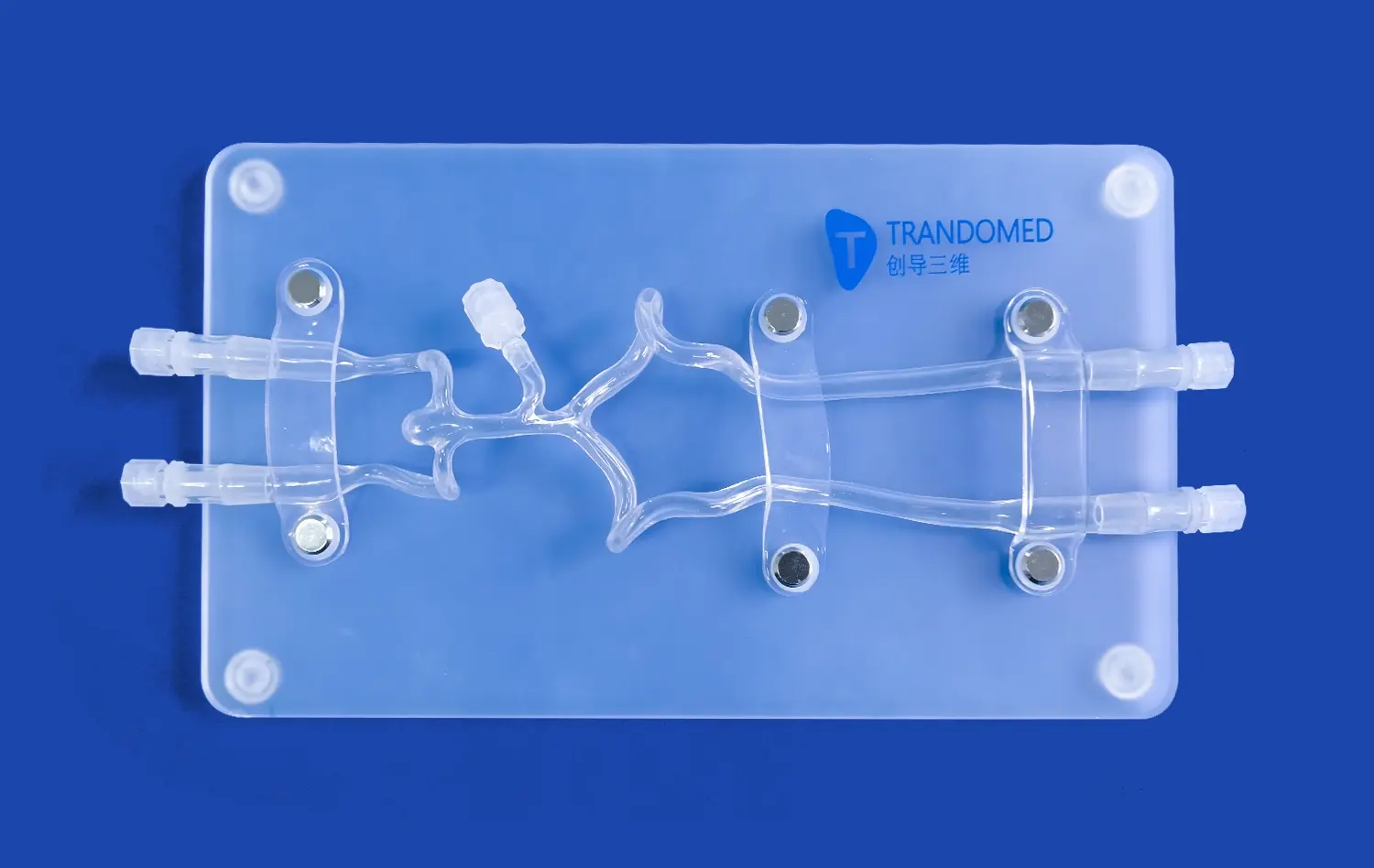
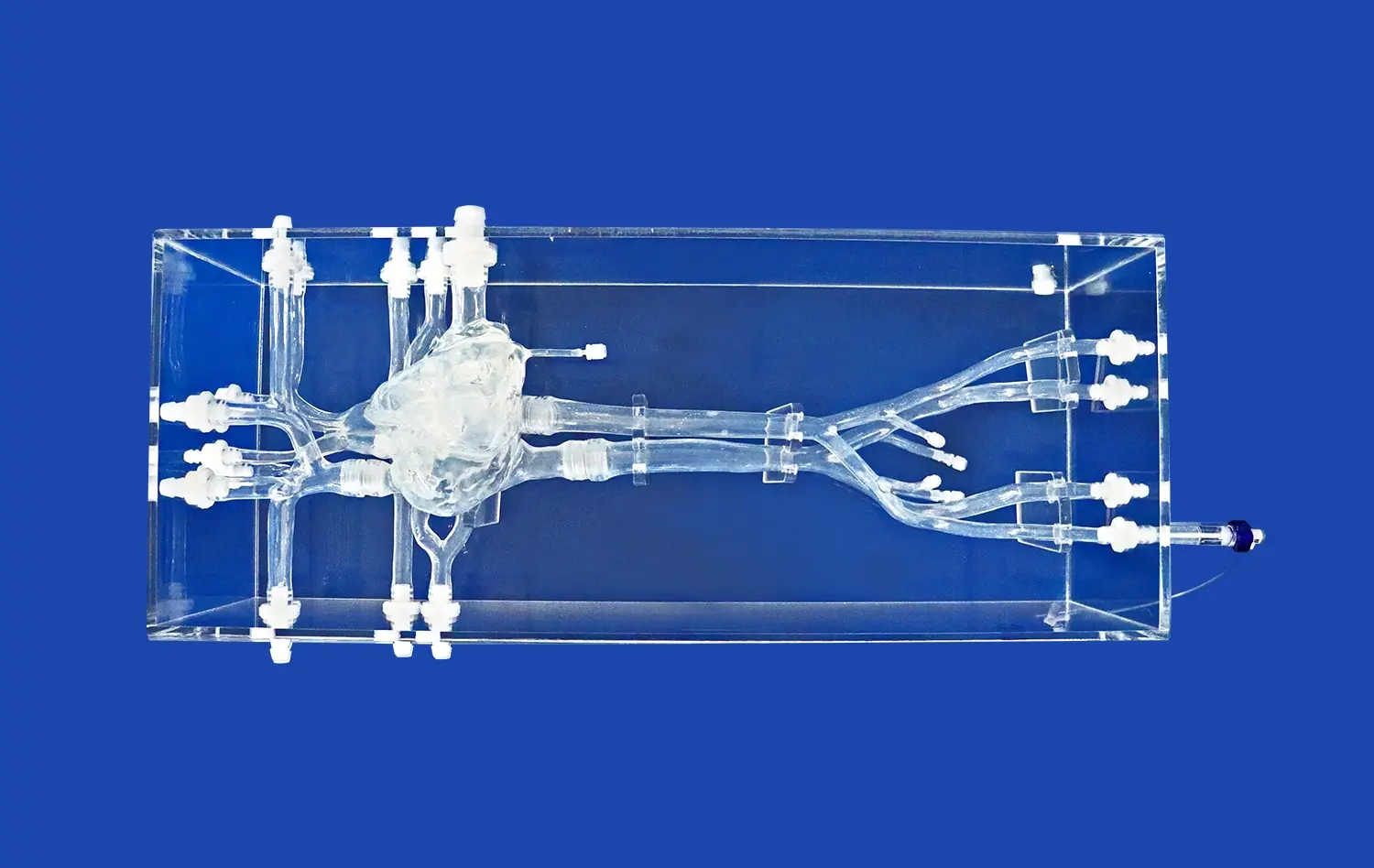
How does Simulation with an Atrial Septal Puncture Training Model Reduce Procedural Complications?
Replicating Real-World Challenges
Atrial septal puncture models are designed to mimic the intricate anatomy and tissue properties of the human heart. These high-fidelity simulators incorporate various features such as the femoral vein, iliac vein, superior and inferior vena cava, left and right atria, and pulmonary veins. The inclusion of interchangeable atrial septal inserts, including normal and pathological variants, allows trainees to encounter diverse clinical scenarios.
By practicing on these models, clinicians can familiarize themselves with the tactile feedback and visual cues essential for successful transseptal punctures. This hands-on experience helps reduce the likelihood of complications such as inadvertent puncture of the aortic root or cardiac tamponade, which can occur when operators are less experienced with the procedure.
Mastering Equipment Handling
Simulation training with atrial septal puncture models enables practitioners to become proficient in handling specialized equipment. From maneuvering the Brockenbrough needle to navigating catheters through complex vascular structures, these models provide a safe environment for mastering the nuances of tool manipulation. This familiarity with equipment translates directly to improved dexterity and precision during actual procedures, minimizing the risk of complications associated with improper device handling.
Practicing Complication Management
One of the most valuable aspects of simulation training is the opportunity to practice managing potential complications. Atrial septal puncture models can be designed to incorporate scenarios such as difficult septum penetration, unusual septal anatomy, or even simulated perforations. By encountering these challenges in a controlled environment, clinicians can develop and refine their problem-solving skills, learning to quickly recognize and address complications without putting patients at risk.
Enhancing Precision in Cardiac Catheterization and Pulmonary Vein Isolation Practice
Improving Spatial Awareness
Atrial septal puncture models play a crucial role in enhancing clinicians' spatial awareness within the cardiac anatomy. These models provide a three-dimensional representation of the heart's structures, allowing practitioners to develop a more intuitive understanding of the spatial relationships between different cardiac chambers and vessels. This improved spatial cognition is particularly valuable during procedures like pulmonary vein isolation, where precise navigation and positioning of catheters are essential for successful outcomes.
Through repeated practice on these models, operators can refine their ability to mentally map the cardiac anatomy, even when relying primarily on two-dimensional imaging modalities such as fluoroscopy during actual procedures. This enhanced spatial awareness contributes to more accurate catheter placement and reduces the likelihood of procedural errors.
Refining Catheter Navigation Techniques
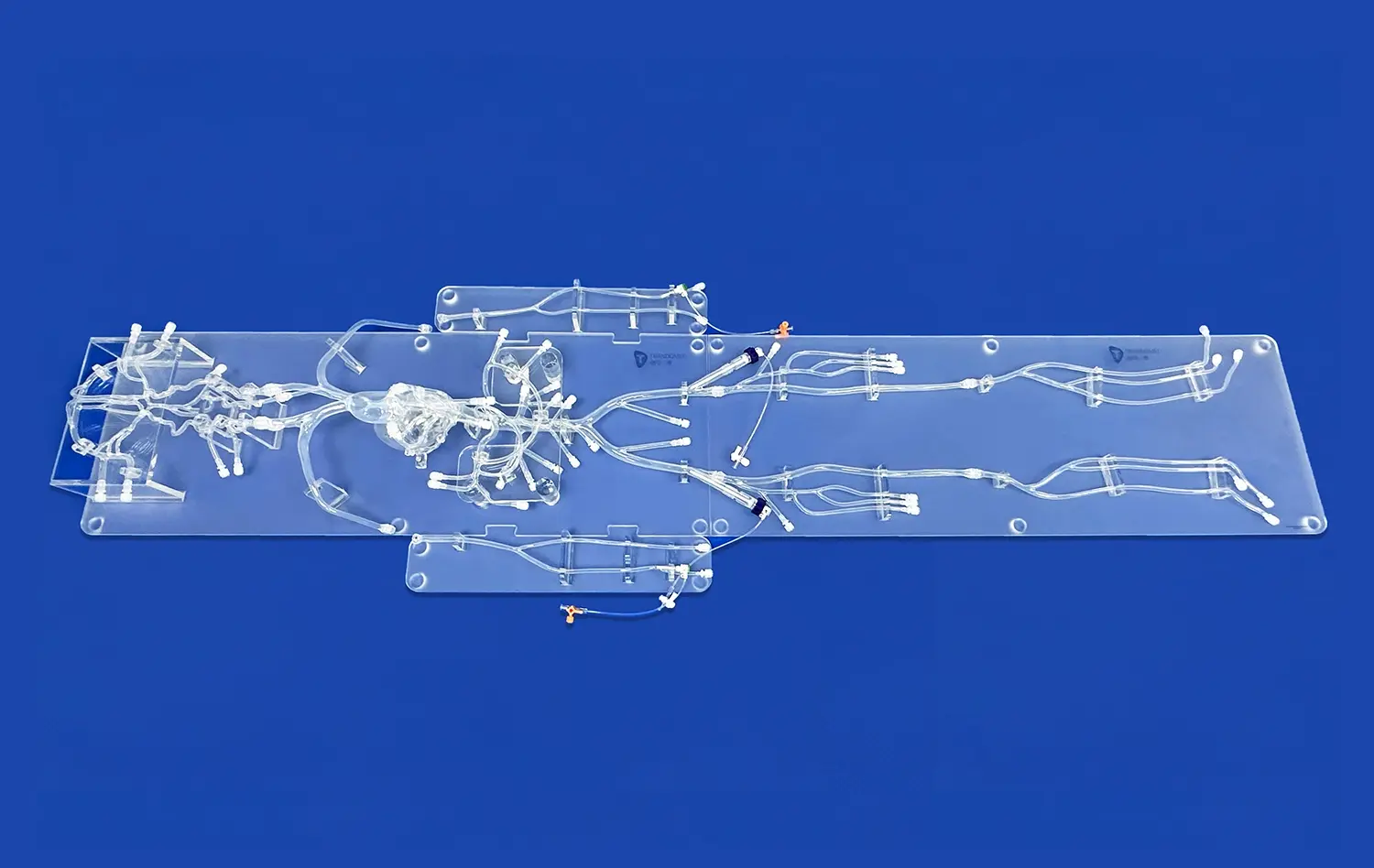
The atrial septal puncture model serves as an excellent platform for perfecting catheter navigation techniques. The modular design of these simulators, often featuring detachable upper (SVC with heart) and lower (IVC) parts, allows for customization of the training experience. Practitioners can practice navigating catheters through various anatomical variations and degrees of vascular tortuosity, mimicking the diverse patient anatomies encountered in clinical practice.
This targeted practice helps clinicians develop the fine motor skills and tactile sensitivity required for smooth and efficient catheter manipulation. As a result, operators can achieve more precise catheter positioning during cardiac catheterization procedures, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy.
Optimizing Transseptal Puncture Techniques
The transseptal puncture is a critical step in many left atrial interventions, including pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation treatment. Atrial septal puncture models allow clinicians to refine their technique for this delicate procedure. By practicing on simulators with interchangeable septal inserts, operators can experience different septal thicknesses and anatomies, learning to adjust their approach based on the specific characteristics of each case.
This focused practice helps clinicians develop a nuanced understanding of the optimal needle positioning, angle of approach, and amount of force required for successful transseptal punctures. As a result, practitioners can perform these procedures with greater confidence and precision, minimizing the risk of complications such as inadvertent puncture of adjacent structures or failure to cross the septum.
Measurable Improvements in Patient Safety and Procedural Outcomes Through Training
Reducing Procedural Time and Radiation Exposure
One of the significant benefits of training with atrial septal puncture models is the reduction in procedural time and radiation exposure for both patients and medical staff. As practitioners become more proficient through simulation training, they can perform procedures more efficiently, leading to shorter fluoroscopy times. This efficiency not only improves patient safety by reducing radiation exposure but also enhances overall procedural outcomes by minimizing the risk of complications associated with prolonged interventions.
Studies have shown that clinicians who undergo simulation training demonstrate markedly improved performance in terms of procedure duration and fluoroscopy time. This improvement is particularly notable in complex cases, where the enhanced skills and confidence gained through simulation practice translate into more streamlined and effective real-world procedures.
Increasing First-Attempt Success Rates
The use of atrial septal puncture models in training programs has been associated with a significant increase in first-attempt success rates for transseptal punctures and related procedures. By providing opportunities for repeated practice and refinement of techniques, these simulators help clinicians develop the skills and judgment necessary to achieve successful outcomes more consistently.
Improved first-attempt success rates not only enhance patient safety by reducing the need for multiple attempts but also contribute to better overall procedural efficiency. This increased success rate is particularly valuable in high-stakes procedures such as left atrial appendage closure or mitral valve interventions, where precise transseptal access is crucial for optimal device placement and therapeutic efficacy.
Enhancing Team Communication and Coordination
Simulation training with atrial septal puncture models offers valuable opportunities for enhancing team communication and coordination in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. These models can be incorporated into team-based training scenarios, allowing interventional cardiologists, electrophysiologists, nurses, and technicians to practice together in a realistic setting.
By simulating various procedural steps and potential complications, team members can refine their communication strategies, clarify roles and responsibilities, and develop more effective workflows. This improved team dynamics translates directly to enhanced patient safety and procedural outcomes in real-world settings, as team members are better prepared to collaborate efficiently and respond cohesively to challenges that may arise during complex cardiac interventions.
Conclusion
The atrial septal puncture model has emerged as an indispensable tool in advancing cardiac procedure practice and improving patient outcomes. By providing a realistic and risk-free environment for training, these models enable clinicians to refine their skills, enhance precision, and reduce complications in critical cardiac interventions. The measurable improvements in procedural efficiency, success rates, and team performance underscore the value of simulation-based training in modern cardiology. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of high-fidelity simulators like the atrial septal puncture model will play an increasingly vital role in preparing the next generation of cardiac specialists for the challenges of tomorrow.
Contact Us
Elevate your cardiac procedure training with Trandomed's state-of-the-art atrial septal puncture models. Our customizable, high-fidelity simulators offer unparalleled realism and versatility, helping you achieve measurable improvements in procedural outcomes and patient safety. Experience the benefits of cutting-edge medical simulation technology tailored to your specific training needs. For more information or to request a customized solution, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
1_1732869849284.webp)
_1732863713705.webp)