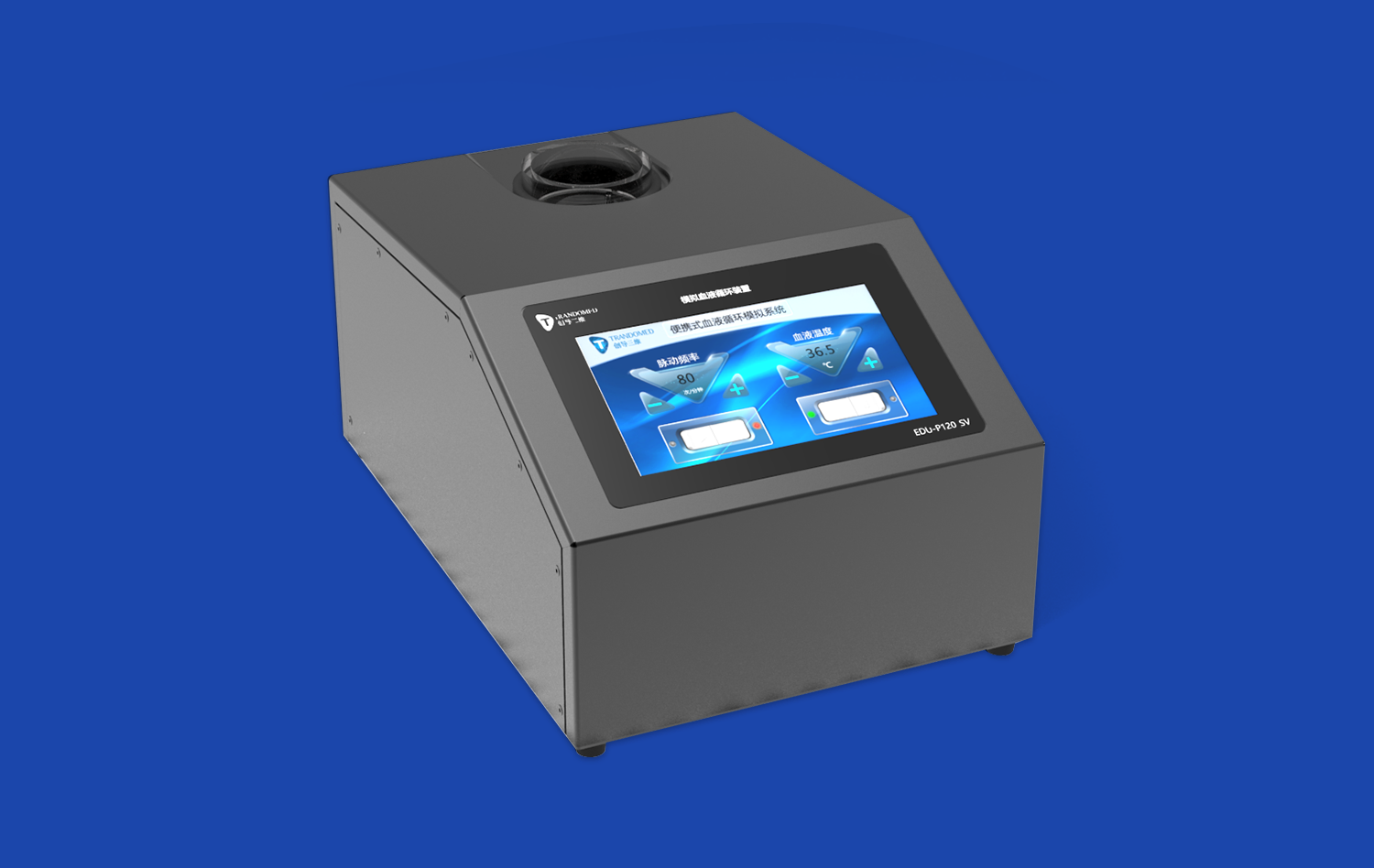
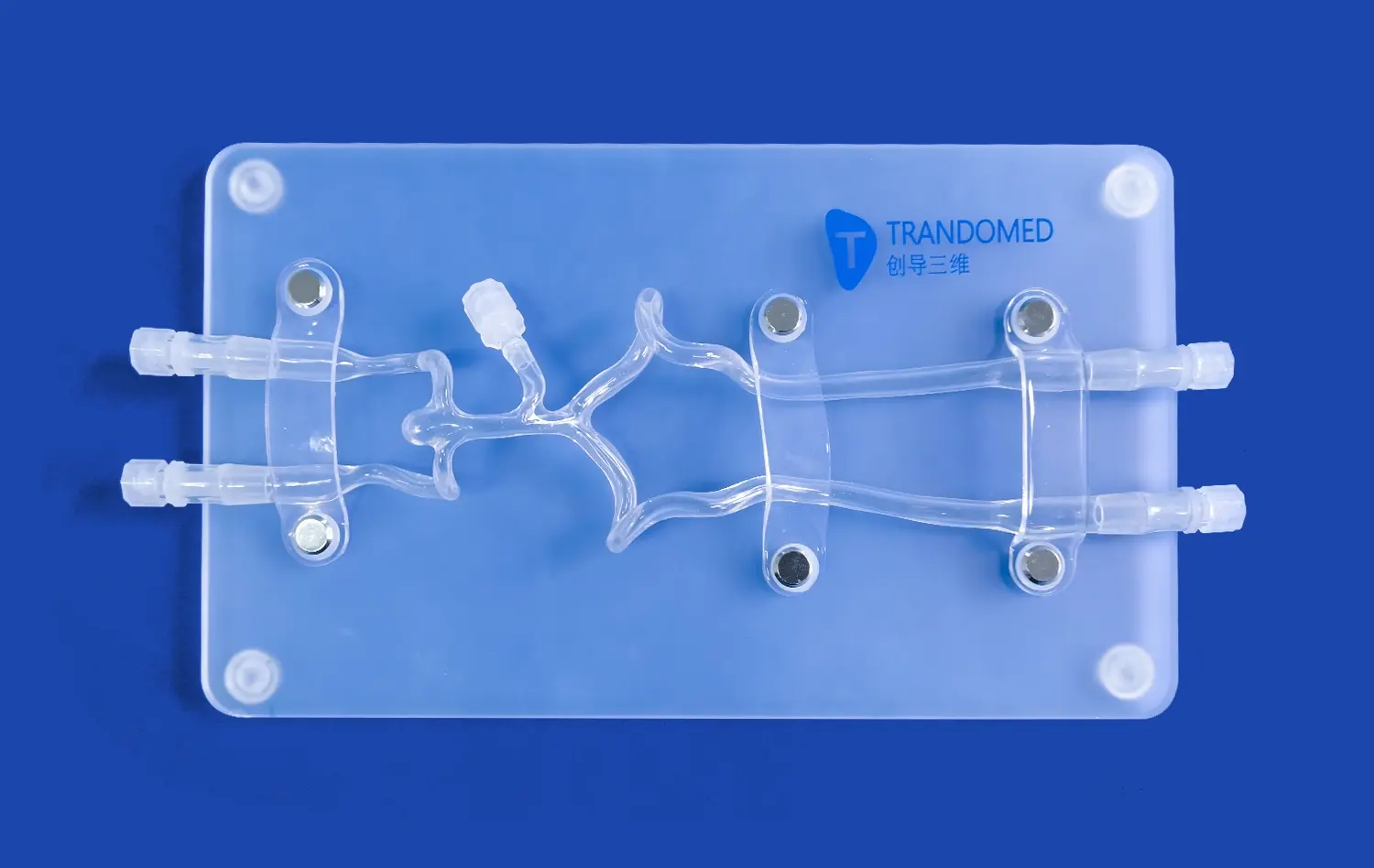
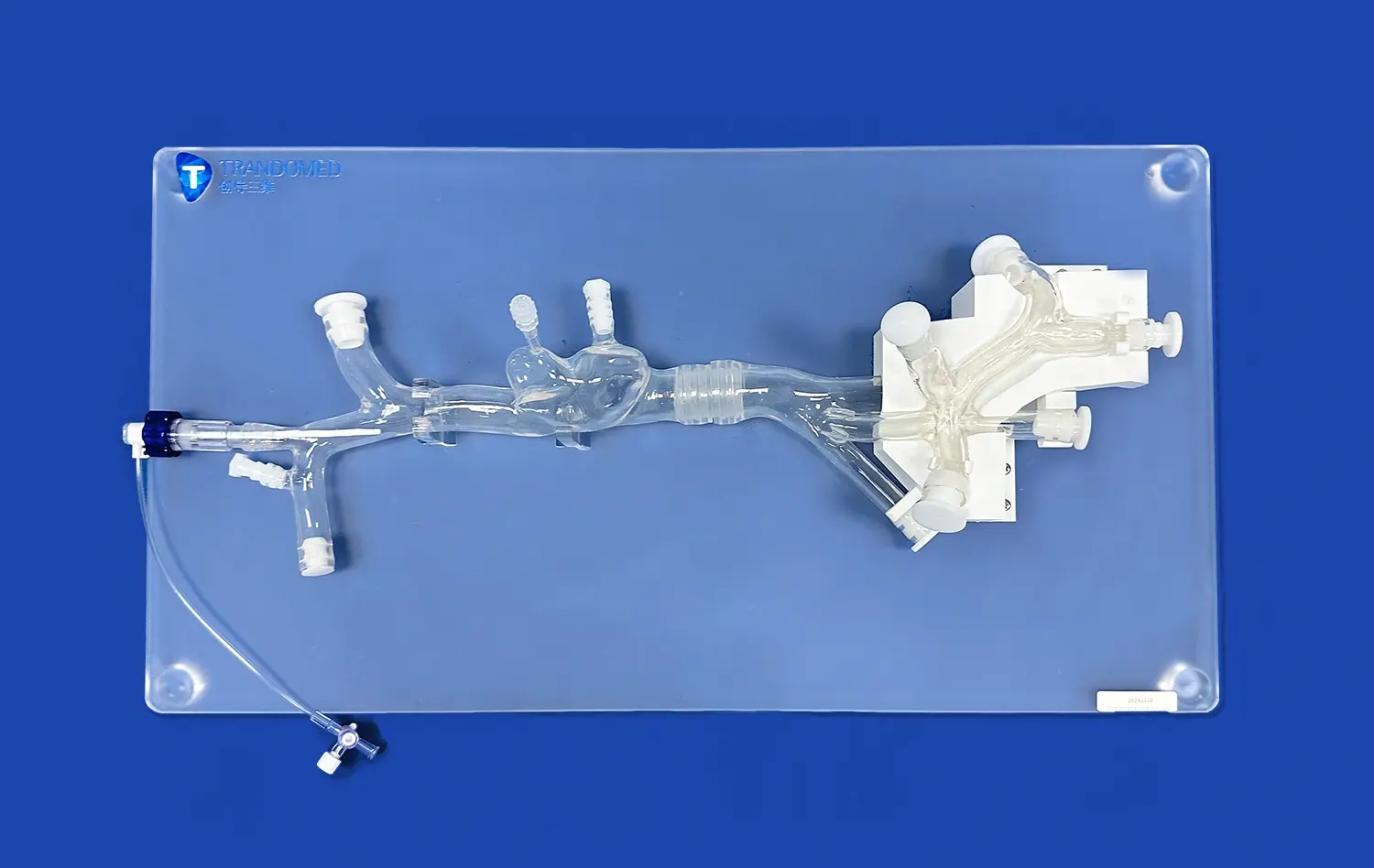
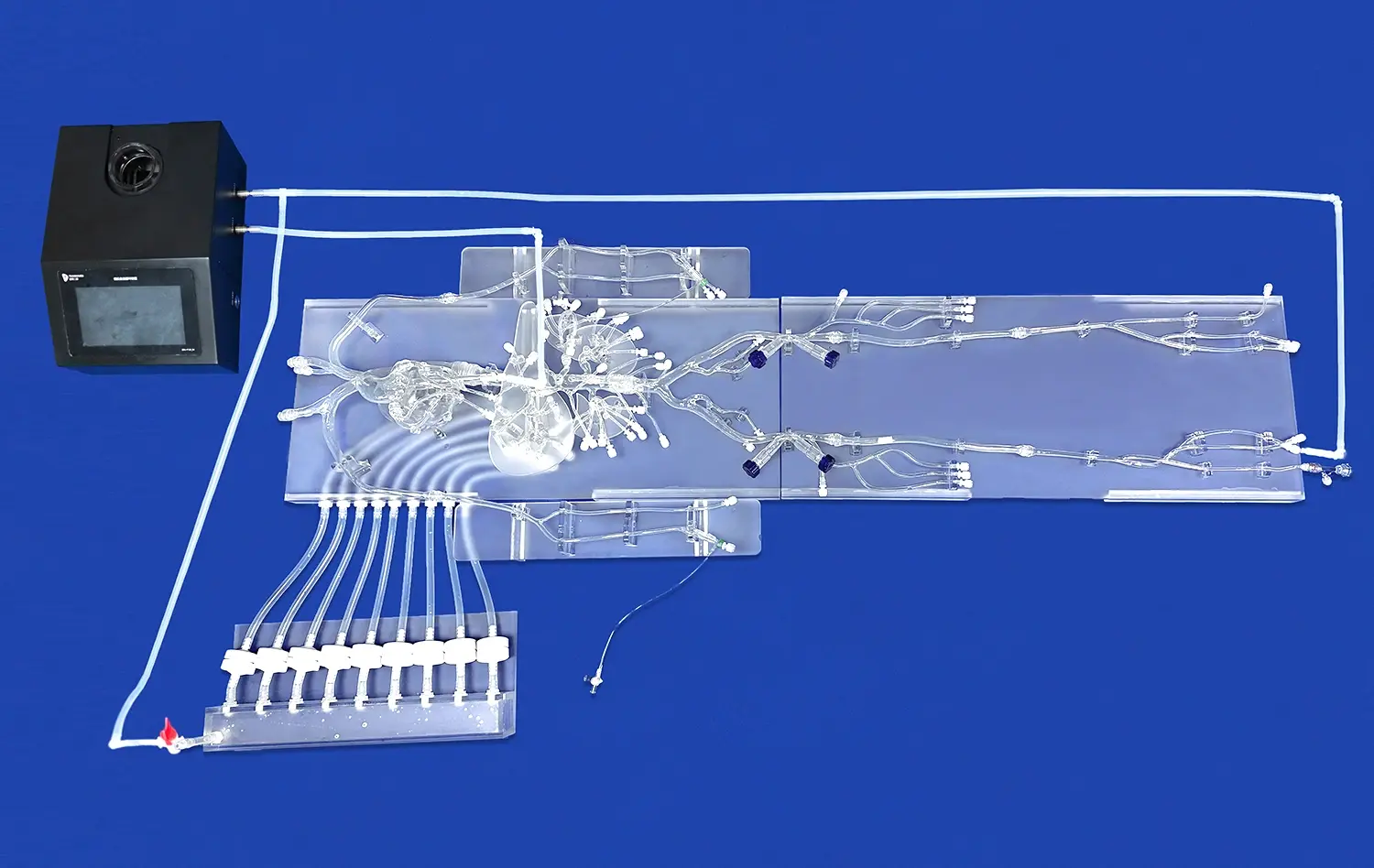
Why is Accurate Septal Puncture Crucial for PVI Success?
Anatomical Precision and Access
Accurate septal puncture is the gateway to successful pulmonary vein isolation. The interatrial septum, a thin wall of tissue separating the left and right atria, must be traversed with utmost precision. A well-placed puncture ensures optimal access to the left atrium, where the pulmonary veins connect. This anatomical accuracy is vital for several reasons:
- It allows for proper positioning of ablation catheters near the pulmonary vein ostia
- It minimizes the risk of inadvertent puncture of adjacent structures
- It facilitates smooth catheter manipulation within the left atrium
Utilizing an atrial septal puncture model enables practitioners to visualize and practice this crucial step, enhancing their understanding of the three-dimensional cardiac anatomy.
Procedural Safety and Efficacy
The safety of the patient is paramount in any interventional procedure. An accurate septal puncture significantly reduces the risk of complications such as cardiac tamponade, aortic perforation, or damage to the atrial wall. Moreover, a precise puncture contributes to the overall efficacy of the PVI procedure by:
- Ensuring complete isolation of all pulmonary veins
- Reducing procedure time and fluoroscopy exposure
- Minimizing the need for repeated punctures or catheter repositioning
Practice on a high-fidelity atrial septal puncture model allows operators to refine their technique, thereby enhancing both safety and efficacy in clinical settings.
Long-term Outcomes and Patient Benefit
The impact of a well-executed septal puncture extends beyond the immediate procedural success. It influences long-term outcomes for patients undergoing PVI. Accurate puncture and subsequent catheter positioning contribute to:
- More durable pulmonary vein isolation
- Reduced likelihood of arrhythmia recurrence
- Lower rates of repeat procedures
By mastering this critical step through repeated practice on an atrial septal puncture model, clinicians can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Hands-On Practice for Transseptal Catheterization
Simulating Real-world Scenarios
Atrial septal puncture models offer a unique opportunity to simulate a wide range of clinical scenarios. These models can be designed to replicate various anatomical variations and pathologies, allowing practitioners to encounter and navigate challenges they may face in actual procedures. Key features of these simulations include:
- Adjustable septum thickness and elasticity
- Representation of common anatomical variants
- Incorporation of pathological conditions like atrial septal defects
By practicing on models that closely mimic real-world conditions, operators can build a diverse skill set applicable to a broad patient population.
Refining Technique and Motor Skills
The act of performing a transseptal puncture requires precise hand-eye coordination and fine motor control. Regular practice on an atrial septal puncture model allows operators to refine these skills in a controlled environment. This hands-on experience helps in:
- Developing a feel for the correct amount of pressure needed
- Improving needle and catheter manipulation
- Enhancing spatial awareness within the cardiac chambers
As operators repeat the procedure, they develop muscle memory and intuitive understanding of the mechanics involved, leading to smoother and more confident performance in actual cases.
Integrating Imaging Techniques
Modern transseptal catheterization often involves the use of advanced imaging techniques such as intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) or transesophageal echocardiography (TEE). Atrial septal puncture models can be designed to be compatible with these imaging modalities, allowing practitioners to:
- Practice image interpretation in real-time
- Correlate visual cues with tactile feedback
- Improve coordination between imaging and catheter manipulation
This integrated approach ensures that operators are well-prepared to utilize all available tools during actual procedures, enhancing overall procedural success and safety.
Improving Precision and Reducing Procedural Risks
Advanced Model Features for Risk Mitigation
State-of-the-art atrial septal puncture models incorporate features specifically designed to address potential risks associated with transseptal catheterization. These advanced models often include:
- Pressure-sensitive septum to simulate tissue resistance
- Fluid-filled chambers to mimic blood flow and pressure
- Anatomically correct surrounding structures like the aorta
By practicing on models with these features, operators can develop a heightened awareness of the forces involved and the potential consequences of misplaced punctures, thereby reducing procedural risks in clinical practice.
Iterative Learning and Performance Metrics
The use of atrial septal puncture models allows for iterative learning, where operators can repeat the procedure multiple times, analyzing and improving their performance with each attempt. Some advanced simulation systems even incorporate performance metrics, providing objective feedback on factors such as:
- Puncture accuracy and location
- Time to successful puncture
- Force applied during the procedure
This data-driven approach enables targeted skill improvement and helps identify areas needing further practice, ultimately leading to enhanced precision and reduced risks in real procedures.
Team Training and Communication
Effective communication among the cardiac team is crucial for procedural success and risk mitigation. Atrial septal puncture models provide an excellent platform for team-based training, allowing for:
- Practice of clear communication protocols
- Simulation of emergency scenarios and complication management
- Role-specific training for each team member
By engaging in team simulations using these models, the entire cardiac intervention team can improve their collective performance, leading to smoother procedures and better handling of unexpected situations in the clinical setting.
Conclusion
The atrial septal puncture model stands as an invaluable tool in the realm of pulmonary vein isolation practice. By providing a realistic, risk-free environment for hands-on training, these models significantly enhance the skills and confidence of medical professionals performing transseptal catheterization. The benefits extend beyond individual proficiency, encompassing improved patient safety, procedural efficiency, and long-term outcomes. As the field of electrophysiology continues to advance, the role of high-fidelity simulation in medical education and skill refinement becomes increasingly crucial. Embracing these innovative training tools paves the way for more precise, safer, and more effective pulmonary vein isolation procedures.
Contact Us
For medical professionals and institutions seeking to elevate their training programs and improve patient outcomes, Trandomed offers state-of-the-art atrial septal puncture models. Our advanced simulators provide unparalleled realism and versatility, allowing for comprehensive practice in transseptal catheterization and pulmonary vein isolation techniques. Experience the benefits of cutting-edge medical simulation technology and take your skills to the next level. To learn more about our atrial septal puncture models and how they can enhance your training program, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.