Cholangioscopy Training: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy with ERCP Simulators
2025-07-04 09:00:00
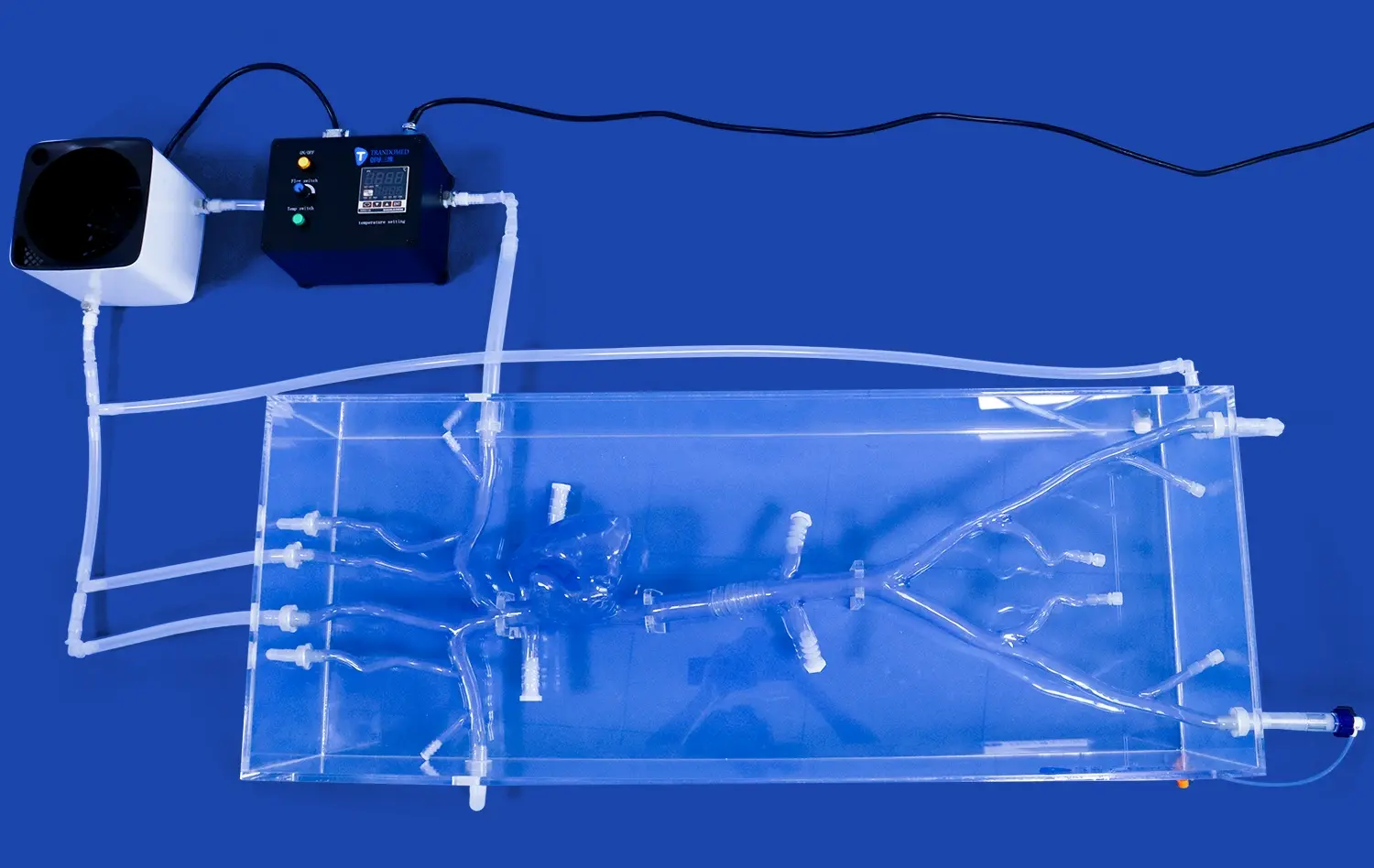
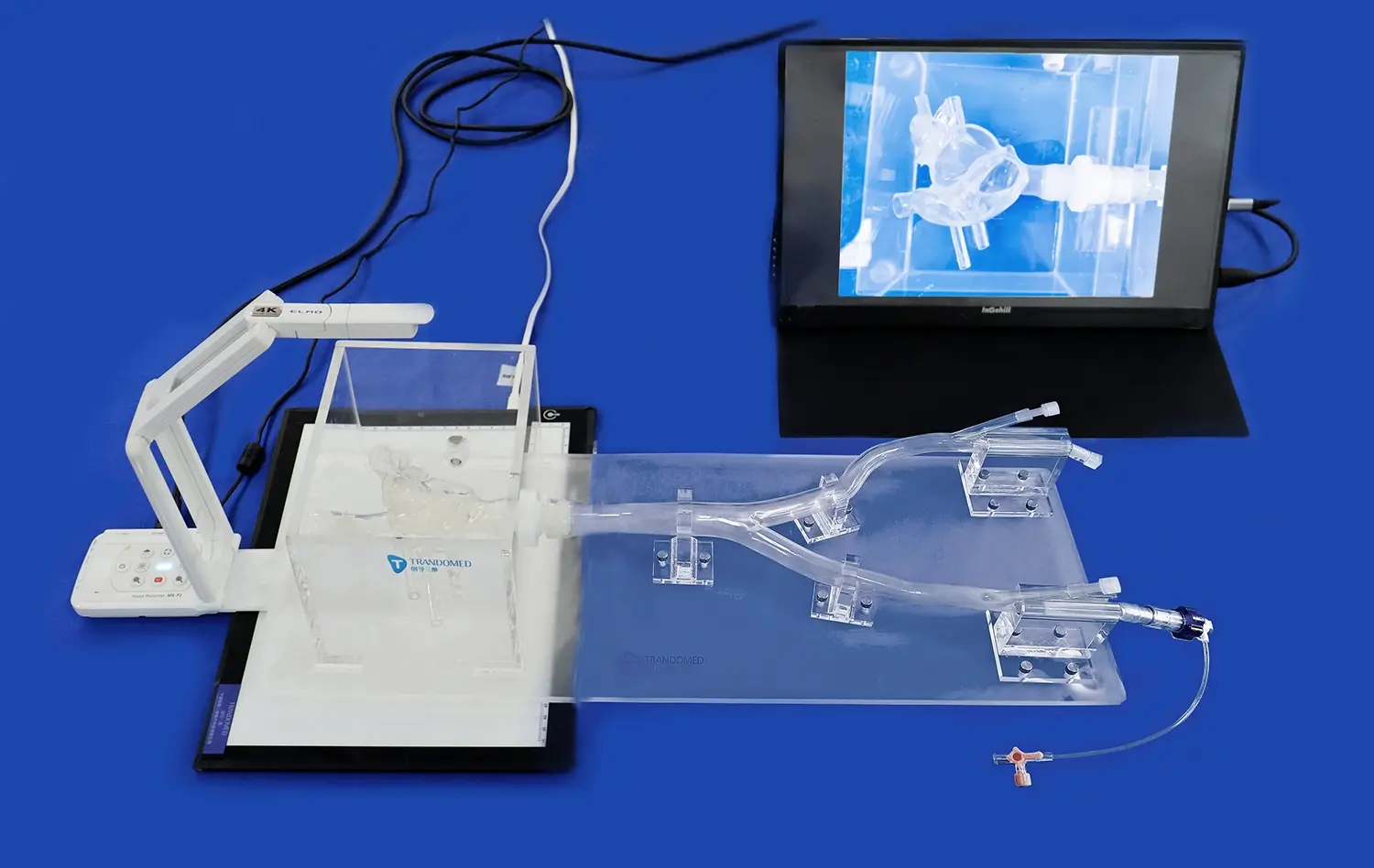
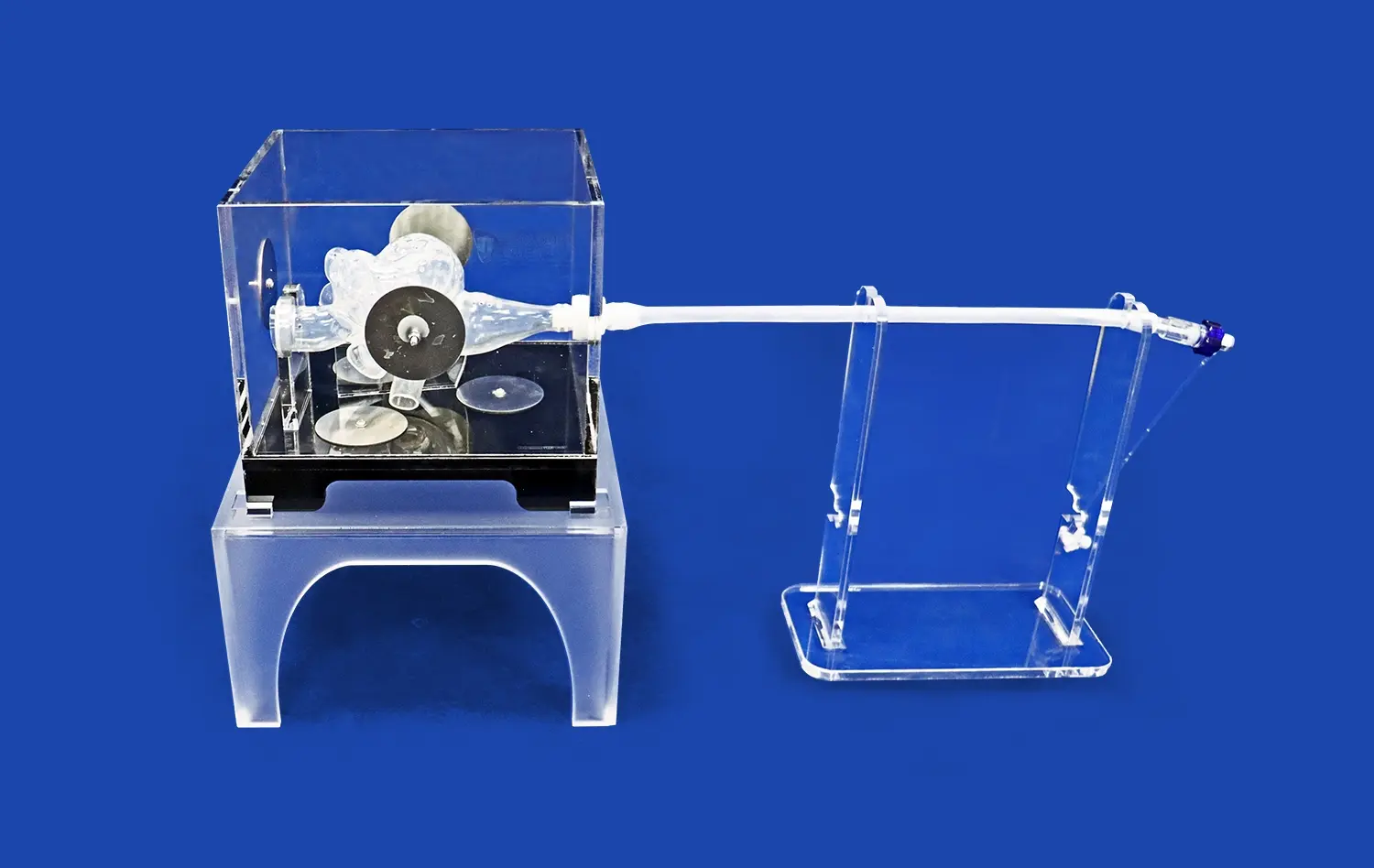
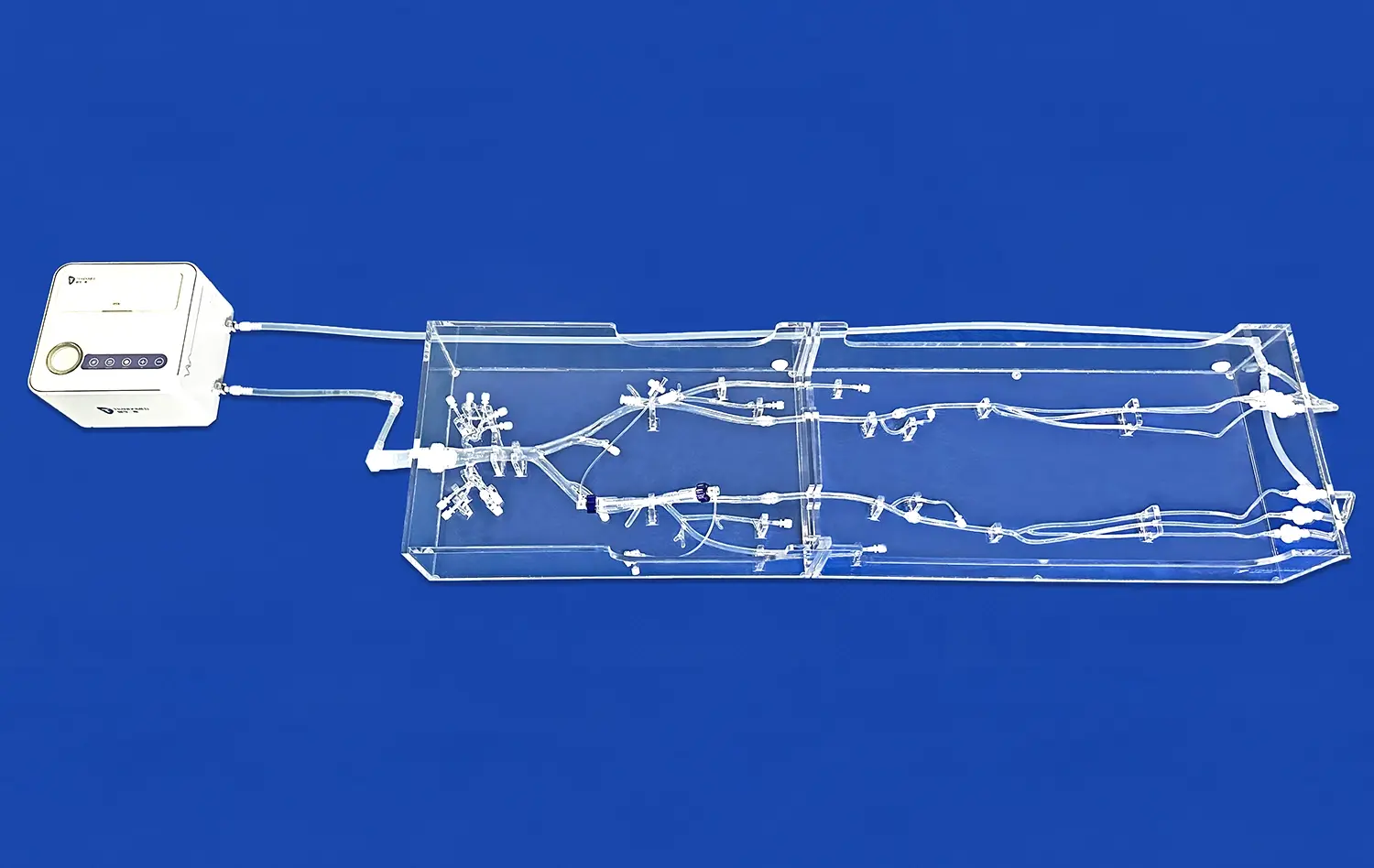
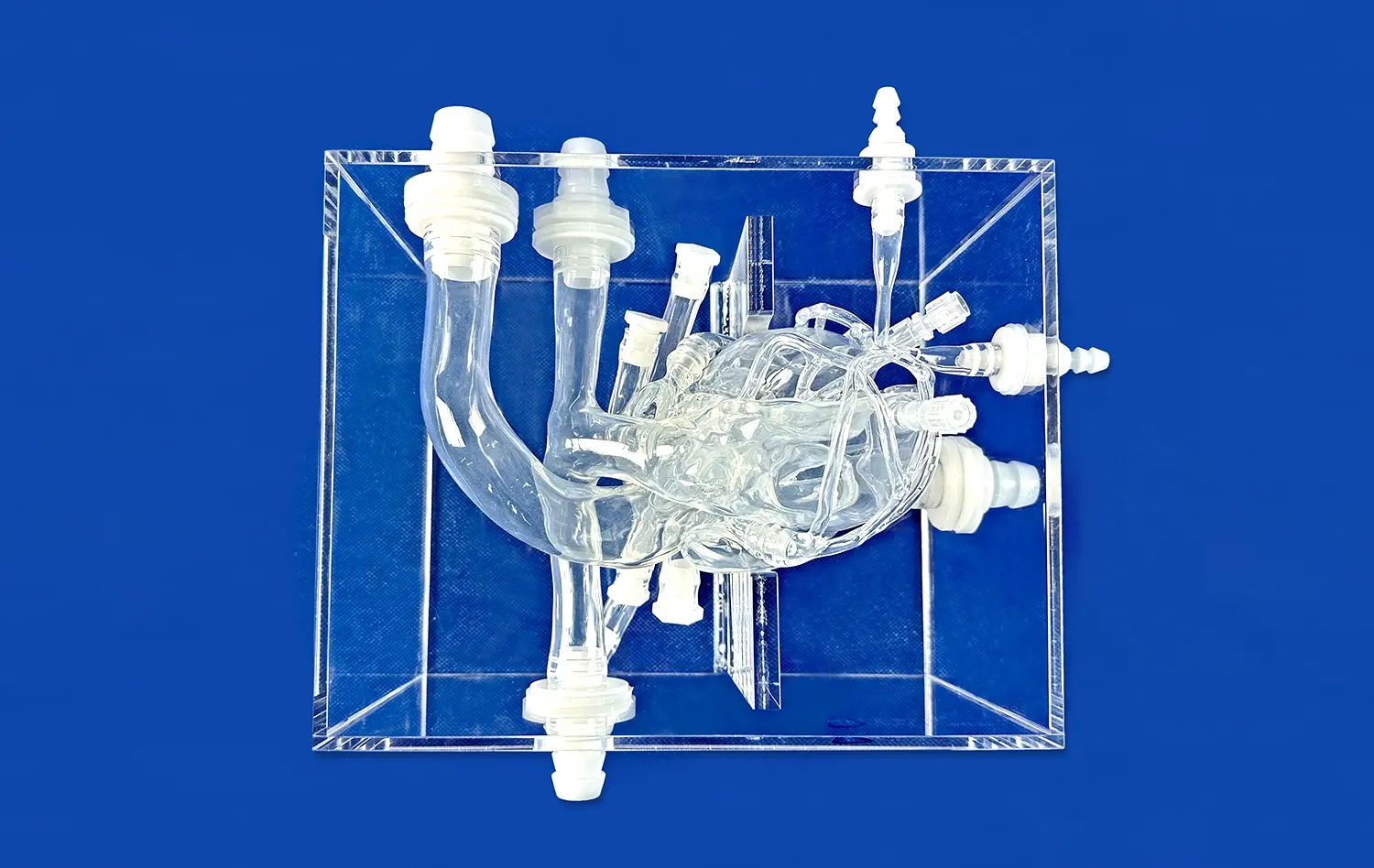
Cholangioscopy training using ERCP simulators represents a significant advancement in medical education, offering a realistic and risk-free environment for practitioners to hone their skills. These innovative training tools replicate the intricacies of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures, allowing clinicians to gain proficiency in navigating the biliary system and identifying various pathologies. By utilizing state-of-the-art 3D printing technology, ERCP simulators provide a tactile and visual experience that closely mimics real-world scenarios. This approach not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also improves procedural competence, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of simulation-based training in cholangioscopy marks a crucial step towards more effective and safer healthcare practices.
How ERCP Simulators Replicate the Cholangioscopy Experience?
Anatomical Accuracy and Haptic Feedback
ERCP simulators excel in replicating the cholangioscopy experience through their remarkable anatomical accuracy. These advanced training tools are meticulously crafted using high-resolution imaging data, ensuring that every curve, duct, and tissue structure mirrors the complexity of the human biliary system. The use of cutting-edge 3D printing technology allows for the creation of models with precise dimensions and textures, providing trainees with a visually and tactilely authentic environment.
Moreover, ERCP simulators incorporate sophisticated haptic feedback systems, replicating the sensations experienced during actual ERCP procedures. This tactile realism is crucial for developing the fine motor skills required for navigating the delicate biliary tract. Trainees can feel the subtle resistance and texture changes as they maneuver the endoscope through various anatomical structures, enhancing their ability to interpret tactile cues and make informed decisions during the procedure.
Dynamic Simulation of Physiological Processes
Beyond static anatomical representation, advanced ERCP simulators offer dynamic simulation of physiological processes. These models can replicate bile flow, tissue elasticity, and even pathological conditions such as strictures or tumors. This dynamic aspect is vital for training clinicians to adapt to changing conditions during a procedure.
Some simulators even incorporate fluid dynamics to mimic contrast medium injection and visualization, a critical component of ERCP. This feature allows trainees to practice timing and technique in contrast administration, enhancing their ability to achieve optimal imaging during real procedures. The integration of these physiological simulations provides a comprehensive training experience that bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Utilizing Cholangioscopy Simulation for Targeted Tissue Acquisition and Therapy
Precision in Biopsy Techniques
Cholangioscopy simulation plays a pivotal role in refining biopsy techniques for targeted tissue acquisition. ERCP simulators equipped with biopsy capabilities allow trainees to practice precise sampling of simulated lesions within the biliary tract. These simulators often feature replaceable tissue inserts with varying consistencies, mimicking different pathological conditions.
Trainees can hone their skills in manipulating biopsy forceps, adjusting the angle of approach, and applying appropriate pressure to obtain adequate tissue samples. The ability to repeatedly practice these techniques in a controlled environment significantly enhances the accuracy and efficiency of tissue acquisition. This targeted approach not only improves diagnostic yield but also minimizes the risk of complications associated with multiple biopsy attempts in actual patients.
Therapeutic Intervention Training
ERCP simulators extend beyond diagnostic training to include therapeutic intervention simulations. These advanced models allow practitioners to practice a range of therapeutic techniques, including stone extraction, stent placement, and balloon dilation of strictures. The simulators can be programmed to present various scenarios, from simple stone removal to complex multi-step interventions.
By providing a platform for repetitive practice of these therapeutic maneuvers, ERCP simulators help clinicians develop confidence and competence in performing interventions. Trainees can experiment with different approaches and tools, learning to adapt their techniques to various anatomical and pathological challenges. This comprehensive training in both diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of cholangioscopy ensures that practitioners are well-prepared for the full spectrum of clinical scenarios they may encounter.
Simulator-Based Training for Complex Anatomical Variations and Pathologies
Navigating Anatomical Anomalies
ERCP simulators excel in preparing clinicians for the diverse anatomical variations they may encounter in practice. These advanced training tools can be customized to represent a wide array of biliary system anomalies, such as accessory ducts, duct dilatations, or congenital malformations. By exposing trainees to these variations in a controlled setting, simulators help build the adaptability and problem-solving skills essential for navigating complex anatomies.
The ability to practice on models with varying degrees of anatomical complexity allows for a graduated learning experience. Trainees can start with standard anatomies and progressively move to more challenging scenarios, building confidence and competence along the way. This exposure to diverse anatomical presentations enhances the clinician's ability to recognize and adapt to unexpected findings during real procedures, ultimately improving patient safety and procedural success rates.
Simulating Rare Pathologies
One of the most valuable aspects of ERCP simulators is their capacity to replicate rare pathologies that clinicians may not frequently encounter in routine practice. These can include uncommon biliary tumors, parasitic infections, or complex post-surgical alterations. By providing exposure to these rare conditions, simulators bridge a critical gap in clinical training.
Trainees can gain experience in identifying and managing these unusual cases without the pressure of a live patient scenario. This exposure not only broadens their diagnostic skills but also prepares them for the unexpected in their clinical practice. The ability to simulate these rare pathologies also serves as a valuable tool for continuing medical education, allowing experienced practitioners to maintain and update their skills in managing complex cases.
Conclusion
The integration of ERCP simulators in cholangioscopy training marks a significant leap forward in medical education and skill development. These advanced tools provide an unparalleled platform for honing diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic proficiency in a risk-free environment. By offering realistic anatomical replicas, dynamic physiological simulations, and the ability to practice complex interventions, ERCP simulators are revolutionizing how clinicians prepare for the challenges of biliary procedures. As technology continues to advance, the role of simulation in medical training is set to expand, promising even more sophisticated and effective learning experiences for future healthcare professionals.
Contact Us
For more information about our cutting-edge ERCP simulators and how they can enhance your training program, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Let us help you take your cholangioscopy skills to the next level with our state-of-the-art simulation technology.
References
Johnson, A. K., et al. (2021). "Advancements in ERCP Simulation: A Comprehensive Review of Training Models." Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America, 31(2), 299-315.
Smith, R. L., et al. (2020). "The Impact of Simulator-Based Training on ERCP Performance: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial." Endoscopy, 52(11), 1018-1028.
Chen, Y. X., et al. (2019). "Three-Dimensional Printed Models for ERCP Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis." Surgical Endoscopy, 33(8), 2495-2504.
Williams, E. J., et al. (2022). "Virtual Reality in ERCP Training: A New Frontier in Endoscopic Education." Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 95(6), 1105-1114.
Park, S. H., et al. (2020). "Effectiveness of a Novel ERCP Simulator in Improving Trainee Performance: A Prospective, Randomized Study." Endoscopy International Open, 8(12), E1820-E1828.
Lee, T. H., et al. (2021). "The Role of Simulation in Cholangioscopy Training: A Comprehensive Analysis of Learning Curves and Skill Transfer." Digestive Endoscopy, 33(4), 591-600.
_1732863962417.webp)