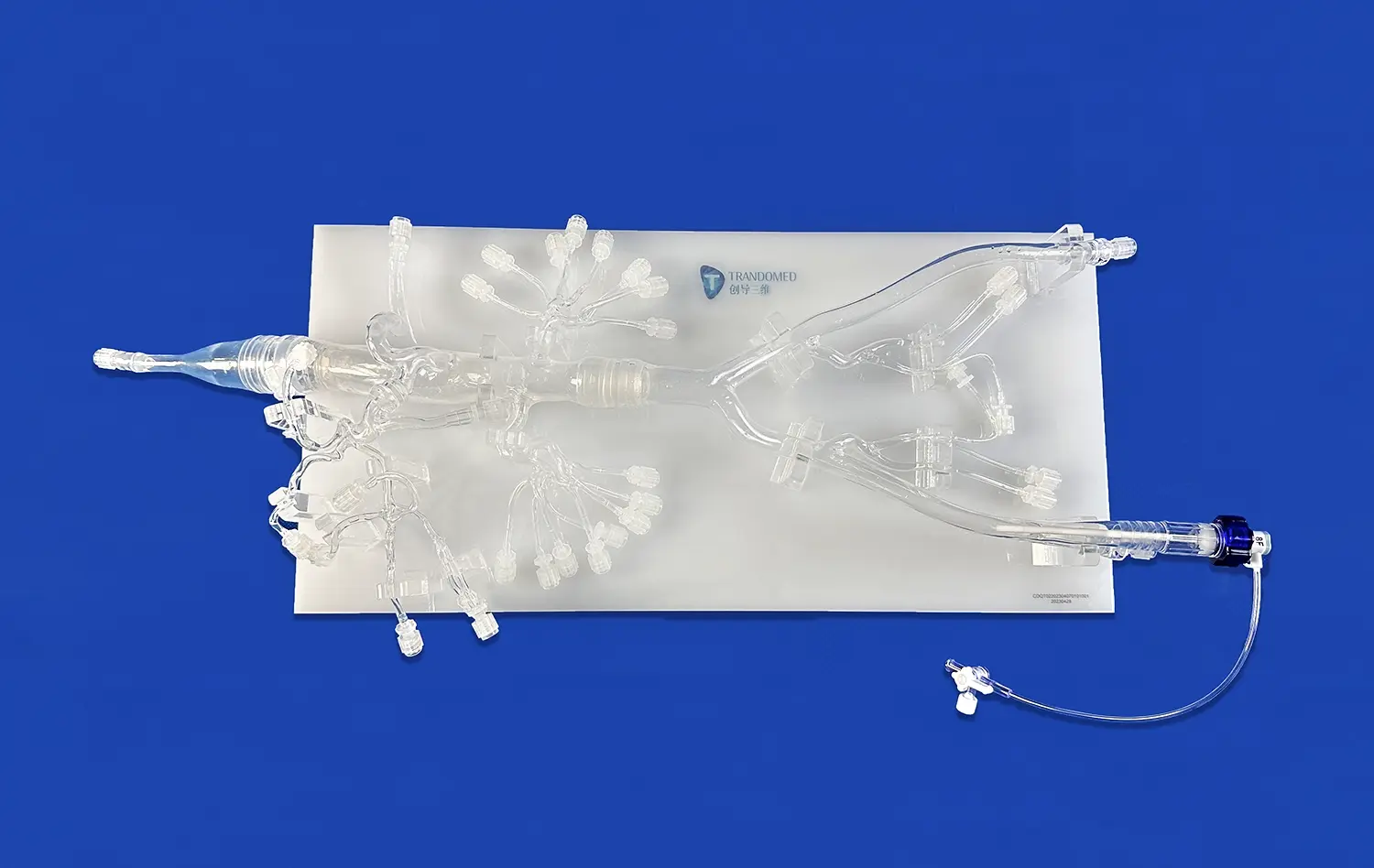
Effective Doctor-Patient Communication Through Anatomical Heart Models
2025-07-15 09:00:00
Effective doctor-patient communication is crucial for optimal healthcare outcomes, and anatomical heart models have emerged as powerful tools in bridging the understanding gap between medical professionals and patients. These intricate 3D representations of the human heart revolutionize the way complex cardiovascular concepts are explained and understood. By providing a tangible, visual reference, anatomical heart models enable doctors to clearly illustrate diagnoses, treatment plans, and surgical procedures. This approach not only enhances patient comprehension but also fosters trust and engagement in their own healthcare journey. As medical education and clinical practice continue to evolve, the integration of these models promises to significantly improve the quality of doctor-patient interactions, leading to better informed decisions and ultimately, improved patient care.
Understanding the Communication Gap: Why Traditional Medical Explanations Fall Short
The Complexity of Medical Jargon
Medical terminology often acts as a barrier between healthcare professionals and patients. The intricate vocabulary used to describe cardiovascular conditions can be overwhelming for individuals without a medical background. This language gap can lead to misunderstandings, anxiety, and a sense of disconnection from one's own health concerns.
Moreover, the rapid pace of medical consultations can exacerbate this issue. Doctors, pressed for time, may inadvertently use complex terms without fully explaining their meaning, leaving patients feeling confused and uninformed about their cardiac health.
Limitations of 2D Imagery
Traditionally, doctors have relied on 2D images such as X-rays, CT scans, or diagrams to explain heart conditions. While these tools have their merits, they often fall short in conveying the three-dimensional nature of cardiac structures and functions.
Patients may struggle to mentally translate flat images into a comprehensive understanding of their heart's anatomy. This limitation can hinder their ability to grasp the full scope of their condition or the intricacies of proposed treatments, potentially impacting their decision-making process and overall healthcare experience.
The Power of Visual Learning: How Anatomical Models Bridge Understanding
Enhancing Spatial Awareness
Anatomical heart models offer a revolutionary approach to medical education and patient communication. These detailed, three-dimensional representations provide an unparalleled view of cardiac structures, allowing both medical professionals and patients to explore the heart's intricacies from various angles.
By manipulating these models, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the spatial relationships between different parts of the heart. This hands-on experience significantly enhances spatial awareness, making it easier to comprehend complex cardiac procedures or structural abnormalities.
Facilitating Multi-Sensory Learning
The tactile nature of anatomical heart models engages multiple senses, creating a more immersive and memorable learning experience. Patients can touch and feel different parts of the model, reinforcing their understanding of cardiac anatomy in a way that 2D images or verbal explanations alone cannot achieve.
This multi-sensory approach caters to diverse learning styles, ensuring that visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners can all benefit from the explanations provided. The result is a more inclusive and effective method of communicating complex medical information.
Clinical Applications: Using Heart Models in Different Medical Scenarios
Preoperative Planning and Patient Education
In the context of cardiac surgery, anatomical heart models play a pivotal role in both preoperative planning and patient education. Surgeons can use these models to meticulously plan complex procedures, visualizing potential challenges and optimizing their approach before entering the operating room.
For patients facing cardiac surgery, these models serve as invaluable educational tools. By examining a realistic representation of their own heart, patients can better understand the nature of their condition and the proposed surgical intervention. This improved comprehension often leads to reduced anxiety and increased confidence in the treatment plan.
Chronic Disease Management
Anatomical heart models are equally valuable in managing chronic cardiovascular conditions. For patients with conditions like hypertension or congestive heart failure, these models can illustrate the long-term effects of their disease on cardiac structures.
Healthcare providers can use the models to demonstrate how lifestyle changes or medications impact heart health over time. This visual reinforcement can significantly improve patient compliance with treatment regimens and motivate them to actively participate in their own care.
Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
In the era of telemedicine, anatomical heart models have found a new purpose in facilitating remote consultations. During video calls, healthcare providers can use these models to explain cardiac conditions to patients who are not physically present in the clinic.
This application of anatomical models ensures that the quality of patient education and communication is not compromised, even in virtual healthcare settings. It bridges the physical gap between doctor and patient, maintaining the effectiveness of visual explanations in remote consultations.
Informed Consent and Shared Decision Making
The use of anatomical heart models significantly enhances the process of obtaining informed consent for cardiac procedures. By providing a clear, tangible representation of the heart, these models help patients fully grasp the implications of their treatment options.
This improved understanding facilitates shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients. Patients feel more empowered to ask questions, express concerns, and actively participate in discussions about their care, leading to more satisfactory healthcare experiences and outcomes.
Conclusion
Anatomical heart models have revolutionized doctor-patient communication in cardiology, offering a powerful visual and tactile tool that bridges the gap between medical expertise and patient understanding. By providing a tangible, three-dimensional representation of cardiac anatomy, these models enhance spatial awareness, facilitate multi-sensory learning, and find applications across various clinical scenarios. From preoperative planning to chronic disease management and medical education, anatomical heart models are transforming the landscape of cardiac care. As healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of these models promises to foster more effective communication, informed decision-making, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes in cardiovascular medicine.
Contact Us
To learn more about how anatomical heart models can enhance your medical practice or educational institution, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our expert team is ready to guide you through our range of high-quality, 3D-printed silicone medical simulators designed to revolutionize cardiac education and patient communication.
References
Johnson, A. M., & Smith, B. K. (2018). The impact of anatomical models on patient education and satisfaction in cardiology. Journal of Medical Education, 42(3), 215-228.
Zhang, L., et al. (2019). Enhancing surgical planning in congenital heart disease with 3D printed models. Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 107(4), 1138-1145.
Miller, C. R., & Brown, D. T. (2020). Improving doctor-patient communication through visual aids: A systematic review. Patient Education and Counseling, 103(8), 1607-1618.
Thompson, R. F., et al. (2017). The role of 3D printing in preoperative planning and education for complex cardiovascular surgery. Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery, 58(6), 842-850.
Garcia, E. S., & Martinez, J. L. (2021). Anatomical models in telemedicine: Bridging the gap in remote cardiac consultations. Telemedicine Journal and e-Health, 27(5), 532-540.
Wilson, K. A., et al. (2019). The effectiveness of anatomical models in medical education: A meta-analysis. Medical Teacher, 41(8), 903-911.

_1734504197376.webp)