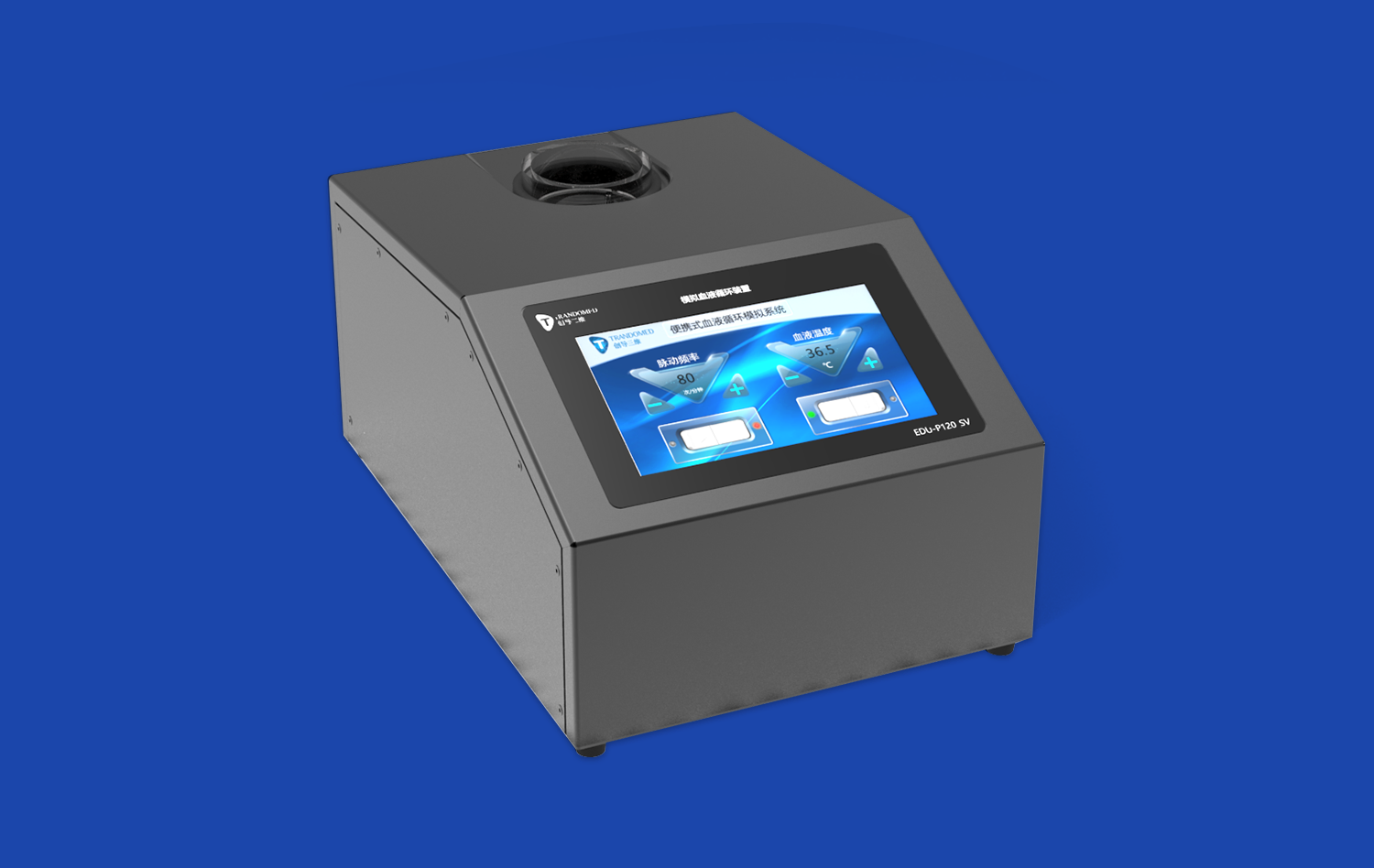
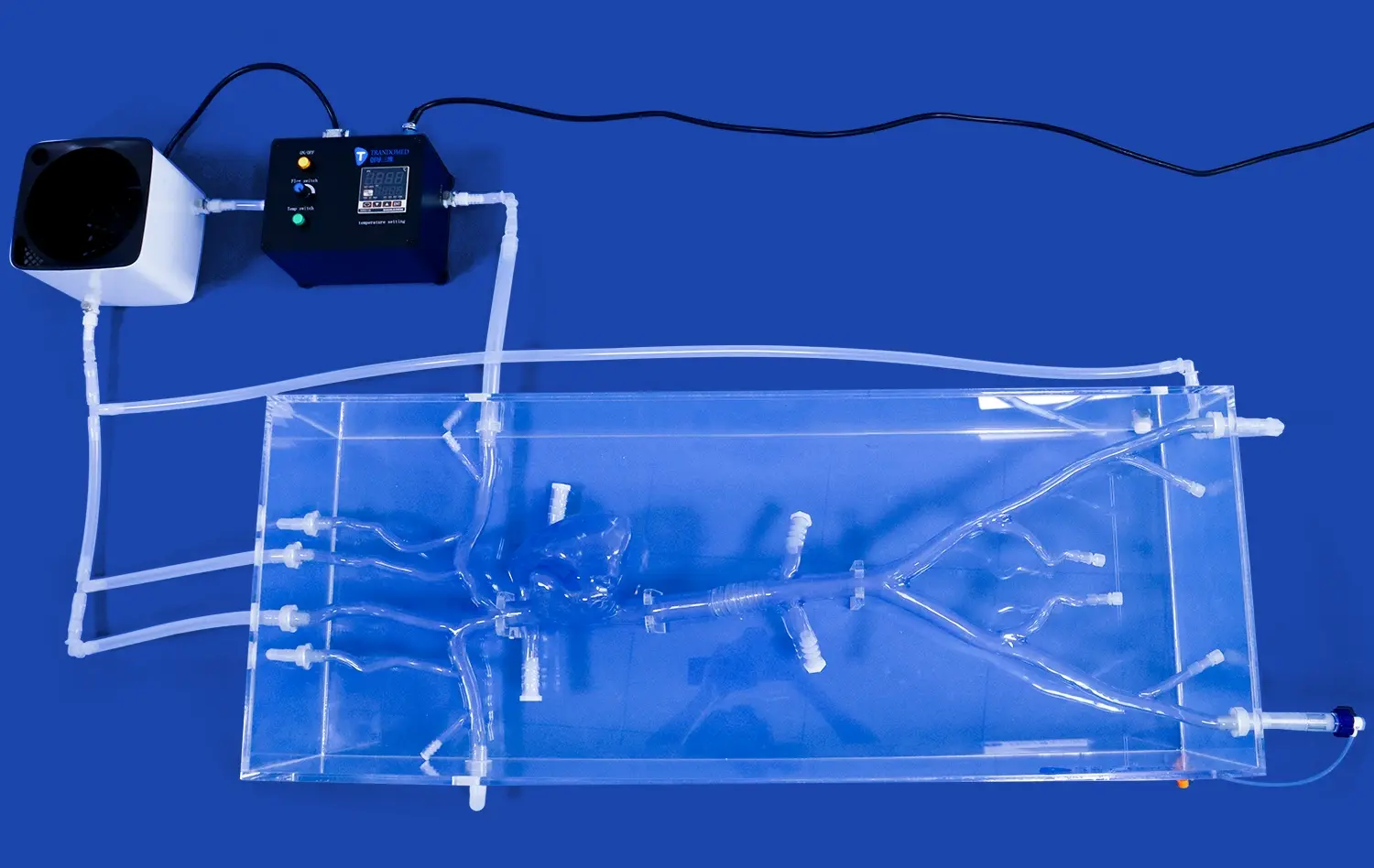
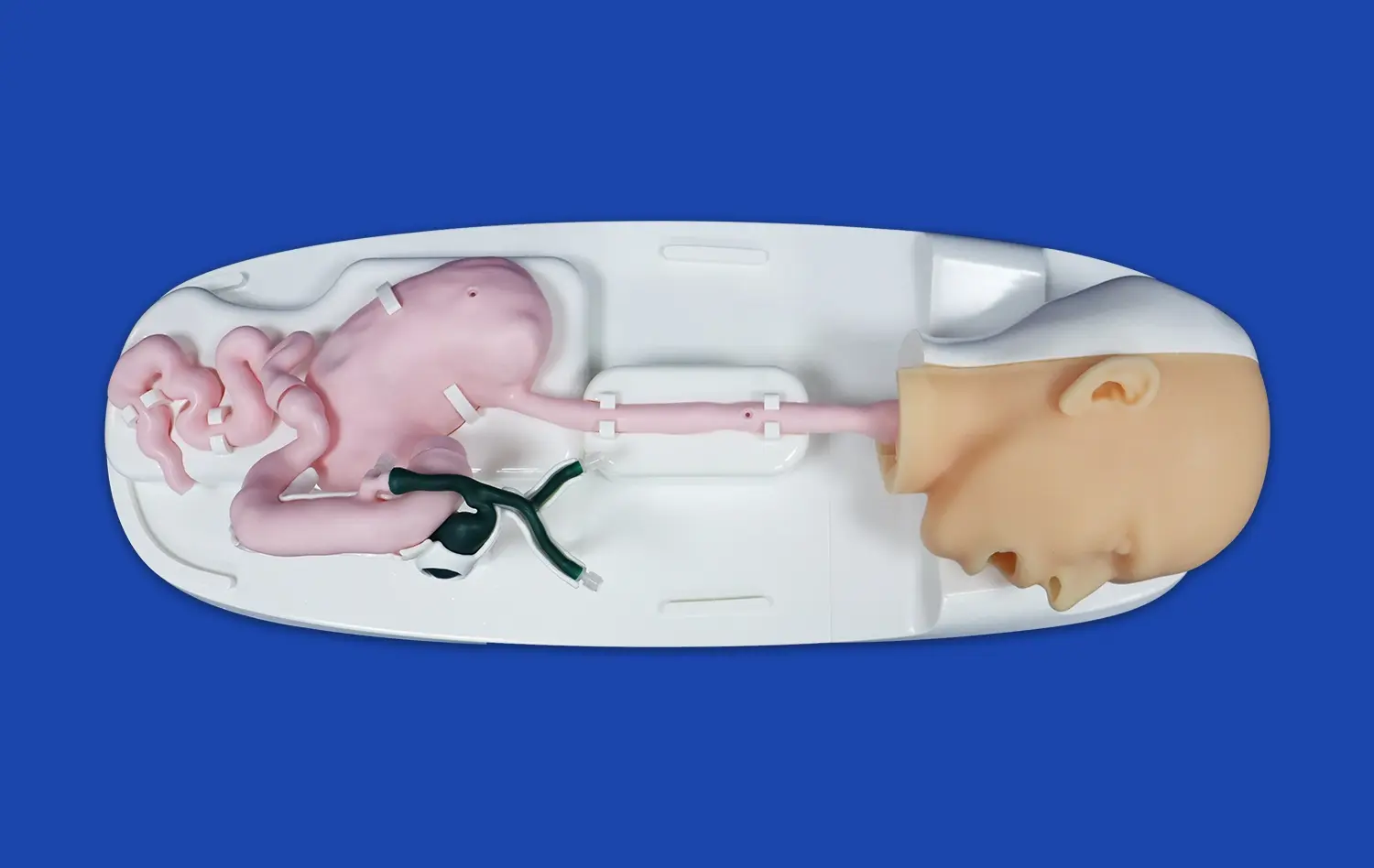
How Does It Support EVAR and TEVAR Procedure Practice?
Realistic Anatomical Modeling
Endovascular intervention trainers excel in providing highly accurate anatomical models for EVAR and TEVAR practice. These simulators utilize advanced 3D printing technology to create lifelike silicone vascular structures based on actual patient data. The models replicate the intricate details of aortic aneurysms, including challenging anatomical variations such as angulated necks, calcified plaques, and tortuous iliac arteries. This level of realism allows surgeons to encounter and overcome the same obstacles they might face in real procedures, enhancing their preparedness for complex cases.
Simulated Fluoroscopy and Angiography
A crucial aspect of EVAR and TEVAR procedures is the ability to navigate through blood vessels using fluoroscopic guidance. Modern endovascular intervention trainers incorporate simulated C-arm functionality and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) imaging software. This feature enables trainees to practice wire and catheter manipulation, contrast injection techniques, and precise graft deployment - all while interpreting real-time fluoroscopic images. The ability to rehearse these critical skills in a controlled environment significantly boosts surgeon confidence and competence.
Endograft Deployment Practice
One of the most challenging aspects of EVAR and TEVAR procedures is the accurate deployment of endografts. Endovascular intervention trainers offer a platform for surgeons to practice this crucial step repeatedly. Trainees can experiment with various endograft designs, sizes, and deployment techniques, learning to navigate the complexities of graft positioning, alignment, and fixation. This hands-on experience is invaluable in developing the fine motor skills and decision-making abilities required for successful endograft placement in live procedures.
Training for Complex Aortic Anatomy and Endograft Navigation
Customizable Anatomical Variations
Aortic aneurysms often present with complex anatomical variations that can complicate endovascular repair. Advanced endovascular trainers offer customizable modules that simulate a wide range of challenging scenarios. These may include aneurysms with short or angulated necks, thrombus-lined sacs, or involvement of visceral arteries. By practicing on these diverse anatomical models, surgeons can develop strategies to overcome the unique challenges posed by each variation, enhancing their ability to tackle even the most complex cases in clinical practice.
Endograft Selection and Sizing
Choosing the appropriate endograft and ensuring correct sizing is crucial for successful EVAR and TEVAR procedures. Endovascular intervention trainers allow surgeons to practice the critical decision-making process of graft selection. Through repeated simulations, trainees learn to accurately measure aortic dimensions, assess landing zones, and select the optimal graft configuration. This experience translates directly to improved clinical outcomes, as proper graft selection and sizing are key factors in preventing complications such as endoleaks and graft migration.
Navigation of Tortuous Vessels
Navigating through tortuous vessels is a common challenge in endovascular procedures. Advanced simulators incorporate modules that mimic the complexities of navigating through highly angulated aortic arches, tortuous iliac arteries, and stenotic vessels. Surgeons can practice wire and catheter manipulation techniques, learning to overcome these anatomical obstacles safely and efficiently. This training is particularly valuable for complex TEVAR cases, where navigation through the aortic arch can be especially challenging.
Reducing Surgical Risk Through Preoperative Simulation
Patient-Specific Procedure Planning
One of the most significant advantages of endovascular intervention trainers is the ability to conduct patient-specific preoperative simulations. By importing a patient's CT or MRI data into the simulator, surgeons can create a 3D-printed model of the exact anatomy they will encounter during the actual procedure. This allows for meticulous planning, including selection of optimal access routes, identification of potential complications, and determination of the most suitable endograft configuration. Such detailed preoperative simulation significantly reduces procedural risks and improves overall surgical outcomes.
Complication Management Training
While EVAR and TEVAR procedures have become increasingly safe, complications can still occur. Endovascular intervention trainers provide a risk-free environment for surgeons to practice managing potential complications such as endoleaks, graft migration, or inadvertent coverage of critical branch vessels. By simulating these scenarios, surgeons can develop and refine their troubleshooting skills, learning to quickly recognize and address complications. This training is invaluable in preparing surgeons to handle unexpected challenges during live procedures, ultimately enhancing patient safety.
Team-Based Simulation Exercises
Successful endovascular procedures require seamless coordination among the surgical team. Advanced endovascular trainers support team-based simulation exercises, allowing surgeons, nurses, and technicians to practice their roles in a realistic setting. These simulations help improve communication, streamline workflow, and enhance overall team performance. By rehearsing complex procedures as a unit, teams can identify and address potential inefficiencies or communication gaps before they arise in the operating room, leading to smoother and safer real-world procedures.
Conclusion
Endovascular intervention trainers have emerged as indispensable tools in the field of aortic aneurysm repair, offering surgeons a comprehensive platform to refine their skills and push the boundaries of endovascular techniques. By providing realistic anatomical models, simulated imaging capabilities, and opportunities for patient-specific planning, these trainers significantly enhance procedural competence and reduce surgical risks. As endovascular techniques continue to evolve, the role of simulation-based training in preparing surgeons for complex aortic interventions will only grow in importance, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and advancing the field of vascular surgery.
Contact Us
Ready to revolutionize your endovascular training program? Discover Trandomed's state-of-the-art endovascular intervention trainers, designed to provide the most realistic and comprehensive simulation experience for EVAR and TEVAR procedures. Our customizable solutions cater to your specific training needs, ensuring your team is prepared for even the most complex aortic interventions. Take the next step in enhancing your surgical skills and patient outcomes. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our innovative simulation technology.
_1734504221178.webp)
_1734507205192.webp)
_1732866687283.webp)