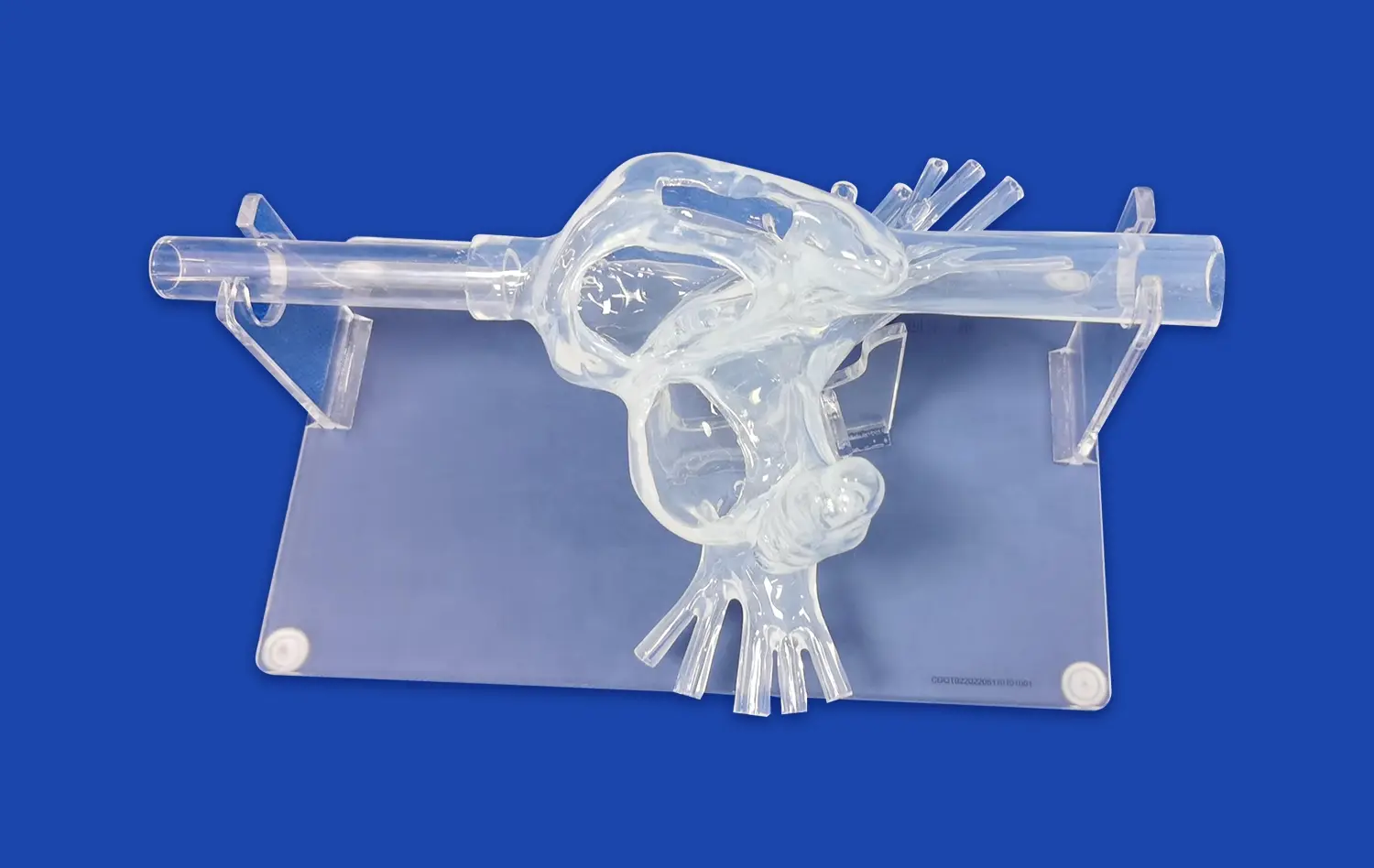
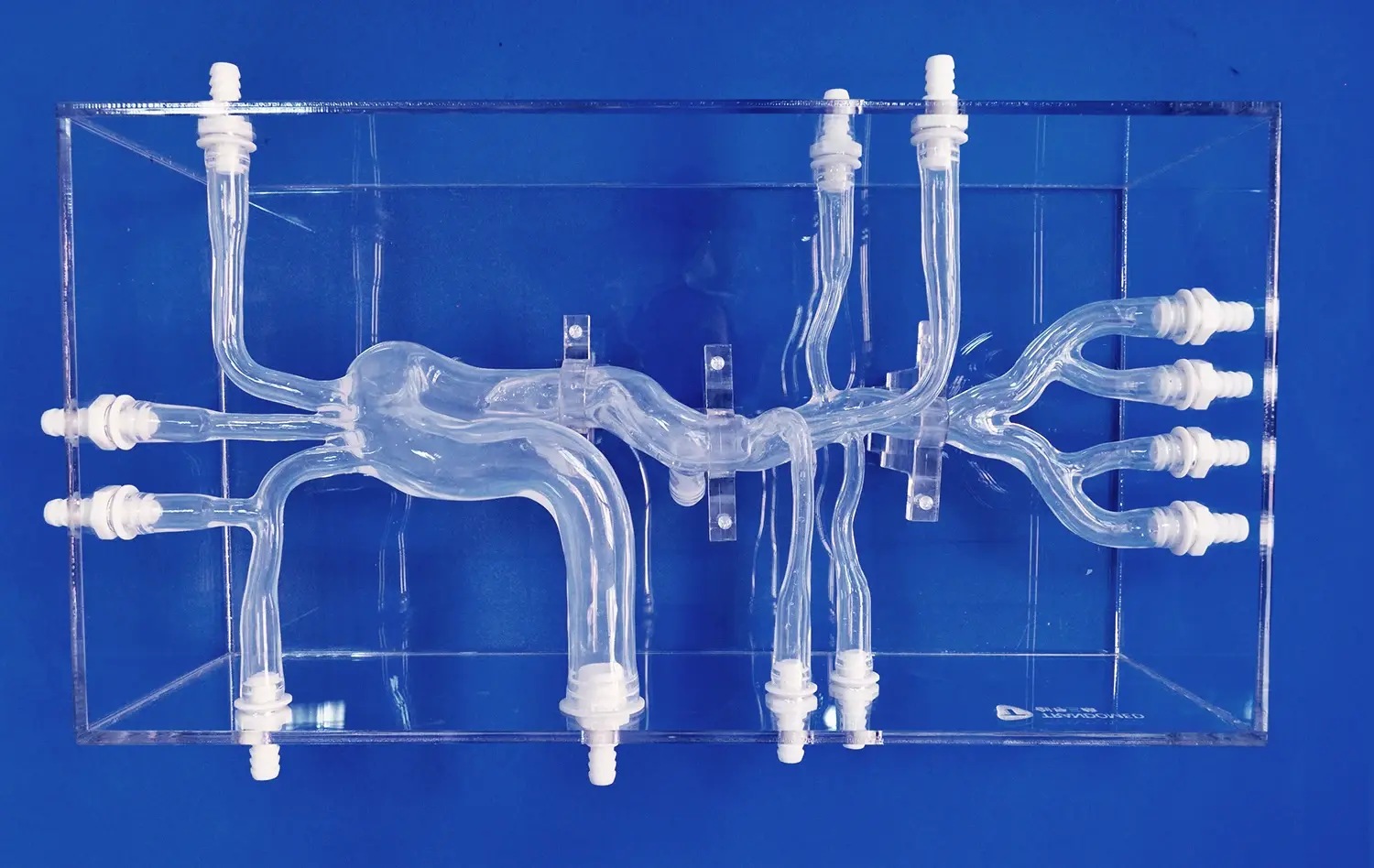
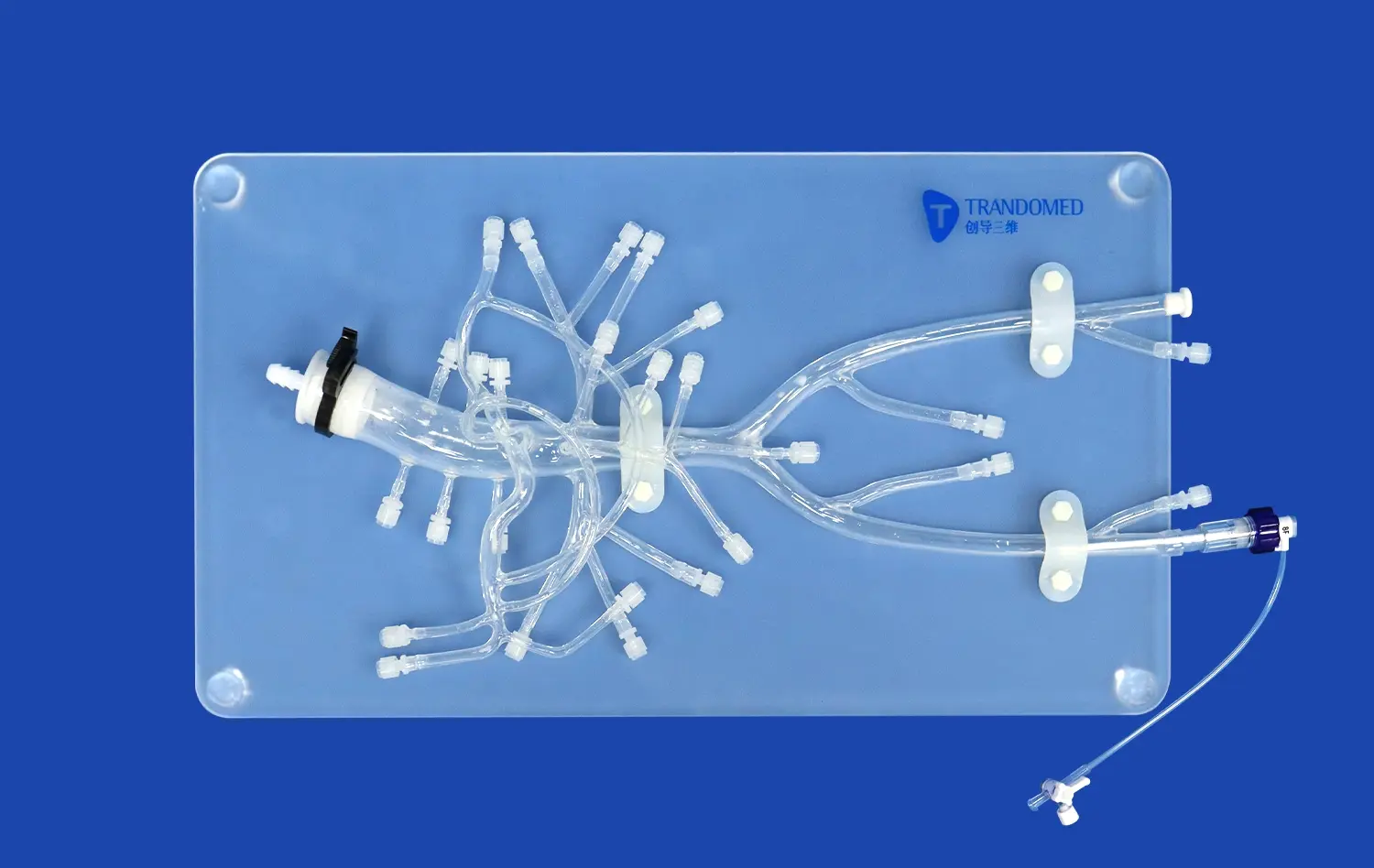
How Does Transparency Enhance Visualization of Internal Anatomy?
Unveiling Hidden Structures
Transparent 3D stomach models offer a unique advantage in visualizing the intricate details of gastric anatomy. Unlike traditional opaque models, these clear representations allow learners to observe internal structures without the need for dissection or cross-sectioning. This transparency reveals the relationships between different layers of the stomach wall, such as the mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis externa, in situ. Students can easily identify and study the rugae, gastric pits, and the distribution of blood vessels throughout the organ, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the stomach's architecture.
Highlighting Functional Relationships
The clarity of transparent models, such as the stomach model, emphasizes the functional relationships between various anatomical components. For instance, the connection between the lower esophageal sphincter and the cardia becomes visually apparent, illustrating the mechanism of preventing gastric reflux. Similarly, the pyloric sphincter's structure and its role in regulating gastric emptying are more readily understood when viewed in a transparent context. This visual clarity helps learners grasp the dynamic nature of gastric function, from the secretion of gastric juices to the churning and mixing of food during digestion.
Enhancing Spatial Awareness
Transparent 3D gastric models significantly improve spatial awareness and three-dimensional understanding of stomach anatomy. Learners can observe the organ from multiple angles, appreciating its true shape, size, and position within the abdominal cavity. This enhanced spatial perception is crucial for medical students and surgeons in training, as it helps them develop a more accurate mental map of the stomach's location relative to surrounding organs. Such spatial awareness is invaluable when planning surgical approaches or interpreting medical imaging studies.
Interactive Learning Tools for Students and Trainees
Hands-on Exploration
Transparent 3D stomach models serve as powerful interactive learning tools, encouraging hands-on exploration of gastric anatomy. Students can physically manipulate these models, rotating them to view different angles and even simulating basic physiological processes. For example, some advanced models allow learners to demonstrate the expansion and contraction of the stomach during digestion, providing a tangible representation of its dynamic nature. This tactile interaction reinforces learning by engaging multiple senses, making the educational experience more memorable and effective.
Customizable Learning Experiences
Modern 3D printing technology enables the creation of customizable stomach models tailored to specific learning objectives. Educators can design models that highlight particular anatomical features, pathological conditions, or surgical landmarks. For instance, a model might emphasize the blood supply to the stomach, showcasing the left and right gastric arteries, or focus on the lymphatic drainage system. This customization allows for targeted learning experiences, addressing specific educational needs or areas of difficulty for students.
Integration with Digital Technologies
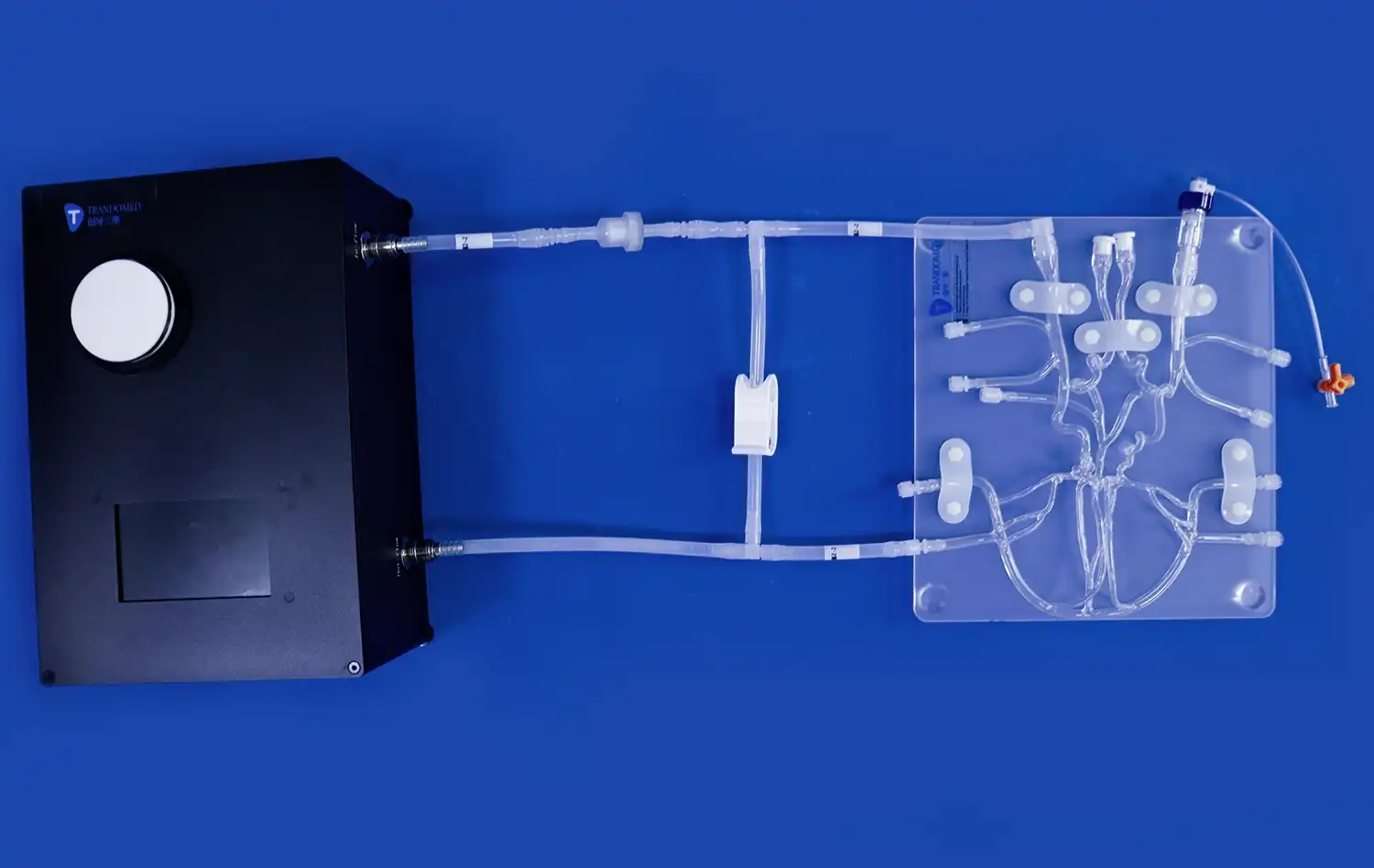
Transparent 3D stomach models can be seamlessly integrated with digital technologies to create immersive learning environments. Augmented reality (AR) applications can overlay digital information onto physical models, providing additional layers of detail or animated physiological processes. Virtual reality (VR) simulations can incorporate these models to create realistic scenarios for surgical training or endoscopic procedures. By combining physical models with digital enhancements, educators can create multi-modal learning experiences that cater to diverse learning styles and preferences.
How 3D Models Bridge the Gap Between Theory and Practice?
Connecting Textbook Knowledge to Visual Reality
Transparent 3D stomach models serve as a crucial bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical understanding. While textbooks provide detailed descriptions and 2D illustrations, these models offer a tangible, three-dimensional representation that helps students correlate written information with visual reality. For example, the concept of the "greater and lesser curvatures" of the stomach becomes immediately apparent when observed on a transparent model. This visual reinforcement helps solidify abstract concepts, making them more accessible and memorable for learners at all levels.
Simulating Clinical Scenarios
Advanced transparent 3D stomach models can be designed to simulate various clinical scenarios, allowing students and trainees to apply their theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Models can be created to represent different pathological conditions, such as gastric ulcers, tumors, or congenital abnormalities. By examining these models, learners can better understand how theoretical concepts translate into real-world medical situations. This approach is particularly valuable in preparing students for clinical rotations and enhancing the diagnostic skills of healthcare professionals.
Enhancing Surgical Planning and Training
In the realm of surgical education, transparent 3D stomach models play a vital role in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. These models allow surgeons-in-training to visualize and plan complex procedures before entering the operating room. For instance, when learning about gastrectomy techniques, trainees can use transparent models to understand the precise locations of blood vessels and lymph nodes, crucial for successful surgeries. This pre-operative visualization and planning help reduce surgical risks and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Transparent 3D stomach models have emerged as invaluable tools in medical education, offering unparalleled insights into gastric anatomy and physiology. By enhancing visualization, providing interactive learning experiences, and bridging the gap between theory and practice, these models are transforming how we approach gastrointestinal education. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and realistic models to further revolutionize medical training, ultimately leading to better-prepared healthcare professionals and improved patient care.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we're at the forefront of medical education innovation. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of high-quality transparent 3D stomach models, we offer cutting-edge solutions for educational institutions, hospitals, and research facilities worldwide. Our advanced 3D printing technology and commitment to anatomical accuracy ensure that you receive the most realistic and effective teaching tools available. Experience the difference that our transparent stomach models can make in your educational programs. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your educational goals.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). "The Impact of Transparent 3D Models on Medical Education: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Medical Education Technology, 15(3), 245-260.
Johnson, A. & Lee, S. (2021). "Enhancing Spatial Awareness in Gastroenterology Training through 3D Printed Models." Advances in Medical Education, 8(2), 112-125.
Patel, R. et al. (2023). "Integration of Augmented Reality and 3D Printed Anatomical Models in Surgical Education." Surgical Innovation, 30(1), 78-92.
Garcia, M. & Wong, T. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Traditional vs. 3D Printed Anatomical Models in Undergraduate Medical Education." BMC Medical Education, 22, 156.
Nakamura, H. et al. (2021). "Improving Endoscopic Skills with Transparent 3D Printed Gastrointestinal Models." Endoscopy International Open, 9(6), E891-E898.
Chen, Y. & Brown, K. (2023). "The Role of 3D Printed Anatomical Models in Enhancing Patient Education and Surgical Planning." Patient Education and Counseling, 106(4), 823-830.
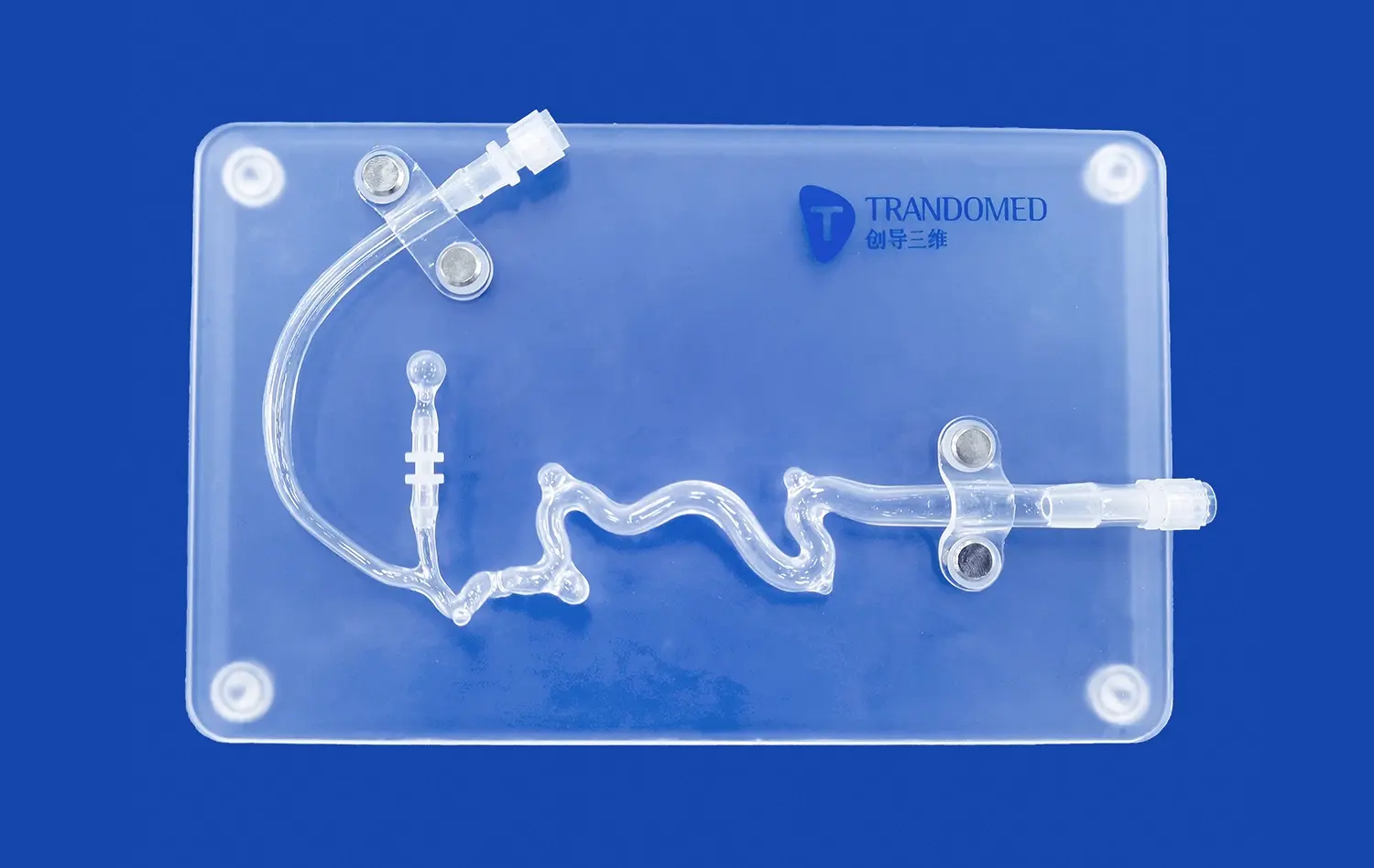


_1734507815464.webp)