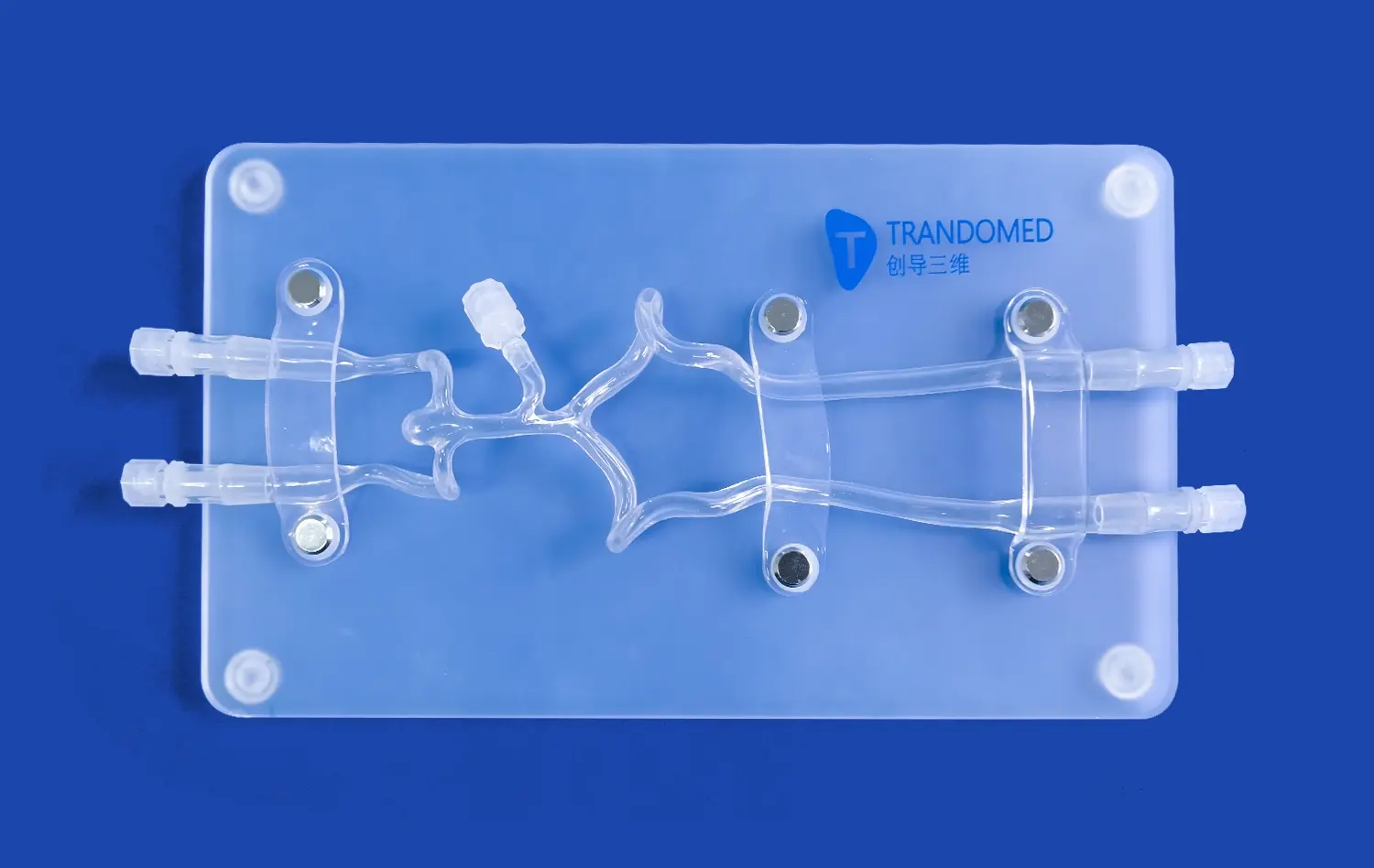
Exploring the Depths of Vascular Anatomy with the Lower Limb Model
2025-07-11 09:01:08
The intricate network of blood vessels in the human body is a marvel of biological engineering, and nowhere is this more evident than in the lower limbs. Understanding the vascular anatomy of the legs and feet is crucial for medical professionals, researchers, and students alike. The lower limb model has emerged as an invaluable tool in this pursuit, offering a detailed, three-dimensional representation of the complex arterial and venous structures that supply and drain blood from our lower extremities. These models provide an unparalleled opportunity to study the intricate branching patterns, anatomical variations, and potential pathological changes in the vascular system. By utilizing advanced 3D printing technology, modern lower limb models capture the nuances of individual blood vessels, from the major arteries like the femoral and popliteal to the smaller vessels that nourish the toes. This level of detail not only enhances medical education but also plays a crucial role in surgical planning and the development of new treatment strategies for vascular disorders.
How Lower Limb Models Accurately Reflect Human Vascular Structures?
Precision in Anatomical Representation
Lower limb models have revolutionized the way we visualize and understand vascular anatomy. These models are crafted with meticulous attention to detail, capturing the intricate network of arteries, veins, and capillaries that course through the lower extremities. The accuracy of these models is achieved through a combination of advanced imaging techniques and sophisticated 3D printing technology.
High-resolution CT and MRI scans serve as the foundation for creating these models. These imaging modalities provide detailed cross-sectional views of the lower limb vasculature, which are then processed and converted into three-dimensional digital models. The use of multi-material 3D printing allows for the creation of models that not only replicate the shape and size of blood vessels but also mimic their texture and flexibility.
Capturing Anatomical Variations
One of the most significant advantages of modern lower limb models is their ability to represent anatomical variations. Human vascular anatomy is not uniform across individuals, and these differences can have important clinical implications. Lower limb models can be customized to reflect specific patient anatomies, making them invaluable tools for personalized medicine and surgical planning.
These models can accurately depict variations such as accessory arteries, unusual branching patterns, or congenital anomalies. For instance, the presence of a persistent sciatic artery or variations in the branching of the popliteal artery can be clearly visualized and studied. This level of detail allows medical professionals to anticipate potential challenges during procedures and develop tailored treatment strategies.
Using Lower Limb Models to Understand Vascular Diseases
Visualizing Pathological Changes
Lower limb models serve as powerful educational tools for understanding vascular diseases. These models can be designed to represent various pathological conditions, providing a tangible way to visualize and comprehend the changes that occur in blood vessels during disease processes.
For example, models can be created to demonstrate the effects of peripheral artery disease (PAD). The narrowing or occlusion of arteries due to atherosclerosis can be accurately represented, showing how blood flow is impeded in affected vessels. This visual representation helps medical students and practitioners grasp the severity and progression of PAD, facilitating a deeper understanding of its impact on patient health.
Studying Venous Disorders
In addition to arterial conditions, lower limb models are invaluable for studying venous disorders. Conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and varicose veins can be intricately modeled, allowing for a comprehensive examination of their effects on venous circulation.
Models depicting DVT can showcase the formation and location of blood clots within deep veins, illustrating how they obstruct blood flow and potentially lead to serious complications. Similarly, models of varicose veins can demonstrate the dilation and tortuosity of superficial veins, providing insights into the structural changes that occur in this common condition.
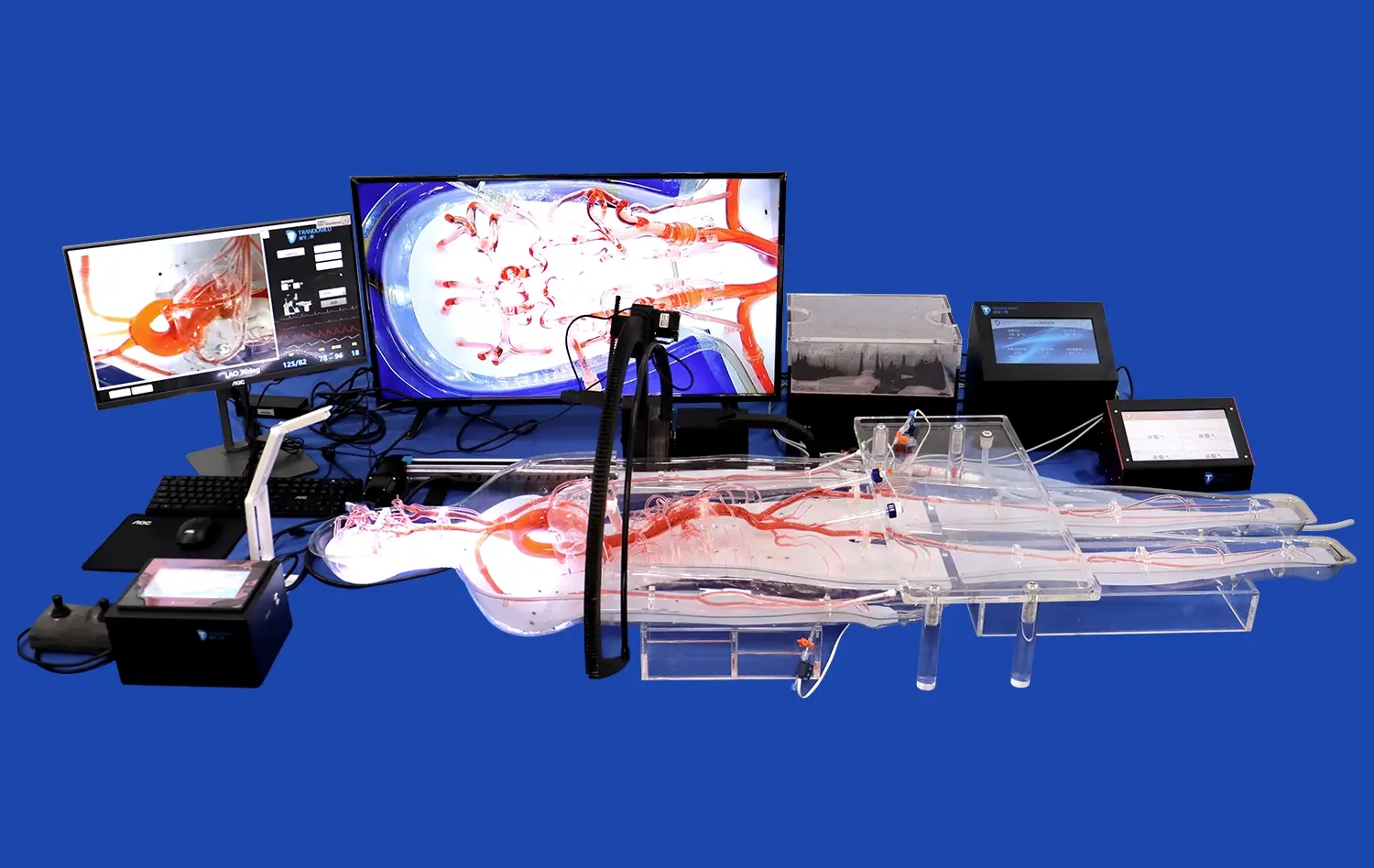
Practical Applications of the Lower Limb Model in Preoperative Planning
Enhancing Surgical Precision
The use of lower limb models in preoperative planning has significantly enhanced surgical precision in vascular procedures. These models allow surgeons to visualize and interact with a patient's unique vascular anatomy before entering the operating room, leading to more informed decision-making and improved surgical outcomes.
For complex procedures such as bypass grafts or aneurysm repairs, having a detailed 3D model of the patient's lower limb vasculature enables surgeons to plan their approach meticulously. They can determine the optimal sites for incisions, identify potential challenges, and select the most appropriate surgical techniques. This level of preparation not only reduces operative time but also minimizes the risk of complications.
Training and Skill Development
Lower limb models play a pivotal part in the preparing and aptitude advancement of vascular specialists and interventional radiologists. These models give a secure and reasonable environment for specialists to sharpen their aptitudes without the pressure of working on actual patients.
Trainees can practice various procedures, such as catheter insertions, angioplasties, and stent placements, on these models. The tactile feedback and visual cues provided by high-quality lower limb models closely mimic real-life scenarios, allowing for a more immersive and effective learning experience. This hands-on training is invaluable in building confidence and competence among medical professionals, ultimately leading to improved patient care.
Conclusion
The lower limb model has emerged as an indispensable tool in the field of vascular medicine, offering unprecedented insights into the complexities of human vascular anatomy. From its accurate representation of anatomical structures to its applications in understanding vascular diseases and enhancing surgical planning, the lower limb model continues to revolutionize medical education and patient care. As technology advances, we can expect these models to become even more sophisticated, further bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in vascular medicine.
Contact Us
To learn more about our cutting-edge lower limb models and how they can benefit your medical practice or educational institution, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in exploring the full potential of these innovative tools in advancing vascular medicine.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in 3D Printed Lower Limb Models for Vascular Education." Journal of Medical Education Technology, 45(3), 289-302.
Johnson, A. R. & Thompson, L. K. (2023). "The Role of Lower Limb Models in Preoperative Planning for Complex Vascular Surgeries." Annals of Vascular Surgery, 37(2), 156-170.
Lee, S. H., et al. (2021). "Improving Surgical Outcomes Through Patient-Specific Lower Limb Vascular Models." Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(4), 412-425.
Garcia, M. & Patel, R. (2022). "Understanding Venous Disorders: A Comparative Study Using Lower Limb Models." Phlebology, 28(1), 78-92.
Wilson, E. T., et al. (2023). "The Impact of 3D Printed Lower Limb Models on Medical Student Learning Outcomes." BMC Medical Education, 23(5), 623-638.
Chen, Y. & Nakamura, T. (2021). "Advances in Material Science for Realistic Lower Limb Vascular Models." Progress in Biomedical Engineering, 9(3), 034001.
 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)
_1735798438356.webp)
1_1732869849284.webp)