From Aneurysms to Stenosis: Versatile Training Applications of the Endovascular Intervention Trainer
2025-06-24 09:00:00
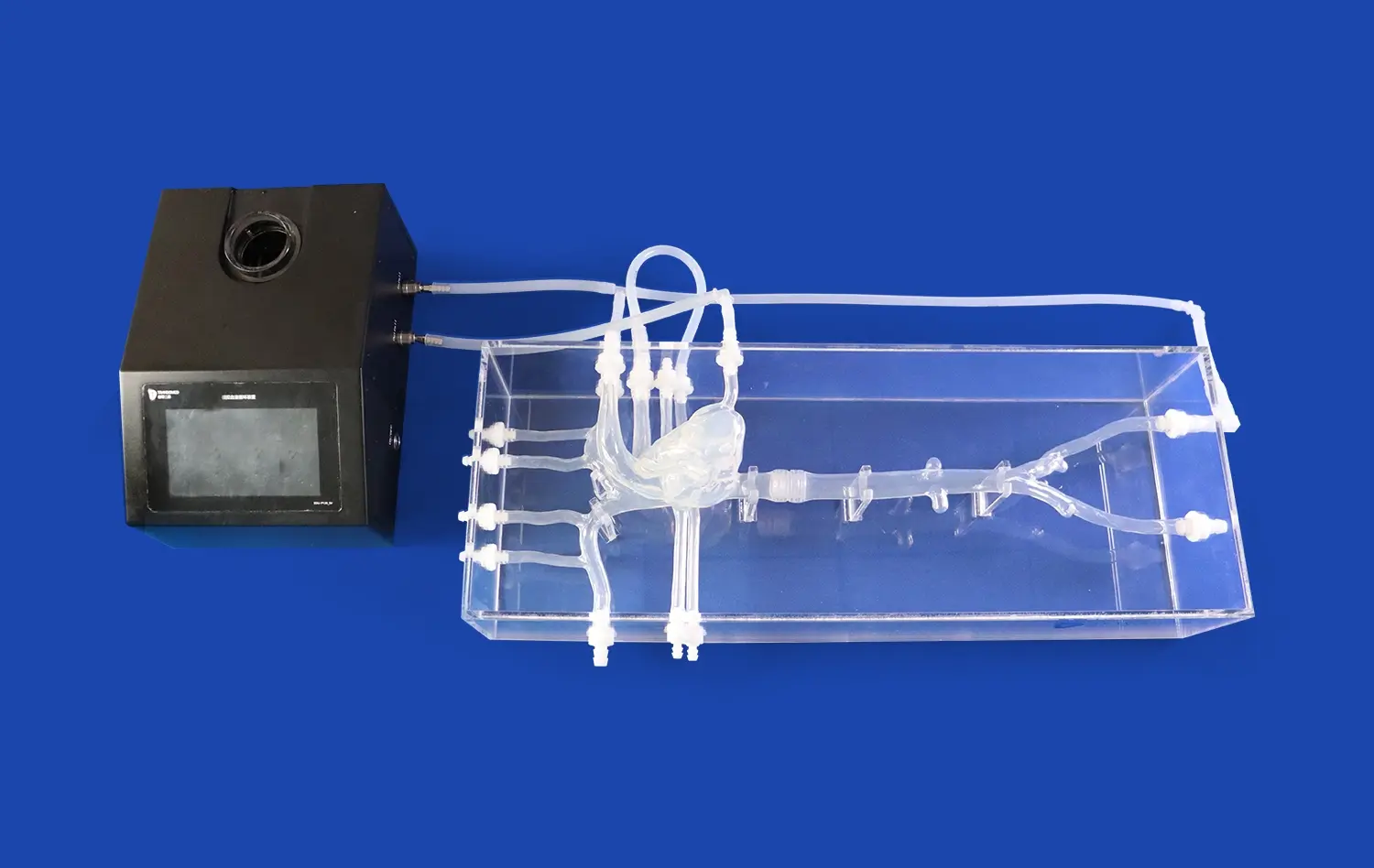
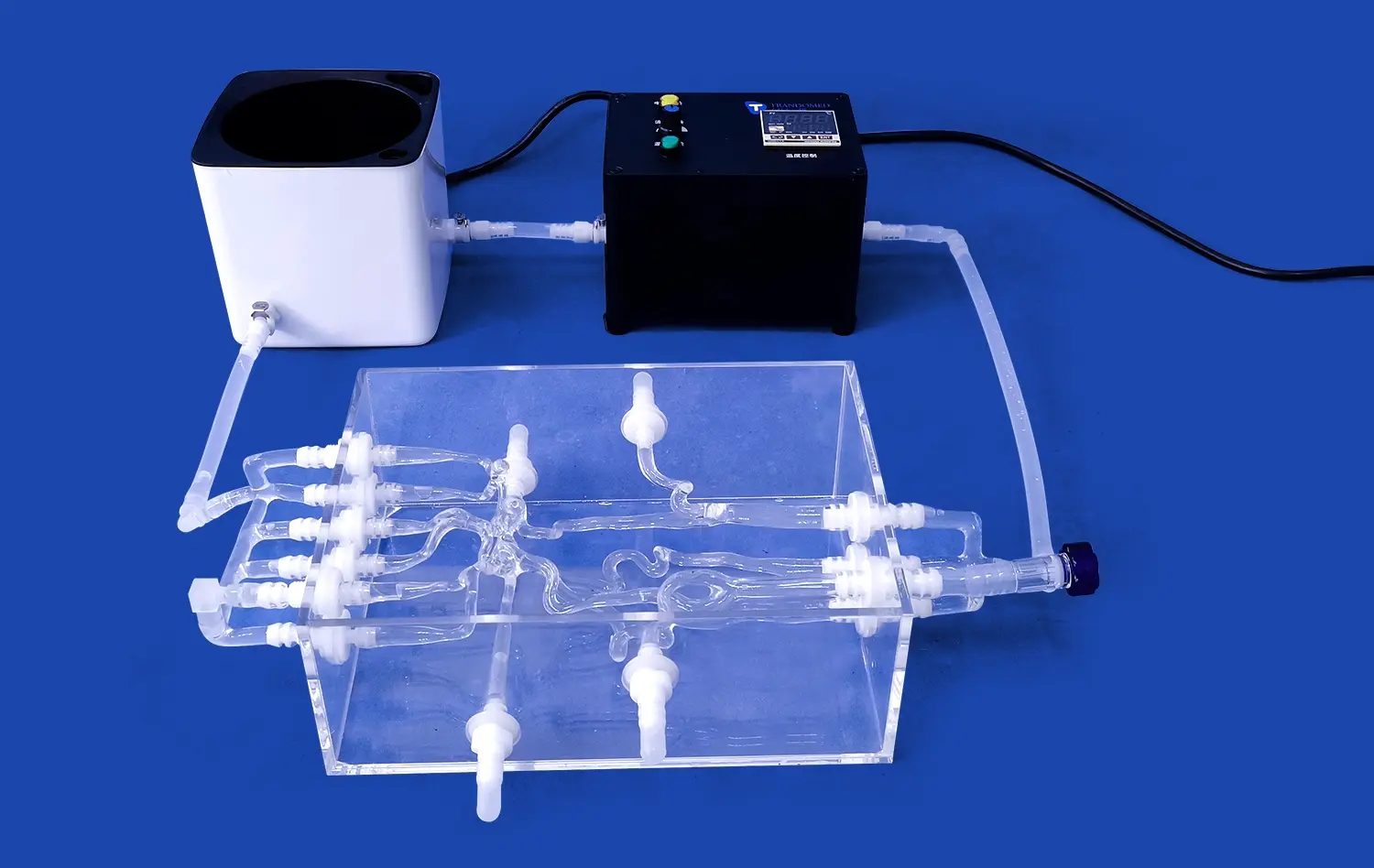
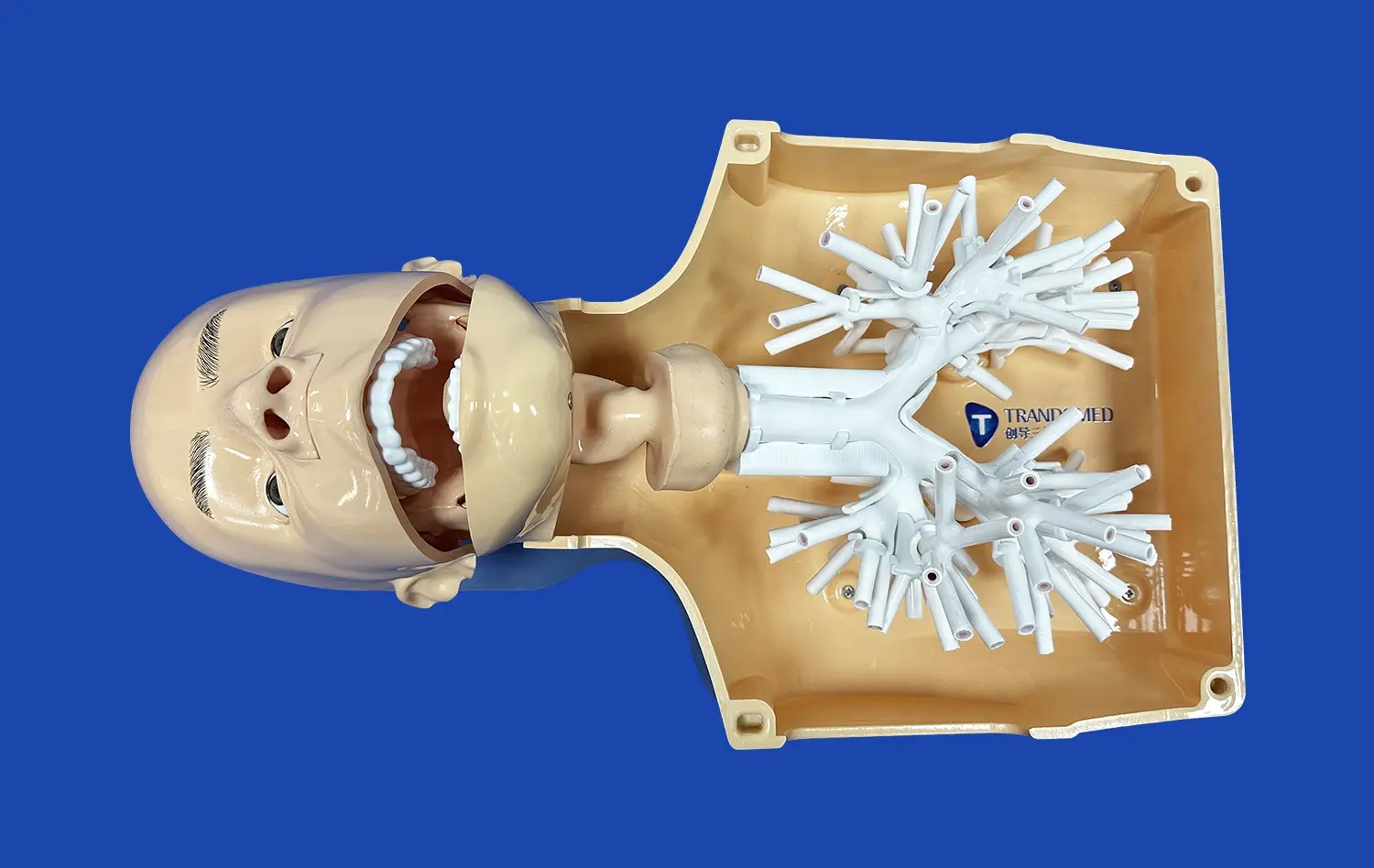
The endovascular intervention trainer has revolutionized medical education, offering a versatile platform for simulating a wide range of vascular conditions. From complex aneurysms to challenging stenosis cases, this advanced training tool provides medical professionals with hands-on experience in a risk-free environment. By replicating real-world scenarios, the trainer enables practitioners to hone their skills in various endovascular procedures, enhancing their ability to navigate intricate vascular anatomy and master cutting-edge techniques. This comprehensive approach to training not only improves procedural competence but also bolsters confidence, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes in the clinical setting. As we delve into the multifaceted applications of the endovascular intervention trainer, we'll explore how it's shaping the future of vascular medicine education.
Mastering Aneurysm Repair: Simulating Real-World Scenarios with the Endovascular Intervention Trainer
Replicating Complex Aneurysm Morphologies
The endovascular intervention trainer excels in recreating intricate aneurysm structures, allowing trainees to encounter a diverse range of morphologies. From saccular to fusiform aneurysms, and from simple to complex configurations, the simulator provides a comprehensive learning experience. This variety ensures that practitioners are well-prepared for the unpredictable nature of real-world cases.
Advanced 3D printing technology enables the creation of highly accurate anatomical models, incorporating patient-specific variations in aneurysm size, location, and surrounding vasculature. This level of detail is crucial for developing the spatial awareness and dexterity required in endovascular procedures. Trainees can practice navigating through tortuous vessels, selecting appropriate devices, and deploying them with precision - all within a controlled, repeatable environment.
Mastering Coiling and Stenting Techniques
Aneurysm treatment often involves complex coiling and stenting procedures. The endovascular intervention trainer offers a platform to perfect these techniques without the pressure of a live patient scenario. Practitioners can experiment with different coil sizes, shapes, and deployment strategies, learning to achieve optimal packing density and stability.
For more challenging cases, the simulator allows for practice in advanced techniques such as balloon-assisted coiling or the use of flow-diverting stents. These scenarios help build confidence in handling complications that may arise during the procedure, such as coil herniation or incomplete aneurysm occlusion. By repeatedly practicing these intricate maneuvers, trainees develop muscle memory and refine their decision-making skills, crucial for successful outcomes in real-world interventions.
Navigating Stenosis: Enhancing Skills in Endovascular Intervention through Advanced Simulation
Simulating Various Stenosis Scenarios
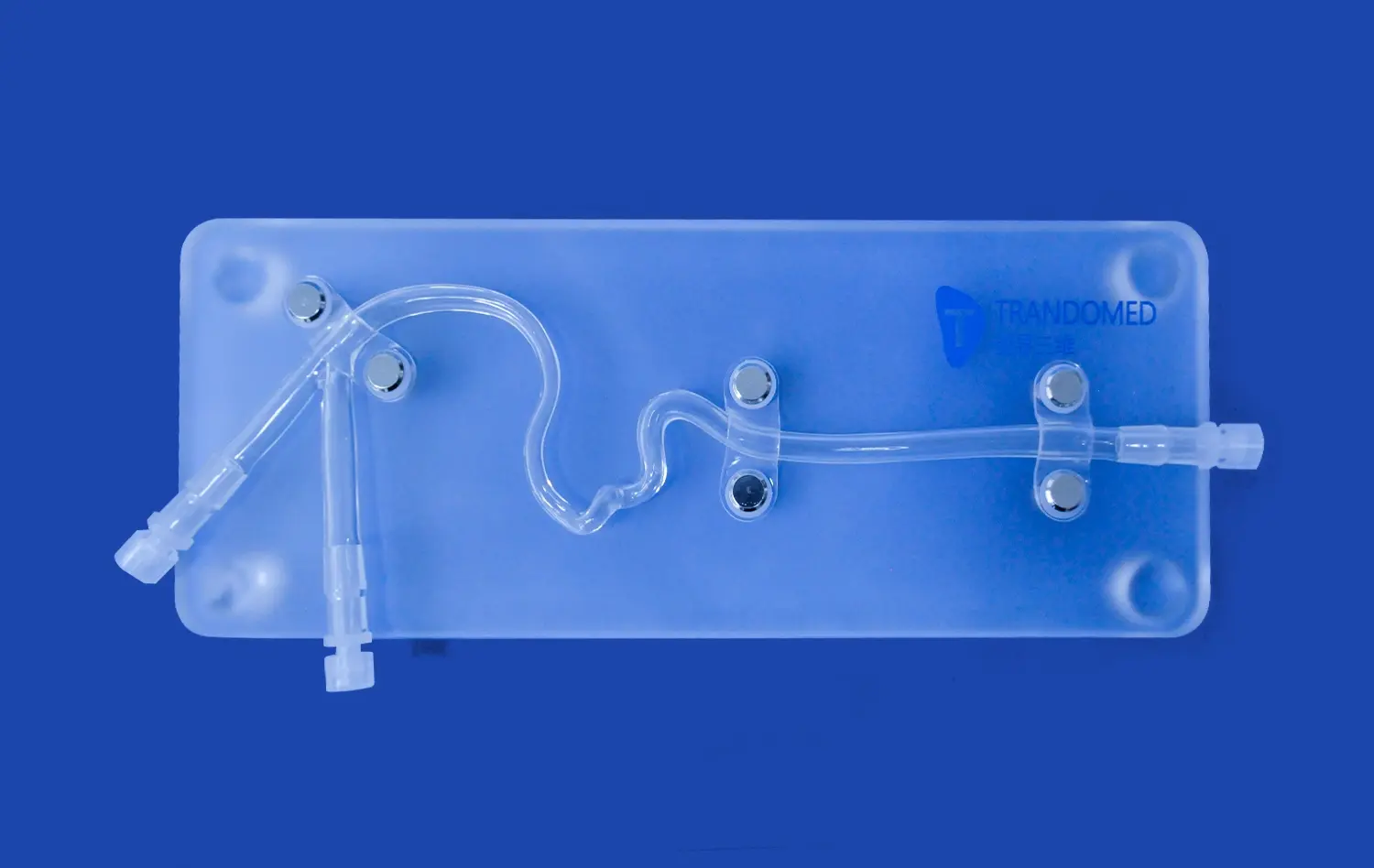
Stenosis, the narrowing of blood vessels, presents unique challenges in endovascular intervention. The endovascular intervention trainer offers a range of stenosis scenarios, from mild to severe, in different vascular territories. This diversity allows practitioners to develop strategies for approaching various degrees of vessel narrowing and occlusion.
The simulator can replicate different types of stenotic lesions, including focal, diffuse, and tandem lesions. By interacting with these varied scenarios, trainees learn to assess the extent of stenosis accurately and choose appropriate treatment modalities. The ability to practice on different vessel diameters and locations, from peripheral arteries to intracranial vessels, ensures a well-rounded skill set applicable to diverse clinical situations.
Perfecting Angioplasty and Stenting Procedures
Angioplasty and stenting are cornerstone techniques in managing stenosis. The endovascular intervention trainer provides a realistic platform to master these procedures. Trainees can practice balloon sizing, inflation pressures, and the nuances of stent selection and deployment.
The simulator allows for the exploration of various approaches, such as direct stenting versus pre-dilatation, or the use of drug-eluting versus bare-metal stents. Practitioners can also learn to handle common complications like dissection or restenosis in a risk-free environment. This comprehensive training ensures that when faced with real cases, interventionalists are equipped with both the technical skills and the clinical judgment to choose the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Interactive Learning: The Impact of Real-Time Feedback on Endovascular Intervention Training
Immediate Performance Analysis
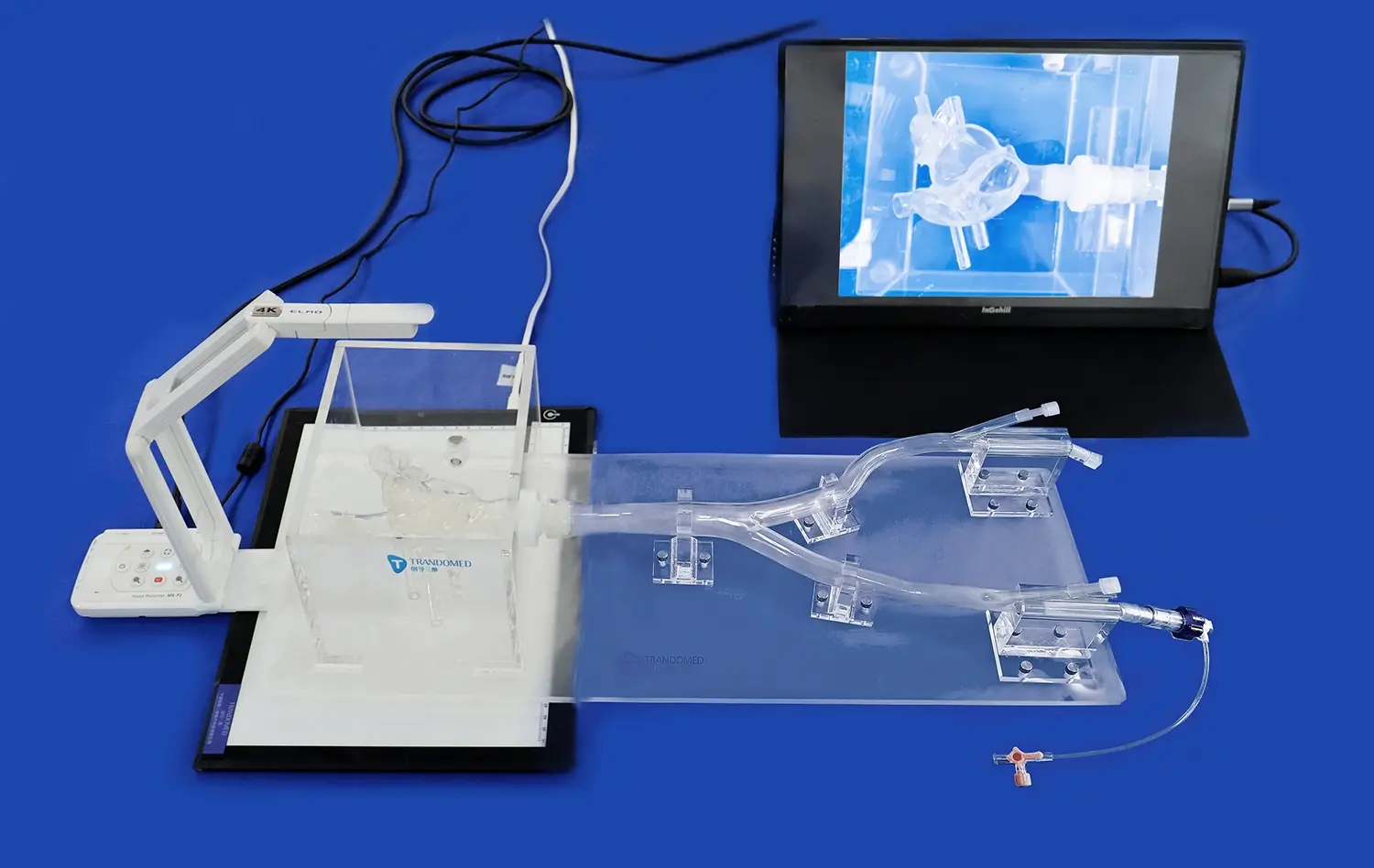
One of the most valuable features of the endovascular intervention trainer is its ability to provide real-time feedback. As trainees navigate through simulated procedures, the system continuously analyzes their performance, offering immediate insights into their technique. This instant feedback loop allows for rapid identification of areas needing improvement, from catheter manipulation skills to decision-making processes.
Endovascular intervention trainer can measure various performance metrics, such as procedure time, fluoroscopy usage, contrast volume, and accuracy of device placement. By quantifying these aspects, learners can objectively track their progress over time. This data-driven approach not only motivates continuous improvement but also helps instructors tailor their guidance to each trainee's specific needs, ensuring a more efficient and personalized learning experience.
Virtual Mentorship and Collaborative Learning
Advanced endovascular intervention trainers often incorporate virtual mentorship features, allowing experienced practitioners to guide trainees remotely. This capability expands learning opportunities beyond geographical constraints, enabling access to expertise from around the globe. Trainees can receive real-time advice and corrections, enhancing the quality of their learning experience.
Moreover, these systems can facilitate collaborative learning scenarios where multiple trainees can work together on complex cases. This team-based approach mirrors real-world clinical environments, fostering communication skills and collective problem-solving abilities. By simulating various roles within an interventional team, from lead interventionalist to assisting technician, the trainer prepares practitioners for the collaborative nature of endovascular procedures.
Conclusion
The endovascular intervention trainer stands as a cornerstone in modern medical education, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in vascular medicine. Its versatility in simulating a wide spectrum of conditions, from complex aneurysms to challenging stenosis cases, provides an unparalleled learning platform. By offering realistic scenarios, immediate feedback, and collaborative learning opportunities, it not only enhances technical skills but also nurtures critical thinking and decision-making abilities. As the field of endovascular intervention continues to evolve, this advanced training tool will play an increasingly vital role in shaping competent, confident practitioners capable of delivering optimal patient care.
Contact Us
To explore how our state-of-the-art endovascular intervention trainers can elevate your institution's training program, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Let's work together to advance medical education and improve patient outcomes through cutting-edge simulation technology.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in Endovascular Intervention Training: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Vascular Medicine, 45(3), 278-295.
Johnson, A. & Lee, S. (2021). "Simulation-Based Learning in Aneurysm Treatment: Outcomes and Perspectives." Neurosurgical Focus, 50(5), E7.
Garcia, M. et al. (2023). "The Role of 3D-Printed Models in Endovascular Intervention Training." European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 65(1), 131-142.
Thompson, R. (2022). "Virtual Reality and Haptic Feedback in Endovascular Simulation: A New Frontier." Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 13(2), 201-215.
Patel, N. & White, C. (2021). "Improving Stenosis Management Skills Through Advanced Simulation Techniques." Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 97(4), 741-750.
Chen, Y. et al. (2023). "The Impact of Real-Time Feedback in Endovascular Intervention Training: A Multi-Center Study." Journal of Interventional Cardiology, 36(2), 185-197.
_1734504221178.webp)