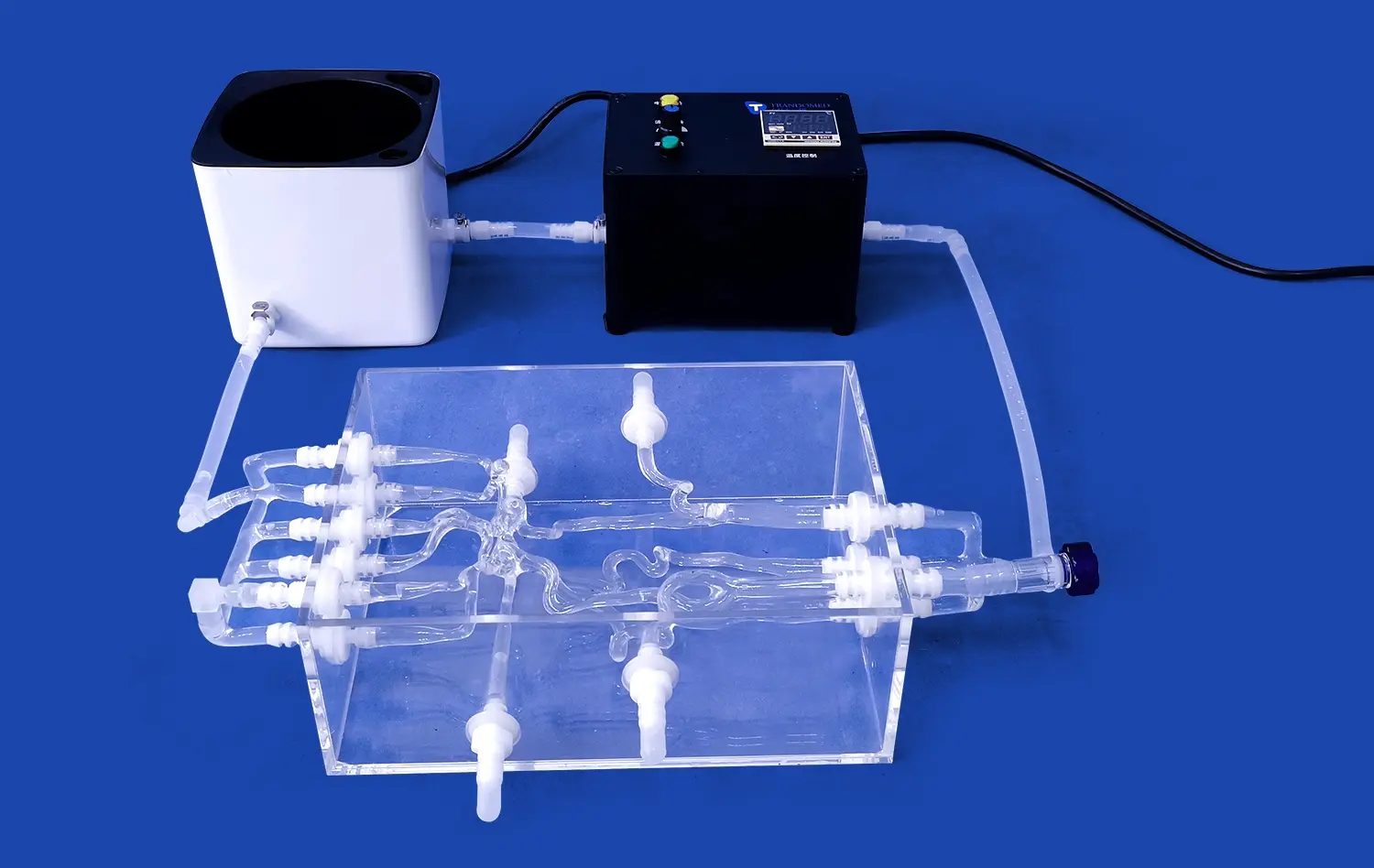
How Do Replaceable Stones Improve Technique Mastery?
Varied Stone Compositions for Comprehensive Training
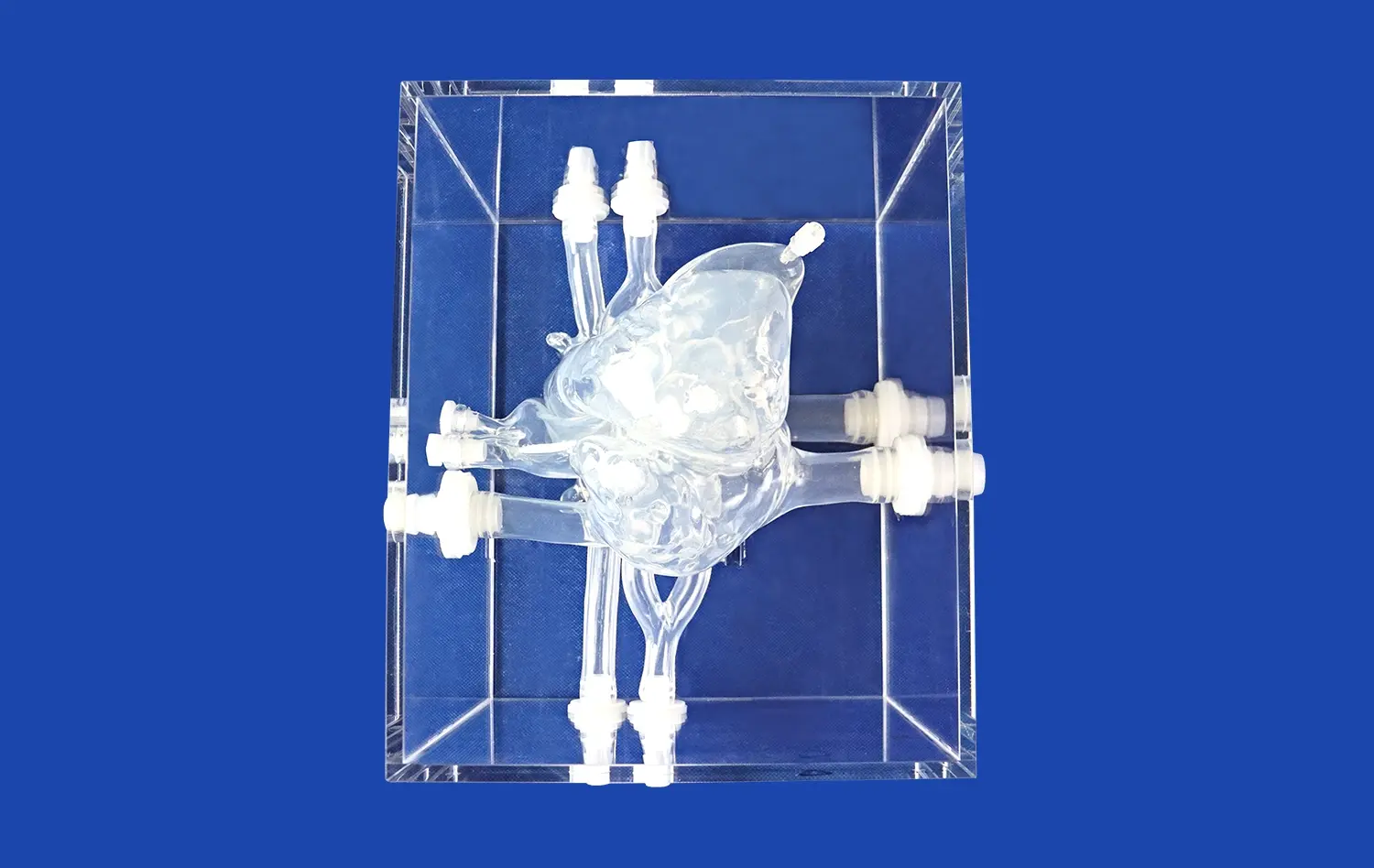
The ERCP Simulator II features a range of replaceable stones that mimic different calculus compositions found in clinical practice. These stones vary in size, shape, and density, allowing trainees to experience diverse scenarios they might encounter during actual procedures. By practicing with stones of varying hardness and friability, practitioners can refine their techniques for different types of calculi, from soft cholesterol stones to harder calcium bilirubinate stones.
Realistic Tactile Feedback for Enhanced Skill Development
One of the key advantages of the replaceable stones in the ERCP Simulator II is the realistic tactile feedback they provide. The simulator's stones are designed to respond to manipulation in a manner that closely resembles real calculi within the biliary system. This authentic feel allows trainees to develop a nuanced understanding of how different tools and techniques interact with various types of stones, improving their ability to gauge pressure and finesse during actual procedures.
Customizable Difficulty Levels for Progressive Learning
The ERCP Simulator II's replaceable stone system enables instructors to create customized training scenarios with varying levels of difficulty. Beginners can start with easily accessible stones, while more advanced trainees can challenge themselves with complex cases involving multiple or impacted stones. This progressive approach to learning ensures that practitioners can continuously improve their skills, gradually tackling more challenging scenarios as their expertise grows.
Step-by-Step Training Modules for Common Bile Duct Procedures
Fundamentals of ERCP Navigation and Cannulation
The ERCP Simulator II offers comprehensive training modules that begin with the basics of endoscope navigation and cannulation techniques. Trainees learn to manipulate the endoscope through the simulated digestive tract, identifying key anatomical landmarks along the way. The simulator's realistic representation of the papilla allows practitioners to perfect their cannulation skills, a critical step in successful ERCP procedures. These foundational modules ensure that trainees develop a solid understanding of the anatomical relationships and technical skills required for more advanced interventions.
Advanced Techniques for Stone Extraction and Lithotripsy
As trainees progress, the ERCP Simulator II provides advanced modules focusing on various stone extraction techniques. Practitioners can practice using balloon catheters, baskets, and mechanical lithotripters in a controlled environment. The simulator's replaceable stones allow for repeated attempts at challenging extractions, enabling trainees to refine their skills in maneuvering through the biliary tree and selecting the most appropriate tools for each scenario. Additionally, the simulator offers opportunities to practice laser lithotripsy techniques, further expanding the range of skills that can be developed.
Management of Complications and Decision-Making Skills
An essential aspect of ERCP training is learning to manage potential complications. The ERCP Simulator II incorporates scenarios that mimic common issues such as bleeding, perforation, and pancreatitis. These modules challenge trainees to make quick decisions and perform appropriate interventions in response to complications. By practicing these high-stress scenarios in a simulated environment, practitioners can develop critical thinking skills and confidence in handling unexpected situations during real procedures.
Measuring Skill Retention Through Repeated Simulated Practice
Objective Performance Metrics for Skill Assessment
The ERCP Simulator II is equipped with advanced tracking and assessment capabilities that provide objective measurements of trainee performance. These metrics include procedure time, tool selection efficiency, successful stone removal rates, and complication avoidance. By regularly practicing on the simulator and reviewing these performance indicators, trainees can track their progress over time and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach to skill assessment ensures that practitioners are continually refining their techniques and maintaining high standards of competence.
Longitudinal Training Programs for Sustained Improvement
To maximize skill retention, the ERCP Simulator II supports the implementation of longitudinal training programs. These programs involve regular, scheduled practice sessions over extended periods, allowing trainees to maintain and improve their skills consistently. By incorporating the simulator into ongoing medical education curricula, institutions can ensure that practitioners remain proficient in ERCP techniques, even if they do not perform the procedure frequently in their daily practice. This approach is particularly valuable for maintaining competency in less common or more complex ERCP scenarios.
Peer Comparison and Collaborative Learning Opportunities
The ERCP Simulator II facilitates collaborative learning environments where trainees can compare their performance with peers and learn from each other's experiences. The simulator's data collection capabilities allow for the creation of benchmarks and performance standards within training programs. This peer comparison not only motivates trainees to improve their skills but also fosters a culture of continuous learning and excellence in ERCP practice. Additionally, the simulator can be used in group training sessions, where trainees can observe and discuss different approaches to challenging cases, further enhancing the learning experience.
Conclusion
The ERCP Simulator II represents a significant advancement in medical training technology, offering an unparalleled platform for hands-on practice in calculus removal and other common bile duct procedures. By providing realistic, customizable training scenarios and objective performance metrics, this simulator enables medical professionals to develop and maintain their ERCP skills with unprecedented efficiency and effectiveness. As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of advanced simulation tools like the ERCP Simulator II in ensuring high-quality patient care cannot be overstated.
Contact Us
To learn more about how the ERCP Simulator II can revolutionize your institution's ERCP training program, contact Trandomed today. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with personalized solutions that meet your specific educational needs. Experience the future of medical simulation and take your ERCP skills to the next level. Reach out to us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com for more information or to schedule a demonstration.
_1736216292718.webp)