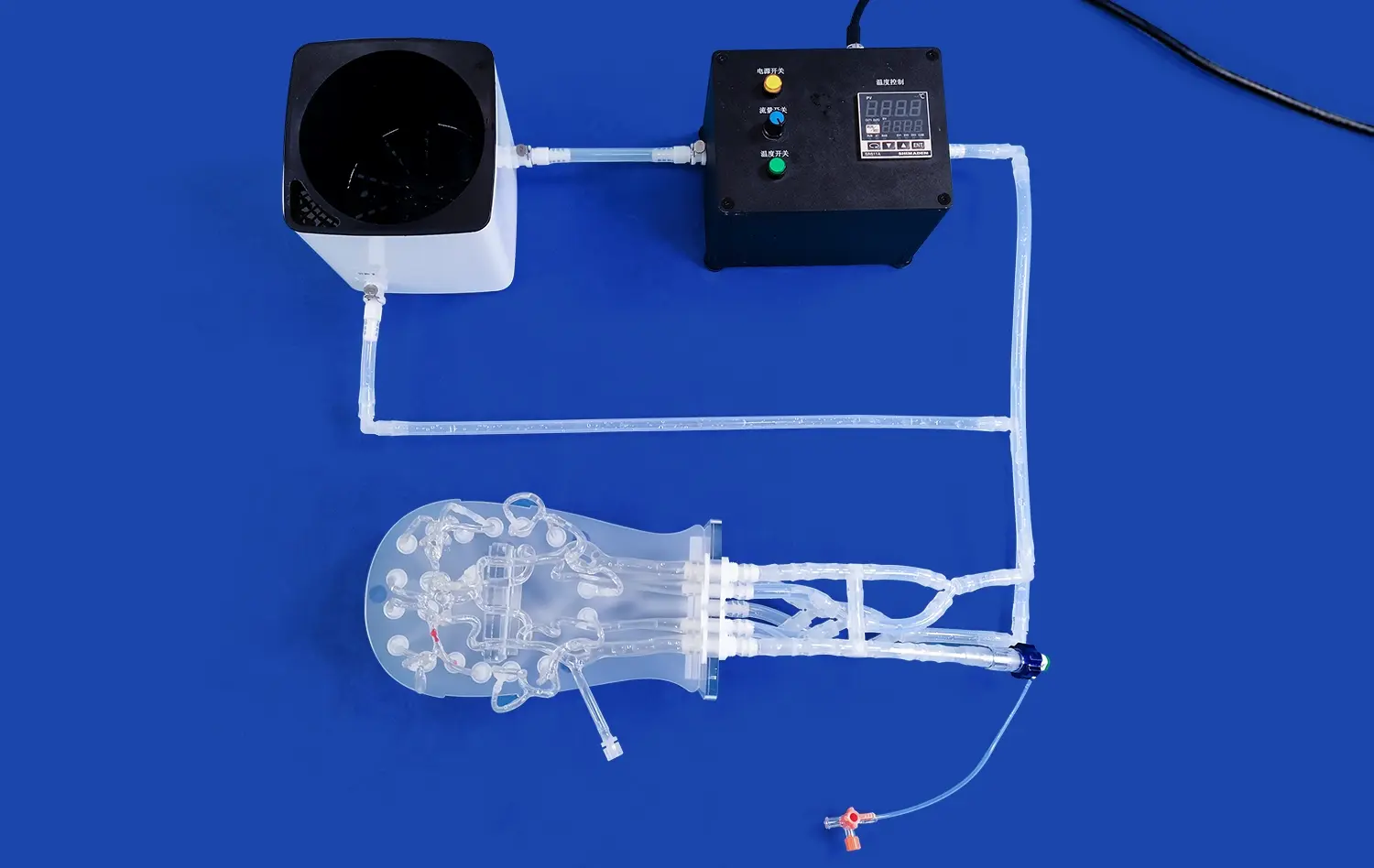
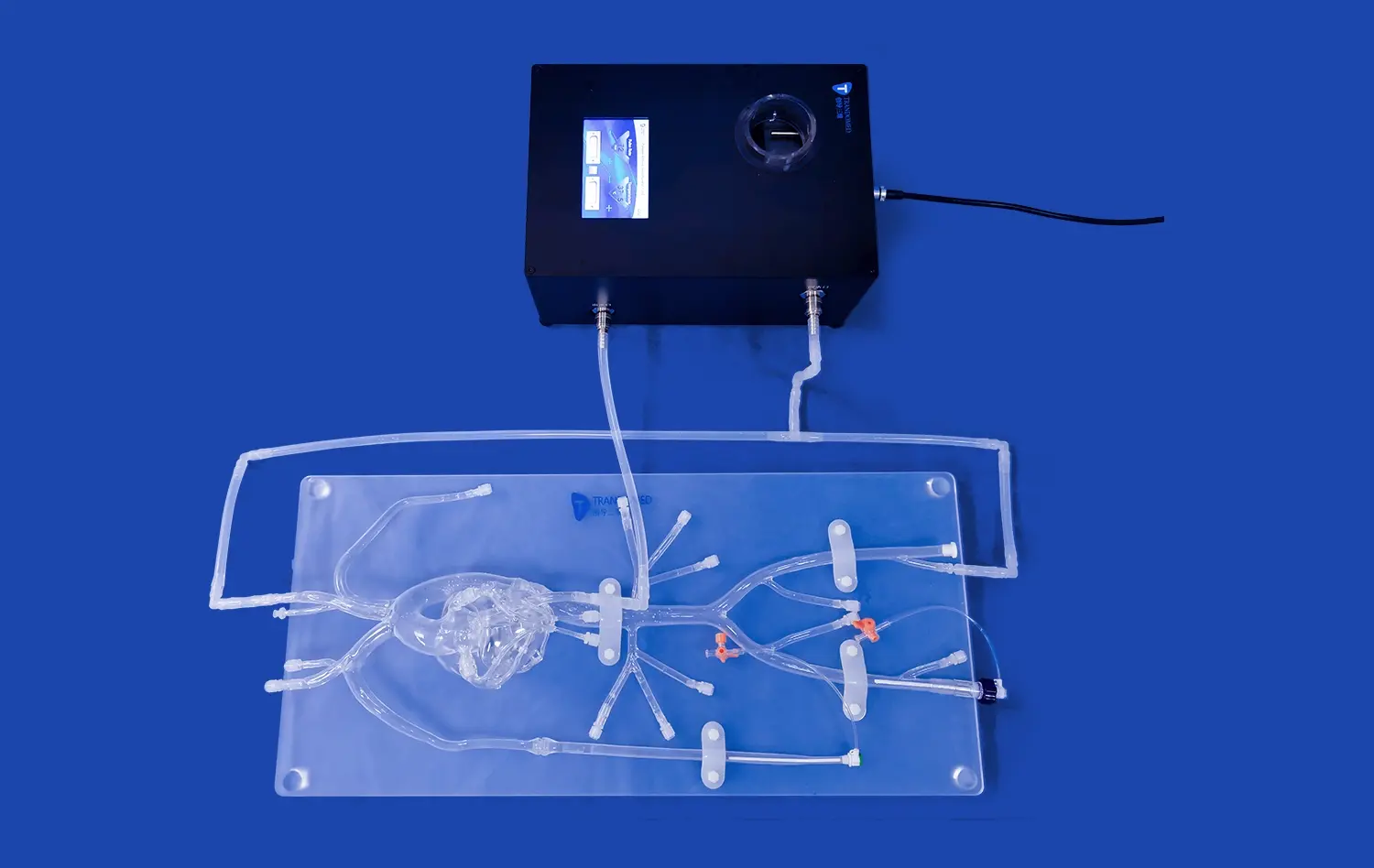
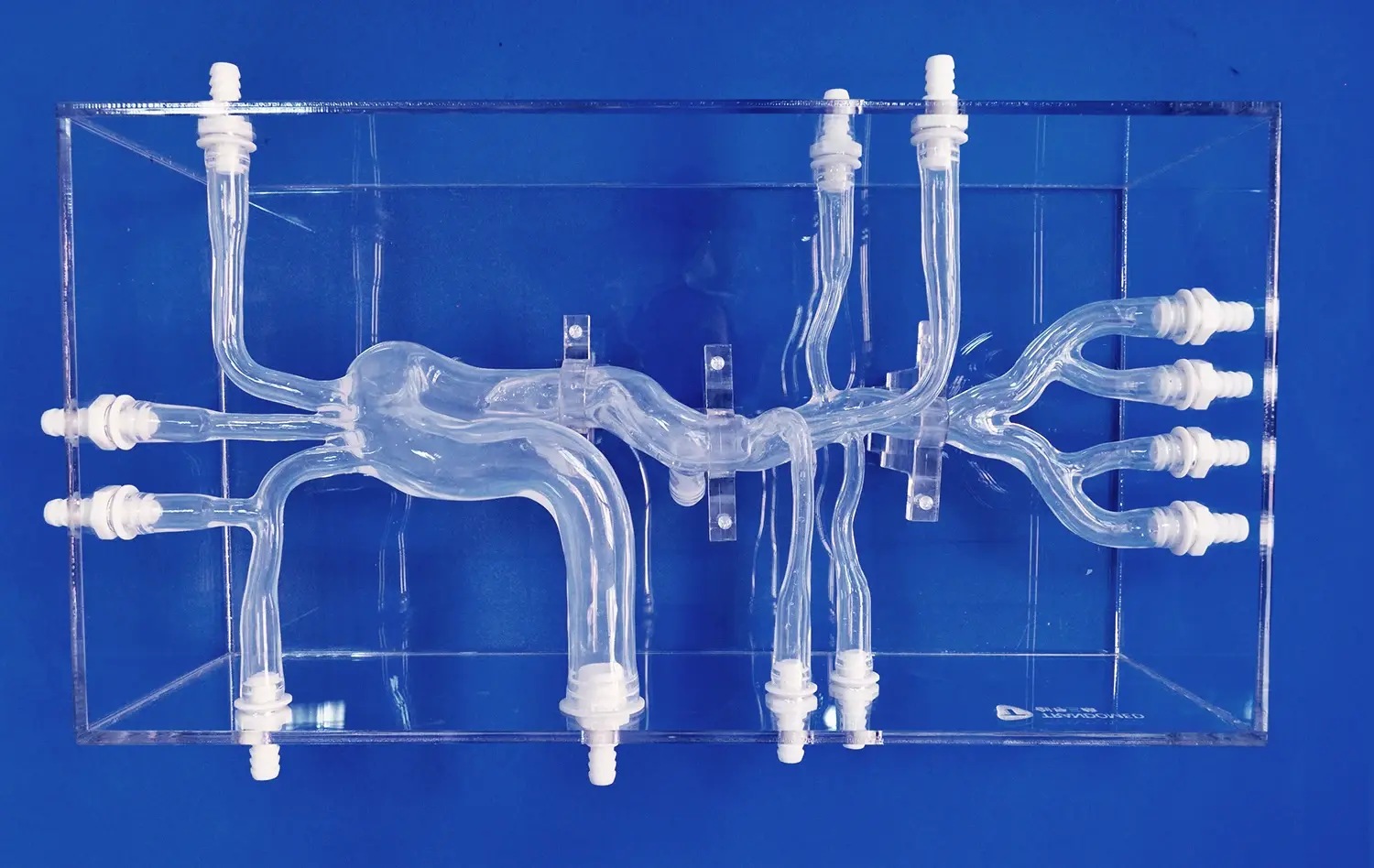
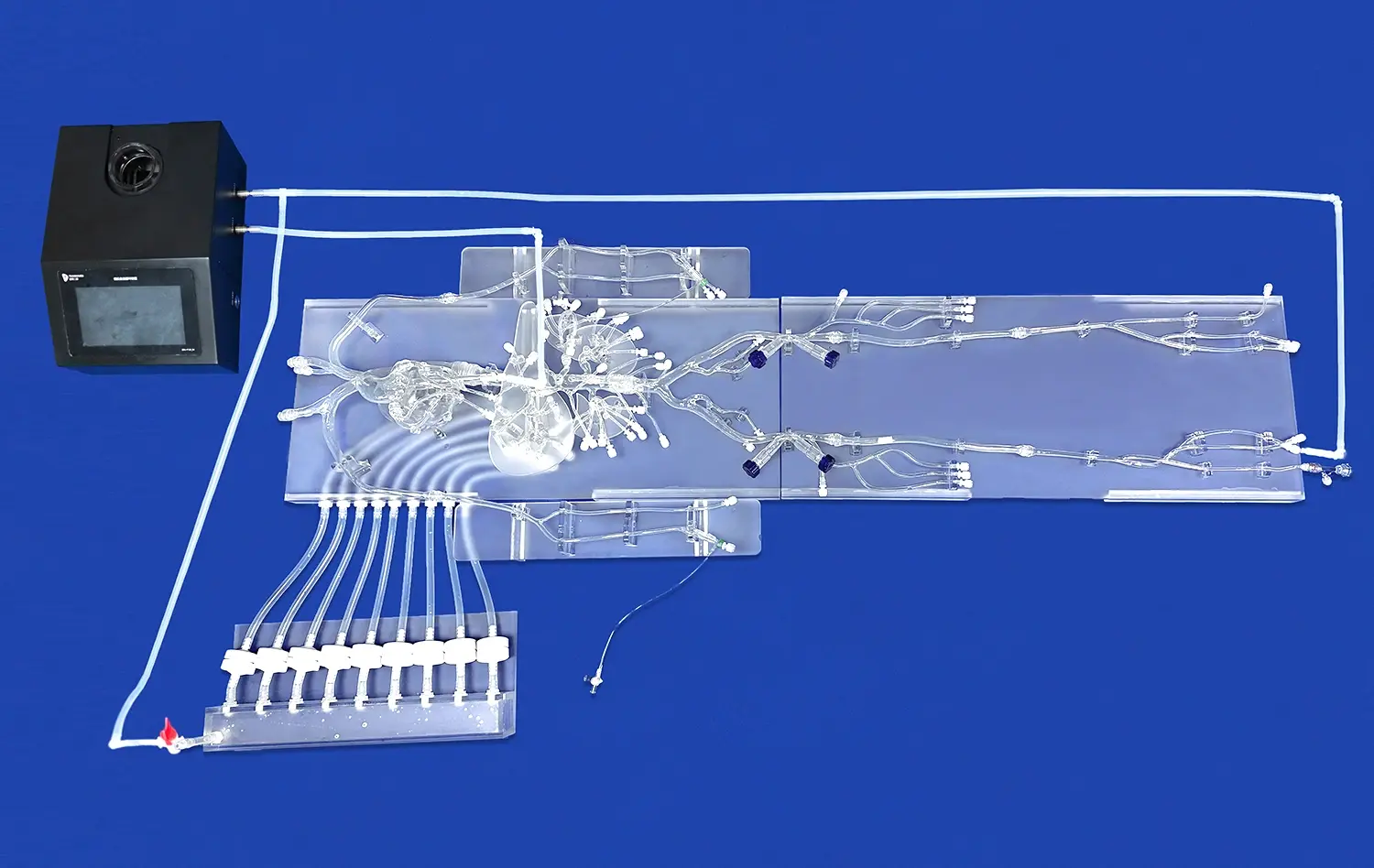
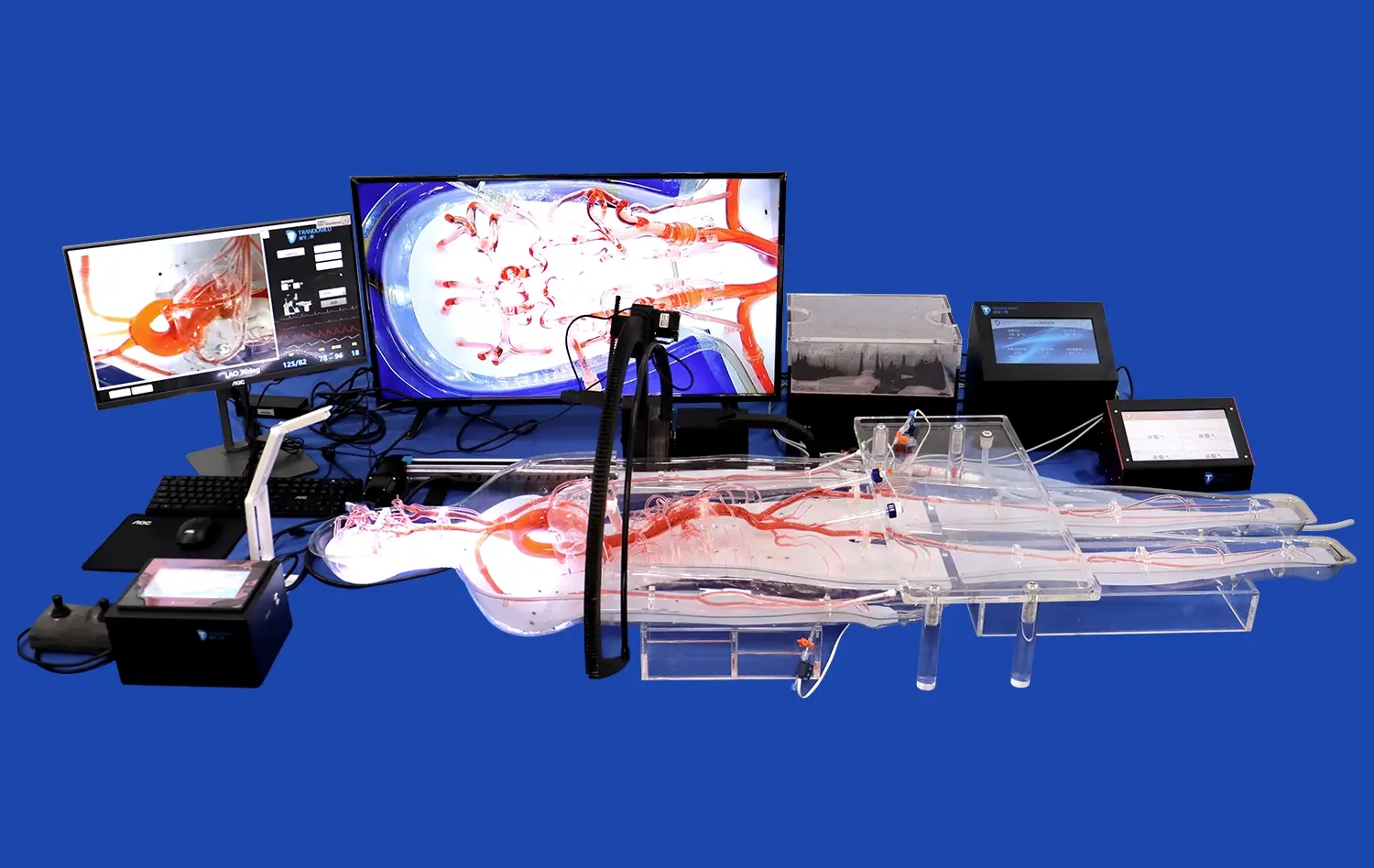
How Do 3D Models Support Surgical Simulation and Device Testing?
Enhancing Surgical Training with Realistic Anatomical Replicas
3D stomach models provide an invaluable resource for surgical trainees, offering a lifelike representation of the gastric anatomy. These models allow surgeons-in-training to familiarize themselves with the intricate structures and spatial relationships within the stomach, fostering a deeper understanding of anatomical variations and potential surgical challenges. By practicing on these high-fidelity replicas, trainees can develop muscle memory and refine their techniques in a low-stakes environment, ultimately leading to improved performance in the operating room.
Facilitating Device Testing and Prototype Evaluation
Medical device manufacturers leverage 3D stomach models to test and refine their products before clinical trials. These models provide a consistent and reproducible environment for evaluating the performance, safety, and efficacy of new surgical instruments, endoscopic devices, and implantable technologies. By using anatomically accurate replicas, researchers can identify potential design flaws, optimize device functionality, and assess the ergonomics of their innovations, ultimately accelerating the development process and improving the likelihood of successful clinical outcomes.
Simulating Complex Procedures and Rare Pathologies
High-fidelity 3D stomach models enable the simulation of complex surgical procedures and rare pathological conditions that surgeons may not frequently encounter in clinical practice. These models can be customized to replicate specific anatomical variations, tumors, or congenital abnormalities, allowing healthcare professionals to practice and refine their approach to challenging cases. By providing exposure to a diverse range of scenarios, 3D models help surgeons build confidence and competence in handling rare and complex gastric conditions.
Controlled Environment for Experimentation and Skill Assessment
Standardized Evaluation of Surgical Competency
3D stomach models offer a standardized platform for assessing surgical skills and competencies. Medical educators can design objective, reproducible scenarios to evaluate trainees' performance across various procedures and techniques. This controlled environment allows for consistent assessment criteria, enabling fair comparisons between individuals and tracking progress over time. By incorporating these models into skill assessments, institutions can ensure that surgeons meet the required proficiency levels before performing procedures on actual patients.
Risk-Free Exploration of Innovative Techniques
Researchers and clinicians can utilize 3D stomach models to explore and refine innovative surgical techniques without putting patients at risk. These models provide a safe space for testing novel approaches, such as minimally invasive procedures or robotic-assisted surgeries. By iterating and perfecting new methodologies on high-fidelity replicas, surgeons can optimize their techniques and identify potential complications before implementing them in clinical practice, ultimately improving patient safety and surgical outcomes.
Replicating Physiological Conditions for Enhanced Realism
Advanced 3D stomach models can incorporate features that mimic physiological conditions, such as tissue elasticity, fluid secretion, and peristaltic movements. These enhancements create a more realistic simulation environment, allowing researchers and clinicians to study the behavior of tissues and devices under conditions that closely resemble those encountered in vivo. By replicating these dynamic aspects of gastric physiology, 3D models provide valuable insights into the performance of surgical techniques and medical devices in real-world scenarios.
How Accurate Stomach Models Drive Innovation in Gastroenterology?
Advancing Endoscopic Techniques and Technologies
High-fidelity 3D stomach models play a crucial role in the development and refinement of endoscopic techniques. These models allow gastroenterologists to practice navigation, visualization, and manipulation skills in a controlled setting, leading to improved proficiency in diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopy. Additionally, researchers can use these models to test and optimize new endoscopic technologies, such as advanced imaging modalities or novel biopsy tools, accelerating the pace of innovation in minimally invasive gastroenterological procedures.
Personalized Treatment Planning and Patient Education
Accurate 3D stomach models derived from patient-specific imaging data enable personalized treatment planning for complex gastric conditions. Surgeons can use these models to visualize anatomical variations, assess tumor locations, and plan optimal surgical approaches tailored to individual patients. Moreover, these tangible representations serve as powerful educational tools, allowing healthcare providers to explain procedures and potential outcomes to patients more effectively, thereby enhancing informed consent and patient engagement in their care.
Fostering Interdisciplinary Collaboration and Research
The availability of high-fidelity 3D stomach models facilitates collaboration between various disciplines, including gastroenterology, surgery, biomedical engineering, and materials science. These models serve as a common platform for researchers from different fields to explore innovative solutions to gastric disorders, develop novel biomaterials for tissue engineering, and investigate the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and augmented reality in gastroenterological practice. By bridging diverse expertise, 3D models catalyze cross-disciplinary innovation and accelerate the translation of research findings into clinical applications.
Conclusion
High-fidelity 3D stomach models have emerged as indispensable tools in advancing gastroenterological research, surgical training, and medical device development. By providing a realistic and controlled environment for experimentation and skill assessment, these models enable healthcare professionals to refine their techniques, explore innovative approaches, and push the boundaries of gastroenterological care. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of more sophisticated features and materials in 3D stomach models will further enhance their utility, driving continuous improvement in patient outcomes and fostering groundbreaking discoveries in the field of gastroenterology.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are at the forefront of 3D medical model manufacturing, offering high-fidelity stomach models that meet the exacting standards of medical professionals and researchers worldwide. As a leading supplier and manufacturer in this specialized field, we combine cutting-edge 3D printing technology with extensive medical expertise to produce anatomically accurate, durable, and customizable models. Experience the unparalleled quality and innovation that have made Trandomed the preferred choice for institutions seeking advanced simulation and research tools. Elevate your gastroenterological training and research capabilities with our state-of-the-art 3D stomach models. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss how we can support your specific needs and contribute to advancing medical education and research in your institution.

1_1732869849284.webp)