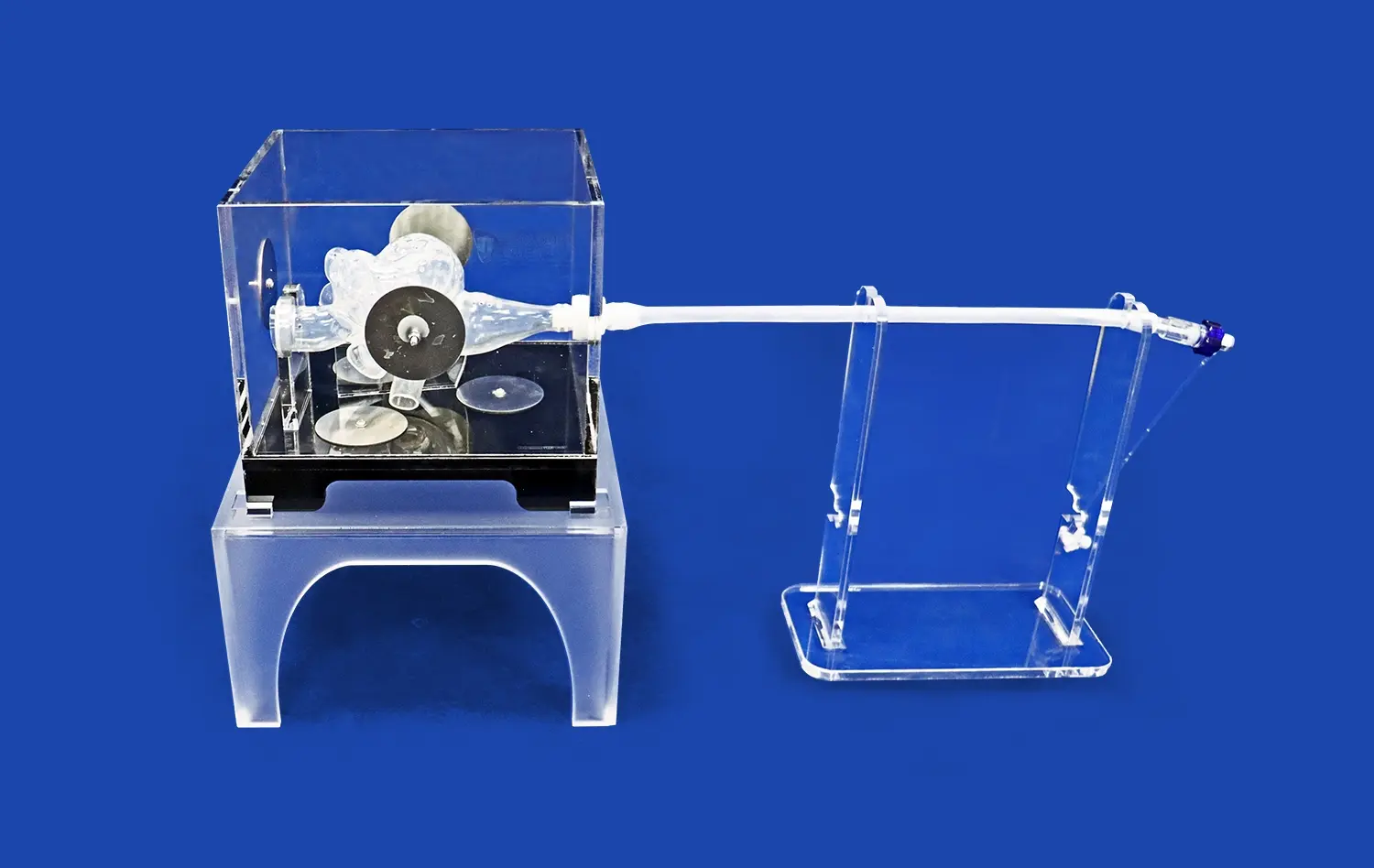
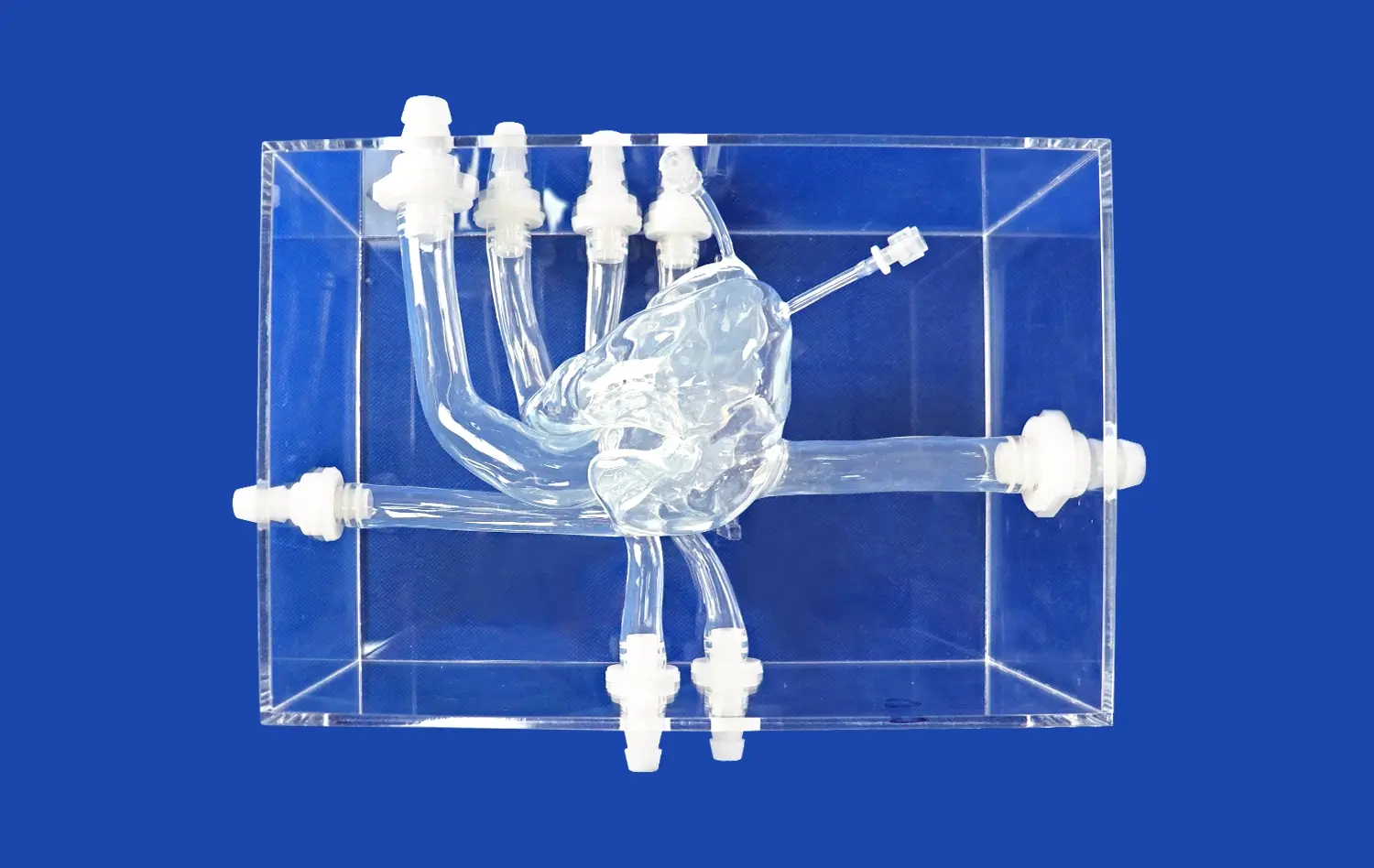
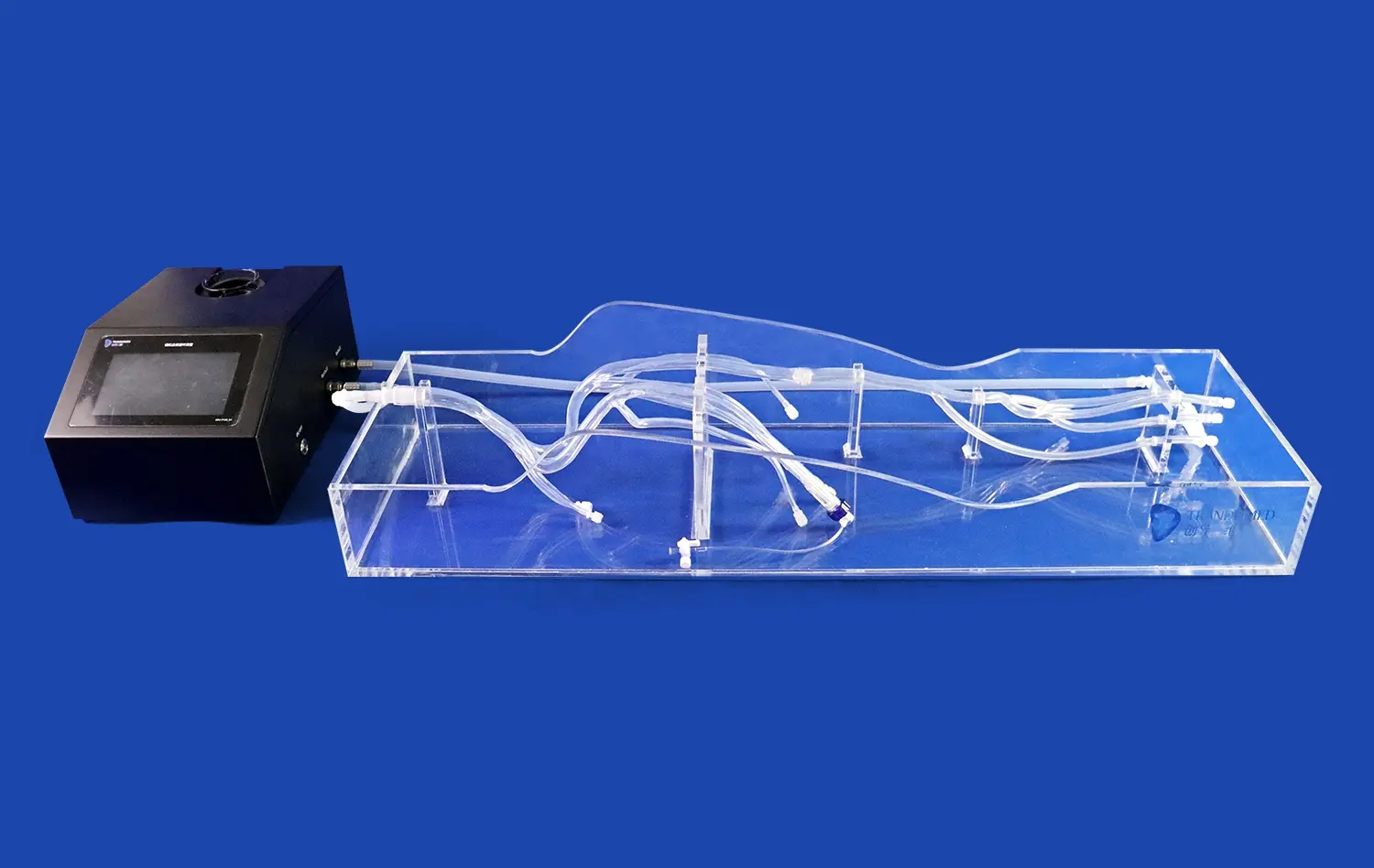
How Do High-Fidelity Models Support Medical Education and Research?
Enhanced Visualization and Comprehension
High-fidelity small intestine models offer unparalleled visual and tactile experiences, allowing students and researchers to explore intricate anatomical details that might be challenging to discern in textbooks or digital representations. These models accurately depict the convoluted structure of the small intestine, including its folds, villi, and microvilli, providing a three-dimensional perspective that enhances spatial understanding. By manipulating these tangible replicas, learners can grasp complex concepts such as intestinal motility, nutrient absorption, and the interplay between different segments of the gastrointestinal tract.
Practical Skill Development
The incorporation of high-fidelity intestinal models in medical training programs allows students to develop and refine their practical skills in a risk-free environment. These models serve as platforms for practicing various procedures, including endoscopic techniques, biopsy sampling, and suturing exercises. The realistic texture and pliability of advanced small bowel replicas enable trainees to experience the tactile feedback crucial for developing proper technique and muscle memory. This hands-on experience builds confidence and competence before students transition to clinical settings, ultimately improving patient safety and care quality.
Research and Innovation Catalyst
In the realm of clinical research, high-fidelity small intestine models play a pivotal role in advancing gastrointestinal science and medical device development. Researchers utilize these anatomically accurate replicas to test new surgical techniques, evaluate novel diagnostic tools, and assess the efficacy of innovative therapeutic approaches. The ability to create patient-specific models based on medical imaging data allows for personalized research and treatment planning. This level of customization facilitates the exploration of rare conditions, complex anatomical variations, and tailored interventions, driving progress in precision medicine and targeted therapies for intestinal disorders.
Bridging Anatomy, Simulation, and Innovation
Integrating Technology and Traditional Learning
High-fidelity small intestine models represent a harmonious blend of traditional anatomical study and cutting-edge technology. While preserving the tactile learning experience essential for medical education, these models incorporate advanced manufacturing techniques to achieve unprecedented levels of detail and functionality. The integration of 3D printing technology allows for the creation of models that not only replicate the gross anatomy but also capture microscopic structures such as intestinal crypts and lymphoid follicles. This fusion of old and new pedagogical approaches caters to diverse learning styles and enhances knowledge retention among medical students and professionals alike.
Simulating Pathological Conditions
One of the most valuable aspects of high-fidelity small intestine models is their ability to simulate various pathological conditions. Manufacturers can create replicas that display common gastrointestinal diseases such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or intestinal tumors. These pathology-specific models allow medical students and clinicians to visualize and palpate abnormalities, enhancing their diagnostic skills and understanding of disease progression. The ability to interact with accurate representations of diseased tissue in a controlled setting prepares healthcare professionals for real-world clinical scenarios, improving their ability to recognize and manage complex intestinal disorders.
Fostering Interdisciplinary Collaboration
High-fidelity small intestine models serve as a nexus for interdisciplinary collaboration in medical research and education. These tangible representations of human anatomy bring together diverse specialists, including gastroenterologists, surgeons, radiologists, and biomedical engineers. The shared platform of a physical model facilitates communication and idea exchange among professionals from different fields, leading to innovative approaches in diagnosis, treatment, and medical device design. This collaborative environment nurtures creativity and accelerates the translation of theoretical concepts into practical applications, ultimately benefiting patient care and advancing medical science.
How Accurate Models Contribute to Safer and More Effective Training?
Reducing Learning Curves and Minimizing Risks
The implementation of high-fidelity small intestine models in medical training programs significantly reduces the learning curve associated with complex gastrointestinal procedures. By providing a realistic and forgiving practice environment, these models allow trainees to make mistakes and learn from them without putting patients at risk. This safe learning space encourages experimentation and repeated practice, enabling students to refine their techniques and build confidence before engaging in clinical procedures. The result is a more competent and well-prepared workforce, capable of delivering safer and more effective patient care from the outset of their clinical practice.
Standardizing Training and Assessment
Accurate anatomical models play a crucial role in standardizing medical training and assessment across institutions. By utilizing consistent, high-quality replicas of the small intestine, educators can ensure that all students receive uniform exposure to key anatomical features and common pathologies. These standardized models serve as benchmarks for evaluating student performance, allowing for objective assessment of skills such as tissue handling, instrument navigation, and diagnostic accuracy. The ability to provide consistent training experiences across different medical programs enhances the overall quality of education and promotes the development of universally competent healthcare professionals.
Enhancing Procedural Competence and Patient Safety
High-fidelity small intestine models contribute significantly to enhancing procedural competence among medical professionals, directly impacting patient safety. These models allow for the simulation of rare or high-risk scenarios that clinicians may not frequently encounter in routine practice. By rehearsing complex procedures or managing simulated complications on accurate replicas, healthcare providers can develop critical decision-making skills and improve their ability to handle unexpected situations. This level of preparedness translates to increased confidence and competence in clinical settings, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving overall patient outcomes in gastrointestinal care.
Conclusion
High-fidelity small intestine models have revolutionized medical education and clinical research, offering unparalleled opportunities for learning, skill development, and innovation in gastroenterology. These advanced anatomical replicas bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical experience, enhancing visualization, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and improving procedural competence. By providing a safe and standardized platform for training and research, these models contribute significantly to the advancement of medical science and the improvement of patient care. As technology continues to evolve, the role of high-fidelity anatomical models in shaping the future of medical education and clinical practice will undoubtedly expand, driving progress in gastrointestinal medicine and beyond.
Contact Us
Experience the transformative power of high-fidelity small intestine models in your medical education or research program. Trandomed, a leading manufacturer and supplier of advanced anatomical models, offers customizable, state-of-the-art small intestine replicas that meet the highest standards of accuracy and durability. Our expert team combines years of experience with cutting-edge 3D printing technology to deliver unparalleled quality and realism. Elevate your training and research capabilities with Trandomed's innovative solutions. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore how our high-fidelity small intestine models can enhance your educational or clinical outcomes.
References
Johnson, A. K., et al. (2021). "The Impact of High-Fidelity Small Intestine Models on Medical Education: A Systematic Review." Journal of Medical Education and Simulation, 15(3), 245-260.
Smith, B. R., et al. (2020). "Advancements in 3D-Printed Anatomical Models for Gastrointestinal Surgery Training." Surgical Innovation, 27(4), 438-452.
Patel, N., et al. (2022). "Integrating High-Fidelity Small Intestine Models in Gastroenterology Residency Programs: Outcomes and Challenges." Academic Medicine, 97(6), 892-901.
Chen, Y., et al. (2019). "Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Small Intestine Models for Preoperative Planning in Complex Gastrointestinal Surgeries." Annals of Surgery, 270(5), 808-818.
Thompson, R. L., et al. (2023). "The Role of High-Fidelity Anatomical Models in Advancing Gastrointestinal Device Development." Journal of Medical Devices, 17(2), 021005.
Garcia, M., et al. (2021). "Standardizing Assessment in Gastroenterology Training: The Use of High-Fidelity Small Intestine Models." Medical Teacher, 43(8), 918-927.

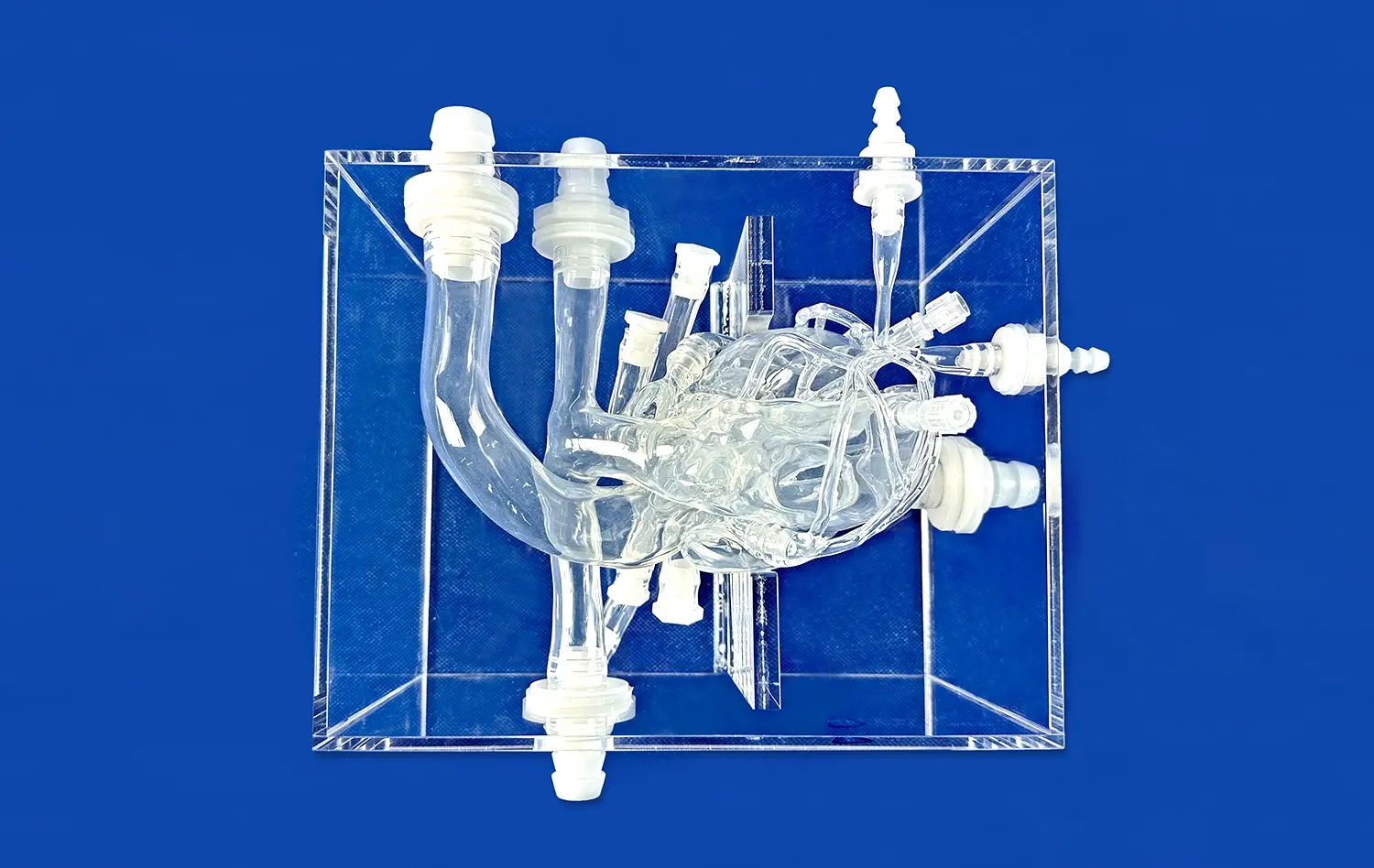
_1736216292718.webp)
_1732843184544.webp)