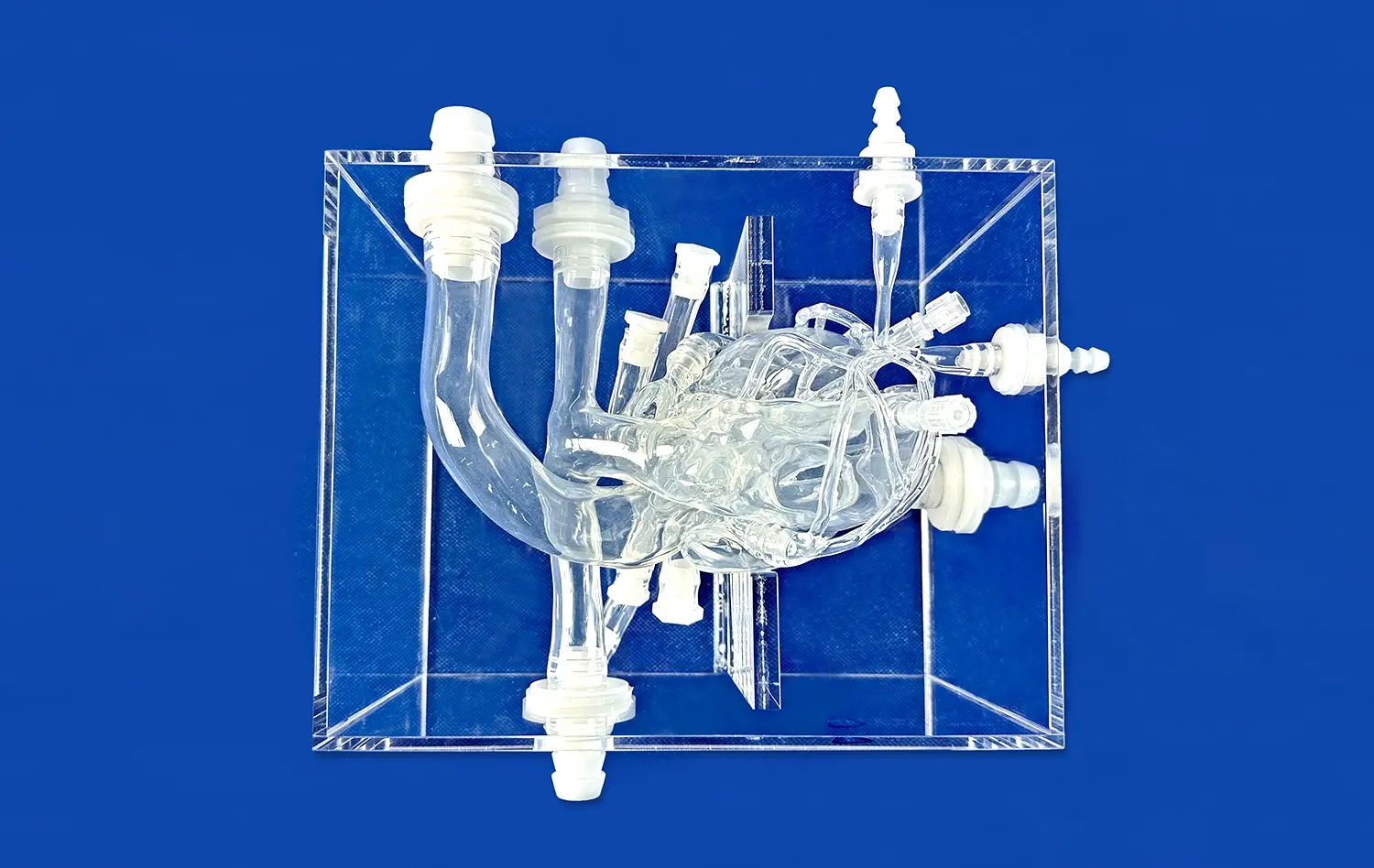
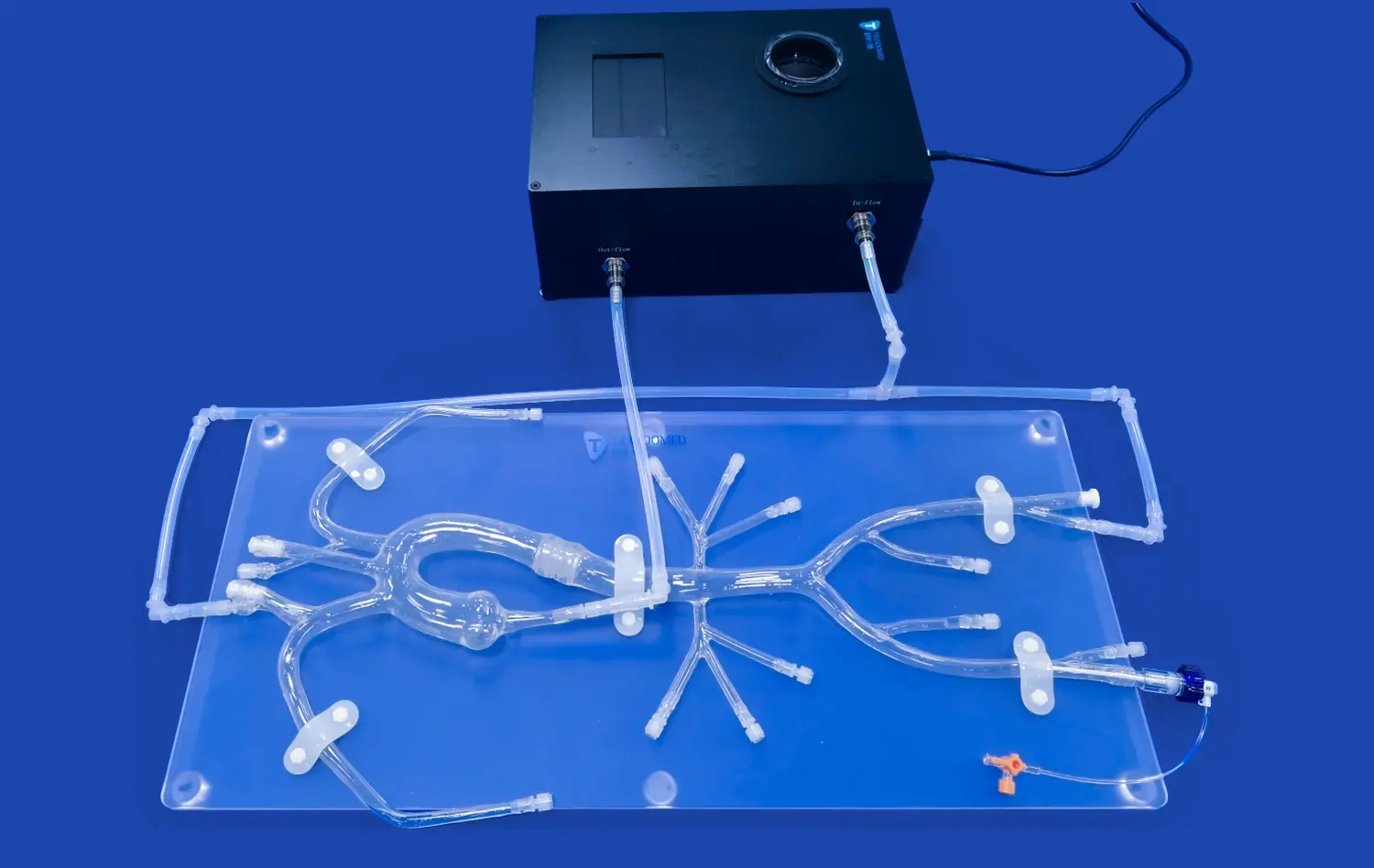
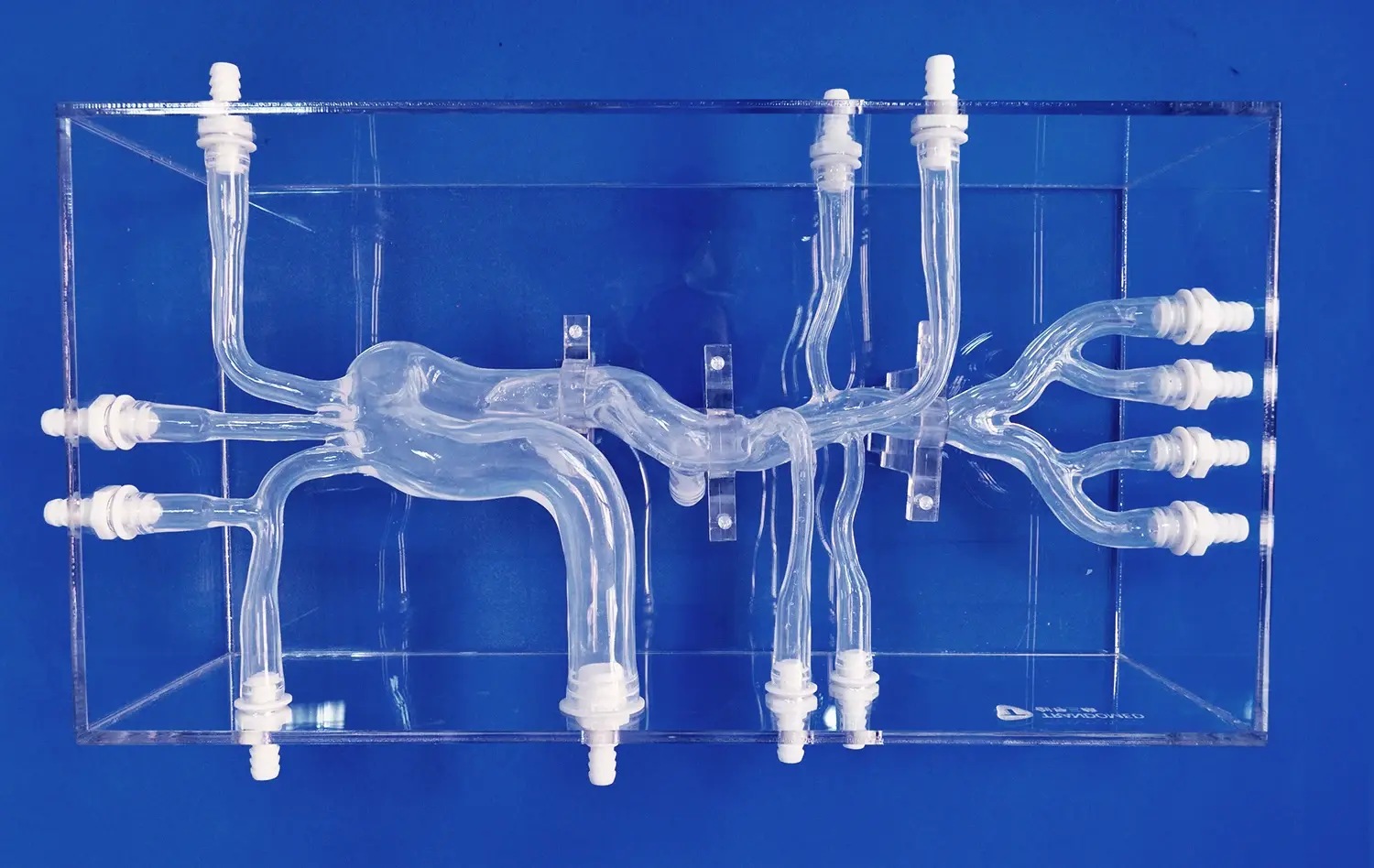
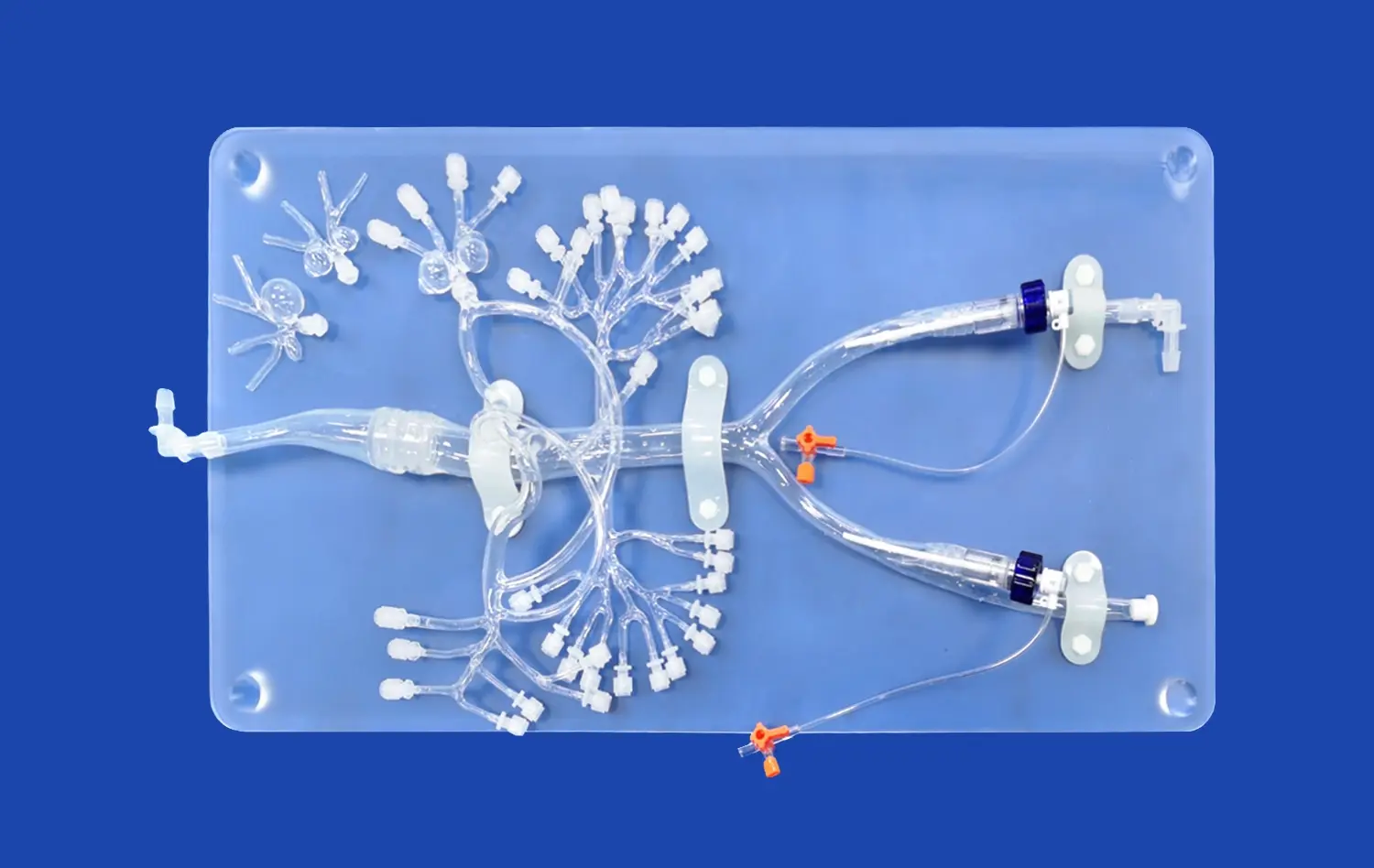
By changing how students and experts comprehend complicated renal anatomy, the 3D kidney model has revolutionized medical education. The complex spatial links in kidney structures are hard to understand with traditional textbooks and 2D diagrams. This can affect clinical performance. Advanced anatomical models now make up for these problems in education by providing hands-on, immersive learning experiences that accurately recreate human anatomy. These new tools make students more interested in learning, help more students stay in school, and create a standard training platform for both surgical processes and diagnostic skills development.

Understanding 3D Kidney Models and Their Role in Medical Education
Three-dimensional visualization tools that can recreate the complex structure of human organs are very important to modern anatomical teaching. These advanced copies include real-life examples and computer versions, and each one has a different use for teaching students about medicine.
Physical vs. Digital Kidney Simulators
Physical models give students a hands-on way to interact with buildings and learn about how different shapes relate to each other in space. Digital options can show things in 3D, letting you turn them, look at cross-sections, and explore anatomy in real time. Medical schools often use both methods together to get the best results and make sure all students can learn in a way that works for them.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
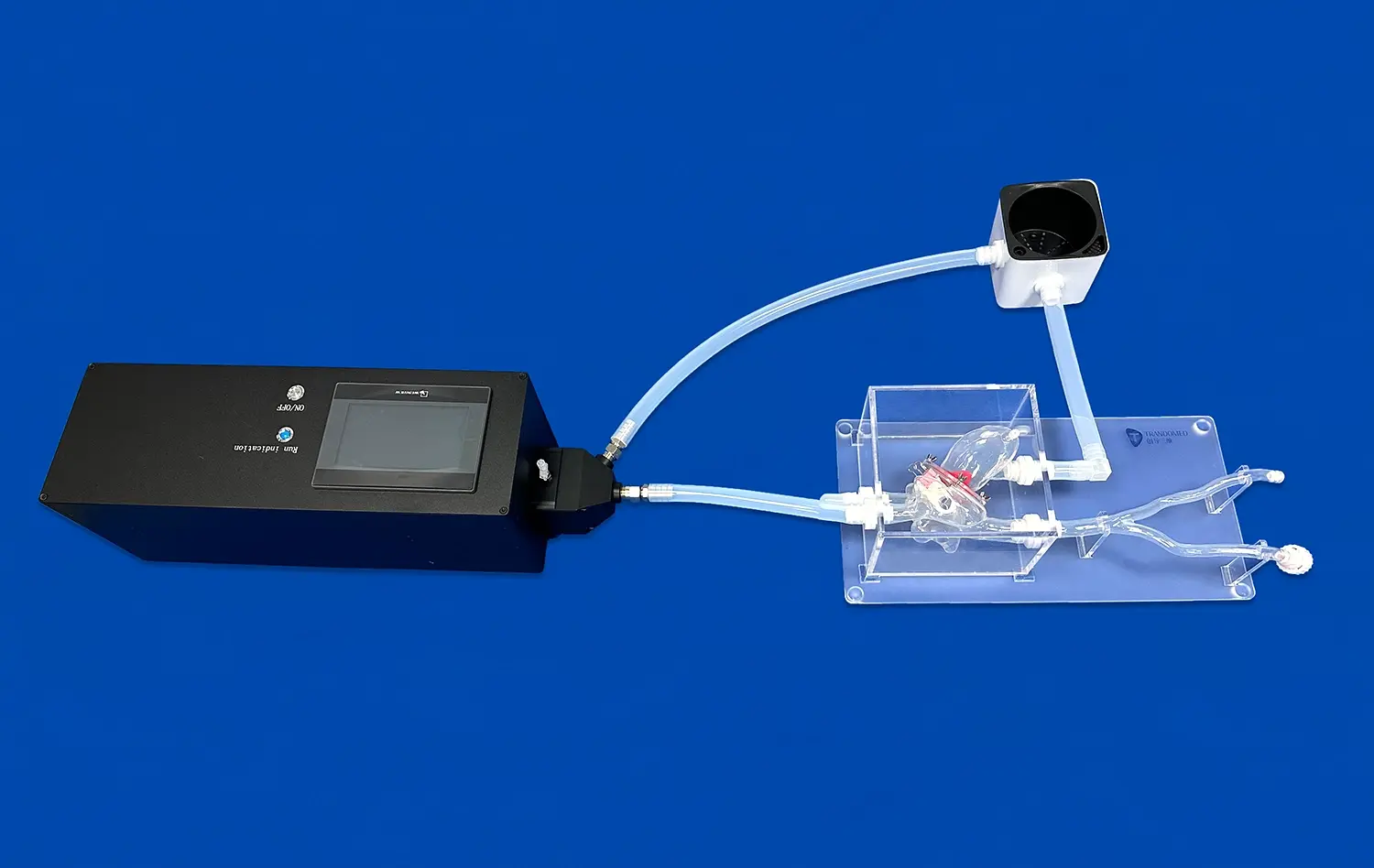
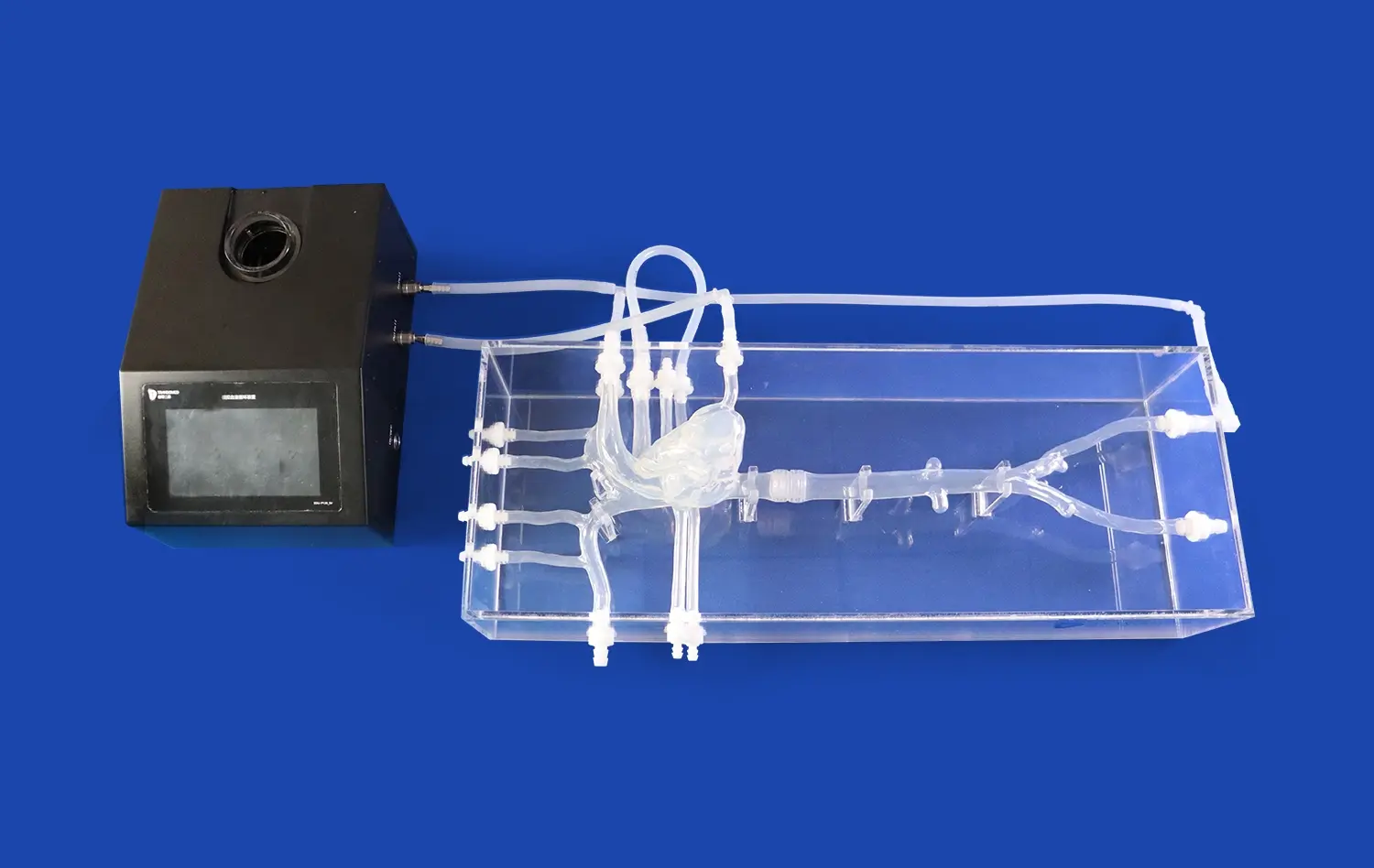
Modern medical models use the latest printing techniques and materials that are safe for the body to get the details right. Synthetic fabrics and hydrogels that are made with care imitate tissue textures, and precision manufacturing makes sure that the size is correct. Thanks to these technological breakthroughs, it is now possible to make models that have outer skin layers, individual adrenal glands, renal pelvis structures, ureters, and full vascular networks.
Comparing 3D Kidney Models with Traditional Educational Tools
Medical schools have changed a lot because schools know that old ways of teaching aren't always best. Moving to three-dimensional learning tools helps with big problems in understanding anatomy and building real skills.
Enhanced Spatial Comprehension
Flat drawings of anatomy don't show the complicated 3D links between the kidneys and other organs that are near them. 3D models give students a full picture of how renal arteries split, how the collecting system links up, and how diseases change the body’s usual structure. Better understanding means better medical and surgical skills.
Interactive Learning Capabilities
Unlike pictures, 3D kidney models of kidneys can be touched and looked at from different angles, which is good for people who learn in different ways. Students can take parts apart, follow vascular paths, and practice procedural methods over and over again. This interactive method helps people remember what they are learning a lot more than just watching pictures in a textbook or a presentation on a talk.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
The first cost of good anatomical models may seem high, but they are useful in the long term because they last and can be used multiple times. Institutions can use the same models with different groups of students, so they are cheaper overall than consumables like cadaveric specimens or materials meant to be used only once.
How 3D Kidney Models Support Advanced Medical Training and Surgical Planning?
Professional medical training goes beyond teaching the basics of anatomy. It also includes learning complex procedures and making plans for surgeries that are special to each patient. In these specific cases, advanced computer models are very important.
Surgical Skill Development
Simulation-based training helps a lot with the exact technical skills needed for kidney donation surgeries. Transplant practice models have working links between the renal pelvis, ureters, and vascular structures. This lets doctors practice how to do anastomosis and figure out how to avoid problems that could happen. These chances to practice lower risks in surgery and help patients get better.
Patient-Specific Planning
Surgeons can plan complicated surgeries with never-before-seen accuracy using custom models made from each patient's CT and MRI files. The anatomy of a particular patient can be copied to show how it differs from the norm, where tumors are located, or how congenital abnormalities look. With this tailored method, surgery teams can practice surgeries, choose the best methods, and think about what might go wrong before they go into the operating room.
Pathology Visualization
Polycystic kidney disease, tumors, and vascular issues are all examples of common pathological diseases that can be used in educational 3D kidney models. Students learn more about how diseases work and how to diagnose them by seeing cases they might not see during clinical rotations.
Procuring 3D Kidney Models: What B2B Clients Need to Know
Institutional procurement decisions require careful evaluation of multiple factors to ensure optimal educational outcomes and long-term value. Understanding key selection criteria helps medical facilities make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Quality and Durability
Educational institutions require models that withstand repeated use across multiple student cohorts. High-quality synthetic materials and specialized hydrogels provide realistic tactile experiences while maintaining structural integrity through extensive handling. Procurement teams should evaluate material specifications, expected lifespan, and replacement policies when comparing suppliers.
Customization Capabilities
Leading manufacturers offer customization services that adapt models to specific educational objectives or clinical requirements. Institutions can request modifications based on their curriculum needs, student population characteristics, or specialized training programs. Custom services may include personalized designs, rapid prototyping capabilities, and integration with existing simulation platforms.
Supplier Reliability and Support
Successful procurement partnerships depend on supplier expertise, manufacturing capabilities, and ongoing support services. Evaluation criteria should include production timelines, quality assurance protocols, technical documentation, and after-sales support availability. Reliable suppliers provide comprehensive product specifications, user training resources, and responsive customer service.
Trandomed: Your Trusted Partner for Medical 3D Printing Solutions
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (Trandomed) is China's first company to use 3D printing technology in the medical field. They have more than 20 years of experience in the field and are now working to improve healthcare education around the world. Our wide range of products includes very accurate kidney models that are made just for medical schools, hospitals, and study institutions around the world.
Product Excellence and Innovation
Our main 3D Kidney Model (Product No.: HSX005) is a great example of how dedicated we are to making sure that our products are anatomically correct and useful for teaching. Using cutting-edge 3D printing methods and real CT and MRI scan data as a guide, each model has layers of skin, their own adrenal glands, and a full network of blood vessels. The model links easily to the renal pelvis, ureter, and arterial structures. This makes it possible to do full kidney transplants and test the urinary system.
Customization and Service Excellence
Trandomed will fully customize its products to meet your needs without charging extra for design. This helps meet one-of-a-kind educational and study needs. With our fast prototyping, we can be sure to deliver in 7 to 10 days. Our global shipping network uses dependable carriers like FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT to serve customers around the world quickly.
Conclusion
The integration of three-dimensional kidney models into medical education represents a fundamental advancement in anatomical training and surgical preparation. These innovative tools address traditional limitations of textbook learning while providing hands-on experiences that improve comprehension, retention, and practical skills. As medical education continues evolving toward simulation-based learning, institutions that invest in quality anatomical models position themselves at the forefront of educational excellence. The proven benefits of enhanced spatial awareness, interactive learning capabilities, and surgical planning applications make these tools essential components of modern medical curricula.
FAQs
How accurate are 3D printed kidney models compared to real anatomy?
Modern 3D printed kidney models achieve remarkable anatomical accuracy through advanced imaging data integration. Models based on CT and MRI scans replicate human anatomy with precision suitable for both educational and clinical applications, often exceeding 95% dimensional accuracy.
Can 3D kidney models be customized for specific medical cases or educational needs?
Yes, leading manufacturers like Trandomed offer comprehensive customization services using patient-specific imaging data, CAD designs, or specialized educational requirements. Custom models can highlight specific pathologies, anatomical variations, or procedural training objectives.
What materials are best suited for durable and detailed 3D kidney models?
High-quality hydrogels and specialized synthetic materials provide optimal combinations of durability, tactile realism, and fine anatomical detail. These materials withstand repeated handling while maintaining structural integrity and realistic tissue characteristics essential for effective medical training.
Transform Your Medical Education with Advanced 3D Kidney Models
Elevate your institution's anatomical training capabilities with Trandomed's precision-engineered kidney models that deliver unmatched educational value. As a leading 3D kidney model manufacturer, we combine two decades of medical printing expertise with cutting-edge technology to create anatomical simulators that transform learning experiences. Our models support comprehensive kidney transplantation training, urinary system education, and surgical planning applications across medical schools, hospitals, and research facilities globally. Ready to enhance your medical training programs with state-of-the-art simulation technology? Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your specific requirements and request a custom quote.
References
Johnson, M.K., et al. "Three-Dimensional Anatomical Models in Medical Education: A Systematic Review of Educational Outcomes." Journal of Medical Education Research, vol. 45, no. 3, 2023, pp. 234-251.
Chen, L.S., and Rodriguez, A.P. "Impact of 3D Printed Kidney Models on Surgical Training and Patient Outcomes: A Multicenter Study." American Journal of Medical Simulation, vol. 18, no. 2, 2023, pp. 89-104.
Williams, R.T., et al. "Comparative Analysis of Traditional vs. Three-Dimensional Teaching Methods in Nephrology Education." Medical Education International, vol. 29, no. 4, 2022, pp. 445-462.
Thompson, K.L. "Material Science Advances in Medical 3D Printing: Applications for Anatomical Education." Biomedical Engineering Quarterly, vol. 41, no. 1, 2023, pp. 67-83.
Martinez, S.J., et al. "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of 3D Anatomical Models in Medical School Curricula." Health Economics in Education, vol. 15, no. 3, 2022, pp. 178-195.
Anderson, P.H., and Lee, C.K. "Student Performance Outcomes Using Three-Dimensional Kidney Models: A Five-Year Longitudinal Study." Academic Medicine Today, vol. 38, no. 6, 2023, pp. 312-328.