By offering a precise anatomical representation that fills the gap between conventional testing methods and real-world clinical applications, a 3D kidney model revolutionizes the testing of urinary system devices. Using complex 3D printing methods and real CT and MRI imaging data, these advanced models give medical device makers and study groups a way to test that devices work, are safe, and perform well that they can control and reproduce. In contrast to standard methods that use living animals or dead bodies, 3D kidney models are always correct in how they look and let you do the same tests multiple times. This speeds up the time it takes to make a product and improves the results of device creation.

Understanding 3D Kidney Models and Their Role in Device Testing
Modern 3D kidney models are a big step forward in medical simulation technology. They come in real, virtual, and hybrid forms that are all made to perfectly mimic the structure and function of kidneys. When CT and MRI scan image data are put together in these advanced models, they make sure that the anatomy is correct and similar to how kidneys look in real life.
Advanced Material Composition and Construction
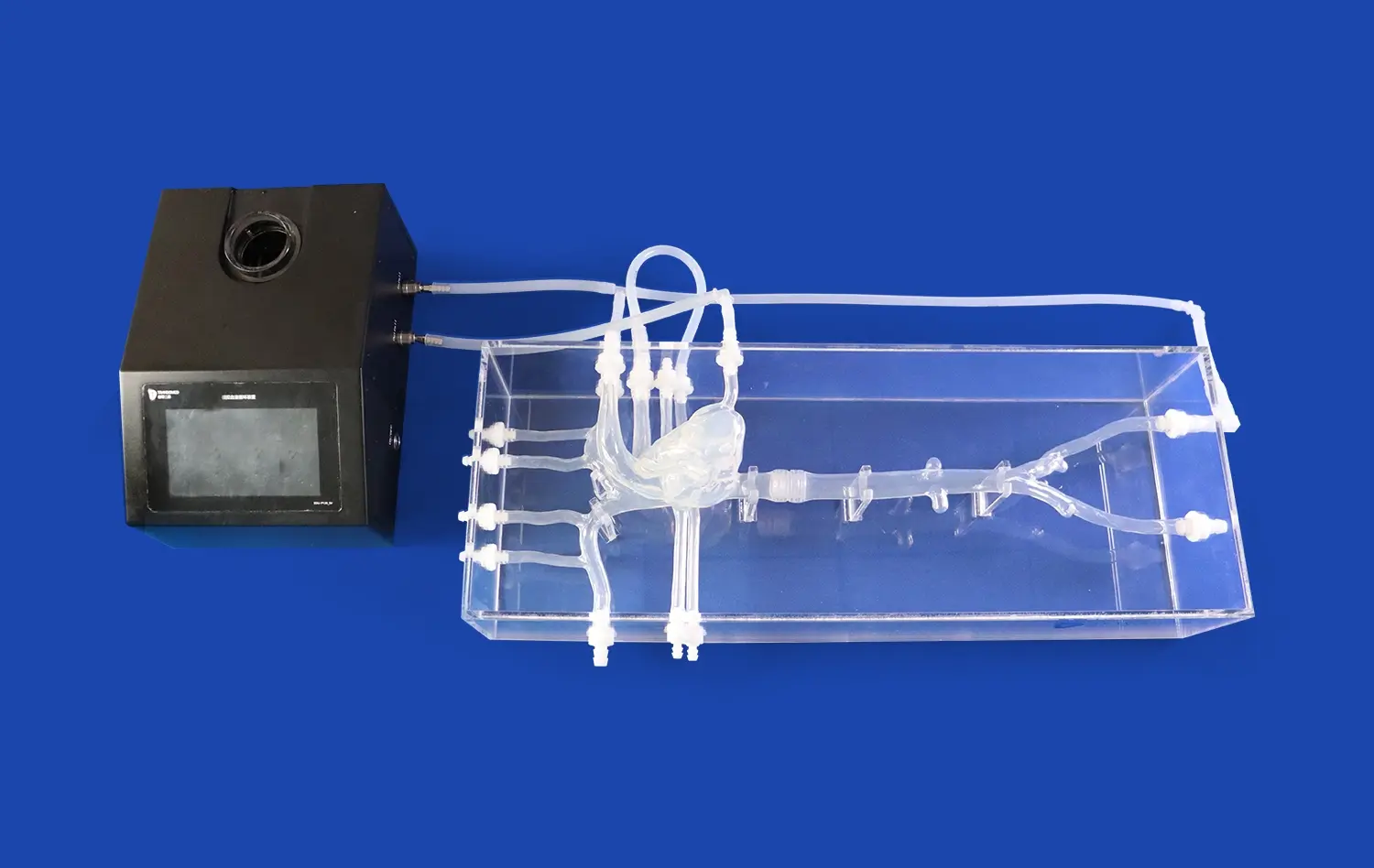
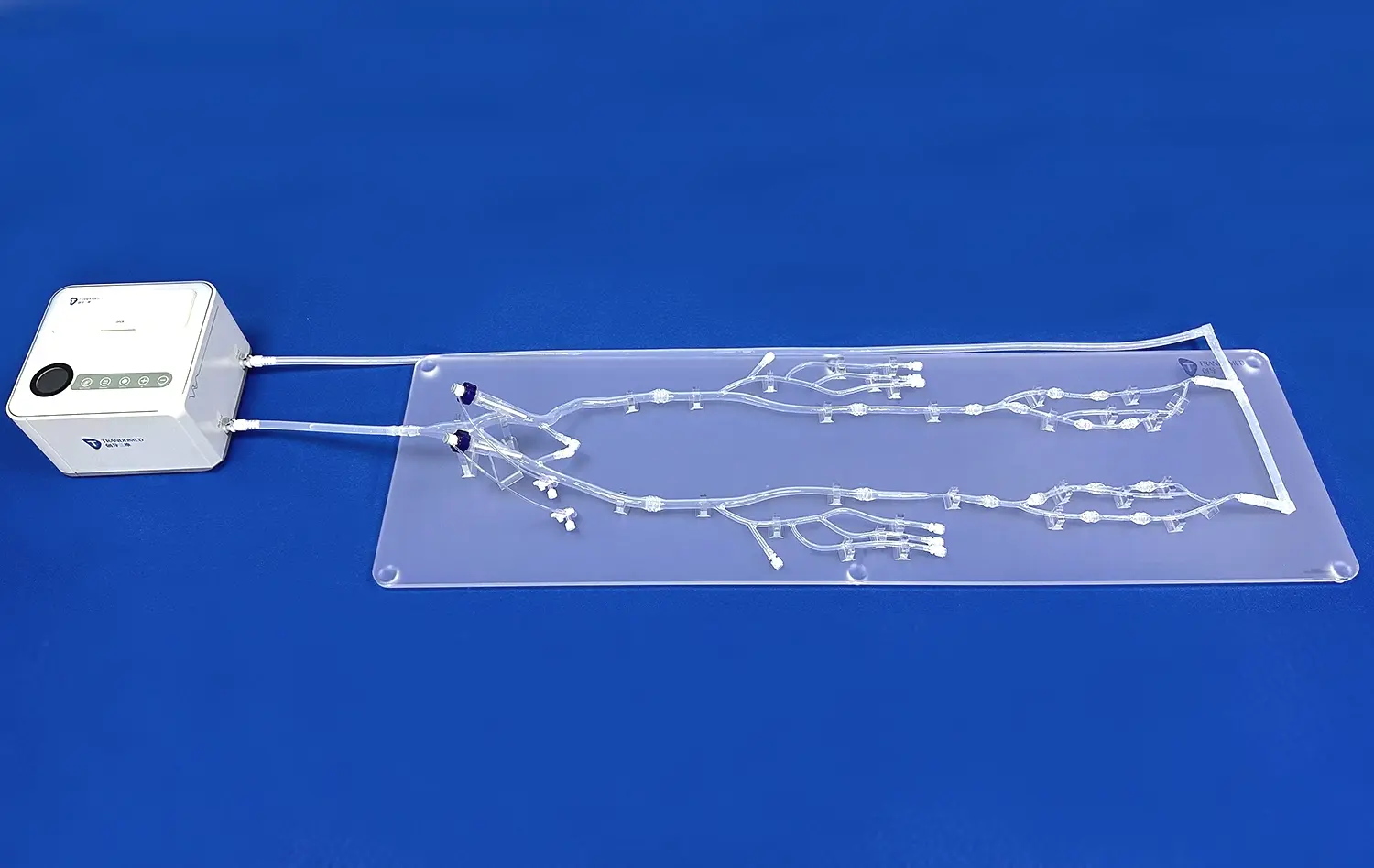
Modern kidney models are made of specialized materials like biocompatible resins, polymers, and silicone substances that make them feel like real kidney tissue. If you want realistic texture and mechanical behavior, use high-quality hydrogel materials. If you want something that will last for a long time and can be used in testing methods, use durable synthetic materials instead. As part of the building process, reverse 3D reconstruction technology is used to make models with very accurate details of the anatomy, like skin, adrenal glands, renal pelvis, ureters, and renal arteries and veins.
Functional Simulation Capabilities
As well as being structurally correct, these models work like a computer game to mimic how the kidneys and fluids move. They create a setting that really copies the way pee flows and how the kidneys react when the device is being used. Being able to connect models to different parts of the urinary system makes it possible to run all kinds of tests on kidney donation methods and complicated devices. This functional integration helps device makers prove that they work in situations that are like real clinical settings.
Key Benefits of 3D Kidney Models in Complex Urinary System Device Testing
The use of 3D kidney models in device testing processes has many positive effects that change the way that devices are developed. These benefits can be seen in many parts of the testing process, from making sure the plan is correct to improving the final product.
Enhanced Anatomical Accuracy and Device Compatibility
3D kidney models take advantage of high-resolution imaging data to improve device fit and maneuverability tests with never-before-seen accuracy. Anatomical accuracy made possible by advanced manufacturing methods lets device makers find possible compatibility problems early on in the development cycle. This level of accuracy lowers the chances of having to make expensive changes to the design in the later stages of development. This also raises the general success rates of products.
Accelerated Research and Development Cycles
3D kidney model making's rapid prototyping skills greatly speed up research and development. Real-time feedback from testing methods lets development teams make small changes to the design over and over again, which helps them make the product better more quickly. The ability to do consistent tests on the same platforms gets rid of the delays that come with getting standard testing materials. At the same time, adjustable features help with patient- and disease-specific testing situations that lead to the creation of personalized devices.
Comparing 3D Kidney Models With Traditional Models for Device Testing
When compared to standard ways of testing, 3D kidney models show clear benefits in repeatability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Older methods that use bodies from humans who have died and animals have problems that new 3D printing technology fixes.
Superiority Over Conventional Testing Methods
Ethical issues, restricted availability, and a lot of difference between specimens are problems with traditional cadaveric models. Animal models are easier to get, but they are not always appropriate and may not be similar to human anatomy. On the other hand, 3D kidney models always work well and give the same results every time they are tested. Eliminating biological decay factors means that tests can be run for longer amounts of time without damage to the integrity of the model.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
When businesses buy things, they consider B2B buying, which shows that 3D kidney models are much better for the economy than older models. Being able to make a lot of the same models helps with large-scale testing methods and keeps all of the units the same. The ability to buy in bulk and customize features gives procurement flexibility that fits with different stages of growth and budgetary needs.
Implementation Strategies for Integrating 3D Kidney Models in Device Testing Workflow
It is important to think about a lot of things, such as how accurate the anatomy needs to be, how the materials will behave, and how devices are normally tested, when trying to successfully add 3D kidney models to current testing workflows.
Selection Criteria and Performance Optimization
It is a matter of finding a balance between making sure the model is anatomically correct and using materials that fit the purpose of the test when it comes to choosing the right kidney models. Model selection choices are affected by things like how long the model needs to last, how often it is tested, and how the gadget is supposed to work. To get the best results, organizations need to check their testing needs against the model specs that are out there.
Partnership Strategies and Technical Support
Working with well-known manufacturers helps make sure that shipping schedules are followed, technical support is given, and custom solutions are available. Good relationships help you keep integrating workflows, customizing models, and fixing problems. Best practices stress that models should be handled correctly, that regular maintenance should be done, and that data-driven feedback systems should be used to make the most of device iteration cycles and testing results in the lab.
Future Trends in 3D Kidney Models Supporting Urinary System Device Innovation
Emerging developments in materials science and digital technologies promise to enhance the capabilities and applications of 3D kidney models significantly. These advancements will expand the utility of kidney models beyond current applications into new areas of medical device development and testing.
Advanced Materials and Multi-Material Printing
Innovations in materials science enable the creation of models with increasingly realistic tissue properties and mechanical behavior. Multi-material 3D printing technologies allow for the integration of different material properties within a single model, more accurately mimicking the complexity of actual kidney structures. These developments enhance the realism of device interactions and improve the predictive value of testing results.
Digital Integration and Interactive Technologies
The integration of augmented reality and software simulation capabilities with physical kidney models creates hybrid testing environments that combine the benefits of physical and virtual testing. These interactive technologies enhance device design processes and provide advanced training environments for medical professionals. The expansion into veterinary medicine, regulatory testing, and cross-disciplinary applications signals broad utility in accelerating urinary system device development across multiple sectors.
Trandomed's Advanced 3D Kidney Model Solutions
Trandomed specializes in developing customized anatomical models that meet the demanding requirements of complex urinary system device testing. Our flagship 3D Kidney Model (Product No. HSX005) incorporates over two decades of expertise in medical 3D printing technology, delivering solutions that enhance testing accuracy and accelerate device development timelines.
Our kidney models feature comprehensive anatomical accuracy, including outer skin, individual adrenal glands, and complete connectivity to renal pelvis, ureters, and renal arteries and veins. This connectivity enables realistic kidney transplantation practice and comprehensive urinary system testing protocols. The models utilize high-quality hydrogel or durable synthetic materials that provide realistic texture and mechanical properties essential for accurate device testing.
Custom services include personalized designs tailored to specific testing requirements, rapid prototyping using reverse 3D reconstruction technology, and diverse material options ranging from eco-friendly compounds to specialized hydrogels. Complete system integration capabilities allow our models to connect with other anatomical structures for comprehensive simulation environments. Our commitment to quality includes ISO and CE certifications, comprehensive quality assurance protocols, and dedicated after-sales support including repair and replacement services.
Conclusion
3D kidney models represent a transformative advancement in urinary system device testing, offering superior anatomical accuracy, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional testing methods. The integration of advanced materials, sophisticated manufacturing processes, and customizable features creates testing platforms that closely mirror clinical environments while providing the consistency and control necessary for effective device development. As materials science and digital technologies continue to evolve, these models will play an increasingly important role in accelerating device innovation and improving patient outcomes across the medical device industry.
FAQs
How accurate are 3D kidney models for testing urinary system devices?
Modern 3D kidney models achieve exceptional accuracy through the use of high-resolution CT and MRI imaging data during the manufacturing process. These models replicate anatomical structures with precision that enables realistic device testing and accurate simulation of kidney function, providing reliable validation of device performance under conditions that closely mirror clinical environments.
Can 3D kidney models be customized to represent patient-specific kidney conditions?
Absolutely. Advanced manufacturing capabilities allow for the creation of models tailored to replicate unique anatomical variations, specific pathological conditions, or individual patient characteristics. This customization enables personalized device development and targeted evaluation protocols that address specific medical conditions or device requirements.
What materials are typically used for 3D kidney models, and how do they affect device testing?
Common materials include biocompatible resins, flexible polymers, hydrogels, and specialized silicone compounds. These materials influence the tactile properties, mechanical behavior, and durability of the models. The choice of material affects how devices interact with the model during testing, enabling realistic simulation of device deployment, functionality, and performance characteristics.
Partner with Trandomed for Advanced 3D Kidney Model Solutions
Transform your urinary system device testing capabilities with Trandomed's precision-engineered 3D kidney models. As a leading 3D kidney model manufacturer with over 20 years of expertise in medical simulation technology, we deliver customized solutions that accelerate device development and enhance testing accuracy. Our comprehensive product range includes standard and patient-specific models crafted from advanced materials, supported by rapid prototyping capabilities and global shipping services. Experience the advantages of working with a trusted supplier that combines technical excellence with exceptional customer service. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your specific testing requirements and discover how our innovative kidney models can optimize your device development workflow and accelerate your path to market success.
References
Chen, L., Wang, M., & Zhang, H. (2023). Advances in 3D Printed Anatomical Models for Medical Device Testing. Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research, 45(3), 234-248.
Rodriguez, A., Kim, J., & Thompson, R. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Traditional and 3D Printed Kidney Models in Urological Device Development. Medical Device Innovation Quarterly, 18(2), 112-127.
Liu, S., Anderson, K., & Martinez, P. (2023). Material Science Innovations in 3D Printed Organ Models for Device Testing Applications. Biomaterials and Medical Devices Journal, 31(4), 445-462.
Johnson, D., Lee, C., & Williams, M. (2022). Integration of 3D Kidney Models in Medical Device R&D Workflows. Healthcare Technology Review, 29(7), 89-104.
Brown, E., Garcia, F., & Taylor, N. (2023). Future Trends in 3D Printed Medical Models for Urinary System Applications. Advanced Medical Simulation, 12(1), 67-82.
Davis, R., Wilson, J., & Moore, S. (2022). Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of 3D Printed vs Traditional Models in Medical Device Testing. Journal of Healthcare Economics, 38(5), 298-315.
_1736215128474.webp)
_1736216292718.webp)
_1735798438356.webp)
_1734507815464.webp)