How Do 3D Models Enhance Learning of Intestinal Anatomy?
Visualizing Complex Structures
3D printed small intestine models offer an unparalleled opportunity for students to visualize the intricate structures of the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike traditional 2D illustrations or diagrams, these models provide a tactile, three-dimensional representation of the small intestine's anatomy. Students can examine the villi, crypts, and mucosal folds in detail, gaining a deeper understanding of the organ's surface area and its role in nutrient absorption. The ability to rotate, handle, and inspect the model from various angles helps learners grasp spatial relationships between different anatomical features, such as the arrangement of blood vessels and lymphatic structures within the intestinal wall.
Understanding Functional Anatomy
3D printed models go beyond static representations by incorporating functional aspects of small intestine anatomy. These models can be designed to demonstrate peristalsis, the wave-like muscular contractions that move food through the digestive tract. By incorporating movable parts or using flexible materials, educators can illustrate how the circular and longitudinal muscles of the intestine work together to propel contents forward. This dynamic representation helps students connect structural features with physiological processes, enhancing their comprehension of gastrointestinal motility and its importance in digestion and absorption.
Exploring Pathological Changes
Advanced 3D printing techniques allow for the creation of small intestine models that showcase various pathological conditions. These models can depict common disorders such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or intestinal tumors, providing students with a visual and tactile understanding of how these conditions affect the intestinal structure. By comparing healthy and diseased models side by side, learners can better appreciate the morphological changes associated with different gastrointestinal disorders. This exposure to pathological variations enhances diagnostic skills and prepares future healthcare professionals to recognize and understand abnormalities they may encounter in clinical practice.
Hands-On Simulation for Gastrointestinal Education
Practicing Endoscopic Procedures
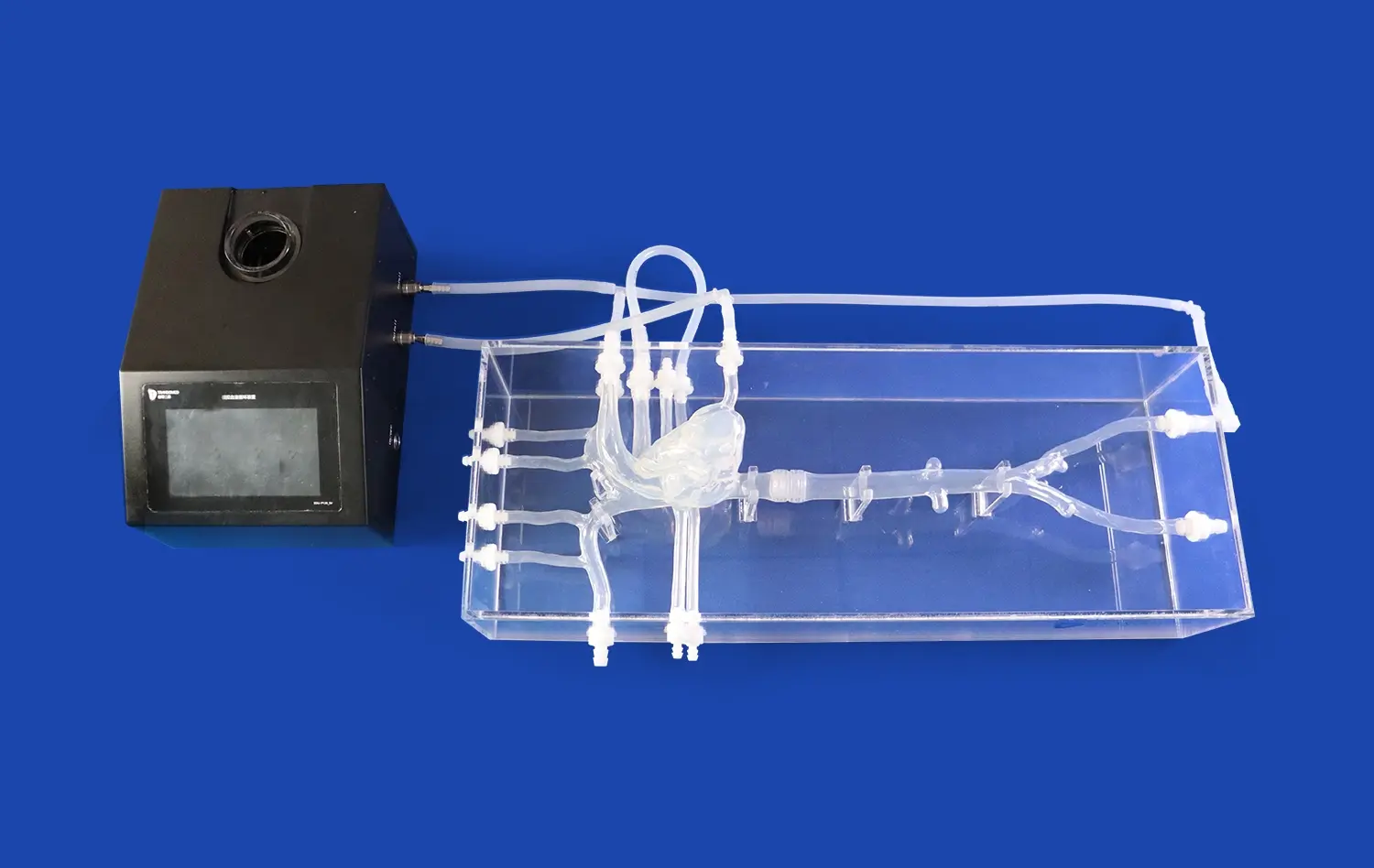
3D printed small intestine models serve as invaluable tools for simulating endoscopic procedures. These models can be designed with hollow interiors that allow for the insertion and manipulation of endoscopes, mimicking real-world scenarios. Medical trainees can practice navigating the twists and turns of the intestinal tract, learning to identify landmarks and potential problem areas. This hands-on experience helps develop the fine motor skills and spatial awareness necessary for performing successful endoscopies. By repeatedly practicing on these realistic models, students can gain confidence and proficiency before progressing to live patient procedures, ultimately improving patient safety and outcomes.
Surgical Planning and Training
In the realm of gastrointestinal surgery, 3D printed small intestine models offer unique advantages for both planning and training. Surgeons can use patient-specific models, created from CT or MRI scans, to plan complex procedures such as tumor resections or bowel reconstructions. These personalized models allow for precise measurements and help surgeons anticipate potential challenges before entering the operating room. For surgical trainees, standardized models provide a platform to practice techniques such as anastomosis or stoma creation. The ability to perform these procedures on realistic, disposable models allows for repetitive practice and skill refinement without the pressure of operating on live patients.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
3D printed small intestine models foster interdisciplinary collaboration in medical education. These tangible representations serve as a common reference point for discussions between various healthcare specialties, including gastroenterologists, surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists. By examining the same model, professionals from different fields can share insights and perspectives, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of gastrointestinal health and disease. This collaborative approach not only enhances the educational experience but also promotes teamwork and communication skills that are essential in modern healthcare settings.
How Realistic Models Improve Student Understanding and Retention?
Multisensory Learning Experience
3D printed small intestine models provide a multisensory learning experience that significantly enhances student understanding and retention. By engaging multiple senses simultaneously, these models create stronger neural connections and memory imprints. Visual learners benefit from the detailed, color-coded representations of different intestinal layers and structures. Tactile learners can explore the texture and contours of the model, reinforcing their understanding of anatomical relationships. This hands-on approach activates kinesthetic learning pathways, making the educational experience more engaging and memorable. The combination of visual, tactile, and kinesthetic inputs creates a rich, immersive learning environment that caters to diverse learning styles and promotes long-term retention of anatomical knowledge.
Active Learning and Critical Thinking
Incorporating 3D printed small intestine models into medical education promotes active learning and critical thinking. Instead of passively absorbing information from lectures or textbooks, students actively engage with the model, formulating questions and hypotheses about structure and function. Educators can design problem-based learning scenarios that require students to use the models to solve clinical cases or explain physiological processes. This approach encourages learners to apply their knowledge in practical contexts, fostering deeper understanding and analytical skills. The tactile nature of the models also allows for immediate feedback and self-correction, as students can quickly verify their understanding by examining the physical representation.
Enhanced Spatial Reasoning
One of the most significant benefits of 3D printed small intestine models is their ability to improve spatial reasoning skills. Understanding the three-dimensional relationships between anatomical structures is crucial for medical professionals, particularly in fields like surgery and radiology. These models allow students to mentally manipulate and rotate complex anatomical structures, developing their spatial intelligence. This enhanced spatial reasoning translates into improved interpretation of medical imaging, better surgical planning, and more accurate diagnoses. As students become more comfortable with 3D representations, they can more easily transition between 2D images (such as CT scans or ultrasounds) and their corresponding 3D realities, a skill that is invaluable in clinical practice.
Conclusion
3D printed small intestine models have emerged as a transformative tool in medical education, offering a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By providing realistic, hands-on learning experiences, these models enhance understanding of intestinal anatomy, facilitate surgical training, and improve retention of complex medical concepts. As technology continues to advance, the integration of 3D printed models in medical curricula will likely expand, further revolutionizing how future healthcare professionals learn and prepare for their careers. The tangible benefits of these innovative educational tools underscore their importance in shaping a new generation of skilled and confident medical practitioners.
Contact Us
Are you looking to elevate your medical education program with cutting-edge 3D printed small intestine models? Look no further than Trandomed, your trusted manufacturer and supplier of high-quality medical simulation products. Our advanced 3D printing technology and expertise in anatomical modeling ensure unparalleled accuracy and realism in every model. Experience the benefits of hands-on learning and improved student outcomes with our customizable solutions. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss how we can meet your specific educational needs and revolutionize your gastrointestinal teaching methods.

_1736214519364.webp)
 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)
_1732843184544.webp)