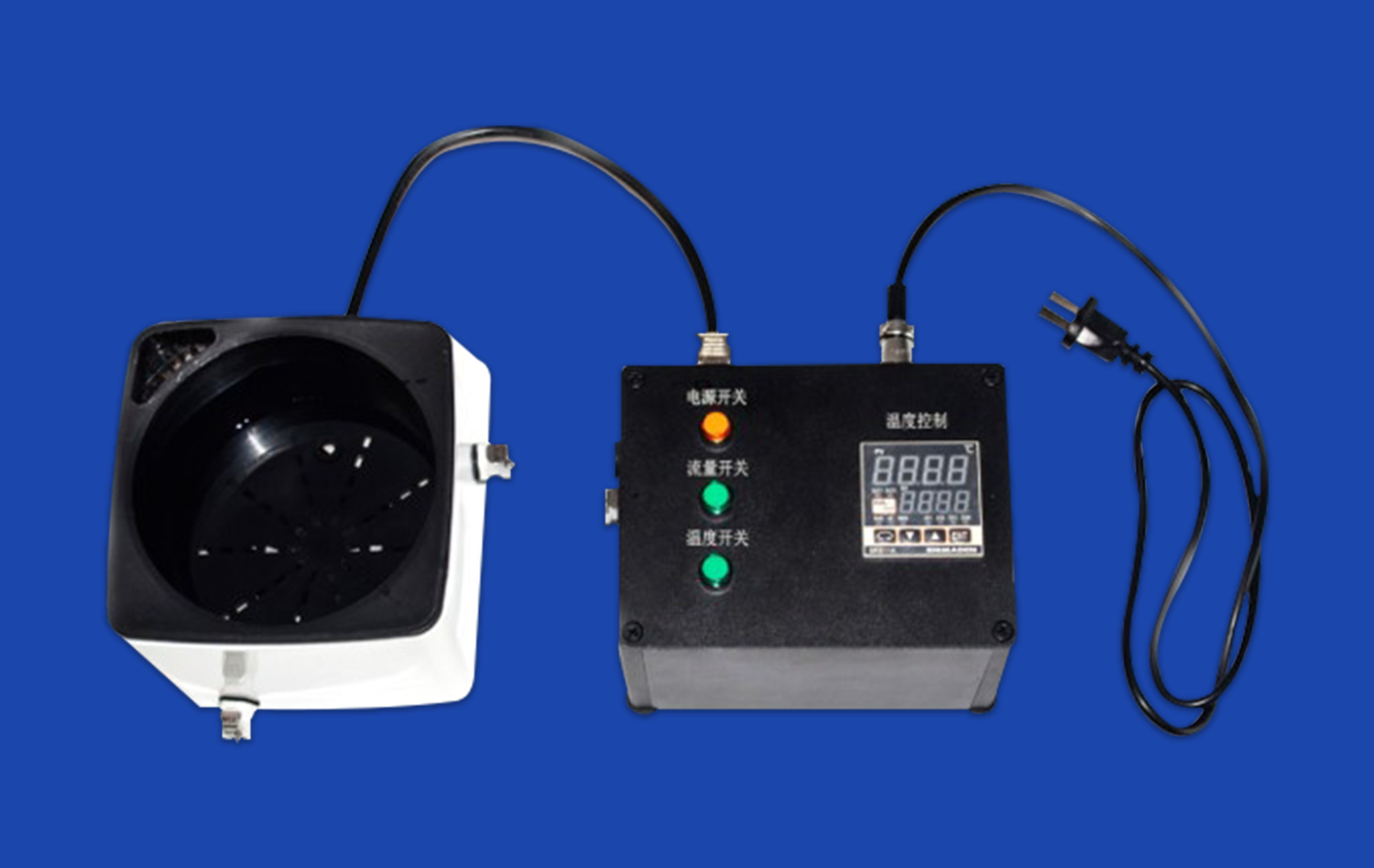
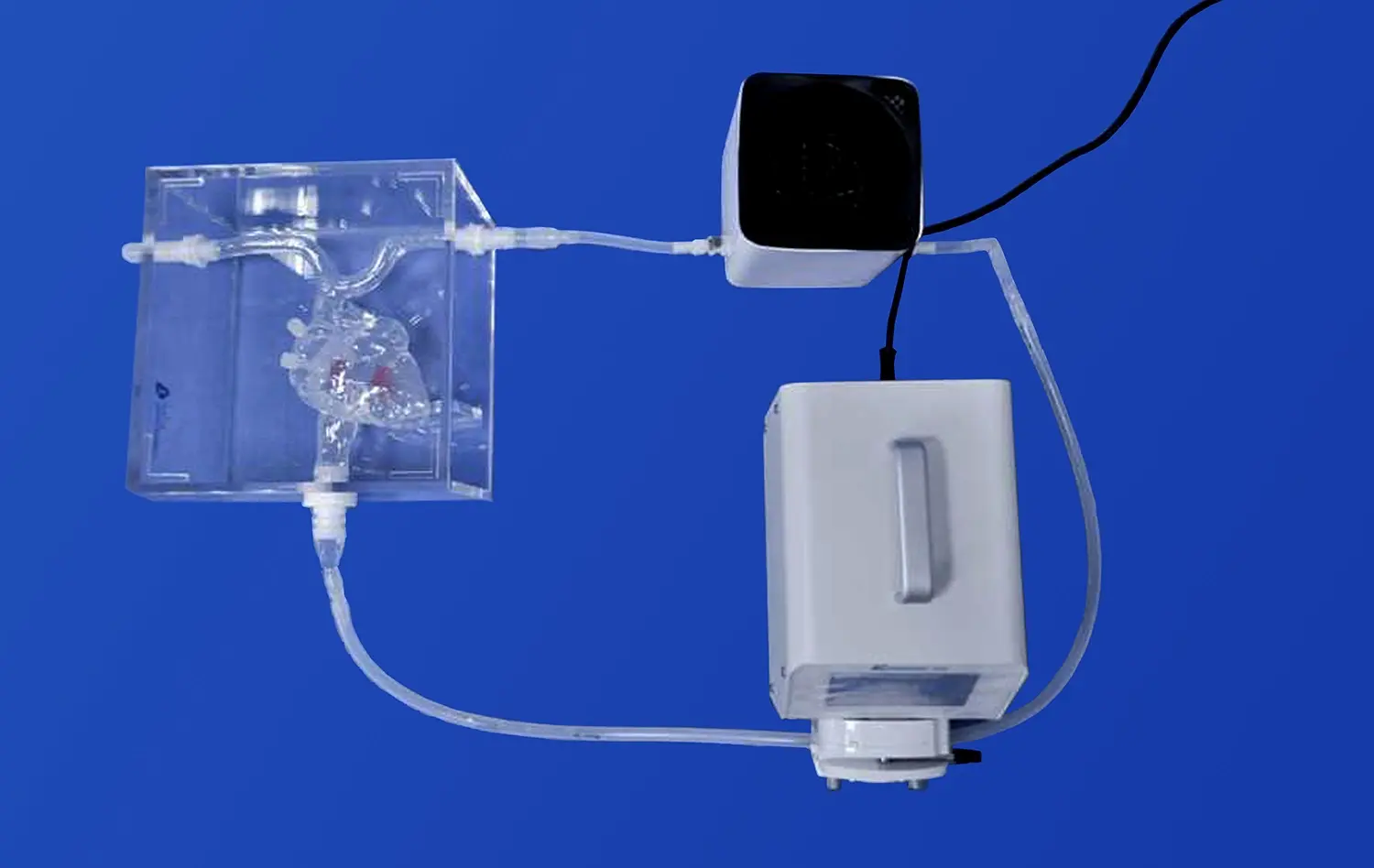
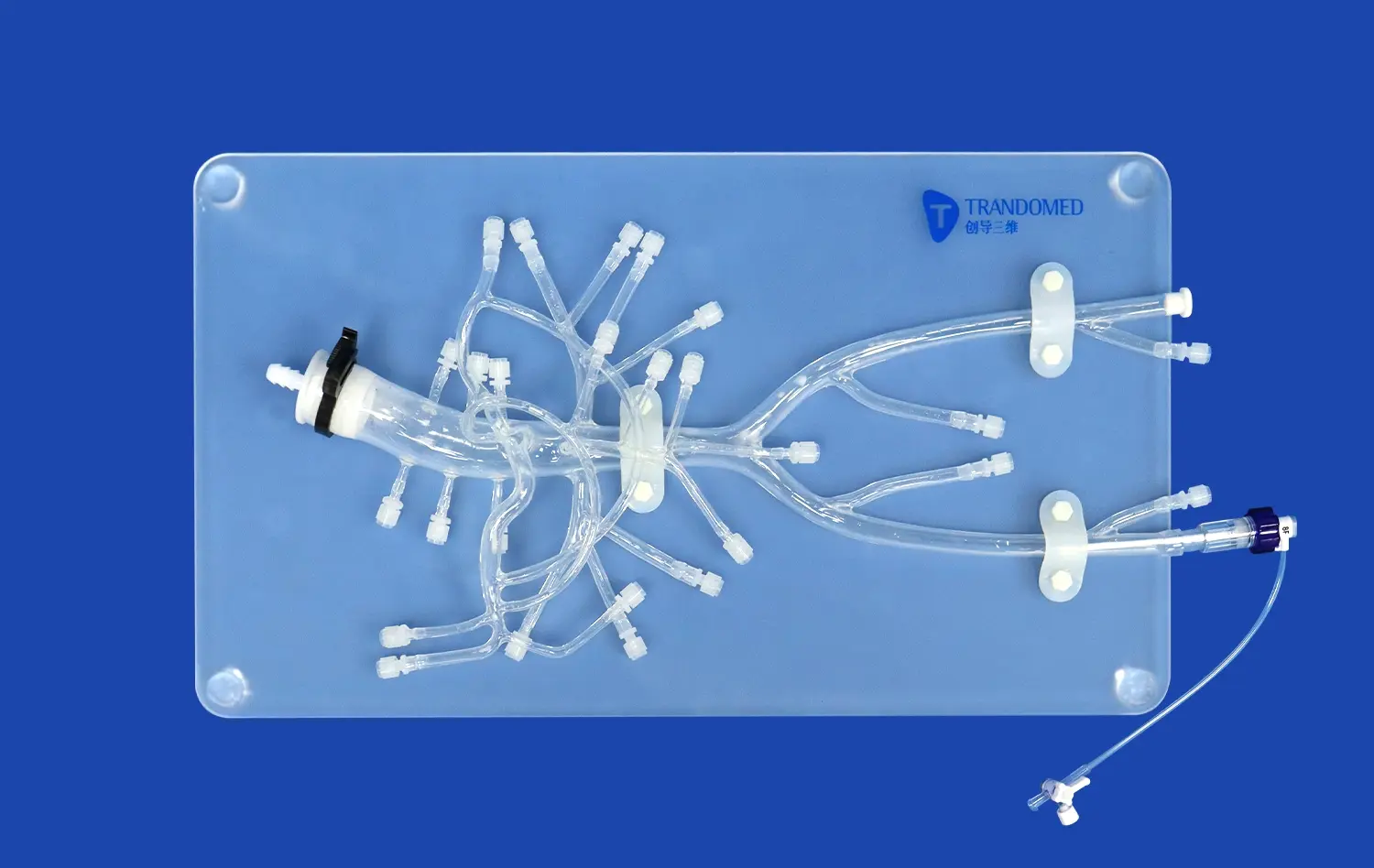
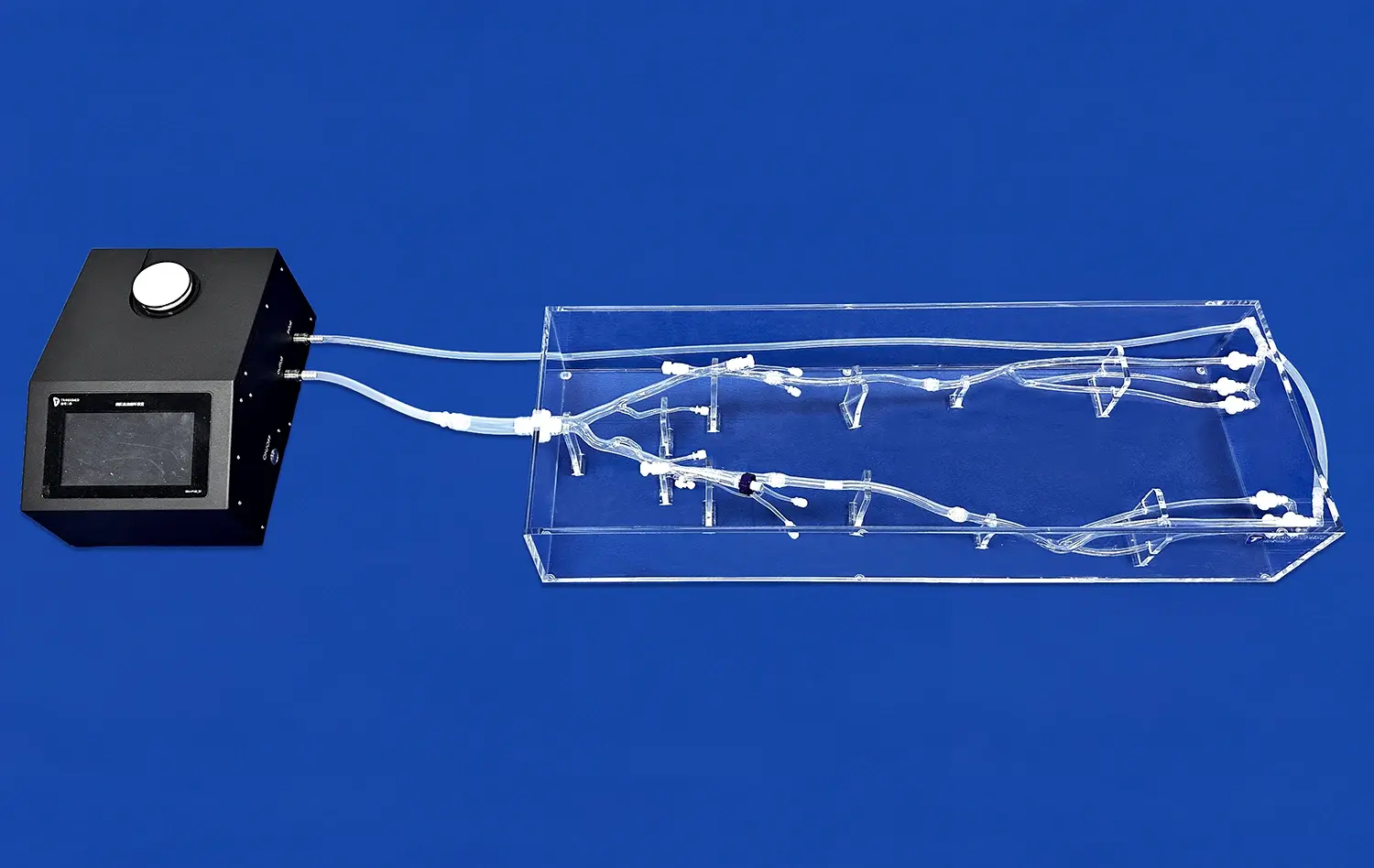
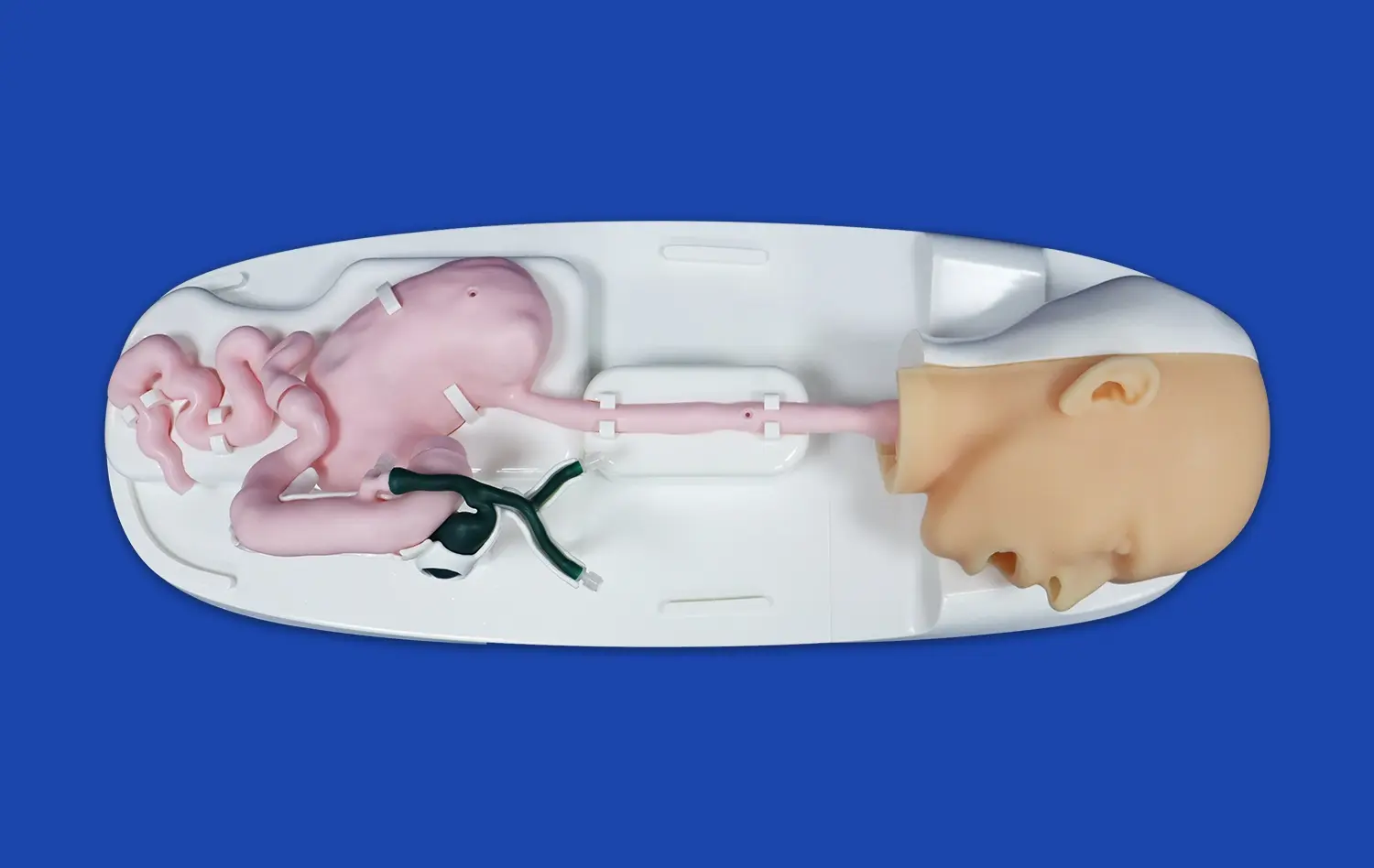
What Makes 3D Stomach Models Effective for Anatomy Learning?
Anatomical Precision and Detail
The effectiveness of 3D printed stomach models in anatomy learning stems from their exceptional anatomical precision. These models, like those produced by Trandomed, are based on real human CT and MRI data, ensuring an accurate representation of the stomach's structure. The level of detail achievable through advanced 3D printing techniques allows for the inclusion of minute features such as gastric folds, blood vessels, and even pathological conditions. This precision enables students to visualize and understand complex anatomical relationships that may be challenging to grasp from textbooks or 2D images alone.
Tactile Learning Experience
One of the key advantages of 3D stomach models is the tactile learning experience they provide. Unlike traditional learning methods, these models allow students to physically interact with a realistic representation of the stomach. They can palpate the model, feeling the texture and contours of different regions. This hands-on approach engages multiple senses, reinforcing learning through touch and visual observation. The ability to manipulate the model, examine it from various angles, and even simulate basic procedures significantly enhances the learning process and improves retention of anatomical knowledge.
Visualization of Internal Structures
3D printed stomach models, especially those made from transparent materials like silicone, offer a unique advantage in visualizing internal structures. These models allow students to see through the stomach wall, observing the relationships between different layers and internal features. This transparency is particularly beneficial for understanding the stomach's mucosal folds, the distribution of blood vessels, and the positioning of sphincters. By providing a clear view of these typically hidden structures, 3D models bridge the gap between surface anatomy and internal morphology, offering a comprehensive understanding of stomach anatomy.
Hands-On Simulation for Gastrointestinal Procedures
Endoscopic Training
3D printed stomach models have become invaluable tools for endoscopic training. These models provide a safe and realistic environment for medical trainees to practice endoscopic procedures without the risks associated with live patients. The anatomical accuracy of these models allows for the simulation of various endoscopic techniques, including gastroscopy and biopsy procedures. Trainees can practice navigating the endoscope through the esophagus and into the stomach, learning to maneuver around gastric folds and identify key landmarks. This hands-on experience builds confidence and proficiency in endoscopic skills before trainees progress to clinical practice.
Surgical Planning and Technique Refinement
For more advanced gastrointestinal procedures, 3D stomach models serve as excellent tools for surgical planning and technique refinement. Surgeons can use these models to plan complex operations, such as gastrectomies or bariatric surgeries, by visualizing the patient-specific anatomy beforehand. The ability to practice on a physical model allows surgeons to refine their techniques, experiment with different approaches, and anticipate potential challenges. This pre-operative planning and practice can lead to improved surgical outcomes, reduced operating times, and enhanced patient safety.
Pathology Simulation
One of the unique advantages of 3D printed stomach models is the ability to incorporate pathological conditions. Manufacturers like Trandomed can customize models to include various gastric pathologies, such as ulcers, tumors, or congenital abnormalities. This feature allows medical students and practitioners to study and practice diagnosing these conditions in a controlled setting. The ability to visualize and palpate abnormalities in a realistic model enhances diagnostic skills and prepares healthcare professionals for encountering these conditions in clinical practice. Furthermore, these pathology simulations can be used to educate patients about their conditions, improving patient understanding and informed consent processes.
How Realistic Models Improve Student Comprehension and Skill
Enhanced Spatial Understanding
Realistic 3D stomach models significantly improve students' spatial understanding of gastric anatomy. Unlike 2D illustrations or computer simulations, physical models allow learners to grasp the three-dimensional relationships between different structures within and surrounding the stomach. This enhanced spatial awareness is crucial for understanding how the stomach interacts with neighboring organs and how its shape and position change during various physiological processes. By manipulating the model and viewing it from multiple angles, students develop a more comprehensive mental map of gastric anatomy, which is essential for clinical reasoning and surgical planning.
Bridging Theory and Practice
One of the most significant benefits of using realistic stomach models in medical education is their ability to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. These models serve as a transitional learning tool, allowing students to apply their textbook knowledge to a tangible, three-dimensional representation. For instance, after learning about the layers of the stomach wall, students can identify and palpate these layers on the model. This hands-on experience reinforces theoretical concepts and helps students connect abstract ideas with physical realities, leading to deeper understanding and better retention of information.
Skill Development in a Low-Stakes Environment
Realistic 3D stomach models provide a low-stakes environment for skill development, which is crucial for building confidence and competence in medical procedures. Students can practice techniques such as palpation, auscultation, and basic endoscopic maneuvers without the pressure and risks associated with real patient interactions. This safe learning environment encourages experimentation and allows for repeated practice, essential for mastering complex medical skills. As students become more comfortable with these procedures on models, they are better prepared for clinical rotations and eventual patient care, reducing anxiety and improving performance in real-world medical settings.
Conclusion
3D printed stomach models have emerged as powerful tools in medical education and training, offering unparalleled benefits in enhancing anatomical understanding, procedural skills, and overall competence in gastroenterology. By providing realistic, hands-on learning experiences, these models bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing healthcare professionals for the complexities of patient care. As technology continues to advance, the integration of these innovative teaching aids promises to elevate the quality of medical education, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and advancements in gastrointestinal medicine.
Contact Us
Elevate your medical training program with Trandomed's cutting-edge 3D printed stomach models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of medical simulators, we offer customizable, anatomically accurate models that meet the highest standards of educational excellence. Experience the difference that realistic, hands-on learning can make in your institution. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore our range of products and discover how our factory-direct pricing can benefit your educational goals. Invest in the future of medical education with Trandomed – your trusted partner in innovative medical simulation technology.
References
Johnson, A. et al. (2022). "The Impact of 3D Printed Anatomical Models on Medical Education: A Systematic Review." Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 9, 238-251.
Smith, R. and Brown, J. (2023). "Enhancing Endoscopic Training with 3D Printed Gastrointestinal Models." Surgical Endoscopy, 37(4), 1823-1832.
Garcia, M. et al. (2021). "3D Printed Stomach Models for Improved Surgical Planning in Gastric Cancer Resections." Annals of Surgical Oncology, 28(6), 3215-3224.
Lee, S. and Kim, H. (2022). "Student Perceptions of 3D Printed Anatomical Models in Medical Education: A Mixed-Methods Study." BMC Medical Education, 22(1), 156.
Patel, N. et al. (2023). "The Role of Realistic Simulation in Gastroenterology Training: A Comprehensive Review." Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 68(5), 1589-1601.
Wong, L. and Chen, Y. (2021). "Advancements in 3D Printing Technology for Medical Education: Current Applications and Future Prospects." Medical Teacher, 43(8), 891-901.