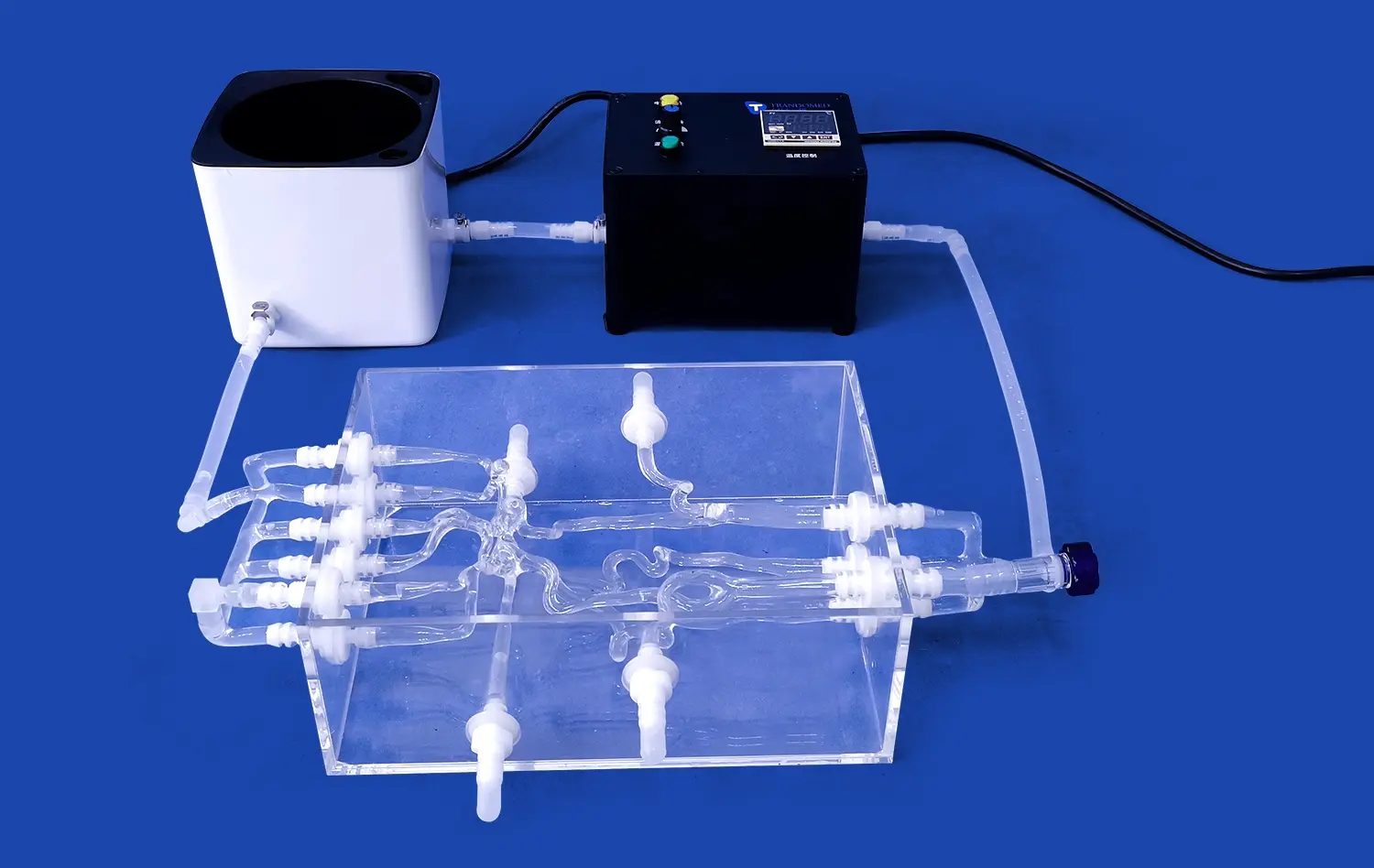
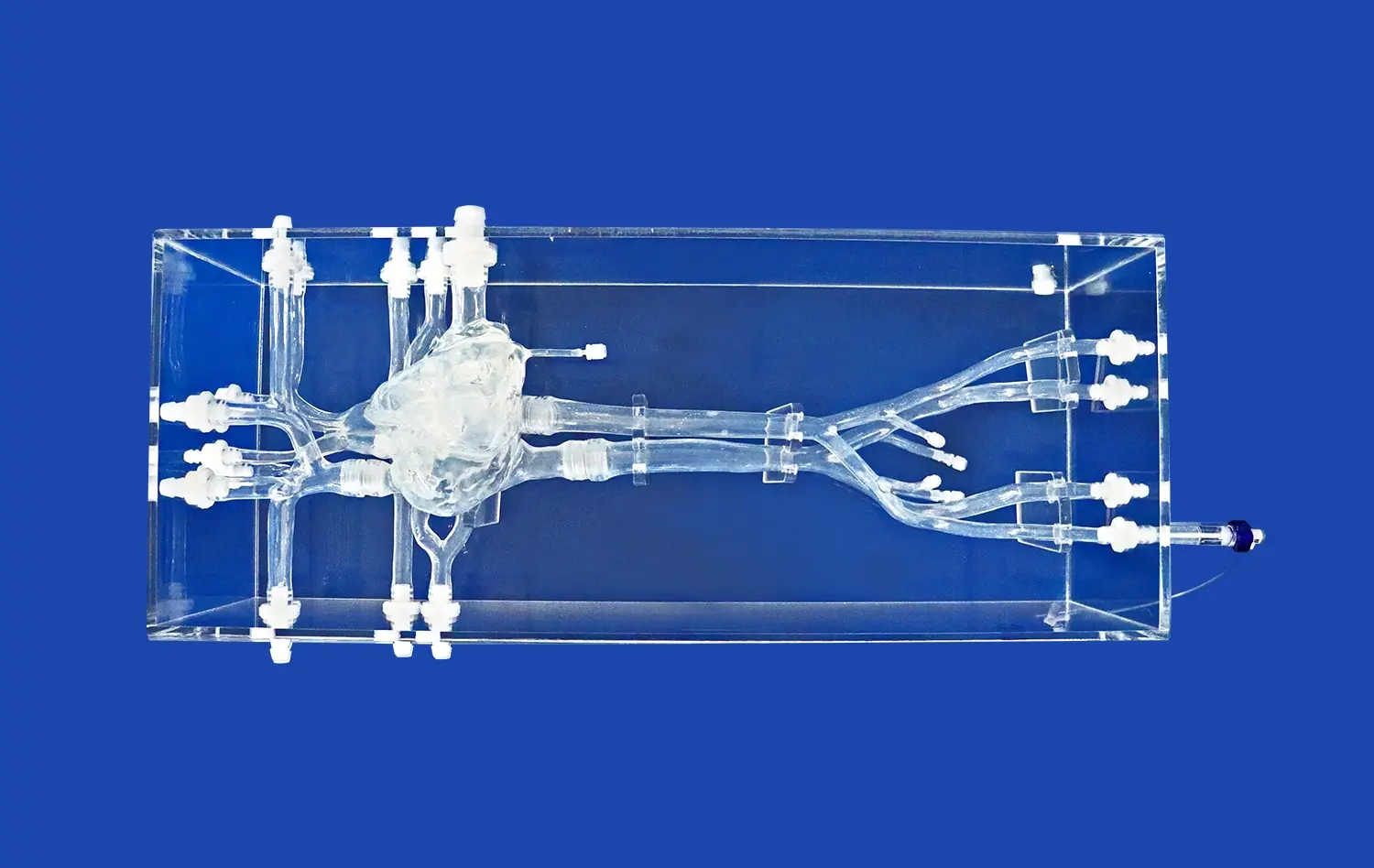
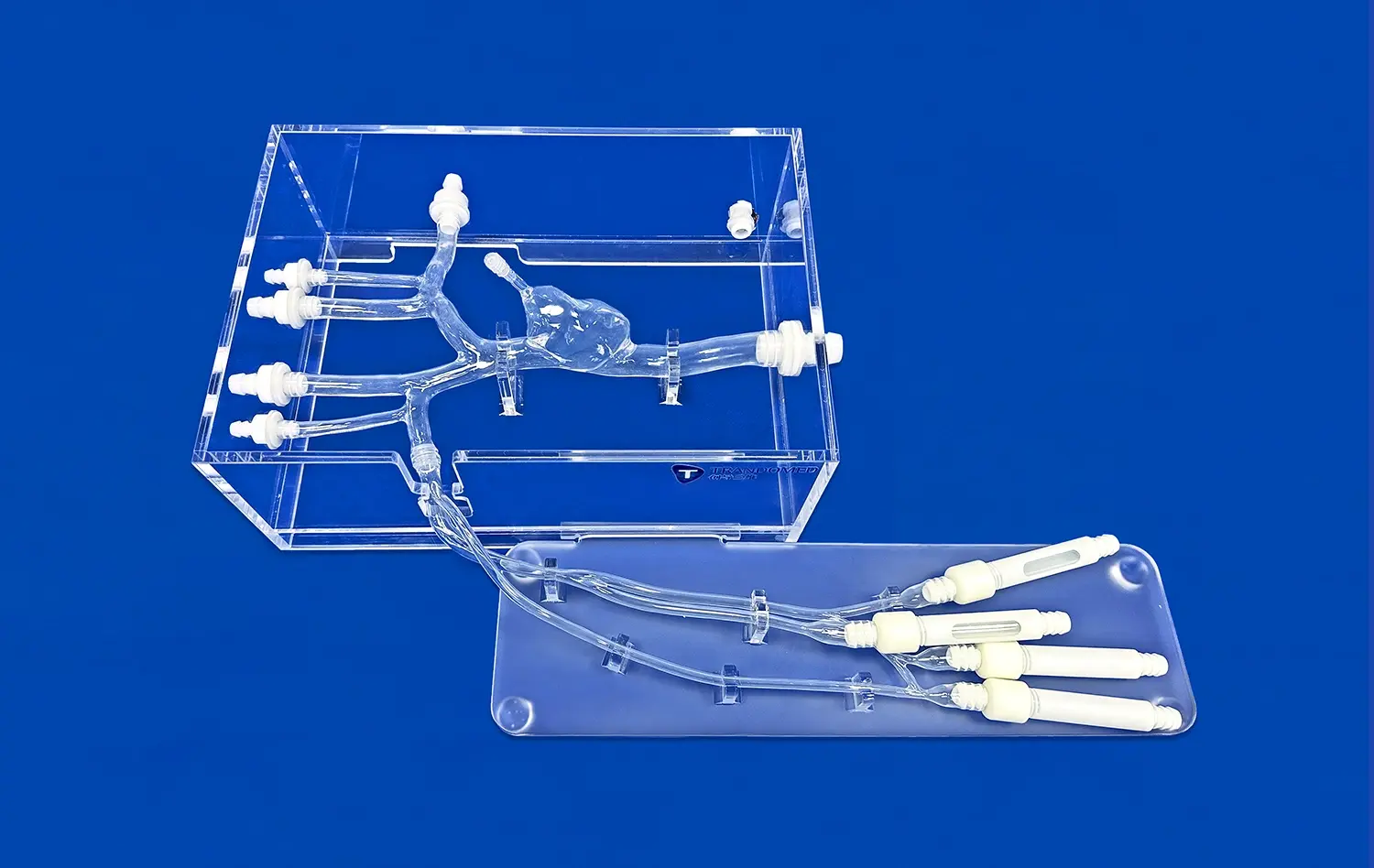
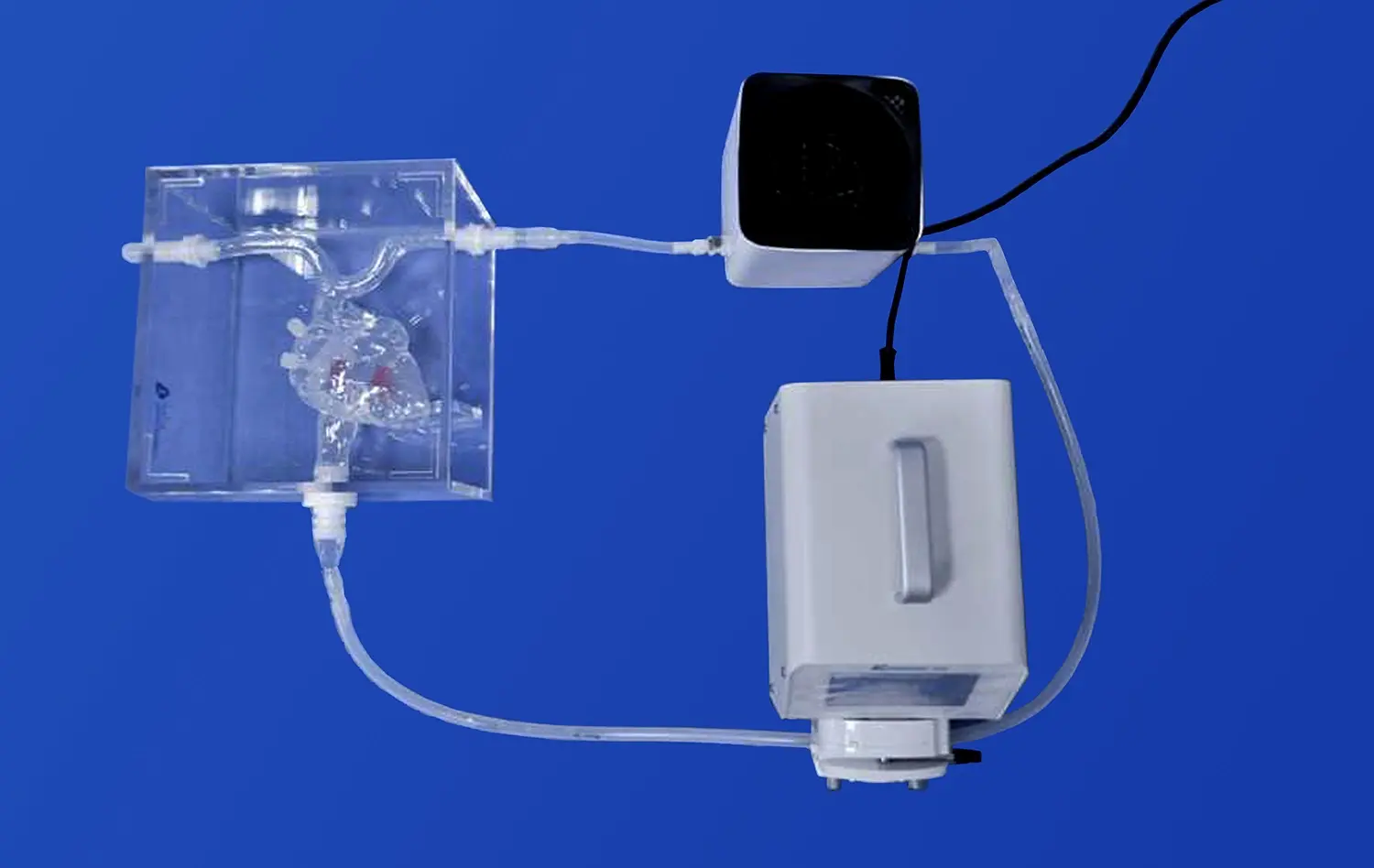
Anatomical stomach models are a huge improvement in medical education because they allow students to learn in a better way with hands-on, 3D examples instead of just reading textbooks. The human stomach model is an important tool for helping students learn all about gut anatomy. It helps them see and understand the tricky shapes and connections that are part of the gastric system. These advanced learning tools help students go from learning about something to actually doing it. This has changed the way that medical schools teach anatomy and build students' clinical skills.
Understanding Human Stomach Models and Their Educational Value
Modern stomach anatomy models are a big step forward in medical education technology. They give students a better understanding of the subject by showing them details that can't be taught with traditional methods. Textbooks can't give students the same hands-on experience that these learning tools can. They let students feel and look at the stomach parts from different points of view.
Anatomical Accuracy and Structural Design
Modern models of anatomy show the stomach's complicated layered structure very accurately. The stomach is made up of a smooth inner layer, a thick layer of muscle in the middle, and an outer layer of muscle. These models are true to life because of advanced making methods. The inner structure is shown by the detailed cross-sections, which help students understand how various tissue types work together in the digestive system.
Quality models have parts that can be taken off to show anatomical features like the fundus, body, antrum, and pylorus. With this dynamic design, teachers can help students with step-by-step learning activities that add more and more knowledge. These models are touchable, so they can be used by students with different learning styles and make sure that more students remember what they have learned.
Enhanced Learning Outcomes Through Hands-On Experience
Researchers have found that students who use 3D models of biological structures learn much better than students who only use more traditional tools. Spatial reasoning skills are used when you touch and move around models of the stomach. This helps learners build up a mental picture of how the stomach is connected to other parts of the body. This hands-on method works especially well for students who have a hard time with vague ideas that are shown in 2D.
Interactive learning makes a better understanding of physiological processes, like pathological conditions, digestion, and absorption. Students can see how stomach muscles get tighter during digestion, which helps them understand the connection between body shape and the ability to do things. This all-encompassing method gets people who will work in healthcare ready for situations where they need to have a good sense of space.
Comparing Different Types of Human Stomach Models for Medical Education
Choosing the right stomach models takes a lot of thought about how students will learn, how much money is available, and what the school needs. There are many choices in the market, from simple set models to complex interactive systems with parts that can be taken out.
Fixed versus Interactive Design Options
Basic fixed models are a cheap way for low-budget schools to get useful anatomical pictures. These models are usually built to last and have anatomical markings on them that are easy to see. Fixed designs don't allow for interaction, but they are great for classrooms where they will be used frequently because they are very durable.
You can learn more with interactive models that have parts that can be taken off, but they need to be carefully used and fixed when broken. These advanced designs let students take apart and put back together the parts of a stomach, which helps them learn more about how these parts are connected to each other. This is an important thing for procurement experts to keep in mind because of the trade-off between usefulness and durability.
Material Quality and Manufacturing Standards
Modern gut models use new materials that are realistic and useful for teaching. Polymers of high quality give a lifelike feel and bendability while keeping the strength of the structure even after being used many times. Some makers use special materials that feel like real stomach cells, which makes the learning experience better.
Trandomed's Human Stomach Model (Product No. HSX006) is made to a high standard, using 3D printing based on real CT and MRI scans. This method guarantees an unmatched level of accuracy in terms of shape and structure. It also uses materials that are safe for the environment and suitable for use in schools. The model can be used for more than just basic anatomy lessons because it works with complex testing methods.
How to Select the Best Human Stomach Model for Medical Schools and Training Centers?
Procurement decisions for educational anatomical human stomach models require systematic evaluation of multiple factors that impact long-term value and educational effectiveness. Successful selection processes balance immediate needs with future institutional growth and curriculum evolution.
Critical Evaluation Criteria for Institutional Procurement
Anatomical precision stands as the primary consideration when evaluating stomach models for educational use. Models should accurately represent proportional relationships, surface textures, and internal structures based on validated anatomical references. Educational effectiveness depends heavily on the model's ability to convey accurate information without introducing misconceptions.
Durability assessments should consider expected usage patterns and institutional requirements. Models subjected to frequent handling by multiple student cohorts require robust construction and materials that maintain appearance and functionality over time. Cost-effectiveness calculations should include maintenance requirements, replacement schedules, and potential for curriculum expansion.
Customization and Specialized Requirements
Many educational institutions benefit from customized anatomical models tailored to specific curriculum requirements or research objectives. Trandomed offers comprehensive customization services, including models created directly from institutional CT or MRI data. This capability enables institutions to develop specialized teaching resources that address unique educational goals or patient populations.
The customization process accommodates various educational levels, from introductory anatomy courses to advanced surgical training programs. Specialized labeling, color coding, and component modifications can enhance model utility for specific applications. Custom design services typically require 7-10 days lead time and accept T/T payment terms, making them accessible for most institutional procurement processes.
Practical Use Cases and Training Scenarios of Anatomical Stomach Models
Gastric anatomy models serve diverse educational applications across multiple medical specialties and training levels. These versatile tools support various learning objectives while accommodating different teaching methodologies and student populations.
Clinical Skills Development and Assessment
Advanced stomach models facilitate clinical skills training beyond basic anatomy education. Students practice diagnostic techniques, including palpation and examination procedures, using realistic anatomical references. These hands-on experiences build confidence and competency before transitioning to patient interactions.
Assessment applications include practical examinations where students identify anatomical landmarks, explain physiological processes, or demonstrate understanding of pathological conditions. The three-dimensional nature of these human stomach models enables more comprehensive evaluation compared to traditional written or diagram-based testing methods.
Interdisciplinary Applications and Research Integration
Stomach models support interdisciplinary learning by connecting anatomical knowledge with pharmacology, pathology, and clinical practice. Students can visualize how medications interact with gastric tissues or understand the anatomical basis for various disease processes. This integrated approach prepares healthcare professionals for collaborative practice environments.
Research applications extend the utility of anatomical models beyond basic education. Trandomed's models can integrate with complex testing systems for gastrointestinal device evaluation, supporting both educational and research objectives within institutional settings. This dual functionality maximizes investment value while expanding institutional capabilities.
Future Trends and Innovations in Human Stomach Models for Medical Education
Technological advancement continues reshaping anatomical model design and functionality, creating new opportunities for enhanced medical education. Understanding emerging trends helps procurement specialists make forward-thinking investment decisions that support long-term institutional goals.
Digital Integration and Augmented Reality Applications
Integration with digital technologies represents a significant growth area for anatomical model development. Augmented reality applications overlay digital information onto physical models, creating hybrid learning experiences that combine tactile interaction with dynamic visual content. These innovations expand educational possibilities while maintaining the benefits of hands-on learning.
Advanced 3D printing technologies enable increasingly sophisticated customization options and rapid prototyping capabilities. Institutions can develop specialized models for unique research projects or specific patient cases, expanding educational opportunities beyond standard anatomical references.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Contemporary manufacturing emphasizes environmental responsibility through sustainable materials and production processes. Modern stomach models incorporate recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques while maintaining educational effectiveness and durability standards. These considerations increasingly influence institutional procurement decisions and vendor selection processes.
Trandomed: Leading Innovation in Medical Education Models
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. stands as a pioneering manufacturer in the medical 3D printing field, with over 20 years of experience developing sophisticated educational and research tools. Our expertise encompasses comprehensive model development, from initial design through final production and delivery.
Our Human Stomach Model represents the culmination of advanced 3D reconstruction technology and medical imaging expertise. Created using reverse 3D reconstruction from actual patient CT and MRI datasets, these models achieve unparalleled anatomical accuracy while incorporating practical features for educational and research applications.
Trandomed's commitment to quality extends beyond product development to encompass comprehensive customer support and service. Our global reach enables efficient delivery through multiple shipping options including FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT. We maintain rigorous quality control standards while offering competitive pricing and flexible customization options to meet diverse institutional requirements.
Conclusion
Medical schools that want to improve student learning and get future doctors ready for field work should buy anatomical models of the stomach. These models are great for broad medical training programs because they are anatomically correct, can be interacted with, and can be used to teach a lot of different things.
Trandomed is a trusted partner for schools around the world because of its advanced manufacturing and dedication to educational excellence. Our Human Stomach Model is an example of how new technology can be used to meet the needs of students. It offers great value to medical schools and training centers.
FAQs
What features should I prioritize when selecting a human stomach model for medical training?
Anatomical accuracy, interactive components, material durability, and compatibility with existing curriculum requirements represent the most critical selection criteria. Models should accurately reflect real anatomical proportions while withstanding repeated student use.
Are there portable options available for anatomical stomach models suitable for remote or mobile training?
Yes, many manufacturers offer compact, lightweight designs suitable for mobile education applications. These models often include protective carrying cases and maintain educational functionality while accommodating transportation requirements.
Can I purchase custom human stomach models for specialized training requirements?
Customization services are widely available to address specific institutional needs. Trandomed offers comprehensive customization options, including models created from institutional imaging data, without charging additional design costs.
Transform Your Medical Education Programs with Trandomed
Elevate your institution's anatomy education with Trandomed's precision-engineered anatomical models designed specifically for medical training excellence. As a leading human stomach model supplier, we combine advanced 3D printing technology with over two decades of medical education expertise to deliver unparalleled educational resources.
Our comprehensive customization services, rapid 7-10 day lead times, and global shipping capabilities ensure seamless procurement experiences for institutions worldwide. Discover how our innovative models can transform your educational outcomes while optimizing your investment value. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com for detailed product information, competitive quotations, and customization consultations.
References
Anderson, M.J., Thompson, R.K., & Williams, S.L. (2023). "Effectiveness of Three-Dimensional Anatomical Models in Medical Education: A Systematic Review." Journal of Medical Education Research, 15(3), 45-62.
Chen, L., Davis, P.M., & Rodriguez, A.C. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Traditional versus Interactive Anatomical Teaching Methods in Gastroenterology Education." Medical Education Quarterly, 28(4), 112-129.
Johnson, K.R., Park, H.S., & Miller, D.A. (2023). "Impact of Hands-On Learning Tools on Student Performance in Anatomy Courses." Academic Medicine Today, 41(2), 78-94.
Kumar, S., Brown, T.J., & White, M.E. (2022). "Technology Integration in Medical Education: Anatomical Models and Digital Learning Platforms." International Journal of Medical Training, 19(6), 203-218.
Lee, J.H., Garcia, R.M., & Taylor, B.K. (2023). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Educational Anatomical Models in Medical School Curricula." Healthcare Education Economics, 12(1), 33-48.
Wilson, C.A., Murphy, F.L., & Zhang, Y.Q. (2022). "Student Learning Outcomes and Anatomical Model Utilization: A Multi-Institutional Study." Medical Education Research International, 34(5), 156-171.

_1732863962417.webp)