What Are the Key Benefits of Simulation in Aortic Dissection Education?
Realistic Anatomical Representation
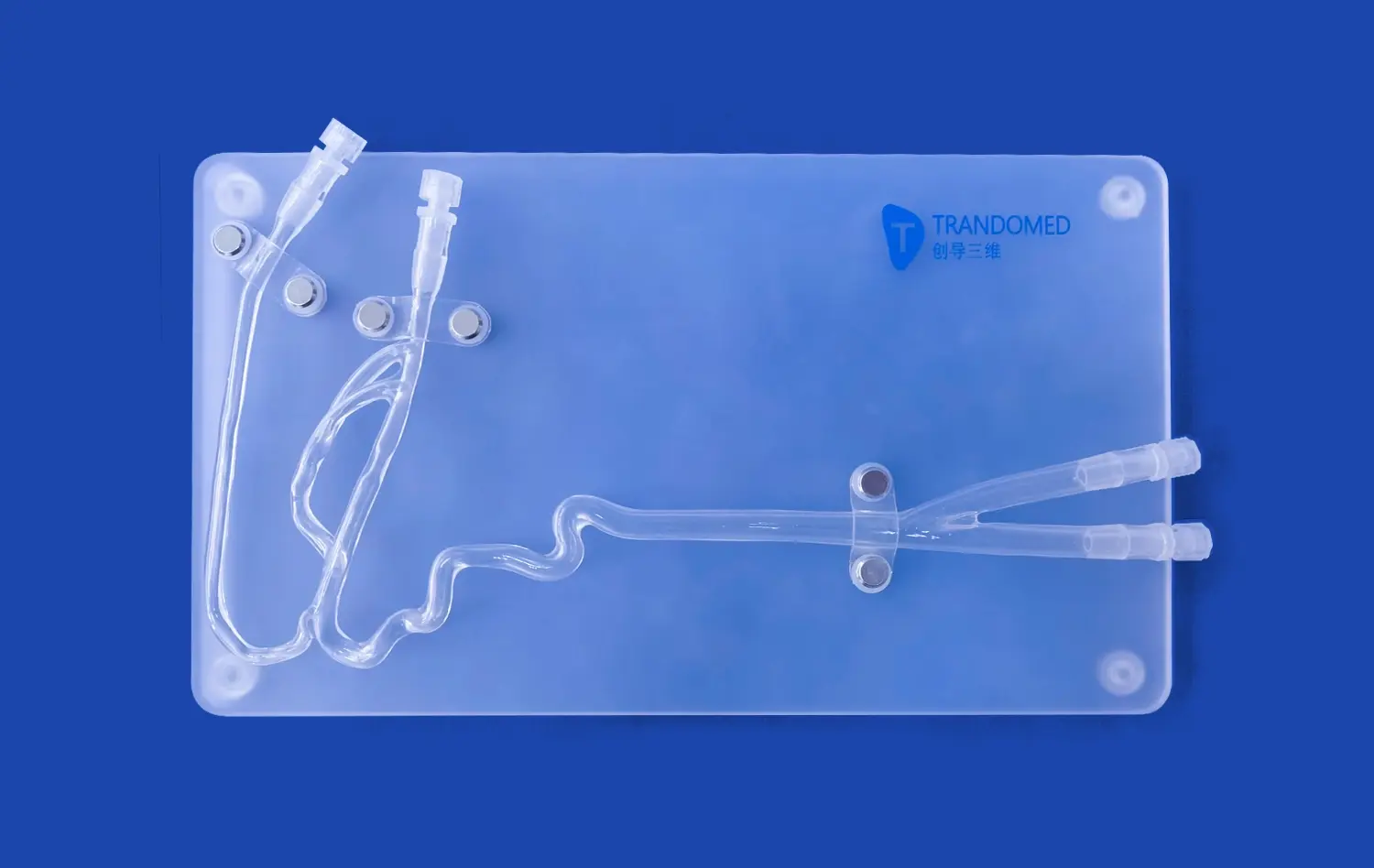
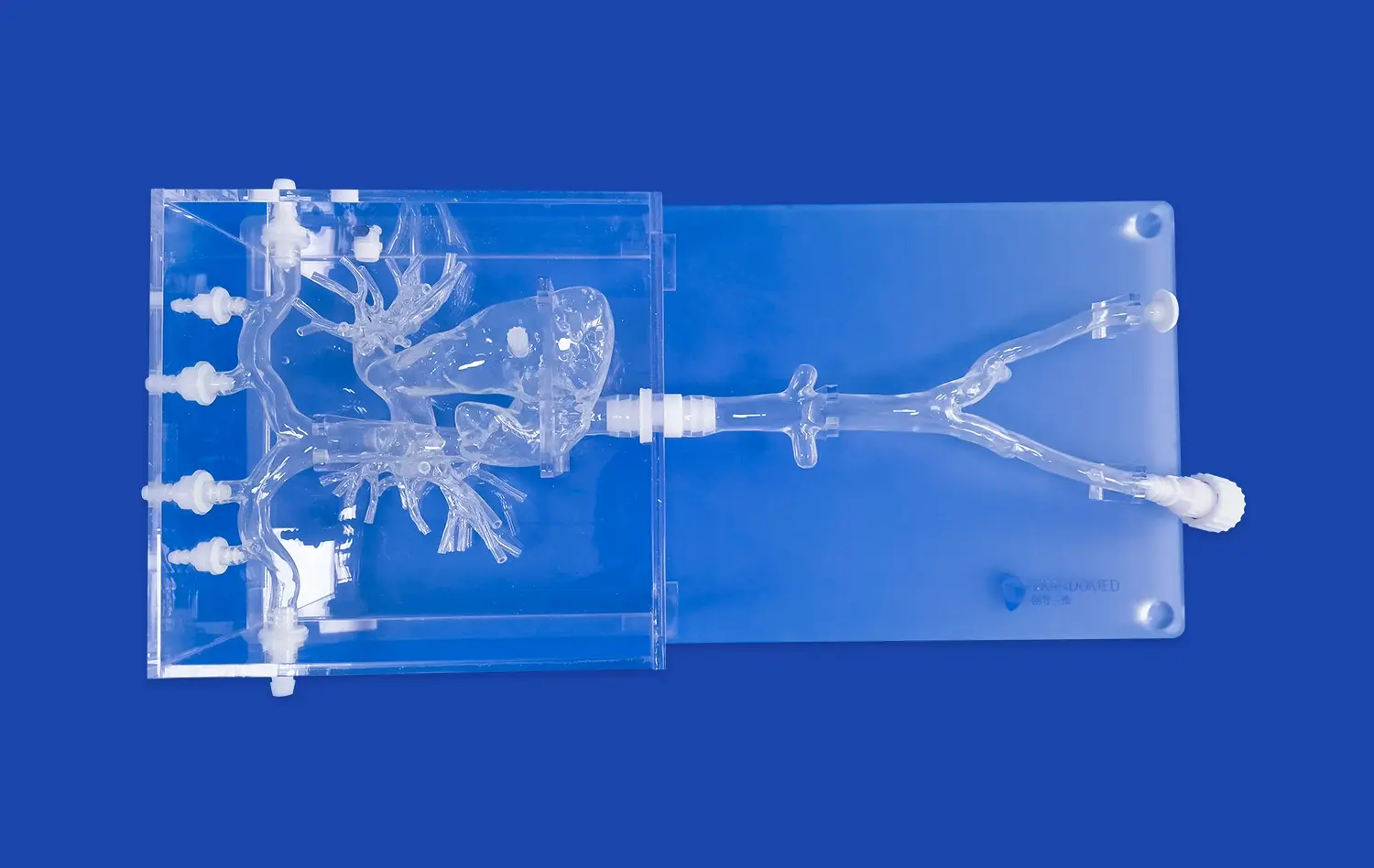
One of the primary advantages of using aortic dissection models in medical training is the accurate representation of anatomical structures. These models, such as the Aortic Dissection Model (XXK004D), provide a comprehensive view of the major arteries involved in aortic dissection scenarios. This includes detailed depictions of the femoral artery, iliac artery, abdominal aorta, renal arteries, celiac trunk, thoracic aorta, aortic arch, ascending aorta, and subclavian artery. The realistic portrayal of these structures allows trainees to develop a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships and anatomical variations they may encounter in clinical practice.
Hands-on Learning Experience
Simulation-based training with aortic dissection models offers an unparalleled hands-on learning experience. Medical professionals can interact with the model, palpate structures, and visualize the progression of the dissection. This tactile experience reinforces theoretical knowledge and helps bridge the gap between classroom learning and clinical application. By manipulating the model, trainees can gain a better appreciation for the complexities of aortic dissections and develop the manual dexterity required for interventional procedures.
Risk-free Practice Environment
Aortic dissection simulators provide a safe and controlled environment for medical trainees to practice their skills without the pressure of real-life consequences. This risk-free setting allows learners to make mistakes, learn from them, and refine their techniques without compromising patient safety. The ability to repeat procedures and explore different scenarios enhances confidence and proficiency, ultimately leading to improved performance in actual clinical situations.
Structured Learning for Diagnosing and Managing Aortic Pathologies
Comprehensive Visualization of Dissection Processes
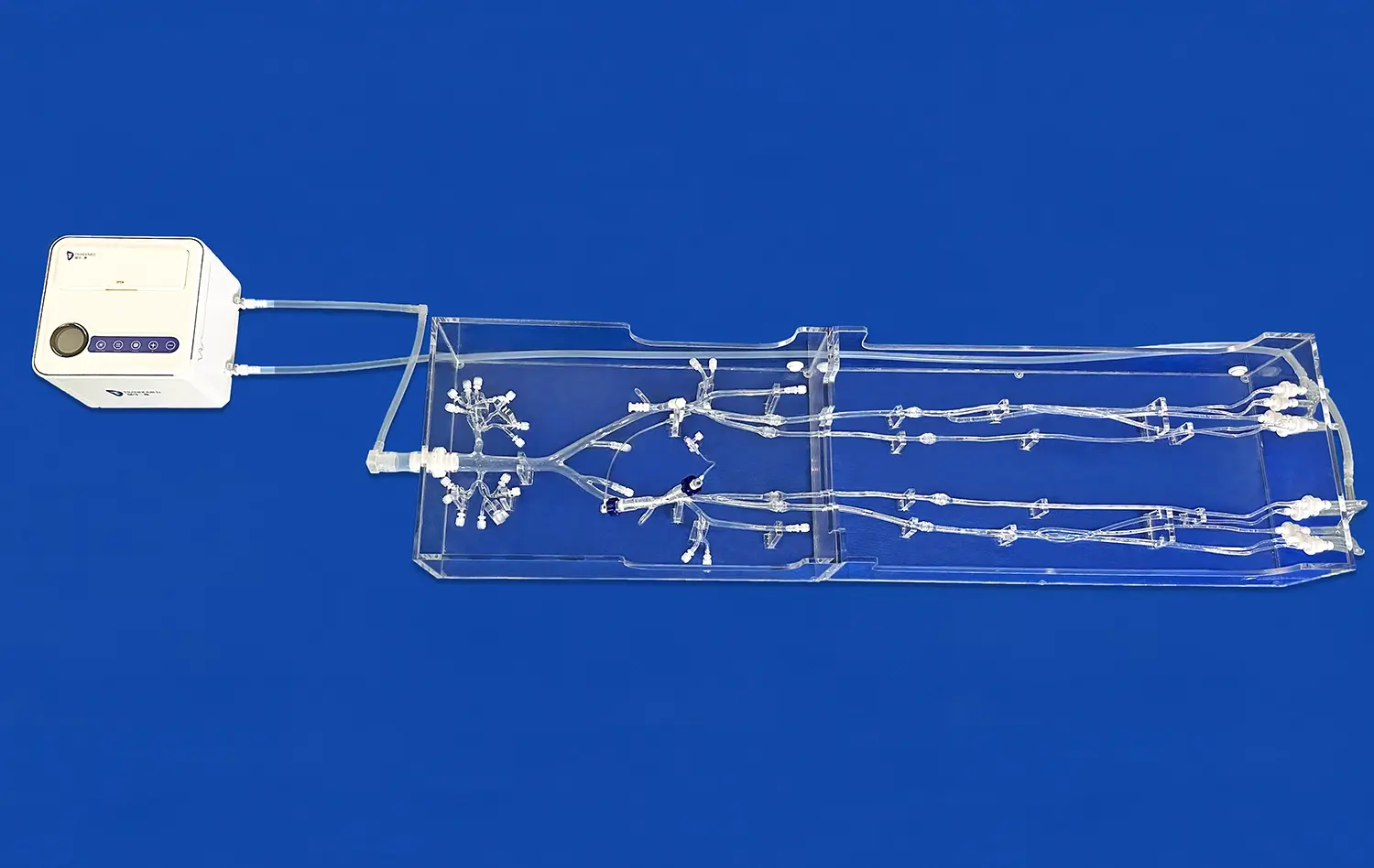
Advanced aortic dissection models, like those developed by Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd, offer a detailed visualization of the dissection process. The models typically feature a realistic depiction of an aortic dissection lesion in the thoracic aorta segment, allowing trainees to observe the intricacies of the condition. This comprehensive view enables learners to understand how the dissection progresses, its impact on surrounding structures, and the potential complications that may arise.
Mastering Diagnostic Techniques
Simulation-based training with aortic dissection models provides an excellent platform for mastering various diagnostic techniques. Trainees can practice identifying key indicators of aortic dissection, such as the presence of an intimal flap, false lumen, and compromised blood flow to vital organs. The ability to repeatedly examine these features in a controlled setting enhances diagnostic accuracy and speed, crucial factors in the timely management of aortic dissections.
Procedural Training for Interventional Techniques
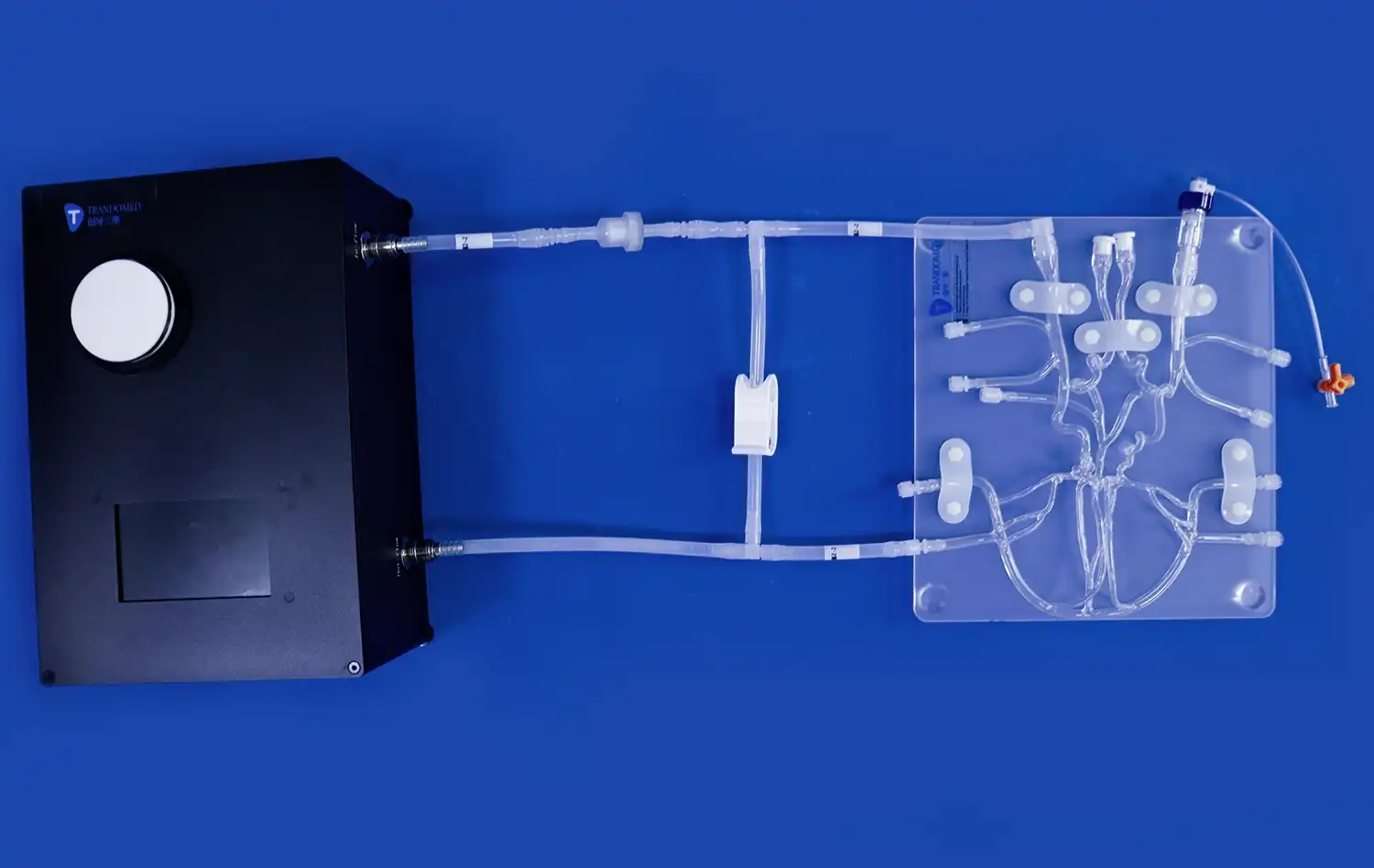
Aortic dissection simulators serve as invaluable tools for procedural training in interventional techniques. Medical professionals can practice endovascular procedures, such as stent graft placement or fenestration, on these models. The realistic representation of the aortic anatomy allows trainees to develop the skills necessary for navigating complex vascular structures and deploying medical devices accurately. This hands-on experience is particularly beneficial for interventional radiologists and vascular surgeons who need to perfect their techniques before performing procedures on actual patients.
Enhancing Clinical Decision-Making Through Interactive Training
Scenario-based Learning
Aortic dissection models facilitate scenario-based learning, allowing educators to create realistic clinical situations for trainees to navigate. These scenarios can range from straightforward cases to complex presentations with multiple complicating factors. By working through these simulated cases, medical professionals can develop their clinical reasoning skills, learn to prioritize information, and make critical decisions under pressure. This type of interactive training helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in real-world clinical settings.
Multidisciplinary Team Training
The management of aortic dissections often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving various medical specialties. Aortic dissection simulators provide an excellent platform for team-based training exercises. Different healthcare professionals, including emergency physicians, radiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, and intensive care specialists, can collaborate on simulated cases. This interdisciplinary approach enhances communication skills, promotes effective teamwork, and helps establish clear roles and responsibilities in the management of aortic dissections.
Performance Assessment and Feedback
Simulation-based training with aortic dissection models offers opportunities for objective performance assessment and constructive feedback. Educators can evaluate trainees' diagnostic accuracy, procedural skills, decision-making processes, and overall management strategies in a standardized manner. This assessment allows for the identification of areas needing improvement and the development of targeted training plans. The ability to provide immediate feedback in a non-threatening environment promotes continuous learning and skill refinement among medical professionals.
Conclusion
Aortic dissection models have revolutionized medical training by providing a realistic, interactive, and risk-free environment for healthcare professionals to hone their skills. These advanced simulators offer numerous benefits, including enhanced anatomical understanding, hands-on experience, and opportunities for scenario-based learning. By incorporating aortic dissection models into medical education programs, institutions can better prepare healthcare providers to diagnose and manage this critical condition effectively. As simulation technology continues to evolve, the role of these models in medical training is likely to expand, further improving patient care and outcomes in the field of vascular medicine.
Contact Us
For cutting-edge aortic dissection models that support comprehensive medical training, look no further than Trandomed. Our advanced 3D printed silicone simulators offer unparalleled realism and versatility, enabling healthcare professionals to enhance their skills and knowledge in a risk-free environment. To learn more about how our innovative products can revolutionize your medical training program, contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
_1734504197376.webp)