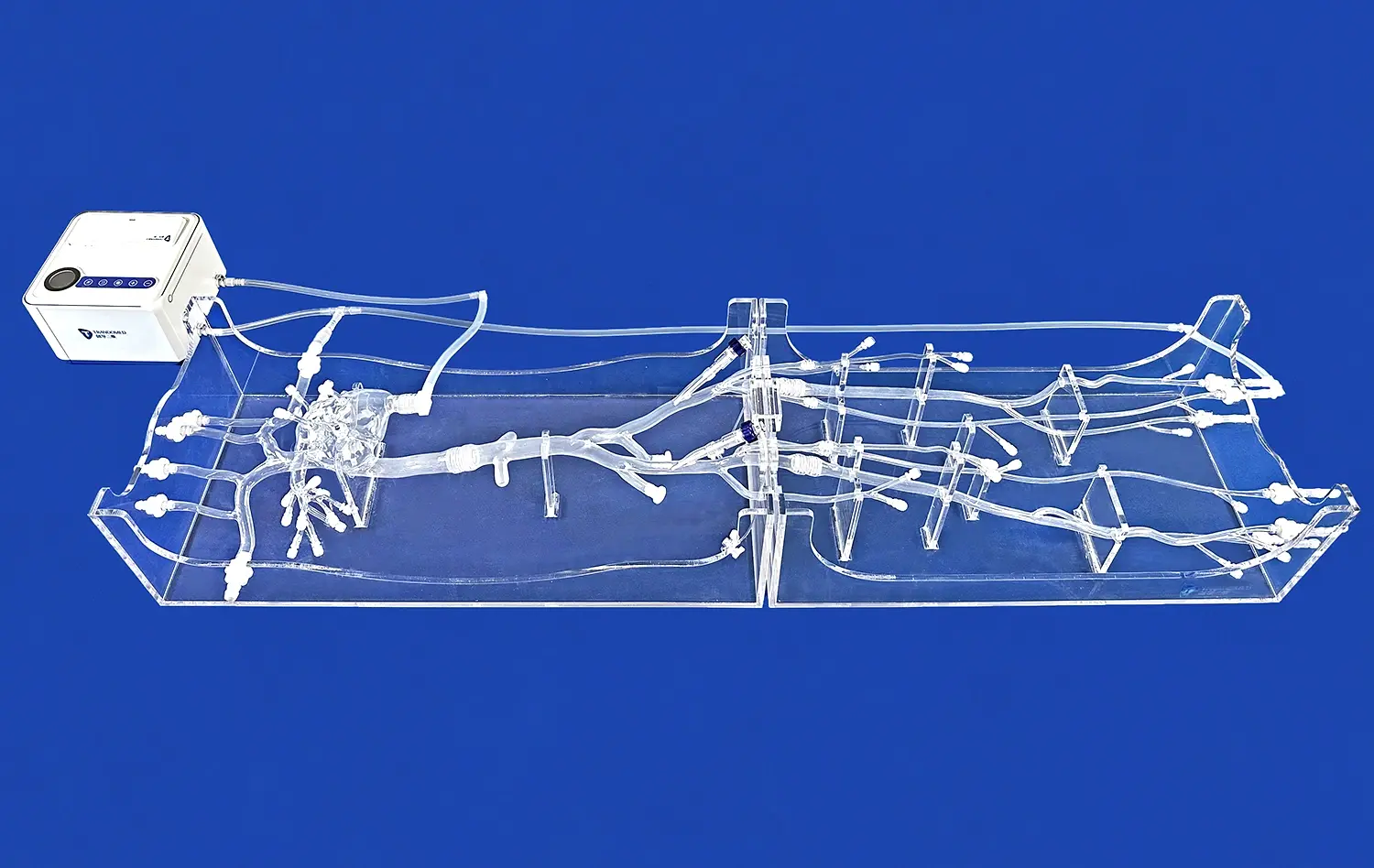
Simulating Critical Hepatic and Renal Procedures Safely
Replicating Complex Vascular Anatomy
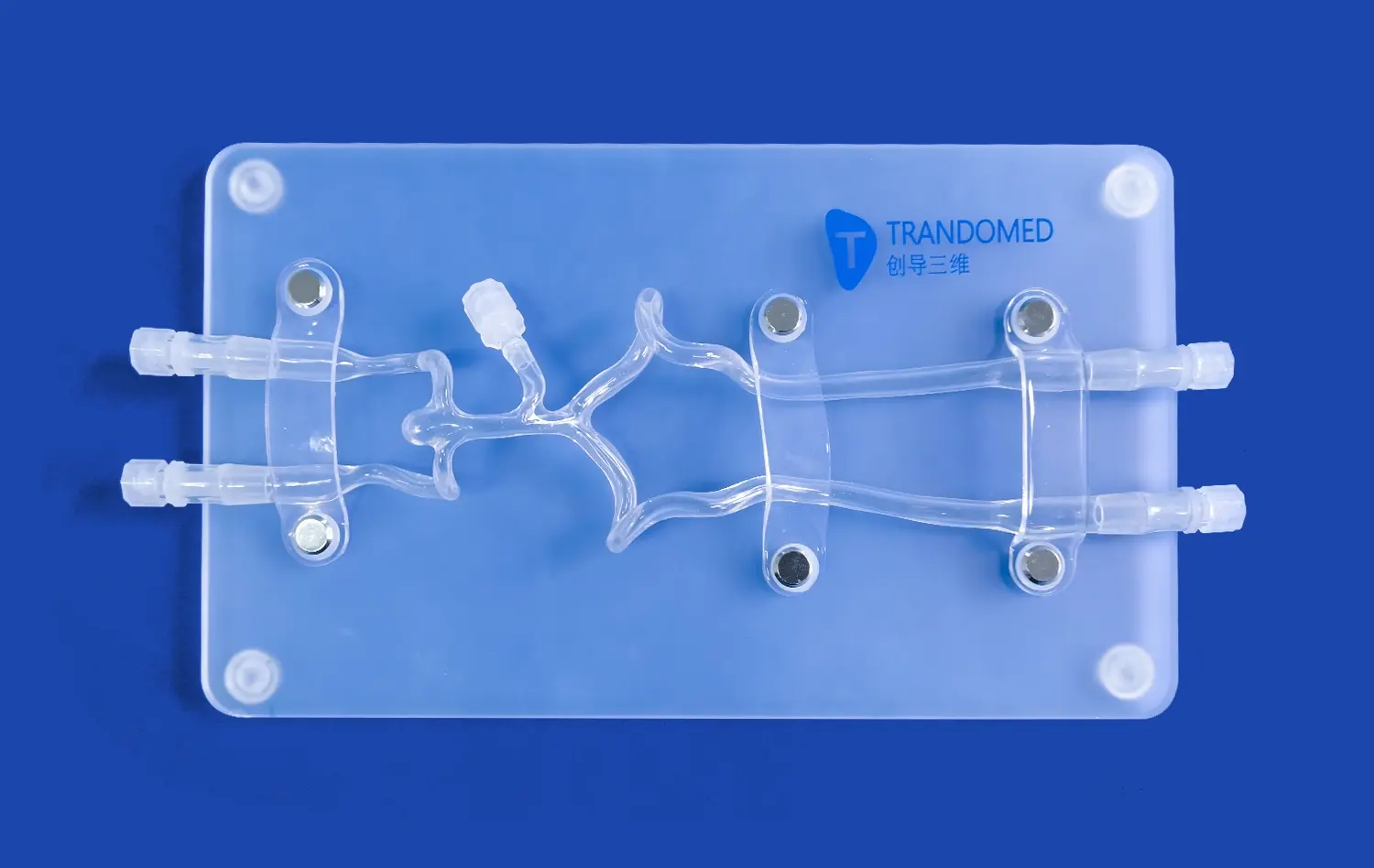
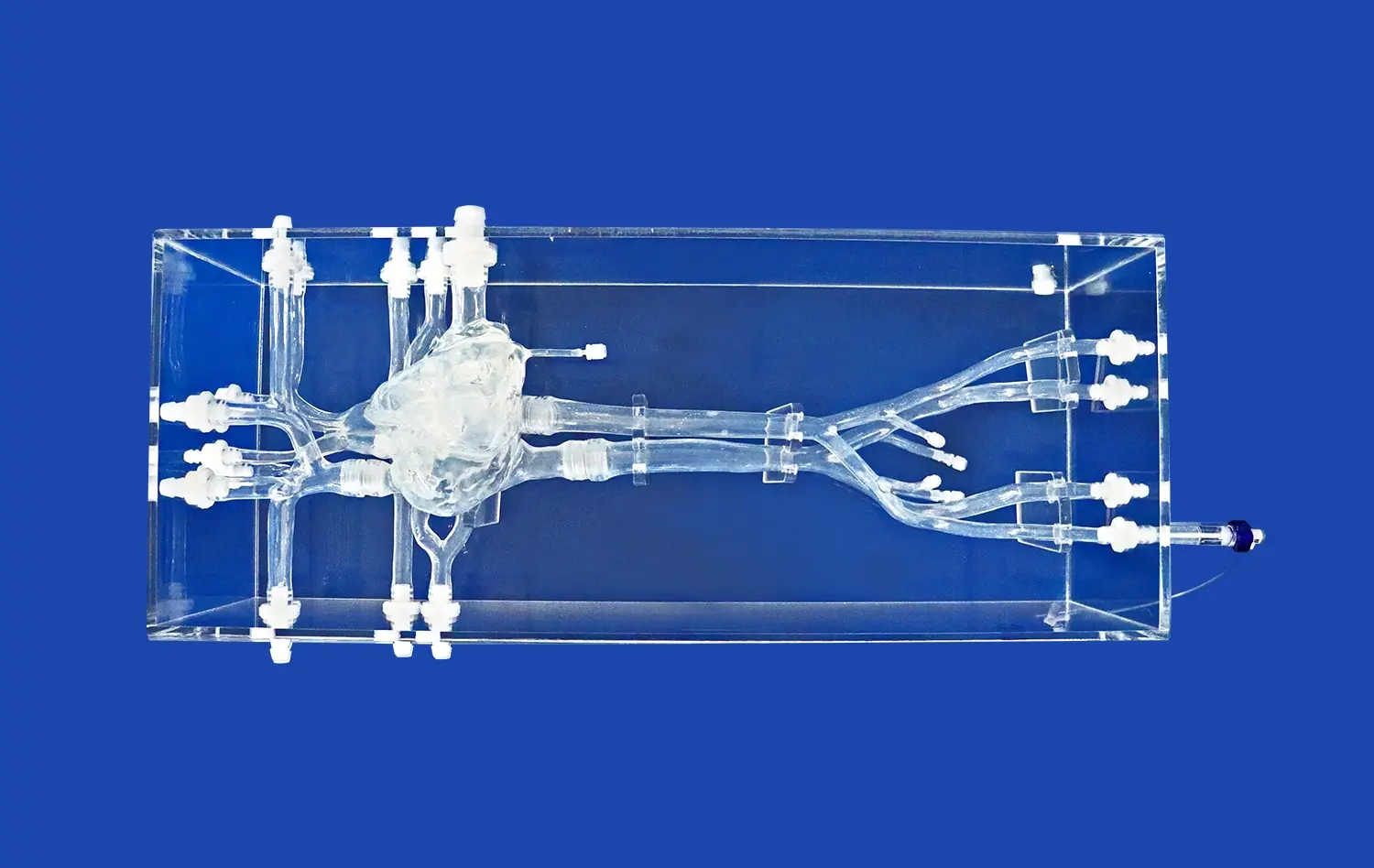
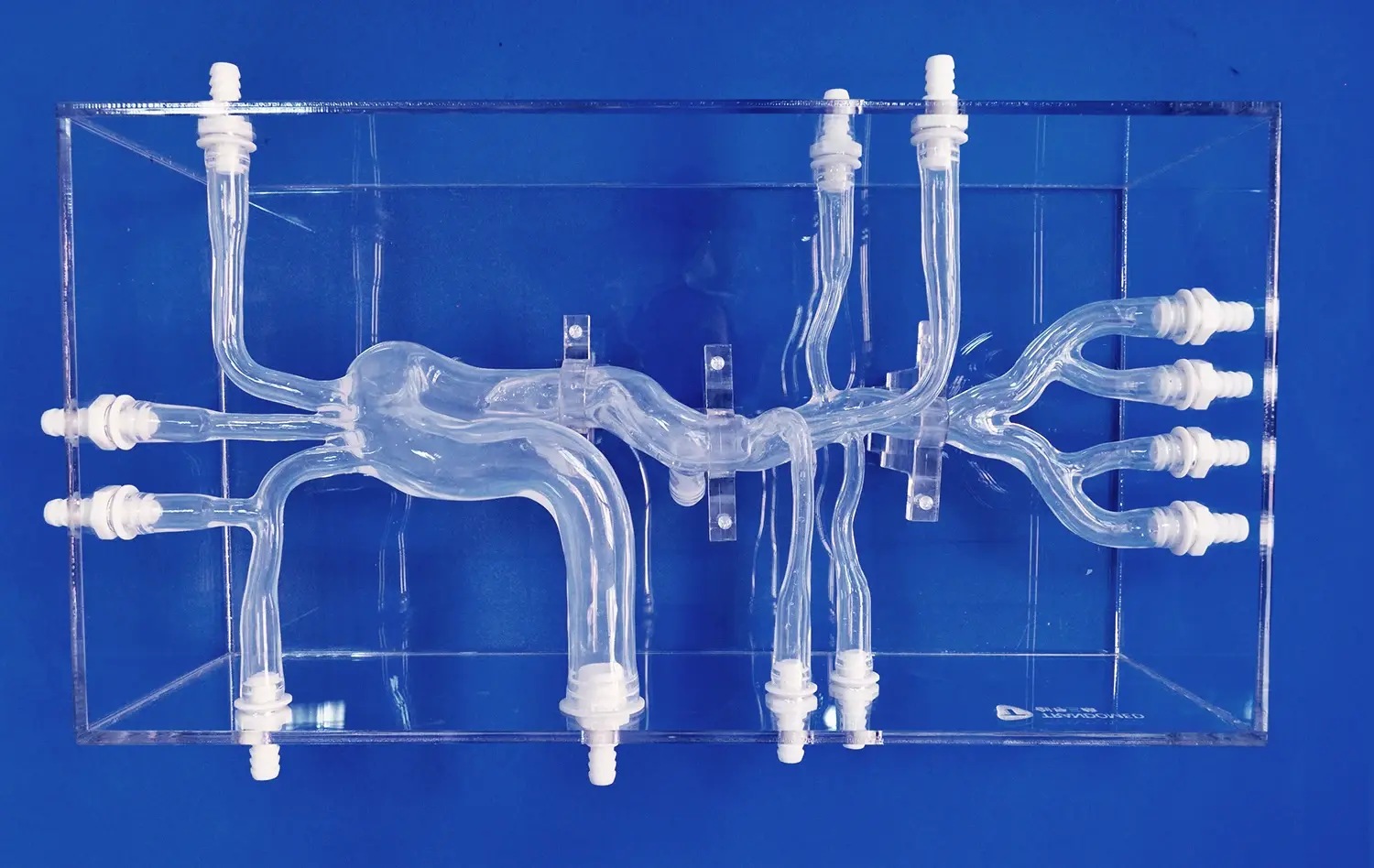
Abdominal vascular models excel in replicating the intricate network of blood vessels in the hepatic and renal regions. These models, crafted with precision using advanced 3D printing technology, capture the nuances of individual patient anatomy. The silicone-based construction, with a Shore 40A hardness, mimics the tactile feel of real tissue, providing a lifelike experience for interventionists. This level of detail is crucial for understanding the spatial relationships between different vessels and surrounding structures, a key factor in successful interventions.
Risk-Free Procedural Practice
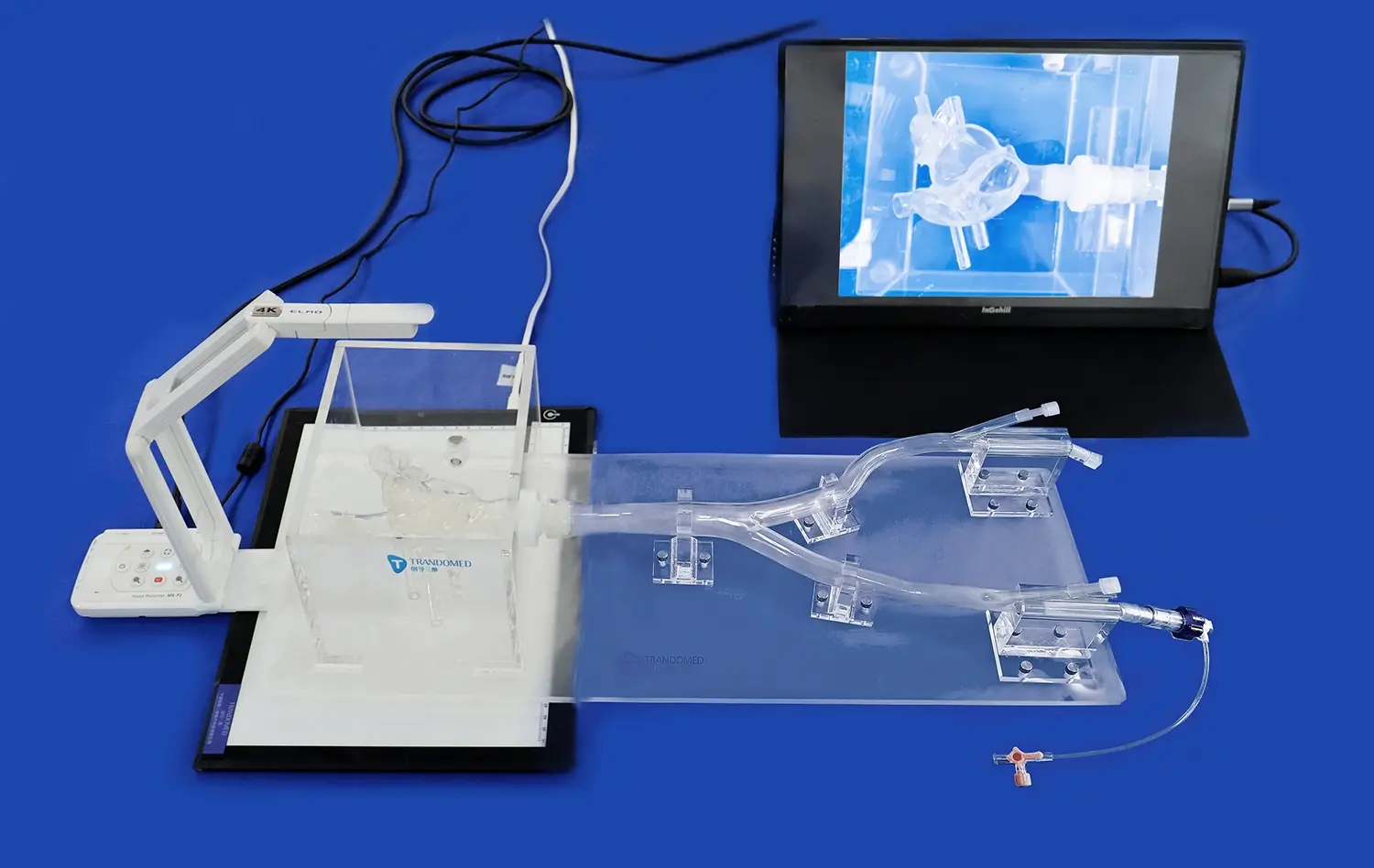
One of the primary advantages of using abdominal vascular model simulators is the ability to practice critical procedures without risking patient safety. Interventionists can repeatedly perform techniques such as catheter navigation, stent placement, and embolization in a controlled setting. This repetitive practice not only refines technical skills but also builds muscle memory, which is invaluable during actual procedures. The models allow for errors and learning from mistakes, a luxury not afforded in real-life situations where the stakes are significantly higher.
Simulating Complications and Rare Scenarios
Abdominal vascular models can be customized to represent various pathological conditions and anatomical variations. This feature enables medical professionals to prepare for rare or complex scenarios they may encounter in clinical practice. By simulating complications like vascular anomalies, stenoses, or aneurysms, these models help interventionists develop problem-solving skills and quick decision-making abilities. This preparation is particularly crucial in hepatic and renal interventions, where unexpected complications can have serious consequences.
Enhancing Clinical Decision-Making Through Vascular Modeling
Pre-Procedural Planning and Strategy Development
Abdominal vascular simulators serve as powerful tools for pre-procedural planning. By creating patient-specific models based on imaging data, interventionists can strategize their approach before entering the operating room. This advanced planning allows for the selection of appropriate instruments, anticipation of potential challenges, and development of tailored intervention strategies. The ability to visualize and interact with a physical representation of the patient's anatomy significantly enhances the interventionist's understanding and confidence in tackling complex cases.
Collaborative Learning and Skill Sharing
These abdominal vascular models foster a collaborative learning environment where experienced practitioners can guide trainees through complex procedures. The transparent design of models like those offered by Trandomed allows for clear visualization of catheter movement and device placement. This transparency facilitates real-time feedback and instruction, accelerating the learning curve for novice interventionists. Furthermore, these models serve as excellent platforms for multidisciplinary team training, improving communication and coordination among different specialists involved in hepatic and renal interventions.
Informed Consent and Patient Education
Abdominal vascular models play a crucial role in patient education and the informed consent process. By using these visual aids, physicians can effectively explain the planned procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes to patients and their families. This tangible representation helps bridge the knowledge gap between medical professionals and patients, leading to better understanding and more informed decision-making. The models can alleviate patient anxiety by demystifying the intervention process and showcasing the precision of modern medical techniques.
Preparing for Complex Interventions with Quantitative Analysis
Advanced Imaging Integration
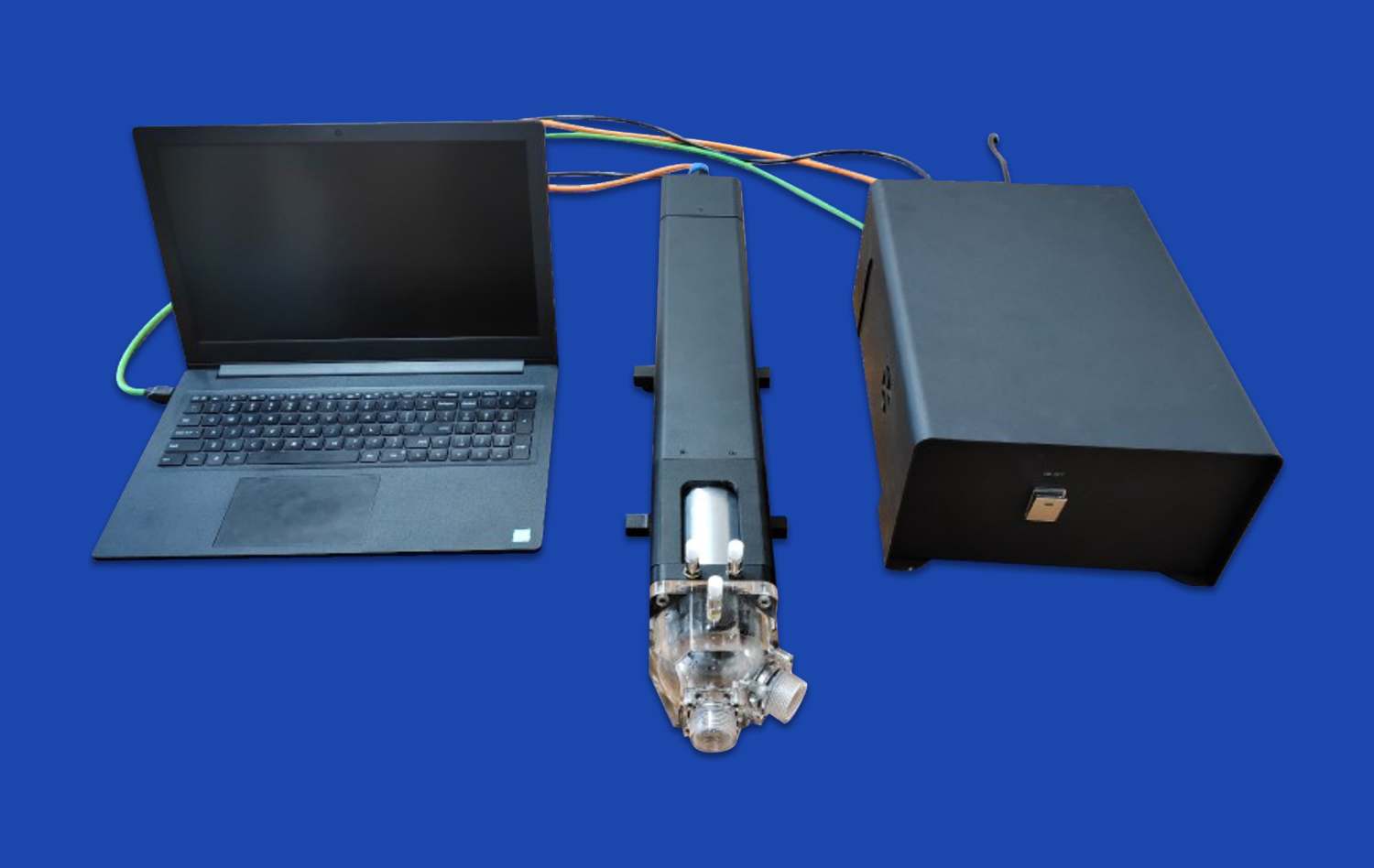
Modern abdominal vascular models integrate seamlessly with advanced imaging techniques such as CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography), DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography), and MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography). This integration allows for comprehensive quantitative analysis of blood flow patterns, vessel dimensions, and pathological features. By combining physical models with digital imaging data, interventionists can gain a more complete understanding of the vascular landscape they will navigate during the procedure. This synergy between physical and digital representations enhances the accuracy of pre-procedural assessments and intervention planning.
Flow Dynamics and Hemodynamic Studies
Abdominal vascular models enable the study of flow dynamics within the hepatic and renal arteries. Using techniques like PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography), researchers and clinicians can analyze blood flow patterns, turbulence, and wall shear stress. These quantitative measurements are crucial for understanding the impact of interventions on blood flow and for predicting potential complications. By simulating various flow conditions, interventionists can optimize their techniques to ensure optimal blood flow restoration in treated vessels.
Device Testing and Optimization
The versatility of abdominal vascular models makes them ideal platforms for testing and optimizing new interventional devices. Manufacturers can use these models to evaluate the performance of catheters, stents, and other vascular devices under various anatomical and physiological conditions. This testing phase is critical for refining device designs and ensuring their efficacy and safety before clinical trials. For interventionists, these models offer the opportunity to familiarize themselves with new technologies and techniques in a controlled environment, thereby facilitating the adoption of innovative approaches in hepatic and renal artery interventions.
Conclusion
Abdominal vascular models have emerged as indispensable tools in supporting hepatic and renal artery interventions. By providing a safe environment for procedural practice, enhancing clinical decision-making, and enabling quantitative analysis, these models significantly contribute to improving interventional outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the integration of more sophisticated materials and imaging techniques will further enhance the realism and utility of these simulators. The continued development and utilization of abdominal vascular models promise to drive innovation in interventional radiology and vascular surgery, ultimately leading to safer procedures and better patient care in hepatic and renal interventions.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are at the forefront of developing cutting-edge abdominal vascular models for medical training and research. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D-printed medical simulators, we offer customizable solutions to meet your specific training needs. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facility ensures precision and quality in every model we produce. Experience the difference that high-fidelity abdominal vascular simulators can make in your interventional training program. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your educational and research objectives.