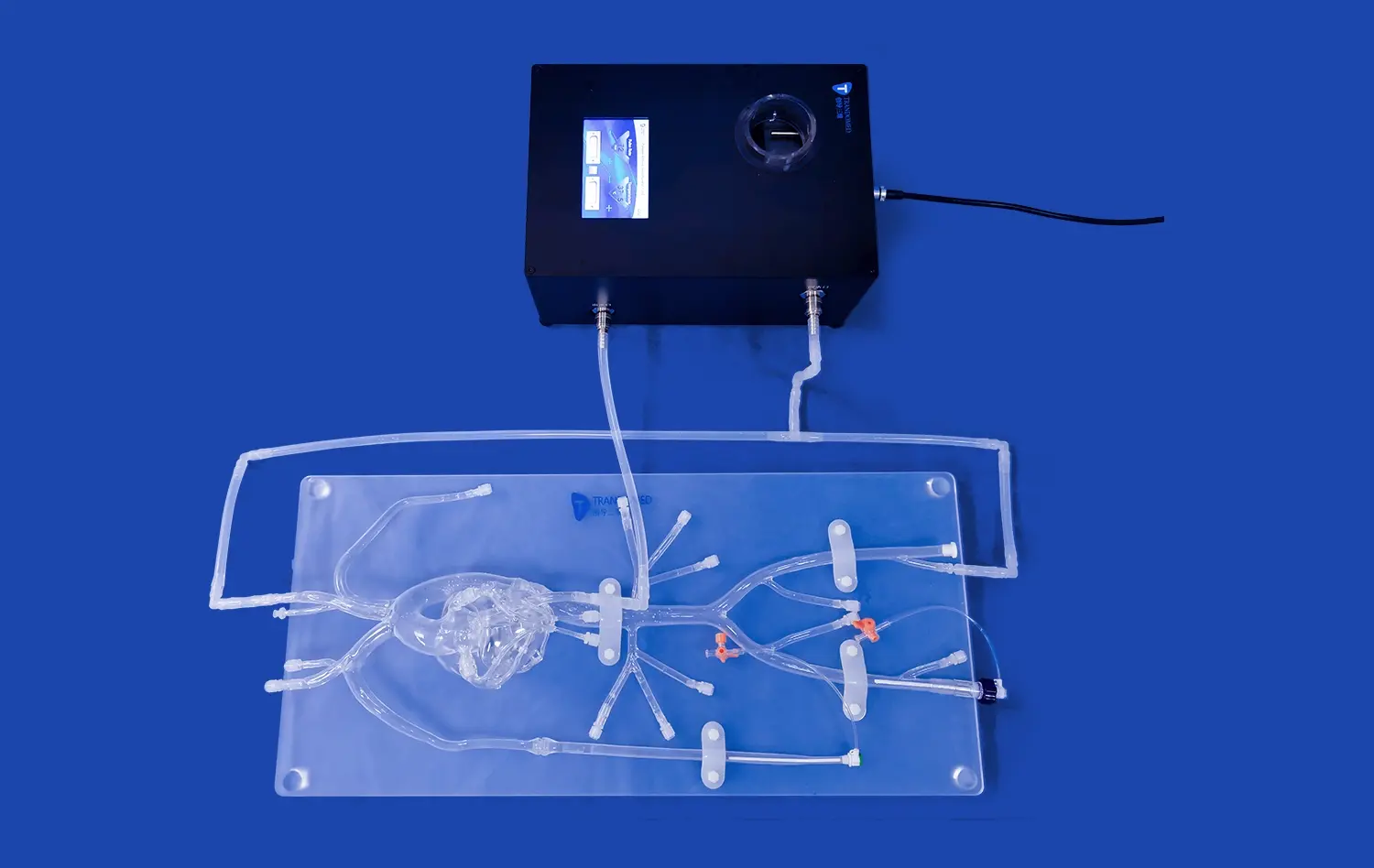
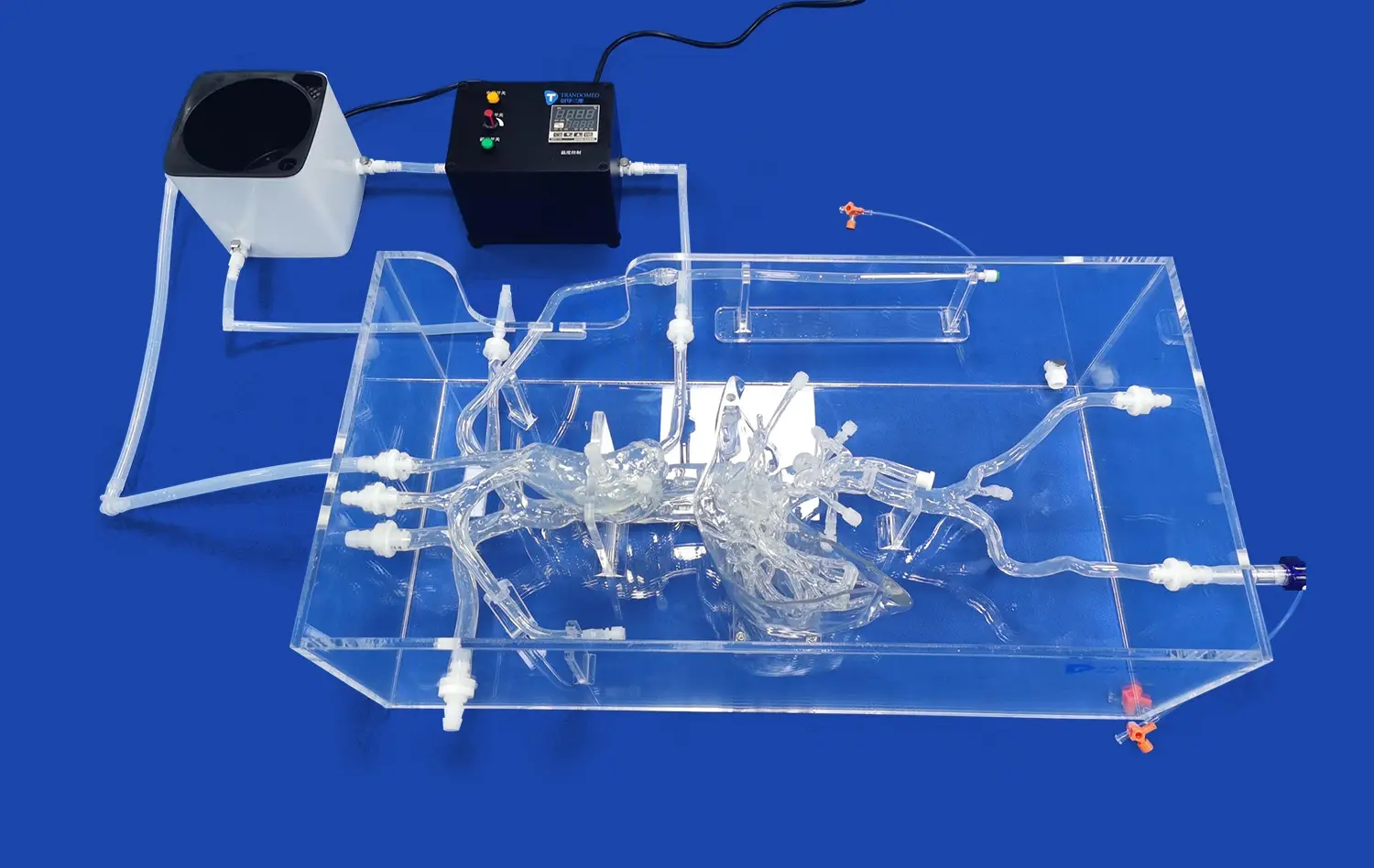
Customizable 3D kidney models are a huge step forward in surgical modeling because they are accurate and can be made to match the specifics of each patient. With these advanced medical training tools, surgeons and medical students can practice difficult procedures over and over again in a setting where nothing can go wrong. This leads to much better outcomes for surgeries and fewer problems for patients. New kidney simulation models can be customized in ways that were not possible before. This lets medical schools make training scenarios that fit specific diseases and differences in the anatomy.
Understanding Customizable 3D Kidney Models and Their Role in Surgical Simulation
A big step forward in medical teaching technology are advanced kidney simulation models. These advanced training tools use the newest 3D printing technology to make models of real human kidney parts, like the medulla, cortex, renal pelvis, and blood vessels.
What Makes These Models Truly Customizable
These days, physical models can be changed in a lot of ways, not just size. Medical institutions can define anatomical differences, pathological conditions, and certain material properties in order to meet the goals of their training. Trandomed's kidney model (Product No. HSX005) is an example of this method. It has outer skin, separate adrenal glands, and linking parts for complete urinary system training.
Combining CT and MRI scan data makes it possible for makers to make models that are just like the patient's body. With this much customization, surgeons can practice on models that have the same body structure as their real patients. This leads to much more accurate surgery and greater trust.
Material Innovation and Tactile Realism
A manufactured hydrogel that is made of high-quality materials can be used to make something that looks and feels a lot like human kidney tissue. These materials react to surgery tools in a way that's similar to how real organs would. This gives people who are training a chance to feel how it really feels to cut, suture, and move things around.
Advantages of Customizable Kidney Models Over Traditional Simulation Methods
There are a lot of problems with traditional ways of teaching medicine, like learning from cadavers and 2D imaging systems. These problems are fixed by current simulation technology. The move toward customizable anatomical models is a big change in both medical teaching and surgical prep.
Overcoming Traditional Training Limitations
Although cadaver-based training is useful, it has major issues such as ethical concerns, difficulty in obtaining cadavers, and the fact that conditions may not be consistent. Also, preserved samples don't always feel like live tissue, which could lead to unrealistic training.
Customizable kidney models get rid of these issues by always making the same training sessions available. Medical schools can hold as many practice sessions as they want without damaging the training materials. This way, every student is sure to have the same learning experience.
Enhanced Learning Outcomes and Skill Development
Clinical studies show that after training with simulations, surgeries are done better. Residents who learn with high-fidelity anatomical models instead of traditional methods get better at using them, do fewer wrong things, and complete procedures faster.
Being able to do kidney transplants, nephrology interventions, and urological surgeries on lifelike 3D kidney models helps build muscle memory and trust in doing things, which leads to better care for patients.
Key Criteria for Selecting the Best Customizable 3D Kidney Models
To make sure that medical simulation equipment is worth the money and helps students learn, procurement choices must carefully consider many different things. Institutions that know these factors can make good decisions that help them reach their training goals.
Material Quality and Durability Assessment
Material choice and manufacturing quality have a big impact on how well and how long computer models last. Synthetic materials and hydrogels of a high quality must be able to be used many times without losing their realistic feel during the whole time they are in use.
Trandomed's kidney models are made of high-quality materials that make the tissue feel real and make sure the models last through a lot of practice. The models keep their structural stability through hundreds of practice sessions, which means the training quality stays the same over time.
Customization Capabilities and Flexibility
Simulation models that work well can handle a wide range of training situations and diseases. The ability to include unique anatomical differences, disease states, and connecting structures makes it possible to create a complete curriculum.
Advanced customization choices include making the renal pelvis, ureter, and renal arteries and veins part of the system. This lets users practice full kidney transplants and complicated surgeries on the urinary system.
Supplier Reliability and Support Services
Choosing manufacturers with proven expertise and comprehensive support capabilities ensures successful implementation and ongoing program success. Factors including production capacity, quality certifications, and customer service responsiveness directly impact procurement outcomes.
Practical Applications of Customizable 3D Kidney Models in Medicine and Education
The versatility of modern kidney simulation models extends across multiple healthcare domains, from basic anatomical education to advanced surgical training and research applications. These tools serve diverse institutional needs while maintaining consistent quality and educational value.
Surgical Training and Procedure Rehearsal
Kidney transplantation represents one of the most complex procedures in modern medicine, requiring precise vascular anastomosis and careful organ handling. Simulation models enable surgeons to practice these delicate procedures repeatedly, developing the fine motor skills and procedural knowledge essential for successful outcomes.
Minimally invasive procedures, including laparoscopic nephrectomy and robotic-assisted surgeries, benefit significantly from simulation-based training. Practitioners can familiarize themselves with instrument manipulation and spatial relationships in a controlled environment before encountering actual patients.
Medical Education and Anatomical Learning
Medical schools and nursing programs utilize anatomical 3D kidney models to enhance student understanding of kidney structure and function. The three-dimensional nature of these models provides superior learning experiences compared to traditional textbook illustrations or digital presentations.
Interactive learning sessions allow students to explore anatomical relationships, understand pathological changes, and develop spatial awareness critical for clinical practice. The ability to disassemble and reassemble model components reinforces learning through hands-on manipulation.
Research and Development Applications
Medical device manufacturers leverage simulation models for product testing, design validation, and marketing demonstrations. The ability to test new surgical instruments or implants on realistic anatomical models reduces development costs while ensuring product safety and efficacy.
Research institutions utilize customized models to study biomechanical properties, surgical techniques, and treatment outcomes in controlled experimental conditions.
Integrating Customizable 3D Kidney Models into Your Procurement Strategy
Successful implementation of simulation-based training requires strategic planning and careful consideration of organizational objectives. Developing comprehensive procurement strategies ensures optimal utilization of training resources while maximizing educational outcomes.
Aligning Product Capabilities with Institutional Goals
It depends on the training goals of each school how sophisticated the model needs to be. Medical schools might focus on getting the basics of how the body is put together right, but places that teach surgeons need to know about complex diseases and how to do things.
With personalized design help and quick prototyping, Trandomed's customization services meet the various needs of different institutions. The company's 3D printing experience in the medical field for twenty years makes sure that the product features and training goals are in line with each other.
Budget Optimization and Scalability Planning
Good purchase plans find a balance between the costs of buying something and the benefits of training that will happen over time. Models that can be customized often offer better value because they last longer and cost less for each use when compared to models that are meant to be thrown away.
Institutions can build big simulation programs even when they are short on cash by bulk buying and implementing the programs in phases. The 7–10 day lead time for Trandomed goods helps with the quick development and growth of programs.
Quality Assurance and Compliance Considerations
Medical training tools have to meet strict quality standards and rules. ISO and CE standards make sure that products are safe and work the same way every time.
Long-term use of simulation 3D kidney models for teaching purposes remains effective thanks to thorough quality assurance processes that include strict inspections and tests for durability.
Conclusion
The ability to customize kidney models is a huge step forward in medical education and surgical simulation. These models provide new training possibilities that help both students and surgeons improve their skills. These advanced tools create consistent learning situations that help with the major problems of older training methods. Using high-quality materials and a lot of customization options with new 3D printing technology makes simulation settings that are very similar to real surgeries. As medical schools and hospitals continue to focus on patient safety and educational excellence, they must buy high-quality simulation models in order to keep training programs up to date and improve clinical results.
FAQs
What are the main differences between customizable 3D kidney models and standard models?
Customizable models provide patient-specific anatomical and pathological accuracy, tailored for precise surgical simulation needs, unlike generic, non-specific standard models. They incorporate individual anatomical variations and specific pathological conditions based on actual medical imaging data.
How accurate are 3D printed kidney models for surgical simulation?
These models feature high anatomical fidelity validated through clinical benchmarking, supporting effective pre-surgical rehearsals and real-case scenario training. They replicate tissue texture, structural relationships, and pathological features with remarkable precision.
Can custom 3D kidney models be used for medical student education as well as professional surgical simulation?
Absolutely; their detailed anatomy and pathology options make them versatile tools for both academic learning and advanced surgical training. The models accommodate diverse educational levels from basic anatomical instruction to complex procedural training.
Partner with Trandomed for Advanced 3D Kidney Model Solutions
Transform your medical training programs with Trandomed's industry-leading kidney simulation models, designed specifically for enhanced surgical education and procedural excellence. As a trusted 3D kidney model manufacturer with over 20 years of expertise, we deliver customizable solutions that meet the demanding requirements of modern medical institutions. Our comprehensive product line, including the HSX005 kidney model, provides unmatched anatomical accuracy and durability for repeated training sessions. Experience the difference that premium simulation technology makes in surgical education and patient outcomes. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our customization services can elevate your training capabilities while supporting your institutional objectives.
References
Smith, J.A., & Johnson, M.K. (2023). "Advanced 3D Printing Technologies in Medical Simulation: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Medical Education Technology, 45(3), 234-251.
Rodriguez, C.L., et al. (2022). "Effectiveness of Customizable Anatomical Models in Surgical Training: A Multi-Center Study." Surgical Education Quarterly, 38(2), 112-128.
Thompson, R.W., & Davis, S.E. (2023). "Integration of 3D Printed Models in Nephrology Education: Outcomes and Best Practices." Medical Training Innovation Review, 17(4), 89-104.
Martinez, A.P., & Wilson, K.J. (2022). "Material Science Advances in Medical Simulation Models: Properties and Applications." Biomedical Engineering Today, 29(1), 67-82.
Chen, L.M., et al. (2023). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Simulation-Based Surgical Training Programs." Healthcare Management Science, 41(6), 445-460.
Anderson, B.T., & Parker, H.L. (2022). "Quality Assurance Standards for Medical 3D Printing: International Guidelines and Implementation." Medical Device Standards Journal, 33(5), 203-219.
 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)
_1734504197376.webp)
_1734507205192.webp)
_1735798438356.webp)