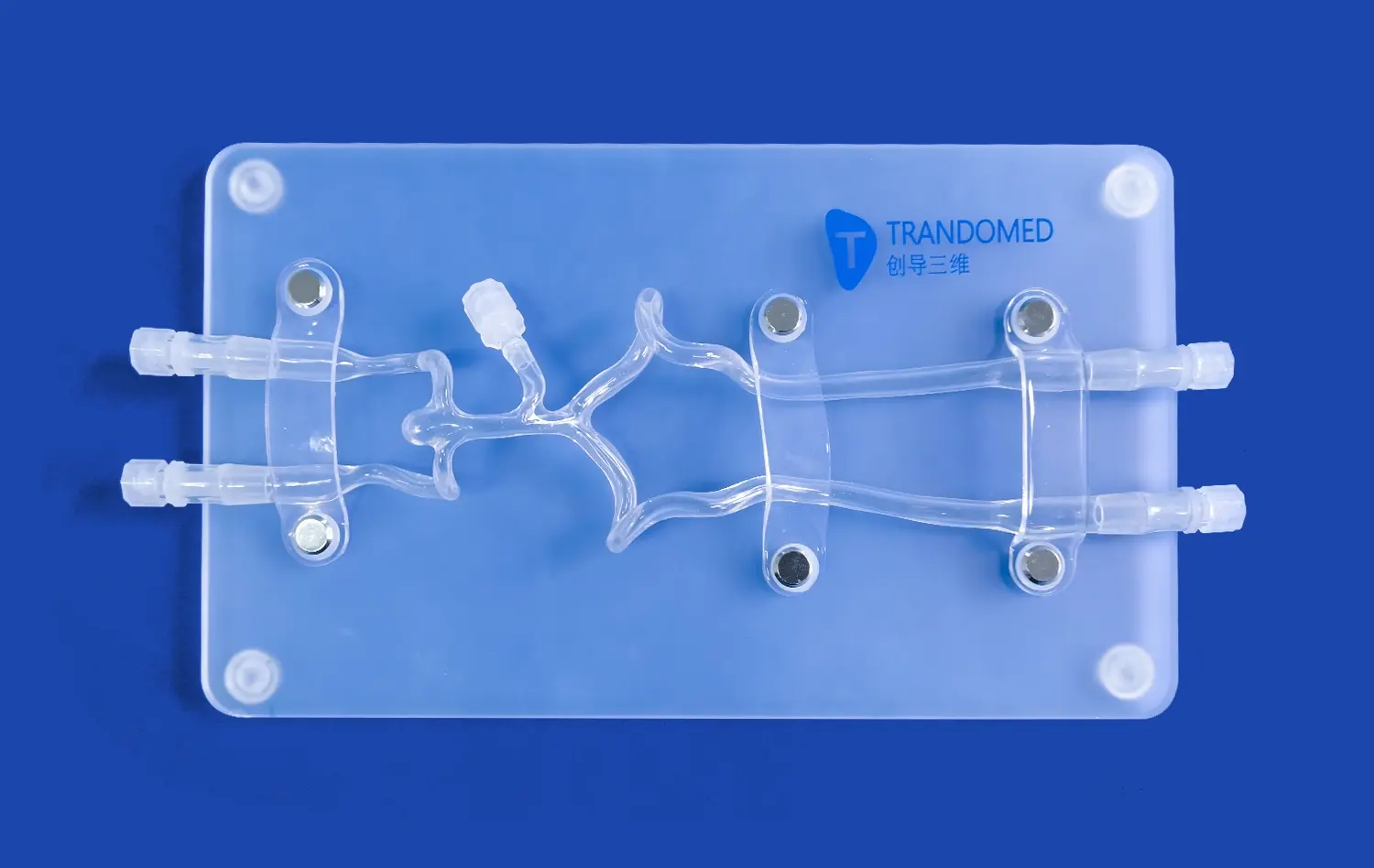
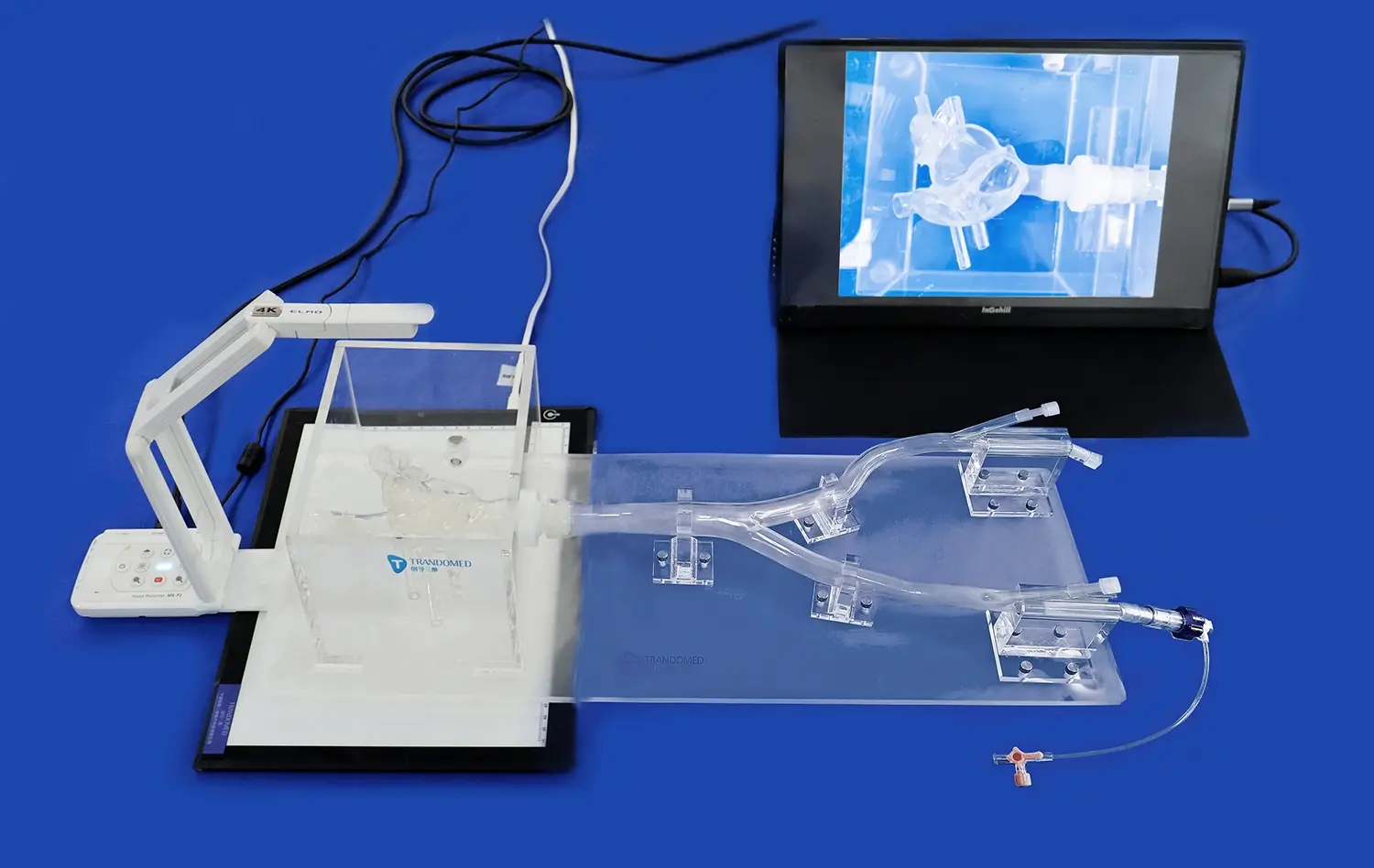
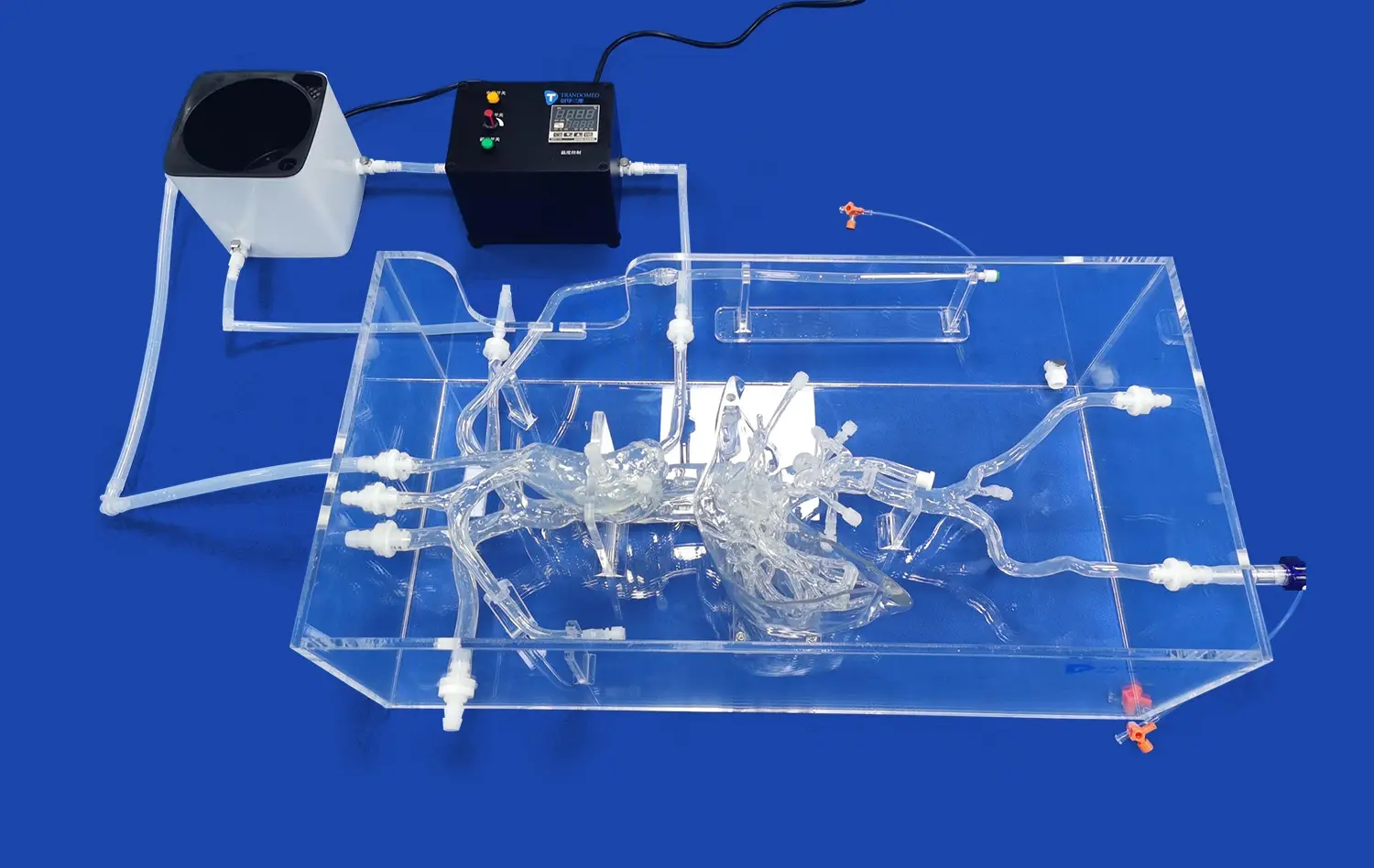
What Are the Advantages of Using Vascular Models in CTA and DSA Imaging
Enhanced Visualization of Complex Vascular Anatomy
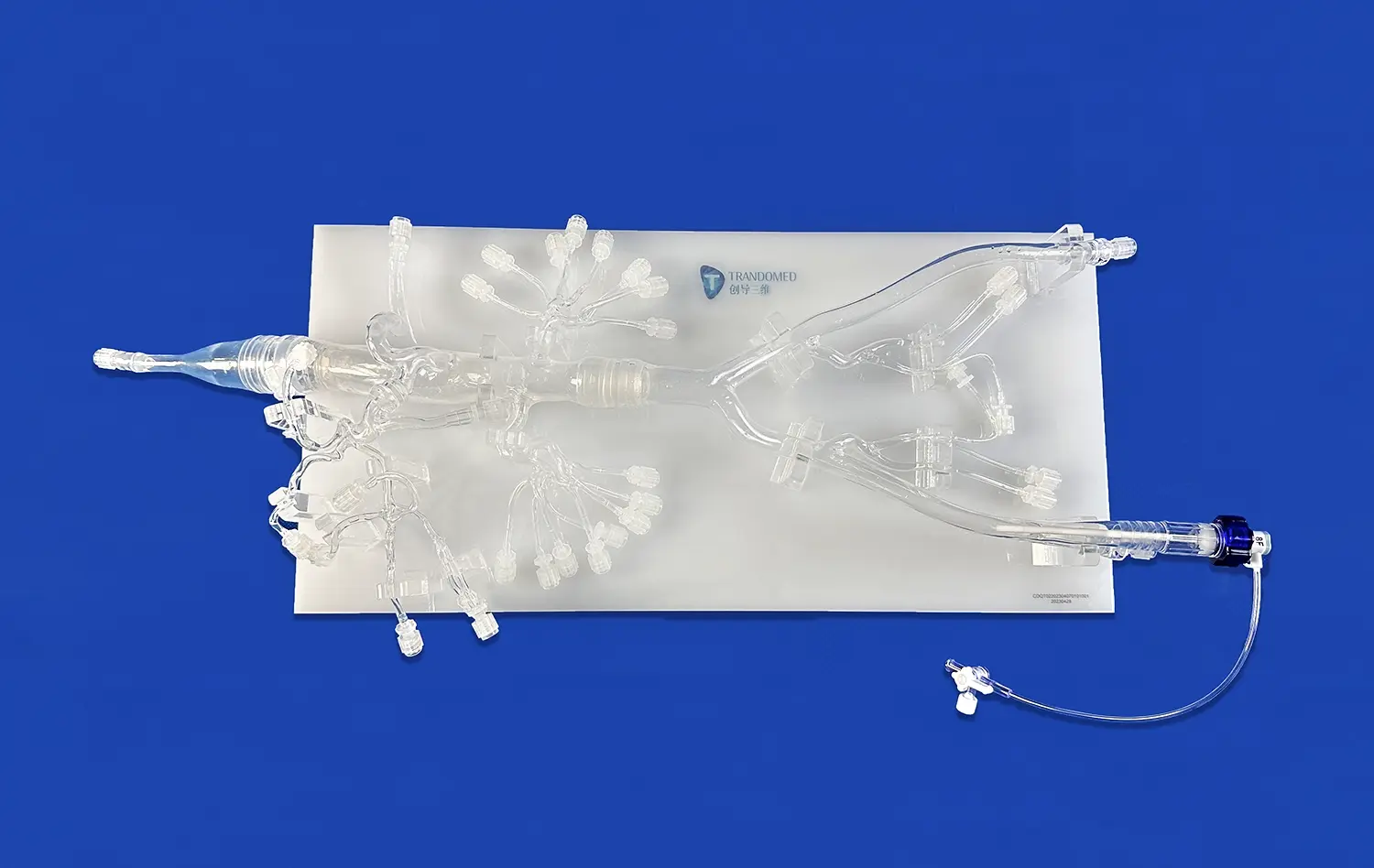
Abdominal vascular models offer unparalleled visualization of intricate blood vessel networks. Unlike traditional 2D imaging, these 3D-printed replicas allow clinicians to examine the spatial relationships between vessels from multiple angles. This enhanced perspective is particularly valuable when dealing with complex anatomical variations or pathological conditions. By integrating CTA and DSA data with physical models, healthcare professionals can better understand the nuances of each patient's unique vascular architecture, leading to more informed decision-making in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Improved Pre-procedural Planning and Risk Assessment
The use of Abdominal vascular models in conjunction with CTA and DSA imaging significantly enhances pre-procedural planning. Surgeons and interventional radiologists can use these models to simulate various approaches, identifying potential challenges and optimizing their strategies before performing actual procedures. This capability is especially crucial in complex cases, such as those involving aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations. By allowing practitioners to rehearse interventions on patient-specific models, the risk of complications during actual procedures is substantially reduced, leading to improved patient safety and outcomes.
Enhanced Education and Training for Medical Professionals
Abdominal vascular models serve as invaluable educational tools for medical students, residents, and practicing clinicians. When combined with CTA and DSA imaging data, these models provide a comprehensive learning experience that bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Trainees can study normal and pathological vascular anatomy in a hands-on manner, gaining a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and flow dynamics. This integration of physical models with advanced imaging techniques accelerates the learning curve for complex vascular interventions, ultimately improving the quality of care provided to patients.
Simulating Realistic Hemodynamics for Accurate Flow Assessment
Replicating Physiological Blood Flow Patterns
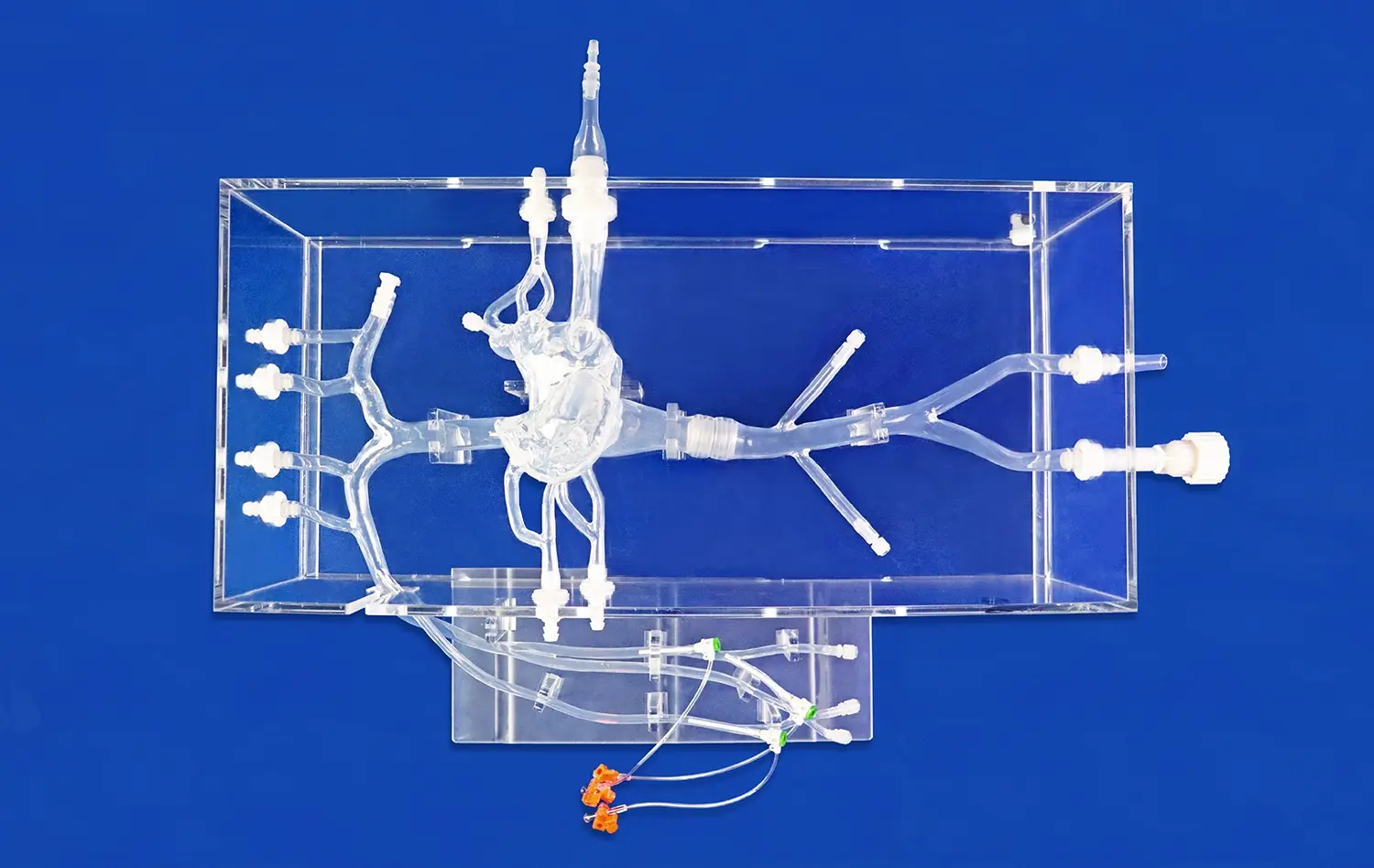
Advanced abdominal vascular models, such as those produced by Trandomed, are designed to replicate physiological blood flow patterns with high fidelity. These models incorporate precise vessel geometries and material properties that mimic the elasticity of actual blood vessels. When used in conjunction with CTA and DSA imaging, these models allow researchers and clinicians to observe and analyze flow dynamics under various conditions. By simulating pulsatile flow and pressure gradients, these models provide insights into how blood behaves in different segments of the abdominal vasculature, including the aorta, renal arteries, and hepatic vessels.
Studying the Impact of Vascular Pathologies on Blood Flow
Abdominal vascular models excel in simulating the effects of various pathologies on blood flow. Conditions such as stenosis, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations can be accurately represented in these models. When combined with CTA and DSA imaging, clinicians can visualize how these abnormalities alter flow patterns and affect downstream perfusion. This capability is particularly valuable in assessing the hemodynamic significance of vascular lesions and predicting the potential outcomes of interventional procedures. By providing a controlled environment for studying these pathologies, vascular models enhance our understanding of disease progression and treatment efficacy.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Vascular Interventions
The integration of abdominal vascular models with CTA and DSA imaging offers a powerful platform for evaluating the effectiveness of various interventional techniques. Clinicians can use these models to simulate procedures such as stent placement, embolization, or bypass grafting. By comparing pre- and post-intervention flow patterns, healthcare professionals can assess the immediate impact of these treatments on blood flow dynamics. This approach allows for the optimization of interventional strategies and helps predict long-term outcomes, ultimately leading to more personalized and effective patient care in vascular medicine.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy Through Quantitative Analysis
Enhancing CTA and DSA Data Interpretation
Abdominal vascular models significantly enhance the interpretation of CTA and DSA imaging data. By providing a physical reference that corresponds to the digital images, these models help clinicians correlate radiographic findings with tangible anatomical structures. This synergy between physical models and imaging data improves the accuracy of diagnoses, particularly in cases where complex vascular anomalies are present. The ability to manipulate and examine the model while reviewing CTA and DSA images allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the patient's vascular anatomy, leading to more precise and confident diagnostic assessments.
Facilitating Quantitative Flow Measurements
The use of abdominal vascular models in conjunction with CTA and DSA enables more accurate quantitative flow measurements. These models can be designed with specific ports or access points that allow for the insertion of flow sensors or pressure transducers. By correlating these direct measurements with imaging data, researchers and clinicians can validate and refine their analysis of blood flow dynamics. This quantitative approach is particularly valuable in assessing the severity of stenoses, evaluating the efficiency of collateral circulation, and determining the need for intervention in cases of compromised blood flow.
Improving Detection and Characterization of Vascular Abnormalities
Abdominal vascular models enhance the detection and characterization of subtle vascular abnormalities that may be challenging to identify through imaging alone. By providing a three-dimensional reference, these models help clinicians spot irregularities in vessel contours, branching patterns, or flow dynamics that might otherwise be overlooked. When used alongside CTA and DSA, these models facilitate a more thorough examination of potential pathologies, such as small aneurysms, early-stage atherosclerotic plaques, or vascular malformations. This improved detection capability leads to earlier diagnosis and intervention, potentially preventing more serious complications and improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Abdominal vascular models have emerged as indispensable tools in enhancing blood flow analysis when used in conjunction with CTA and DSA imaging techniques. These advanced 3D-printed simulators offer unparalleled advantages in visualizing complex vascular anatomy, simulating realistic hemodynamics, and improving diagnostic accuracy through quantitative analysis. By bridging the gap between digital imaging and physical representation, these models enable healthcare professionals to gain deeper insights into vascular pathologies, optimize treatment strategies, and ultimately provide better patient care. As technology continues to advance, the integration of abdominal vascular models with cutting-edge imaging modalities will undoubtedly play an increasingly crucial role in the field of vascular medicine.
Contact Us
Experience the future of vascular education and research with Trandomed's state-of-the-art abdominal vascular models. As a leading 3D-printed medical simulators manufacturer and supplier, we offer custom solutions tailored to your specific needs. Enhance your diagnostic capabilities, improve surgical planning, and elevate your training programs with our high-fidelity vascular models. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn how our innovative products can revolutionize your approach to vascular medicine.
_1734507205192.webp)