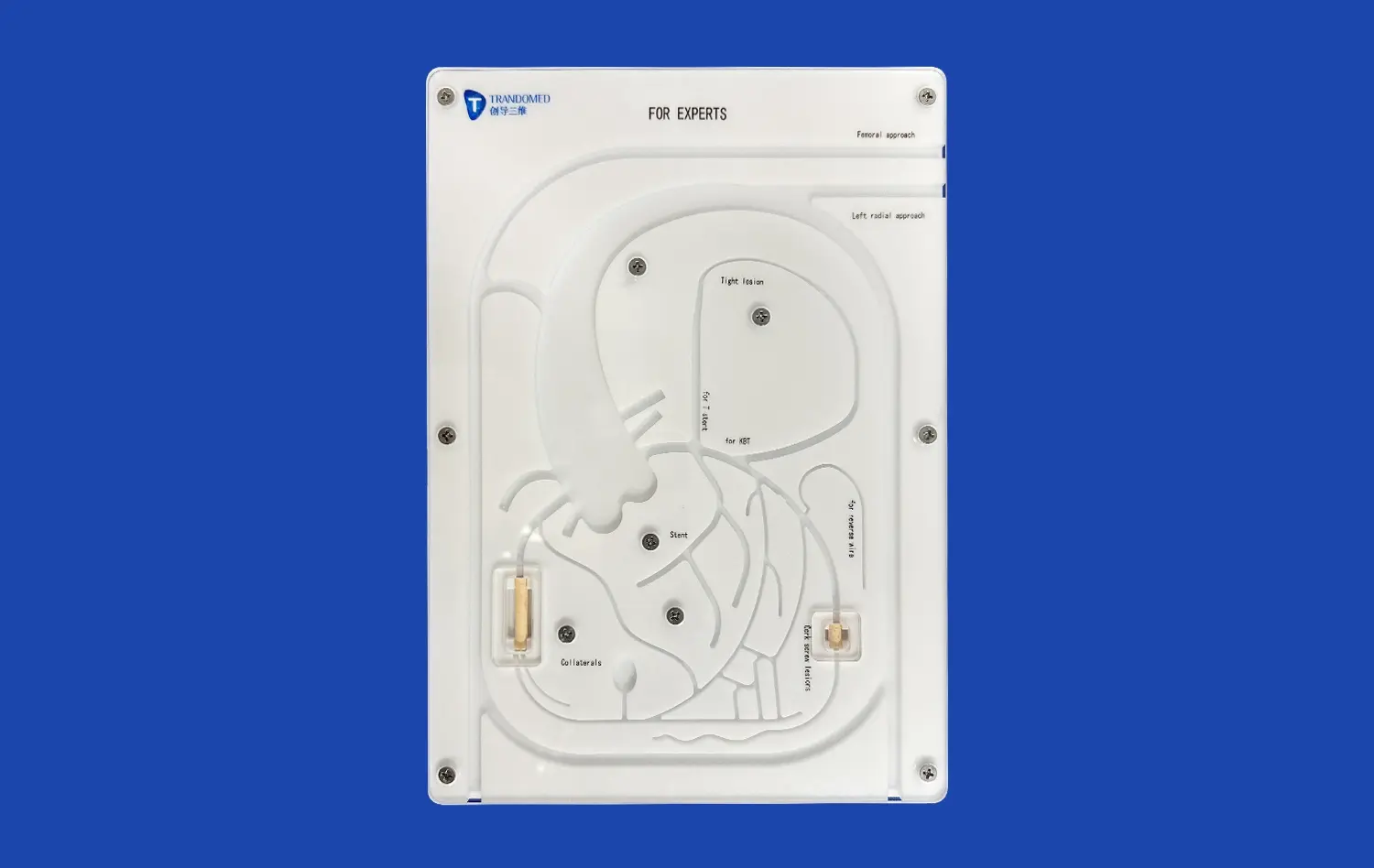
What Are the Common Surgical Risks Addressed by Mitral Valve Models?
Anatomical Complexity and Variability
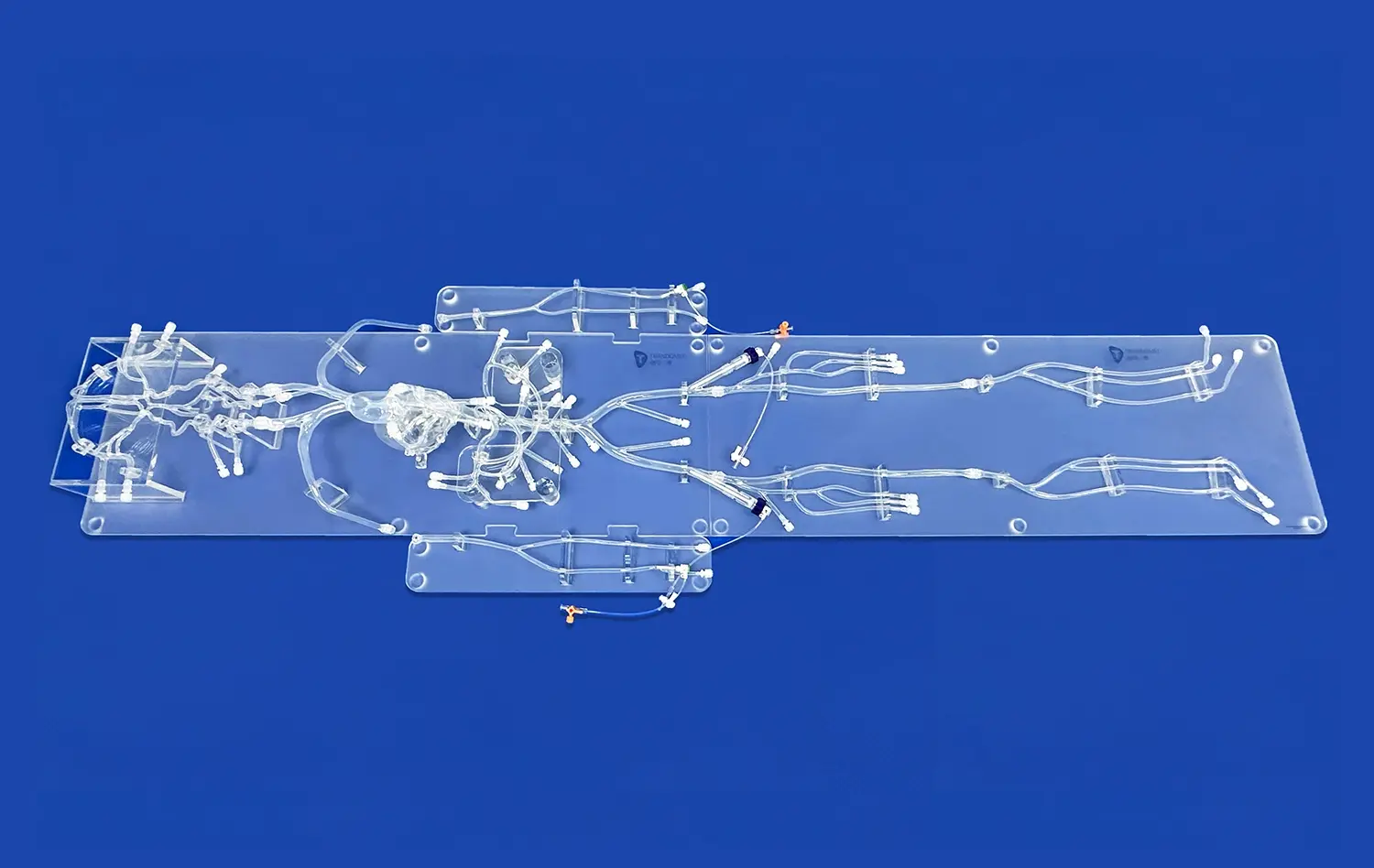
The mitral valve's highly intricate anatomical structure, characterized by its dynamic interplay of multiple components, presents considerable surgical challenges. Mitral valve models, such as the XXD006 from Trandomed, meticulously replicate the valve's true anatomy. This includes precise representations of its five essential elements: the annulus, leaflets, chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, and the adjacent left ventricular wall. Consequently, this detailed simulation provides surgeons with an invaluable opportunity to become thoroughly acquainted with the wide spectrum of anatomical variations and potential pathological anomalies they are likely to encounter during complex real-world surgical interventions, enhancing preoperative preparedness.
Procedural Complications
Mitral valve surgery inherently carries significant risks, including intraoperative or postoperative bleeding, infection, and inadvertent damage to vital surrounding cardiac structures. Utilizing mitral valve models allows surgeons to rigorously practice and refine specific techniques explicitly designed to minimize these complications. For example, by working with the mitral valve model, surgeons can repeatedly practice and perfect critical suturing methods. This focused rehearsal directly contributes to reducing the likelihood of dangerous post-operative complications like paravalvular leaks or catastrophic valve dehiscence in actual patients.
Technical Skill Development
The inherent complexity of mitral valve repair and replacement procedures demands an exceptionally high level of technical dexterity and procedural mastery from surgeons. Mitral valve models serve as an essential, risk-free training platform, enabling surgeons to systematically develop and hone their proficiency in a variety of complex techniques. These include precise leaflet resection, accurate chordal replacement, and secure annuloplasty ring placement. This dedicated practice significantly shortens the learning curve associated with adopting new surgical methods and crucially minimizes the potential for technical errors during high-stakes live operations, thereby improving patient safety.
Risk Mitigation Strategies Using Realistic Valve Simulations
Pre-operative Planning and Rehearsal
Realistic mitral valve models, such as those offered by Trandomed, allow surgical teams to plan and rehearse complex procedures before entering the operating room. By simulating the specific patient's anatomy using customized models based on CT or MRI data, surgeons can anticipate challenges and develop tailored strategies. This approach significantly reduces intraoperative decision-making time and improves overall surgical efficiency.
Team Communication and Coordination
Effective communication among surgical team members is crucial for successful outcomes. Mitral valve models serve as excellent tools for team-based training, allowing surgeons, anesthesiologists, and support staff to practice their roles and improve coordination. This collaborative approach enhances situational awareness and reduces the risk of miscommunication-related errors during actual procedures.
Complication Management Training
Mitral valve models can be designed to simulate various pathological conditions and potential complications. For example, the XXD006 model can be customized to represent different degrees of valve stenosis or regurgitation. This feature allows surgeons to practice managing unexpected situations and complications, improving their ability to handle emergencies during live surgeries and potentially reducing patient morbidity and mortality.
Improving Patient Outcomes Through Pre-Surgical Model Training
Enhanced Surgical Precision
Regular practice with high-fidelity mitral valve models leads to improved surgical precision. The tactile feedback provided by mitral valve model helps surgeons develop a better sense of tissue handling and suture placement. This enhanced precision translates to more successful repairs, reduced cross-clamp times, and potentially shorter hospital stays for patients.
Reduced Learning Curve for New Techniques
As cardiac surgery techniques continue to evolve, mitral valve models play a crucial role in helping surgeons adapt to new approaches. For instance, when learning transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) techniques, surgeons can use models that simulate the entire pathway from the femoral vein to the heart. This comprehensive training reduces the learning curve associated with adopting new procedures, ultimately benefiting patients by providing access to cutting-edge treatments with lower risk.
Personalized Treatment Planning
Advanced mitral valve models, such as those customizable by Trandomed, allow for patient-specific simulations. By creating models based on individual patient imaging data, surgical teams can develop tailored treatment plans. This personalized approach enables surgeons to anticipate challenges unique to each patient's anatomy, leading to more successful outcomes and potentially reducing the need for reoperation.
Conclusion
Mitral valve models have revolutionized surgical training and preparation, significantly reducing the risks associated with complex cardiac procedures. By providing realistic simulations for anatomical study, technique refinement, and team coordination, these models contribute to enhanced surgical precision and improved patient outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the integration of high-fidelity mitral valve models in surgical education and pre-operative planning will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in elevating the standard of care in cardiac surgery.
Contact Us
For more information on how Trandomed's advanced mitral valve models can enhance your surgical training program and improve patient outcomes, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our expert team is ready to discuss customized solutions tailored to your specific needs, helping you stay at the forefront of cardiac surgical innovation.
_1734504197376.webp)
_1734507205192.webp)
_1732866687283.webp)
_1732863713705.webp)









