What Safety Risks Can Models Help Mitigate During Training?
Reducing Procedural Complications
Pulmonary artery models serve as invaluable tools in mitigating various safety risks associated with interventional procedures. By providing a realistic simulation of the pulmonary vasculature, these models allow healthcare professionals to practice navigation techniques, catheter manipulation, and device deployment in a risk-free environment. This hands-on experience helps reduce the likelihood of procedural complications such as vessel perforation, dissection, or embolization during actual interventions.
Enhancing Spatial Awareness
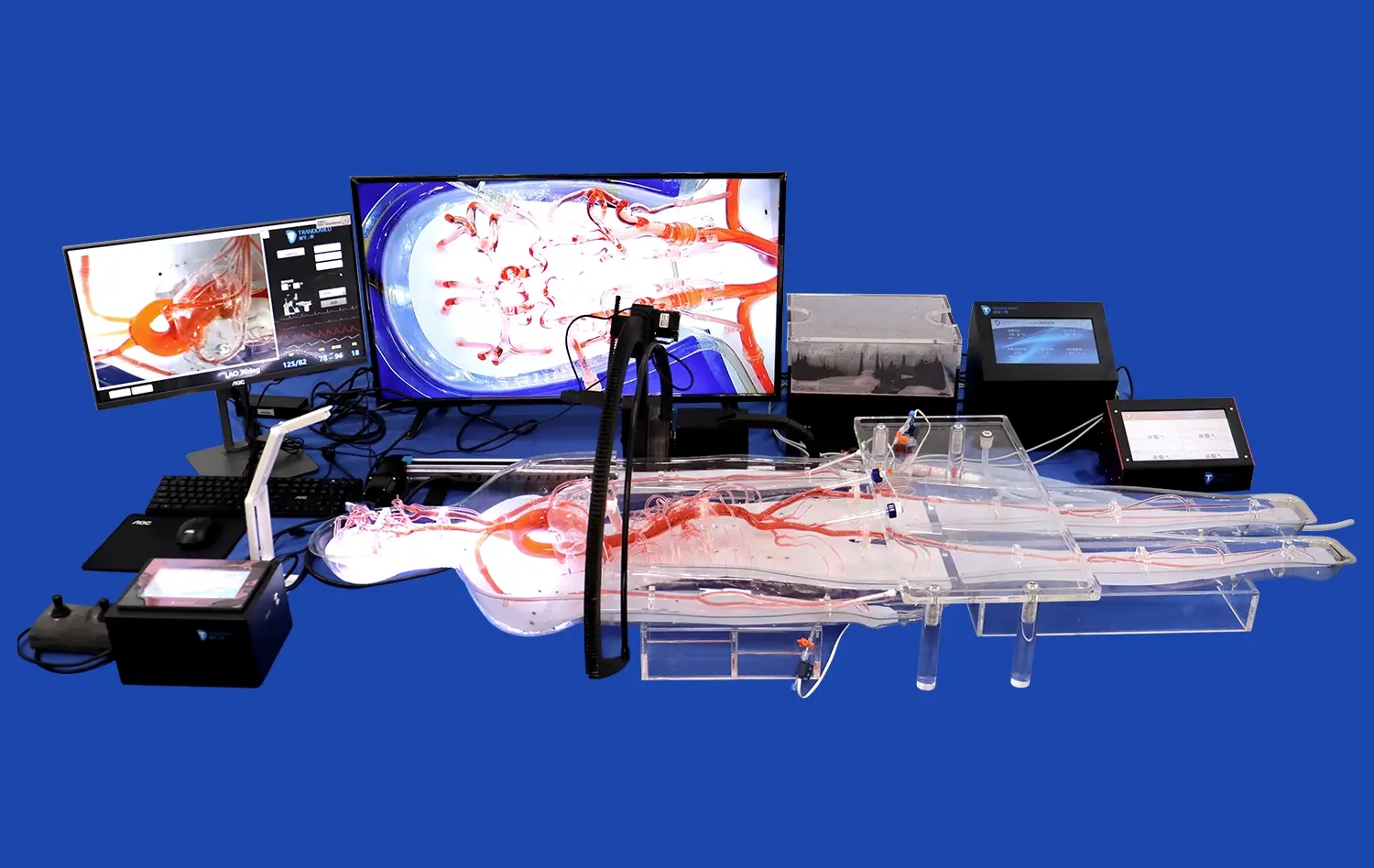
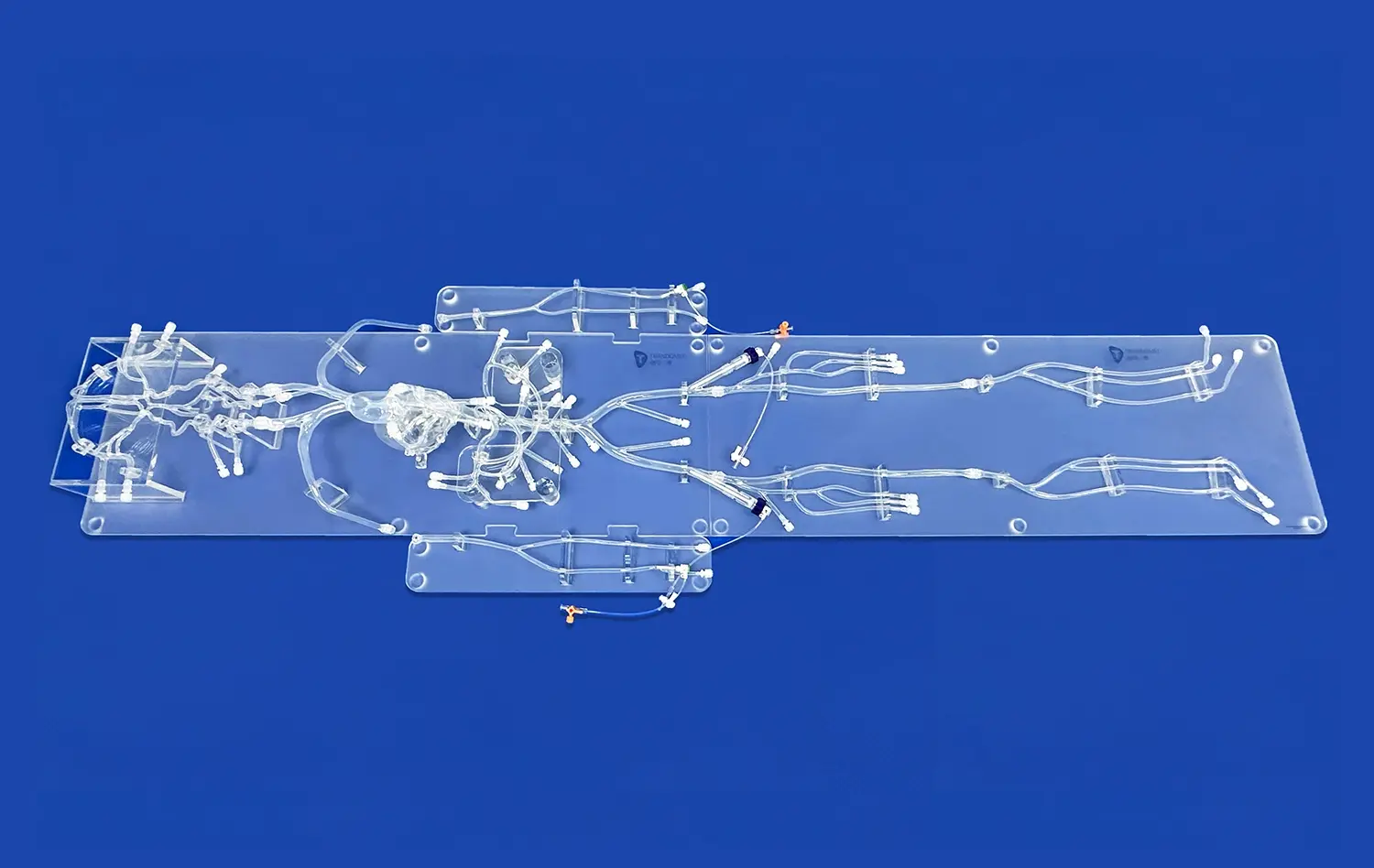
One of the key challenges in pulmonary artery interventions is maintaining spatial awareness within the complex vascular network. Advanced pulmonary artery models, like the PA001 from Trandomed, feature detailed representations of the pulmonary artery branching, including multiple levels of bifurcation. This intricate design allows interventionists to develop a better understanding of the three-dimensional anatomy, improving their ability to navigate through the pulmonary vasculature safely and efficiently.
Addressing Anatomical Variations
Every patient's anatomy is unique, and variations in pulmonary artery structure can pose significant challenges during interventions. High-quality pulmonary artery models can be customized to replicate various anatomical configurations, including tortuosity, stenosis, and malformations. By training with these diverse models, healthcare professionals can better prepare for the wide range of anatomical variations they may encounter in clinical practice, reducing the risk of complications arising from unexpected anatomical challenges.
Simulated Intervention Scenarios for Risk Reduction
Embolism Management Training
Pulmonary artery models offer an excellent platform for simulating embolism scenarios, allowing interventionists to practice critical techniques for managing this potentially life-threatening condition. With customizable models like the PA001, the position and length of pulmonary artery embolisms can be adjusted to create various training scenarios. This enables healthcare professionals to develop and refine their skills in embolectomy procedures, thrombectomy techniques, and the use of specialized devices for clot removal, all within a controlled and safe environment.
Hypertension Intervention Practice
Pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) is a complex condition that often requires interventional management. Advanced pulmonary artery models provide a realistic simulation of the vascular changes associated with PAH, allowing interventionists to practice techniques such as balloon pulmonary angioplasty and stent placement. By repeatedly performing these procedures on models, healthcare professionals can improve their precision and efficiency, reducing the risk of complications when treating actual PAH patients.
Device Deployment Simulation
The deployment of interventional devices, such as stents or occlusion devices, requires precise positioning and technique. Pulmonary artery models offer a valuable platform for practicing device deployment in a variety of anatomical contexts. This simulation allows interventionists to familiarize themselves with different device characteristics, deployment mechanisms, and potential challenges associated with various anatomical configurations. By honing these skills on models, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of device-related complications during actual procedures.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes Through Model-Based Procedural Practice
Improving Technical Proficiency
Regular practice with pulmonary artery models leads to improved technical proficiency among interventionists. The ability to repeatedly perform procedures in a low-stakes environment allows healthcare professionals to refine their catheter manipulation skills, enhance their understanding of device behavior, and develop more efficient techniques. This increased proficiency translates directly to improved patient outcomes, as interventionists can perform procedures more quickly and with greater precision, reducing procedure times and minimizing the risk of complications.
Optimizing Treatment Strategies
Pulmonary artery models enable healthcare teams to plan and optimize treatment strategies for complex cases. By creating patient-specific models based on imaging data, interventionists can simulate various approaches and device selections before the actual procedure. This pre-procedural planning helps identify potential challenges and allows for the development of tailored strategies, leading to more successful interventions and better patient outcomes.
Facilitating Team Training
Effective pulmonary artery interventions often require seamless collaboration between multiple team members. Pulmonary artery models provide an excellent platform for team-based training scenarios, allowing interventionists, nurses, and technicians to practice their roles and improve communication during simulated procedures. This collaborative practice enhances team coordination and efficiency, which is crucial for managing complex cases and responding effectively to potential complications during actual interventions.
Conclusion
Pulmonary artery models have emerged as indispensable tools in the realm of interventional cardiology and pulmonology. By providing a realistic and customizable platform for training and procedure planning, these models significantly contribute to safer and more effective pulmonary artery interventions. From mitigating procedural risks to enhancing technical proficiency and facilitating team coordination, the benefits of model-based training are far-reaching. As medical technology continues to advance, the role of high-quality simulation models in improving patient outcomes and safety in pulmonary artery interventions will undoubtedly grow even more significant.
Contact Us
Experience the cutting-edge in pulmonary artery simulation with Trandomed's advanced models. Our PA001 Pulmonary Artery Model offers unparalleled realism and customization options to support your training and research needs. Elevate your interventional skills and contribute to safer patient outcomes. For more information or to discuss your specific requirements, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
_1736215128474.webp)
_1735798438356.webp)
_1732863713705.webp)