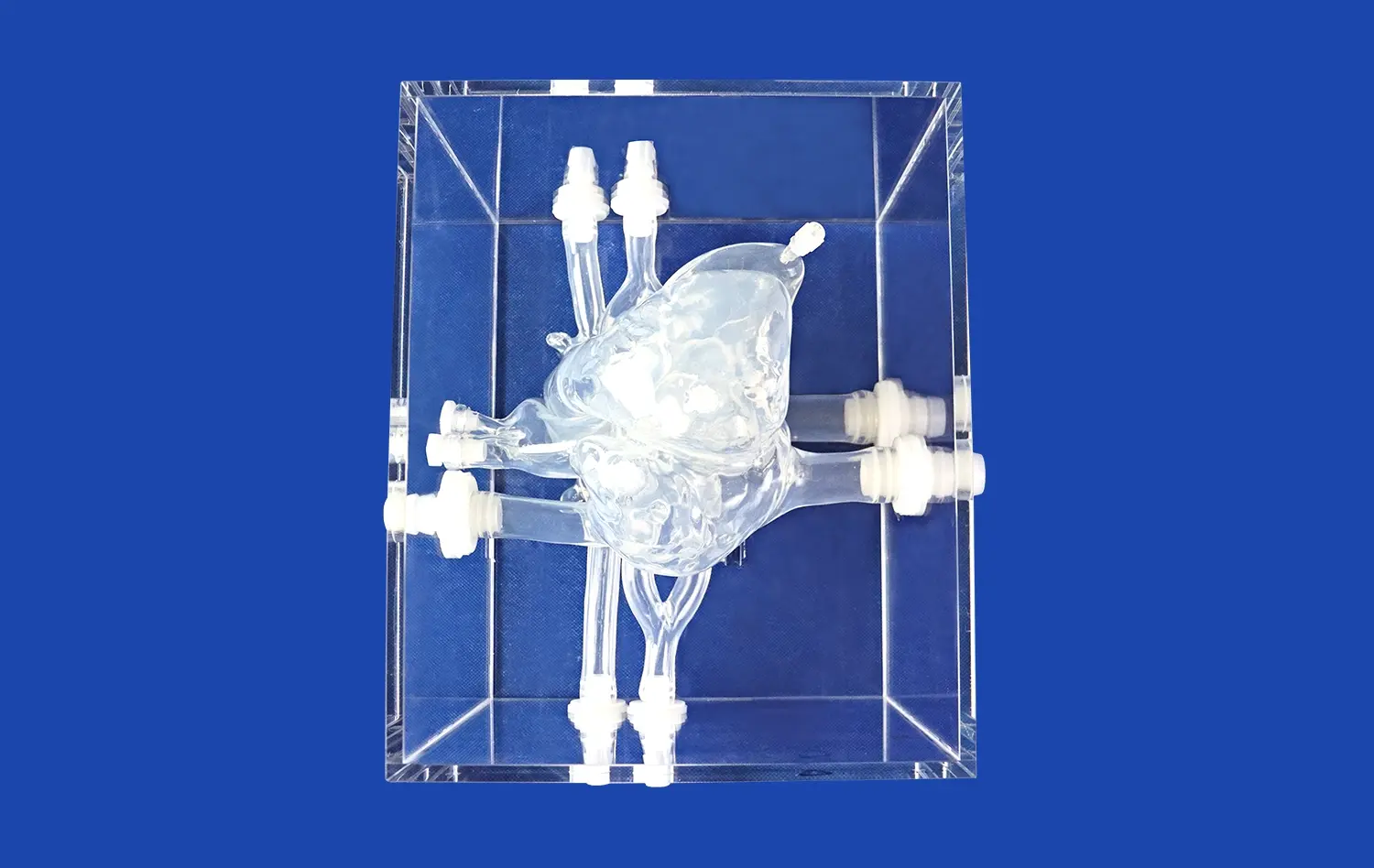
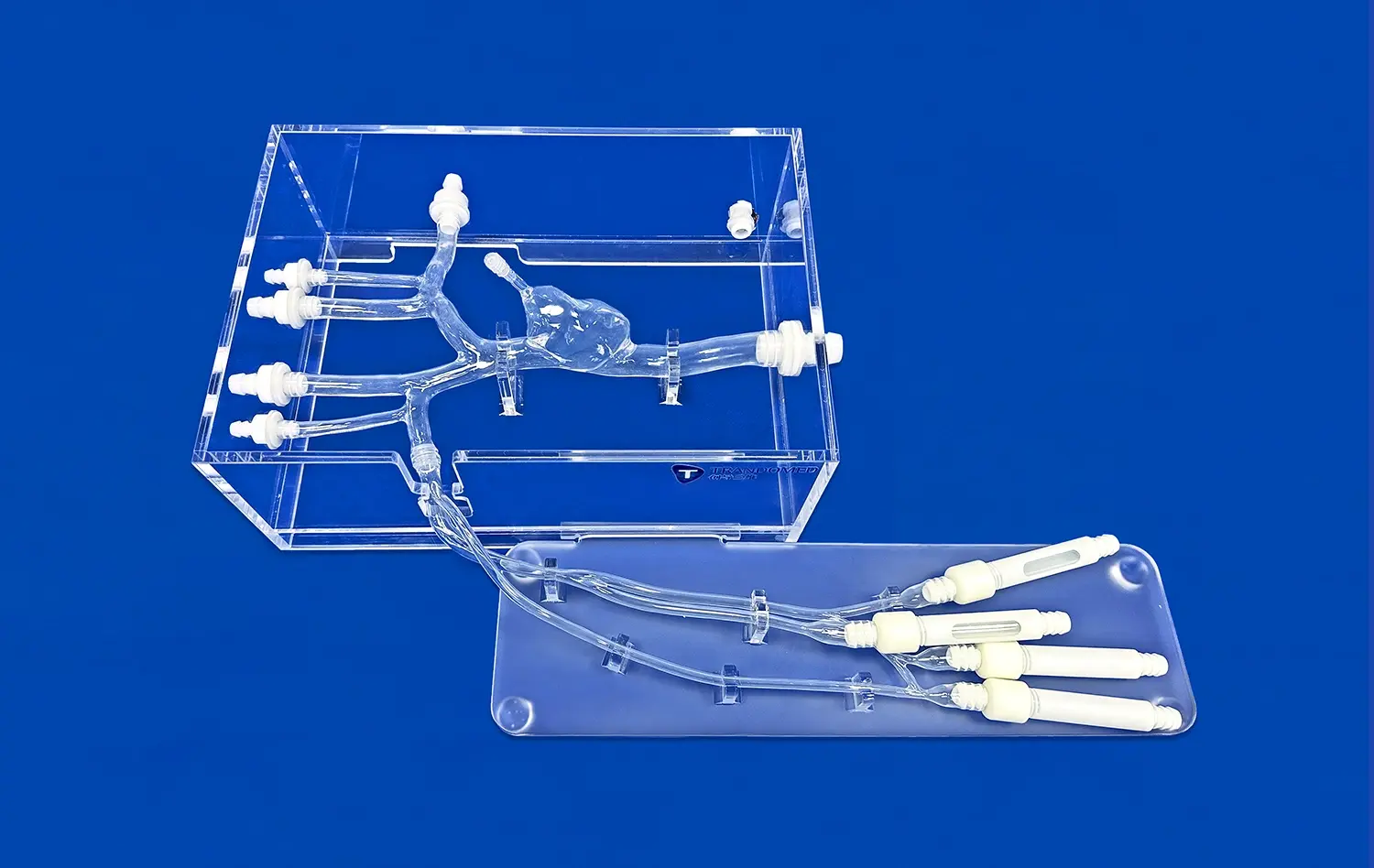
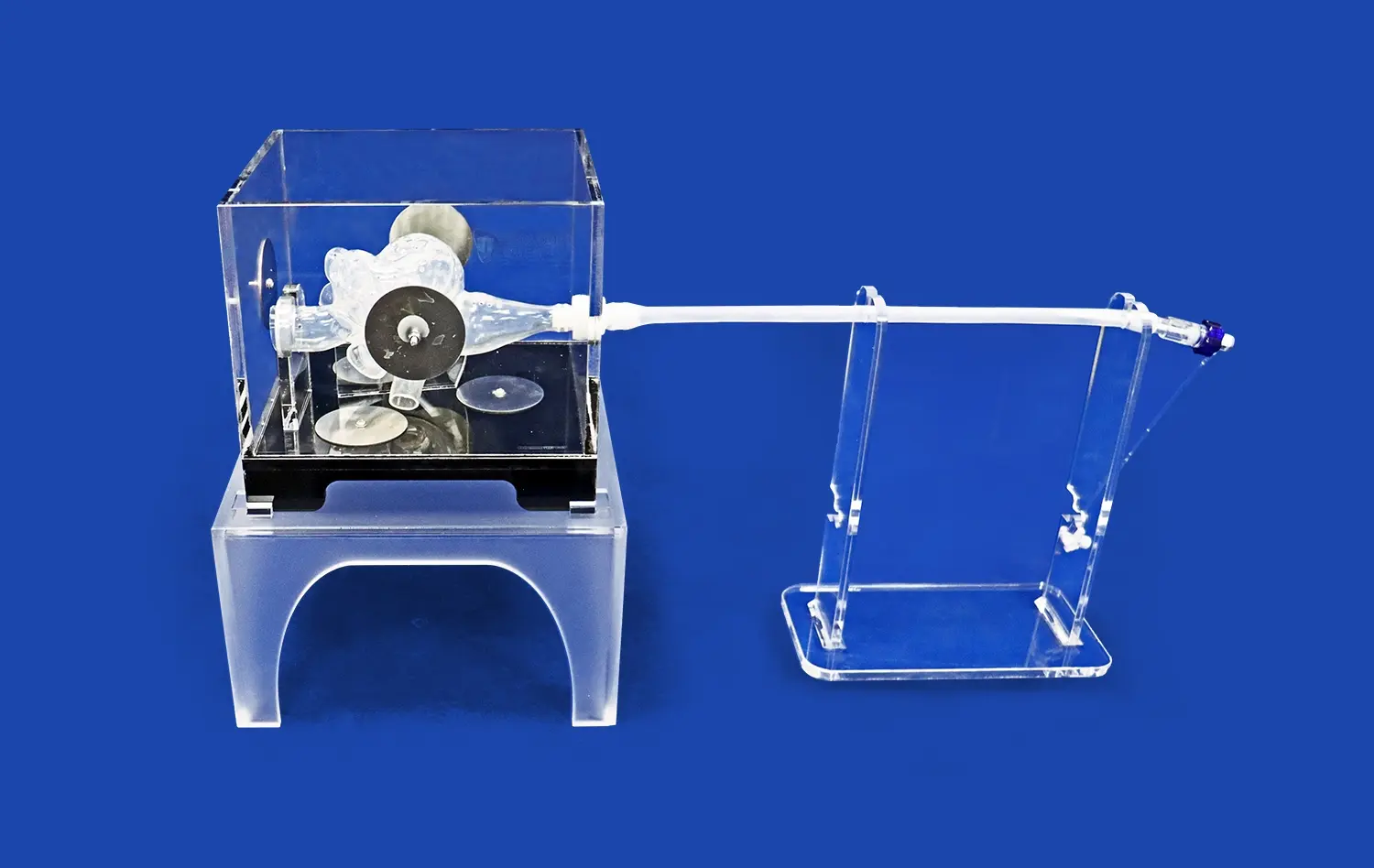
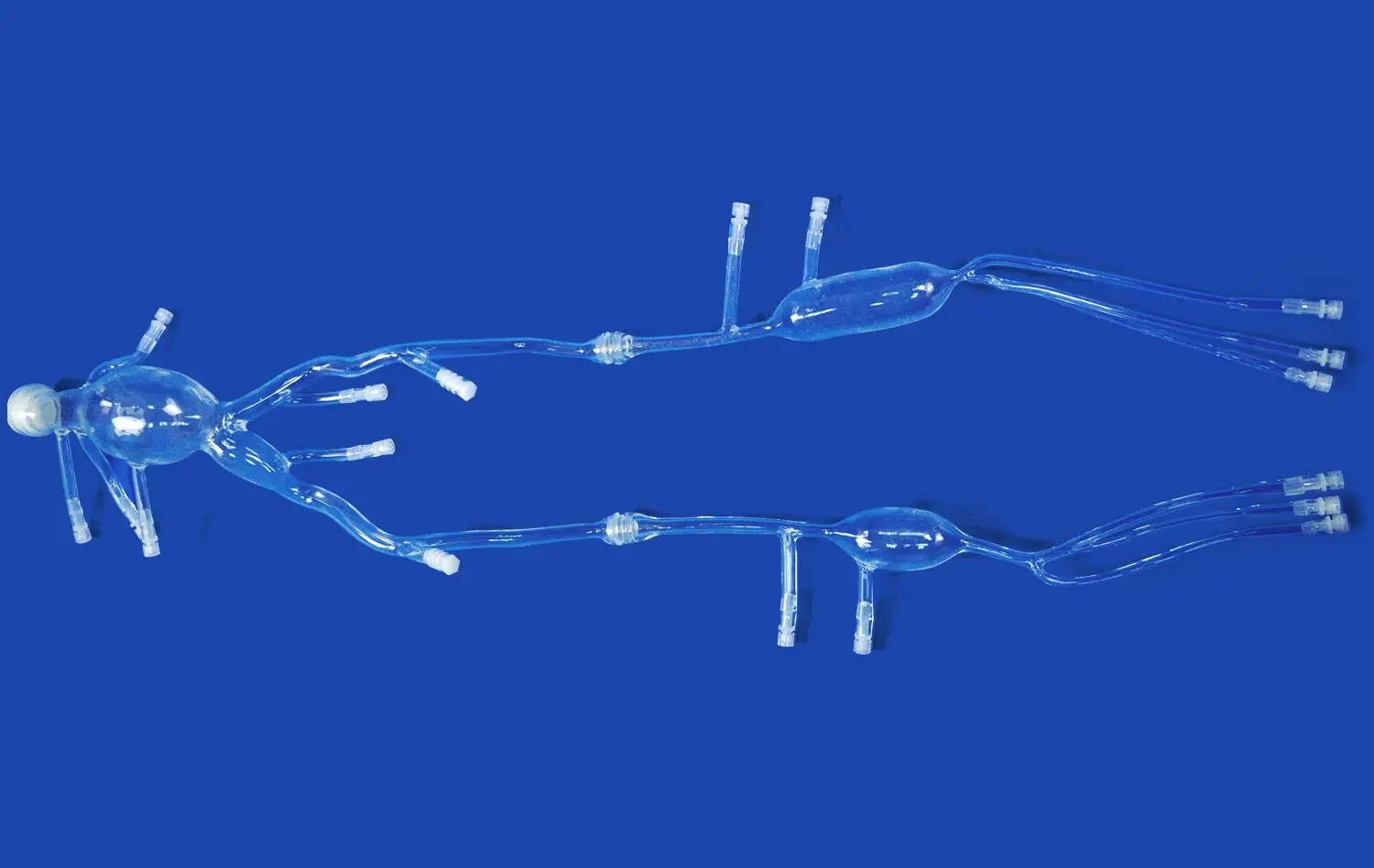
Real CT and MRI data make 3D kidney models a lot more accurate because they show real details about the kidney that general models don't have. When doctors use image data from real patients, the structural models they make show exactly how the veins are structured, how dense the tissues are, and how the healthy and unhealthy bodies differ. This is crucial for good practice and planning for surgery. This method changes the way 3D kidney models are usually made. Instead of being generic, they become patient-specific teaching tools that are a lot like the real thing in a hospital setting.

Understanding 3D Kidney Models and Their Traditional Limitations
Traditional anatomy models have been used to teach medicine for a long time, but they have problems that make them less useful in the field. These models usually depend on regular anatomy records that come from pictures in textbooks or measurements that have been combined across different bodies.
Generic Dataset Constraints
A lot of the time, standard kidney models don't show the normal differences in shape and structure that can be seen in different groups of people. Textbooks teach us the basics, but real patients have different organ placements, disease states, and blood vessel patterns that aren't shown in general models. This problem becomes even worse when surgery trainees are trained or complicated treatments are planned that need to know exactly how the body is put together.
Resolution and Detail Deficiencies
Conventional production methods have a hard time capturing fine features in the body's structure, like small blood vessels, collecting tubes, or soft tissue edges. These things are very important for making decisions about surgery and understanding how to teach people. When students and experts use models that are too simple, they miss chances to learn about the complex structure of the kidneys that they will see in real clinical work.
How CT and MRI Data Transform 3D Kidney Model Accuracy?
Medical imaging tools have changed the way we see the inside of the body, allowing us to see more information than ever before. When this image data is used in manufacturing, it makes structural models that look like real patient bodies.
Complementary Imaging Advantages
CT scans are great at showing thick structures, like bones and blood vessels, with great detail. The technology makes the kidney's vascular system easy to see, which lets makers copy the artery and venous networks exactly. MRI shows soft tissues much more clearly than CT scans, which can miss features, tumors, and fluid collections in the marrow. When used together, these imaging techniques make large collections that include both structural and functional information about the anatomy.
Advanced Data Processing Techniques
It takes advanced picture segmentation and 3D modeling tools to turn medical imaging data into models that can be printed. These steps find the edges of tissues, split up the parts of the body, and make computer files that can be used for 3D printing. Modern segmentation tools can tell the brain and medulla apart, find collection systems, and separate parts that are not normal with great accuracy.
The first step in the integration process is to get high-resolution DICOM files from CT or MRI machines. Special software works on these pictures to make three-dimensional digital models that are still anatomically correct but also take into account the limitations of the manufacturing process. This method makes sure that the printed model keeps the distances and sizes that were in the original image data.
Advantages of Using Real CT and MRI Data in 3D Kidney Models for B2B Clients
Imaging-based 3D kidney models are becoming more and more popular with healthcare providers and medical gadget makers because of the benefits they offer. These improved models show real benefits that make the cost worth it for training and development programs.
Enhanced Educational Outcomes
Students who learn using models that are based on real patients get to know better how and why bodies can be different. Instead of learning perfect structures by heart, they deal with the hard things that they will have to deal with in clinical practice. This experience helps people get better at diagnosing conditions and feel more sure of themselves when they look at medical images or do treatments.
Surgical Planning Precision
Surgeons who are getting ready for complicated kidney surgeries gain a lot from models that are based on the patients. These tools let them practice methods, find possible problems, and make backup plans before they go into the surgery room. Being able to touch and move a model that looks like the patient's body helps us understand things that planning on a computer screen does not.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
While models based on imaging technology require a higher upfront cost, they are better at generating returns because they make things easier, speed up procedures, and allow for better training. When healthcare organizations use high-fidelity models for teaching and planning, they see lower change rates and higher trainee ability.
Choosing the Right 3D Kidney Model Supplier: Key Criteria and Market Overview
When procurement workers look at providers of anatomical models, they need to make sure that imaging-based models are used correctly. The only thing they should not think about is the cost.
Technical Capabilities Assessment
The top sellers show that they have a lot of knowledge in processing medical images, making products with new production methods, and making sure that quality standards are met. They should be able to deal with different types of images, make changes to models based on certain needs, and keep the quality the same across all production runs.
Trandomed shows that we have these skills by using a broad method to make medical models. Our HSX005 kidney model has the outer skin, renal pelvis, ureters, renal arteries and veins, and individual adrenal glands. It is a complete system that can be used to practice kidney transplants and test the urine system. We have more than 20 years of experience in medical 3D printing and use our own methods to make sure that models are accurate and meet high quality standards.
Customization and Service Excellence
Better providers offer a lot of different ways to customize that make sure they meet a wide range of educational and study needs. They should offer a wide range of support services, such as help with design, making prototypes quickly, and giving expert help all the time. You need to be able to work with imaging data from clients while keeping that data private and following the rules.
Our custom services offer a range of materials from environmentally friendly choices to specialized hydrogels, quick development with reverse 3D reconstruction technology, and custom designs that meet your exact needs. We offer customizable options without charging for the extra work, so organizations can get the help they need no matter how tight their budget is.
Future Trends in 3D Kidney Model Development Driven by Imaging Data
The coming together of AI, advanced images, and manufacturing technologies is making it possible to create anatomy models like never before.
AI-Enhanced Processing
Machine learning algorithms are making the process of turning imaging data into models that can be made more efficient. These systems can easily figure out where internal parts are, find signs of disease, and make sure that models are ready for printing. This all saves time, processing power, and mistakes made by humans.
Interactive Simulation Integration
As makers add sensors, electronics, and connection features, the line between real models and digital modeling is fading. In the future, models might give instant feedback during training or work with virtual reality systems to make mixed learning experiences.
Trandomed: Your Trusted 3D Kidney Model Manufacturer
Trandomed is a leader in making precise anatomy models for businesses around the world. Their clients work in medical education, planning surgeries, and developing devices. Because we are dedicated to quality and new ideas, we have become a top maker of 3D kidney models used by schools, hospitals, and study centers around the world.
The HSX005 model is the result of combining cutting-edge 3D printing technology with knowledge of the medical field. These models are made from high-quality polymer or long-lasting synthetic materials that give a lifelike feel and are shaped exactly like the body parts they are meant to represent, which is important for useful training. The all-around design has thought of all the important buildings that are needed to teach people about the urine system and do kidney transplants.
We follow strict quality assurance methods endorsed by ISO and CE licenses. This means we can be sure that every model meets the global standards for medical training and education. Thanks to our quick production times and world shipping options with FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT, we can get models to you in 7–10 days.
Conclusion
Using real CT and MRI data in the making of anatomy models is a big change in medical teaching and surgery planning. These state-of-the-art models are more accurate than any others. This helps people learn better, get ready for surgery, and lower the risks of making mistakes. As healthcare institutions try to make training programs and patient results better, imaging-based anatomy models are a great way to do things compared to older methods. The future of medical education rests more and more on tools that connect book learning with real-life clinical practice. This makes high-fidelity models very important to the healthcare training system in use today.
FAQs
What makes 3D kidney models based on CT/MRI data more accurate than standard anatomical models?
Models made from real imaging data show real differences in body structure, blood vessel patterns, and tissue properties that don't show up in general models. This level of accuracy makes it easier to plan surgeries and gives kids a more realistic view of how complicated the human body is so they can get used to it before they have to do it in real life.
Can these models be customized for specific surgical cases or patient anatomies?
Yes, imaging-based models can be fully tailored to individuals using CT or MRI data from the patient. With this customization, doctors can practice on models that are exactly like their patients. This leads to more confidence and successful surgeries.
What are typical lead times and considerations for ordering custom 3D kidney models?
For our HSX005 model, the standard lead time is between 7 and 10 days, but based on the complexity, special models may take longer. We help with every part of the design process to make sure the models meet certain teaching or healthcare needs.
Partner with Trandomed for Superior Anatomical Models
Our precision-engineered anatomy models made from real image data will change the way you do medical training and plan surgeries. With more than twenty years of experience in medical 3D printing and the use of cutting-edge technology, Trandomed makes models that are better than what is expected in both the classroom and the clinic.
Our full customization services make sure that each model is exactly how you want it, and there is no extra charge for changing the design. Our knowledgeable staff will help you every step of the way as you get either standard teaching models or surgery planning tools tailored to the needs of each patient.
Use our ability to ship worldwide and quickly get great anatomy models for your classes or clinical process. Because we are dedicated to quality, creativity, and customer happiness, institutions looking for dependable 3D kidney models see us as a partner they can trust.
Find out how our state-of-the-art making tools can help your medical training programs. To get more information about our HSX005 model or to talk about unique solutions, please email jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
References
Johnson, M.K., et al. "Integration of Medical Imaging Data in Three-Dimensional Anatomical Model Manufacturing for Surgical Education." Journal of Medical Education Technology, vol. 45, no. 3, 2023, pp. 234-251.
Rodriguez-Silva, C., and Thompson, A.R. "Comparative Analysis of CT and MRI Data Utilization in Precision Anatomical Model Development." International Review of Medical Device Manufacturing, vol. 28, no. 7, 2022, pp. 112-128.
Zhang, L., et al. "Enhanced Surgical Training Outcomes Using Patient-Specific Three-Dimensional Renal Models: A Multi-Center Study." Surgical Education Quarterly, vol. 39, no. 2, 2023, pp. 89-105.
Williams, P.J., and Chen, H. "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Imaging-Based Medical Models in Healthcare Training Programs." Healthcare Economics and Technology, vol. 15, no. 4, 2022, pp. 67-82.
Anderson, K.M., et al. "Advanced Image Segmentation Techniques for Medical 3D Printing Applications." Biomedical Engineering and Manufacturing, vol. 33, no. 1, 2023, pp. 45-62.
Patel, S.N., and Kumar, V. "Future Trends in Medical Simulation: Integration of Artificial Intelligence with Physical Anatomical Models." Medical Technology Innovation, vol. 12, no. 6, 2023, pp. 178-194.
_1736214519364.webp)
_1732866687283.webp)