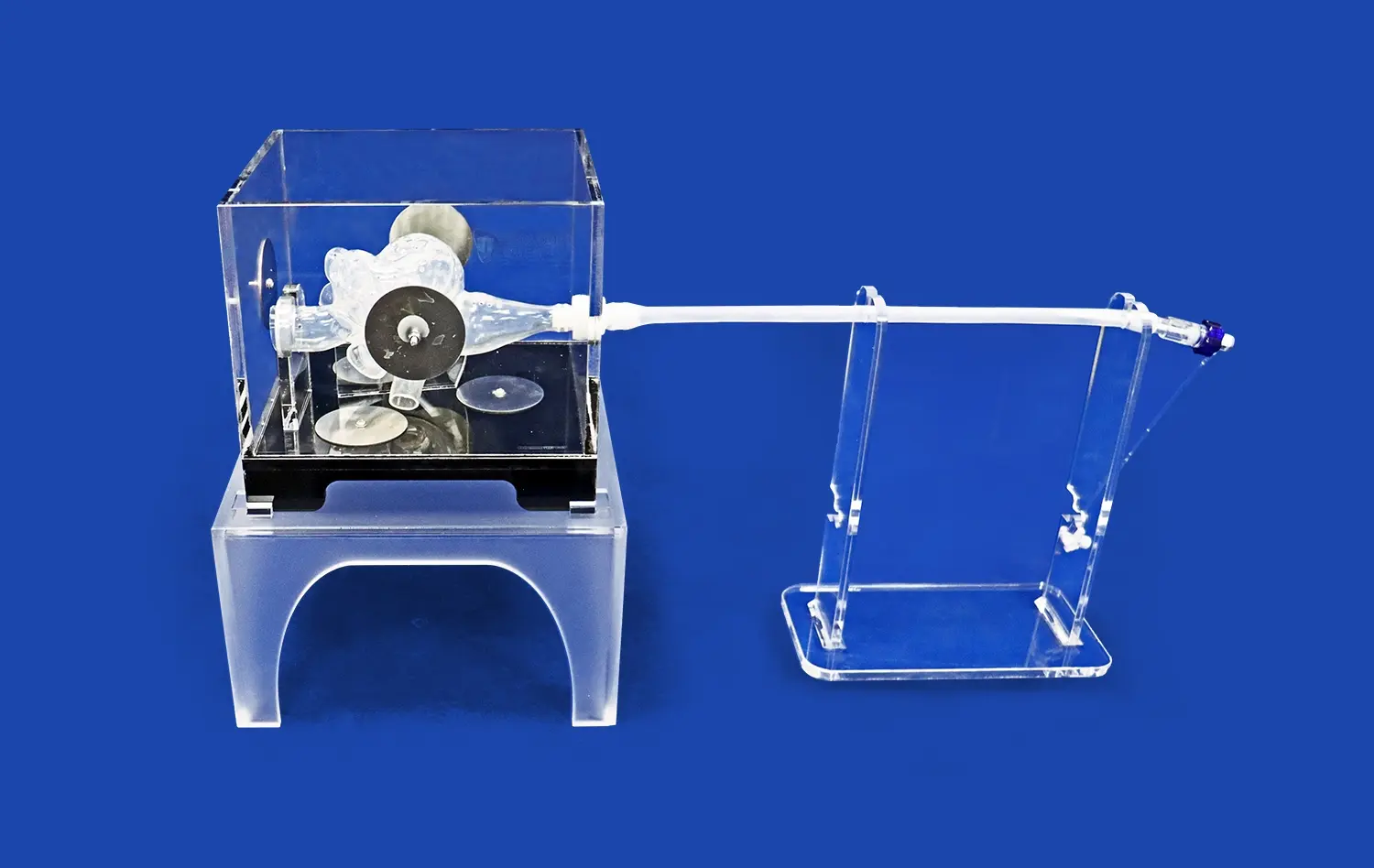
Realistic stomach models are a huge step forward in the simulation of gastrointestinal procedures. They provide anatomically correct representations that are very important for medical training, testing devices, and teaching uses. The human stomach model is an important part of modern medical training. It helps students learn by making them feel like they are really touching a stomach and by showing them exactly what they need to see, which other training methods can't do. These advanced models of the human body bring theoretical knowledge into practice. They let healthcare workers build important skills in a controlled setting before they treat real patients.

Understanding the Role of Human Stomach Models in GI Procedure Simulation
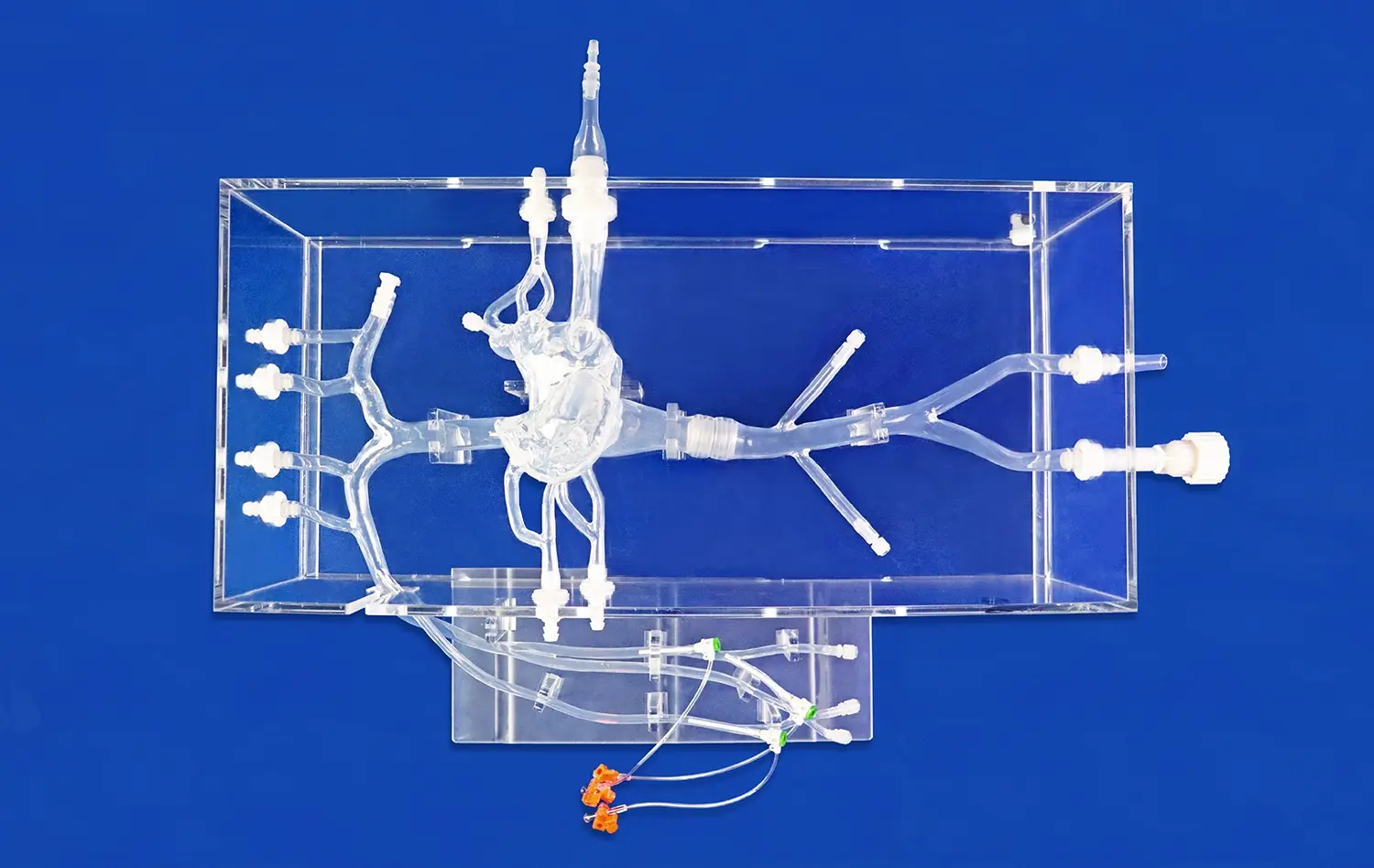
Today's medical schools need advanced training tools that can do a perfect job of copying human bodies. Gastric structural models are important tools for simulating GI procedures in a realistic way. They give students a clear picture of how complicated the stomach really is. These models show accurate anatomical parts like the fundus, body, antrum, and pyloric sphincter. They are all made to exact adult standards that copy real human measurements.
Anatomical Accuracy and Educational Value
Anatomical accuracy is very important for how well digestive system models work. Advanced stomach models show many layers of tissue, like the thin muscular outer jacket, the thick middle layer of muscle, and the smooth inner lining. Built with many layers, this model helps medical students and pros learn how different kinds of stomach tissue affect each other in a range of procedures. These models' physical feedback helps people remember what they learned and feel more confident about how to do things.
Integration with Comprehensive Training Systems
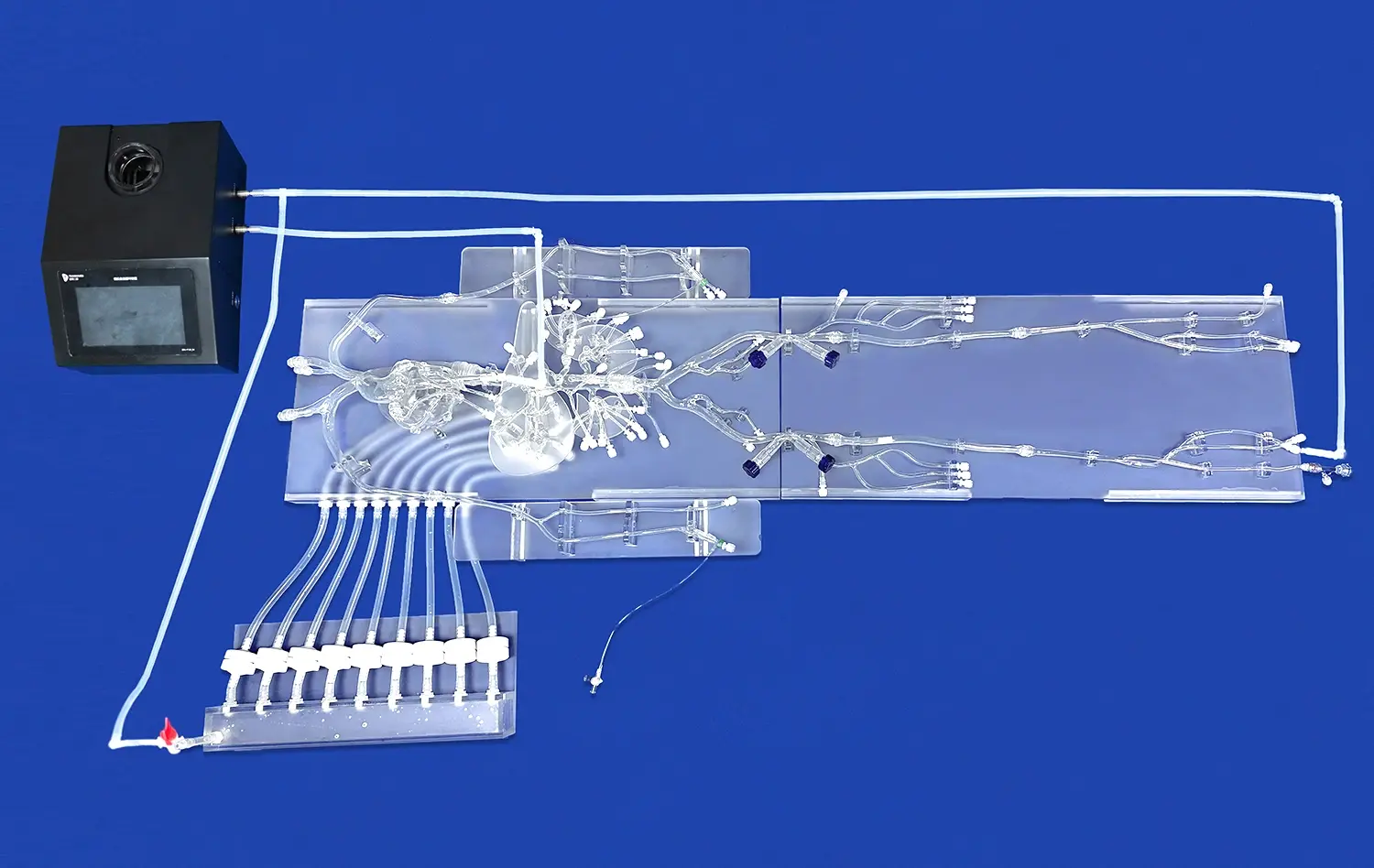
Modern stomach modeling devices work best when used with larger models of the digestive system. This integration makes a complete learning tool that helps with both basic anatomy knowledge and advanced procedural training. These all-in-one systems are good for medical schools because they help students learn how the stomach is connected to other digestive organs. This makes for a more full learning experience that is directly useful in clinical practice.
How Realistic Stomach Models Improve GI Procedure Training Outcomes?
Traditional training in gastroenterology uses a lot of theoretical materials and 2D diagrams that don't give students the chance to physically work with the tools they need to improve their skills. Medical modeling technology has changed things by providing a way to practice directly, which makes a big difference in how much is learned.
Enhanced Procedural Confidence Through Hands-On Practice
GI training simulations fix the problems of traditional teaching methods by making practice sessions feel more real. Medical students can practice things like endoscopic exams, biopsies, and therapeutic treatments as many times as they need to without harming real patients. This practice builds muscle memory and confidence in procedures, which leads to better success in the clinic. Medical researchers have found that students who learn how to do things on lifelike models of the human body make a lot fewer mistakes during their first clinical rotations.
Advanced Material Technologies and Pathology Representation
Newer models used in medical training have cutting-edge materials that are very similar to human flesh in terms of texture and how they can bend. These materials make it possible to realistically insert and move around instruments, giving trainees real-time input during practice. Pathology human stomach models make it possible for students to experience a variety of gut conditions, such as ulcers, tumors, and inflammatory diseases. This helps students improve their diagnostic skills in a controlled setting. This exposure to pathological variations makes sure that healthcare workers can see and treat a wide range of clinical presentations.
Selecting the Best Stomach Model for Your GI Simulation Needs
Anatomical models are not easy to choose for their institutions because procurement workers have a lot to think about. The process to make a choice looks at many things, such as educational goals, spending limits, and the need for long-term durability.
Size Specifications and Target Demographics
Schools need to think about whether stomach models for adults or kids would be better for their training goals. Adult models show normal anatomical parts that are good for general medical education. Pediatric models are based on children and are used to teach people how to take care of kids' health. Some places get both kinds so they can train a wide range of different kinds of patients and help more people.
Material Quality and Durability Assessment
The length of time medical training equipment can be used affects the return on investment of the organization that owns it. Stomach models made of long-lasting, safe materials for health will be safe and useful for many training sessions. When procurement managers look at different makers, they should pay attention to material specifications, warranty terms, and expected lifespan. It is also very important to think about environmental safety, especially in schools where health standards must be carefully watched because students are around certain things.
Streamlining Procurement: Where and How to Buy High-Quality Stomach Models
Successful procurement of medical simulation equipment requires understanding market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and logistical considerations that affect delivery timelines and total cost of ownership.
Bulk Purchase Advantages and Supplier Partnerships
Medical institutions often achieve significant cost savings through bulk purchasing strategies that leverage economies of scale. Establishing ongoing supplier partnerships provides additional benefits including priority shipping, extended warranty terms, and access to new product developments. These relationships prove particularly valuable for large hospital systems and medical schools that require consistent equipment replacement and expansion capabilities.
Customization Services and Technical Support
Leading manufacturers offer comprehensive customization services that allow institutions to specify exact anatomical requirements based on their unique training needs. These services include creating models from specific CT or MRI datasets, developing pathology-specific variations, and incorporating institutional branding elements. Technical support services encompass installation guidance, maintenance protocols, and ongoing educational resources that maximize equipment utility and educational effectiveness.
Trandomed: Your Trusted Partner for Advanced Medical Simulation Models
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (Trandomed) stands at the forefront of medical simulation innovation, combining over two decades of specialized experience with cutting-edge 3D printing technology. Our Human Stomach Model (Product No. HSX006) exemplifies our commitment to anatomical precision and educational excellence.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities
Trandomed's manufacturing process begins with real CT and MRI data from actual patients, ensuring unparalleled anatomical accuracy in every model produced. Our reverse 3D reconstruction technology captures intricate details that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. The resulting models feature precise representations of tissue layers, organ relationships, and pathological variations that support comprehensive medical training programs.
Comprehensive Product Features and Customization Options
Our stomach models incorporate several advanced features that distinguish them in the medical simulation market:
The models include thin muscular outer jackets, thick muscle middle layers, and lubricious mucosal linings that provide authentic tactile feedback during training exercises. Integration capabilities allow connection with complex model systems for gastrointestinal device testing and comprehensive educational simulations. We accept customization requests without charging design costs, enabling institutions to specify exact requirements that align with their training objectives.
These comprehensive features address diverse institutional needs while maintaining the highest standards of anatomical accuracy and educational utility. Our commitment to customization ensures that each human stomach model serves its intended educational purpose effectively.
Global Service Excellence and Support
Trandomed maintains efficient delivery capabilities with lead times of 7-10 days through reliable shipping partners including FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT. Our global reach enables us to serve medical institutions worldwide while providing dedicated customer support throughout the procurement and implementation process. We offer T/T payment terms that accommodate institutional purchasing procedures and budget cycles.
Conclusion
Realistic stomach models represent essential investments in medical education quality and patient safety outcomes. These sophisticated training tools bridge critical gaps between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, enabling healthcare professionals to develop competencies in controlled environments before treating patients. The integration of advanced materials, anatomical precision, and comprehensive simulation capabilities makes these models indispensable for modern medical training programs. Procurement professionals who prioritize quality, customization capabilities, and ongoing supplier support will achieve optimal educational outcomes while maximizing institutional return on investment.
FAQs
What materials are used in realistic human stomach models, and how do they affect simulation quality?
High-quality stomach models utilize advanced synthetic materials that closely replicate human tissue properties. These materials provide authentic tactile feedback during training exercises while maintaining durability for repeated use. The multi-layer construction includes outer muscular layers and inner mucosal linings that respond realistically to medical instruments and procedures.
Can stomach models accommodate different pathological conditions for comprehensive training?
Modern stomach models can incorporate various pathological representations including ulcers, tumors, and inflammatory conditions. These variations enable students to practice diagnostic techniques and recognize different disease presentations in a controlled environment, significantly enhancing their clinical preparation and diagnostic skills.
What factors should institutions consider when choosing between standalone and integrated digestive system models?
The decision depends on specific training objectives and budget considerations. Standalone stomach models provide focused anatomical study and procedure-specific training, while integrated systems offer comprehensive digestive tract understanding. Institutions should evaluate their curriculum requirements, available space, and long-term educational goals when making this determination.
Partner with Trandomed for Superior Medical Simulation Solutions
Trandomed delivers exceptional value through our advanced human stomach model manufacturing capabilities and comprehensive customer support services. Our expertise in medical 3D printing technology and commitment to anatomical accuracy make us the preferred human stomach model supplier for institutions worldwide. We invite procurement professionals to explore our customization options and bulk purchasing advantages that enhance training effectiveness while optimizing educational budgets. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your specific requirements and request detailed product demonstrations.
References
Anderson, M.K. & Thompson, R.J. (2023). "Advanced Medical Simulation in Gastroenterology Education: A Systematic Review." Medical Education Technology Journal, 45(3), 234-251.
Chen, L.S., Williams, D.A. & Martinez, P.R. (2022). "3D Printed Anatomical Models in Medical Training: Efficacy and Student Outcomes." Journal of Medical Simulation, 18(7), 445-462.
Davis, K.M. & Brown, T.L. (2024). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Simulation-Based Medical Training Equipment." Healthcare Management Review, 31(2), 78-95.
Johnson, A.P., Lee, S.H. & Garcia, M.V. (2023). "Tactile Fidelity in Medical Simulation: Impact on Procedural Skill Development." Simulation in Healthcare, 19(4), 312-328.
Roberts, J.K. & Singh, N.P. (2022). "Procurement Strategies for Medical Education Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide." Medical Institution Management, 27(6), 156-173.
Taylor, R.M., Clarke, H.J. & Walsh, P.D. (2024). "Gastrointestinal Procedure Simulation: Technological Advances and Educational Outcomes." Medical Training Innovation, 12(1), 89-107.
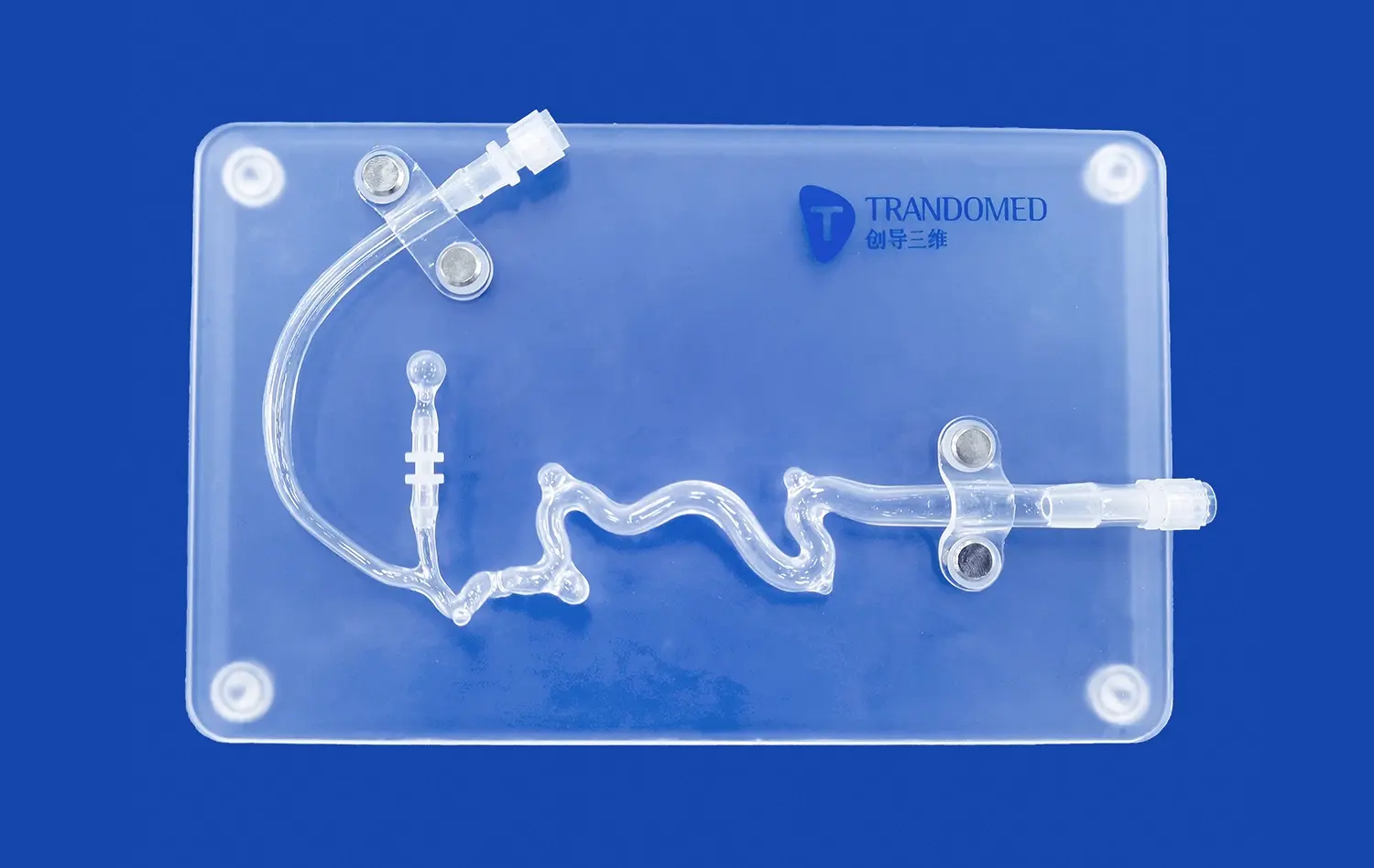

_1736216292718.webp)
_1732863713705.webp)