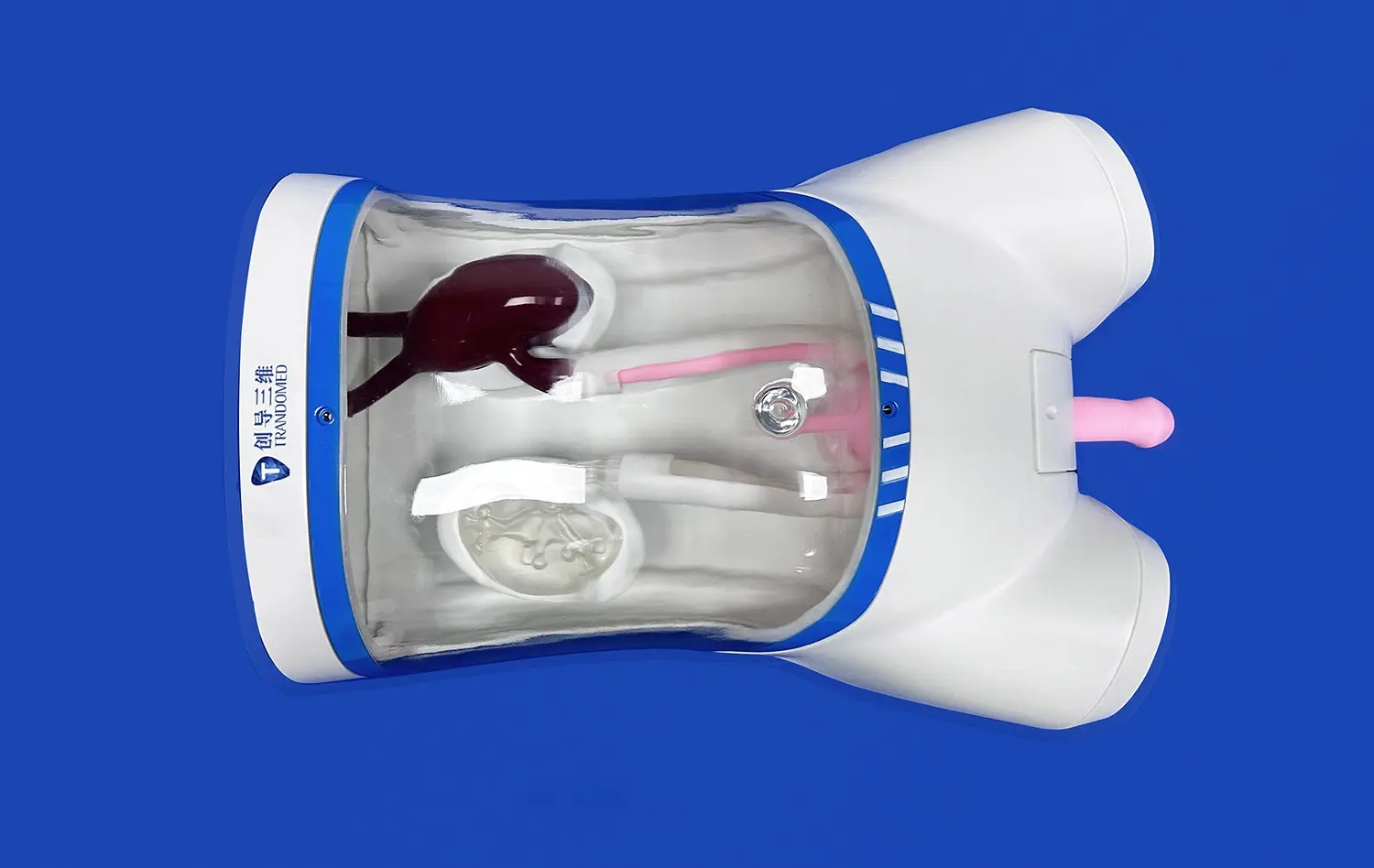
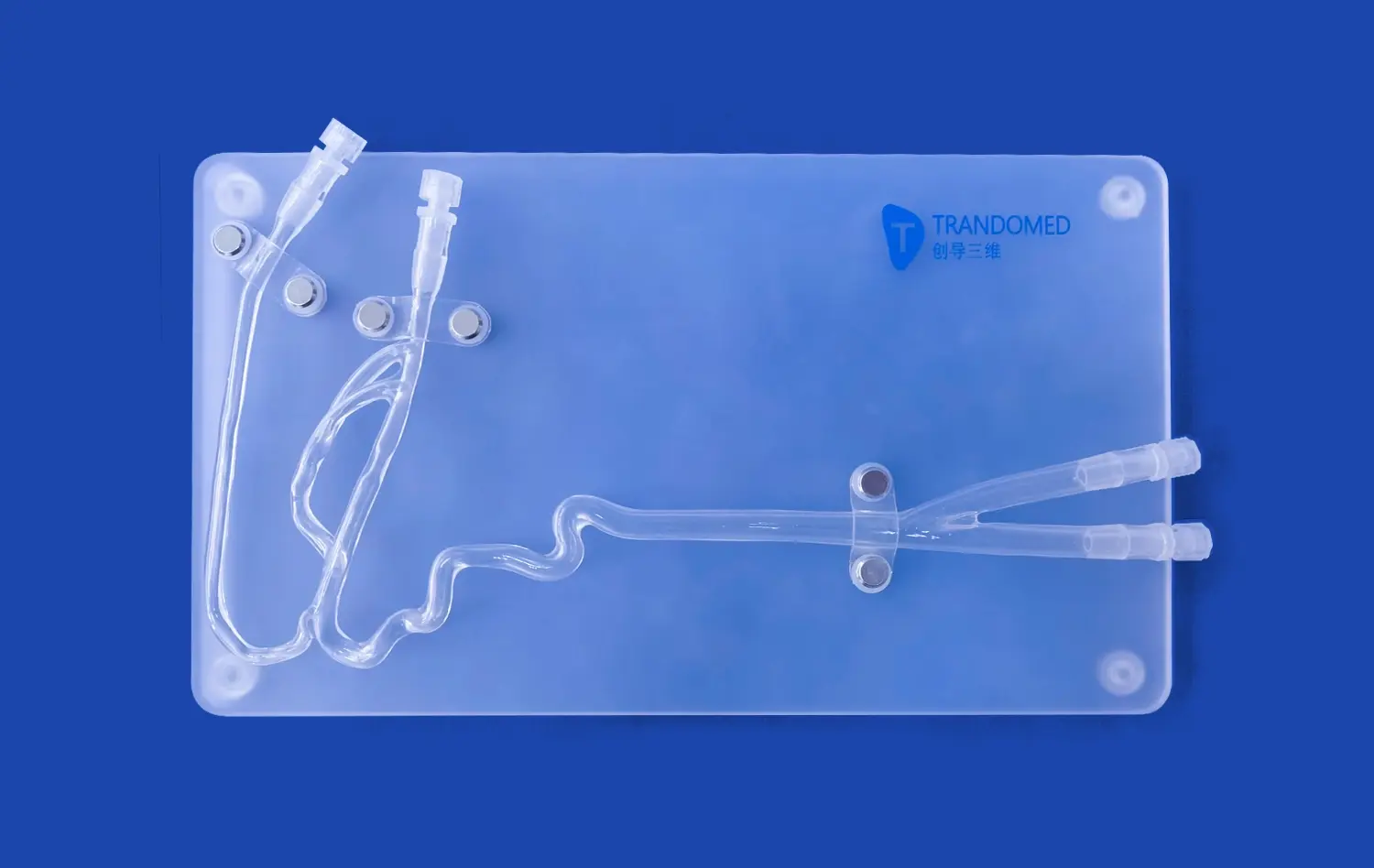
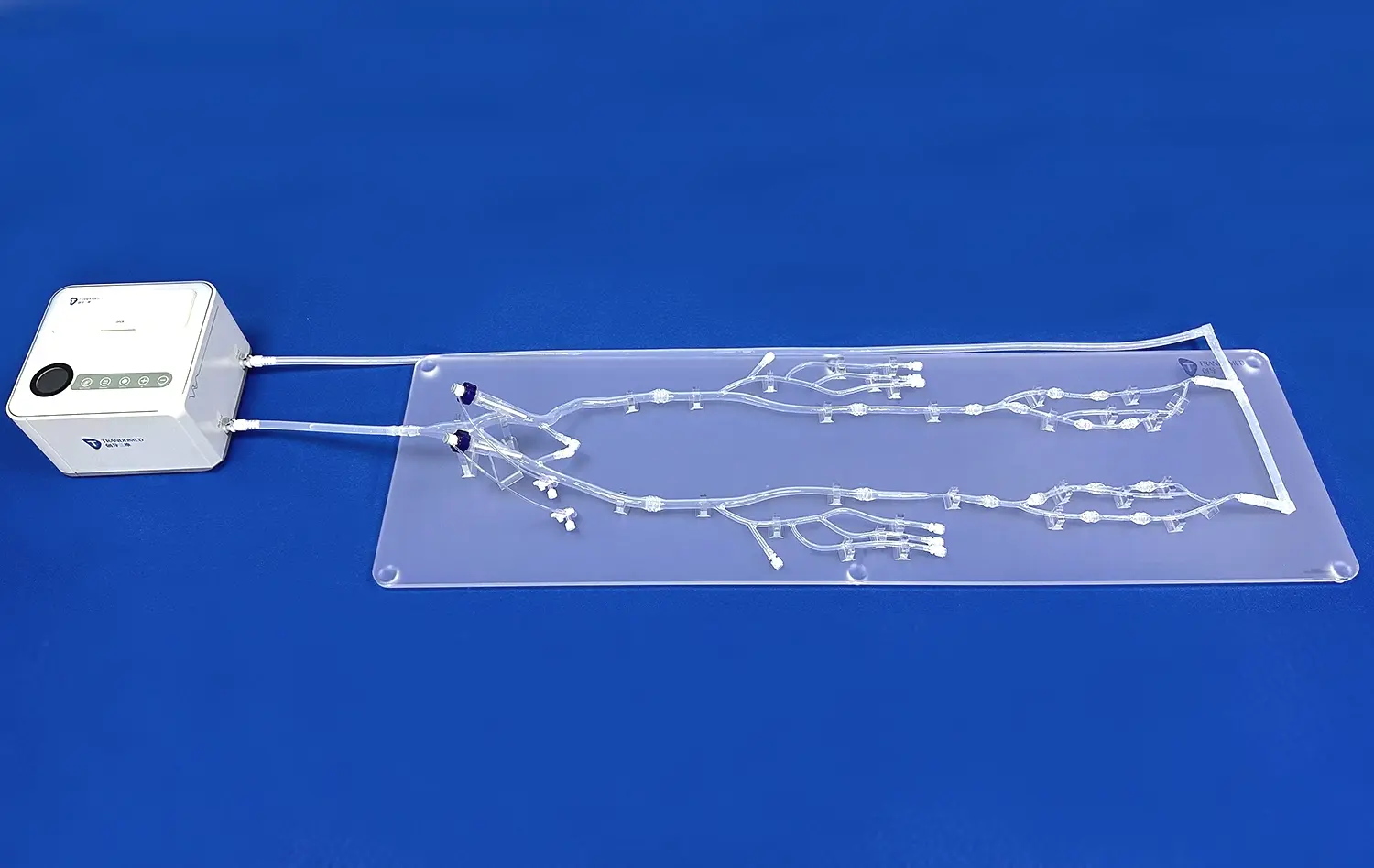
What Anatomical Features Are Best Studied with 3D Models?
Intricate Mucosal Structures
3D small intestine models excel at showcasing the complex mucosal structures that line the intestinal walls. These models accurately depict the villi and microvilli, allowing medical students and professionals to visualize the vast surface area crucial for nutrient absorption. The ability to examine these structures in detail helps in understanding various pathologies that affect the mucosal layer, such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disorders.
Mesenteric Attachments and Blood Supply
Another key anatomical feature best studied with 3D models is the mesenteric attachments and associated blood supply of the small intestine. These models provide a clear view of how the mesentery suspends the intestine within the abdominal cavity and how blood vessels traverse this structure. This visualization is particularly valuable for surgical planning and understanding potential complications during procedures involving the small intestine.
Lymphatic System Integration
3D small intestine models also offer an excellent opportunity to study the integration of the lymphatic system within the intestinal walls. The models can depict Peyer's patches and other lymphoid tissues, which play a crucial role in the immune function of the gastrointestinal tract. Understanding the distribution and appearance of these structures is essential for diagnosing and treating various gastrointestinal disorders and cancers.
Step-by-Step Practice for Surgical and Endoscopic Techniques
Endoscopic Navigation Training
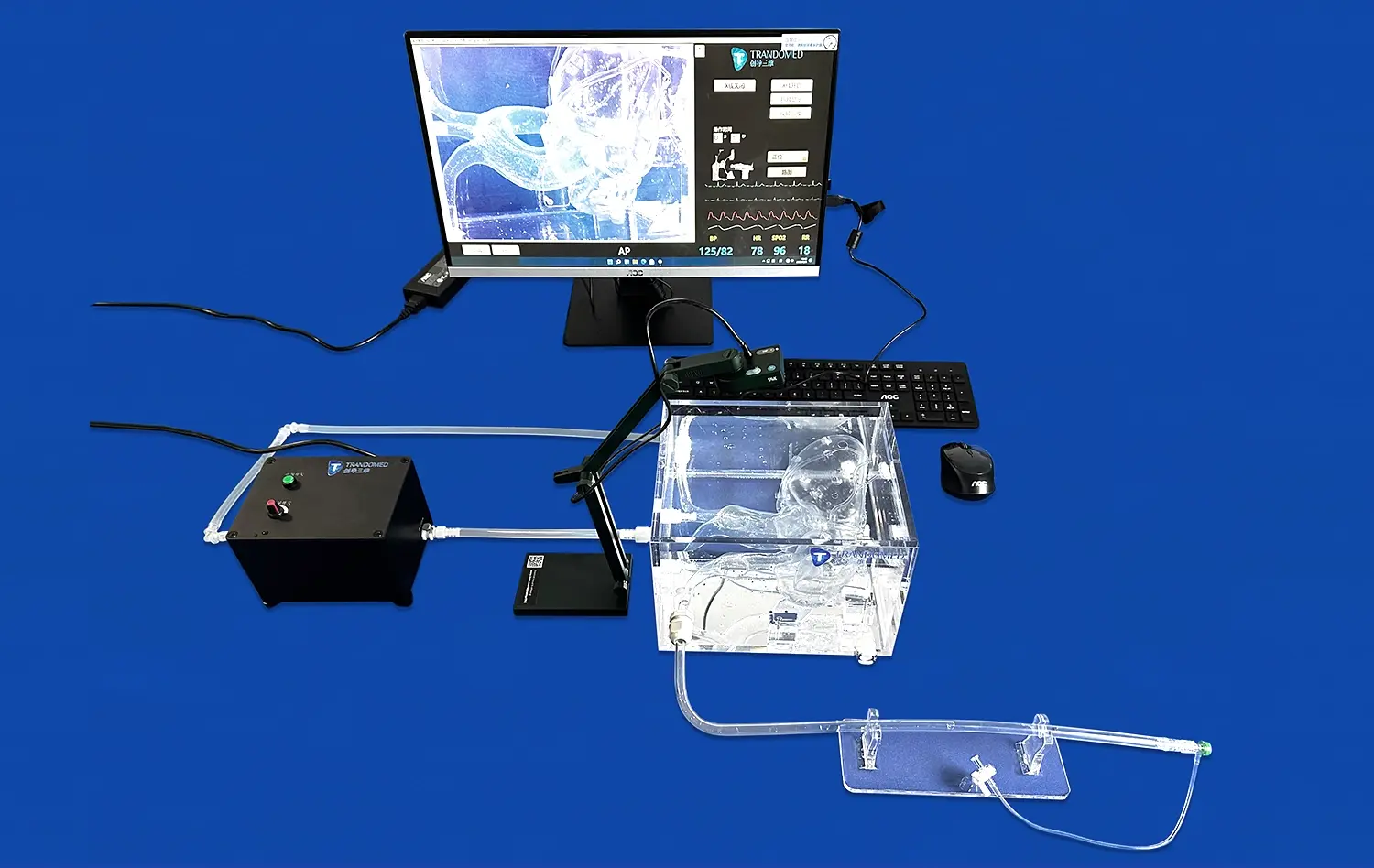
Small intestine models provide an ideal platform for practicing endoscopic navigation techniques. Trainees can use these models to learn how to maneuver an endoscope through the twists and turns of the small intestine, developing the spatial awareness and hand-eye coordination necessary for successful procedures. The models can be designed with varying degrees of difficulty, simulating different patient anatomies and pathological conditions to enhance the learning experience.
Biopsy and Polypectomy Simulation
3D-printed small intestine models enable step-by-step practice of common endoscopic procedures such as biopsies and polypectomies. These models can be crafted with removable sections or attachable simulated lesions, allowing trainees to practice tissue sampling and polyp removal techniques. The tactile feedback provided by these models helps in developing the fine motor skills required for these delicate procedures.
Surgical Anastomosis Practice
For surgical training, small intestine models offer a realistic environment to practice anastomosis techniques. Surgeons can rehearse various suturing methods and stapling procedures on these models, which can be designed to mimic the tissue properties of the actual small intestine. This hands-on practice is invaluable for perfecting techniques before performing them on live patients, ultimately leading to improved surgical outcomes and reduced complications.
How High-Fidelity Models Facilitate Mastery of Gastrointestinal Procedures?
Enhanced Spatial Awareness
High-fidelity small intestine models significantly enhance spatial awareness for medical professionals. These anatomically accurate replicas allow practitioners to visualize the three-dimensional relationships between various structures within the abdominal cavity. This improved spatial understanding is crucial for navigating complex gastrointestinal procedures, whether it's determining the best approach for an endoscopic intervention or planning the optimal surgical route. By interacting with these models, clinicians can develop a more intuitive grasp of intestinal anatomy, leading to more confident and efficient procedural execution.
Repetitive Practice in a Risk-Free Environment
One of the key advantages of high-fidelity small intestine models is the opportunity they provide for repetitive practice in a risk-free setting. Unlike traditional learning methods that rely heavily on textbooks or limited cadaver availability, these models allow for unlimited attempts at perfecting techniques. Trainees can practice endoscopic maneuvers, biopsy techniques, or surgical interventions as many times as needed without the pressure of patient safety concerns. This iterative process is crucial for developing muscle memory and refining skills, ultimately leading to improved performance in real clinical scenarios.
Customizable Pathology Scenarios
High-fidelity small intestine models can be customized to represent various pathological conditions, offering a diverse range of learning opportunities. Manufacturers can create models that simulate different disease states, such as Crohn's disease, intestinal tumors, or congenital abnormalities. This customization allows medical professionals to encounter and practice managing a wide array of clinical scenarios they might face in their careers. By working with these specialized models, practitioners can develop strategies for addressing complex cases, improving their diagnostic skills and treatment planning abilities.
Conclusion
Small intestine models have emerged as indispensable tools in the realm of gastrointestinal medical education and training. These high-fidelity replicas offer unparalleled opportunities for hands-on learning, enhancing spatial awareness, and refining technical skills crucial for GI procedures. By providing a risk-free environment for repetitive practice and the ability to simulate various pathological conditions, these models bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of small intestine models will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping competent, confident healthcare professionals ready to tackle the complexities of gastrointestinal care.
Contact Us
Elevate your medical education and training programs with Trandomed's cutting-edge small intestine models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D-printed medical simulators, we offer unparalleled realism and customization options to meet your specific educational needs. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing processes ensure the highest quality and anatomical accuracy, providing your institution with reliable, durable training tools. Experience the difference that high-fidelity models can make in your GI procedure training. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore how our small intestine models can revolutionize your educational approach and improve learning outcomes.


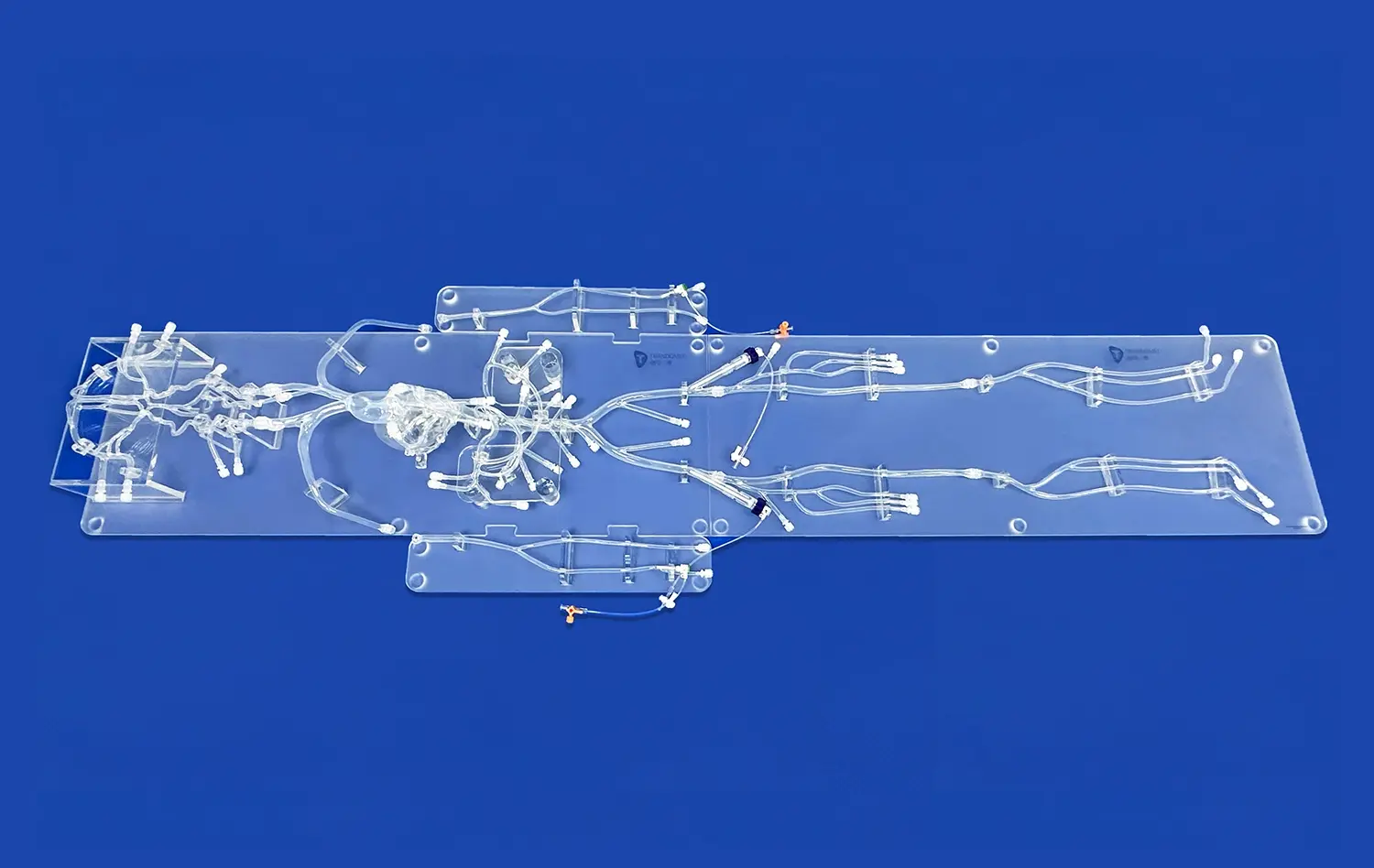
_1732866687283.webp)