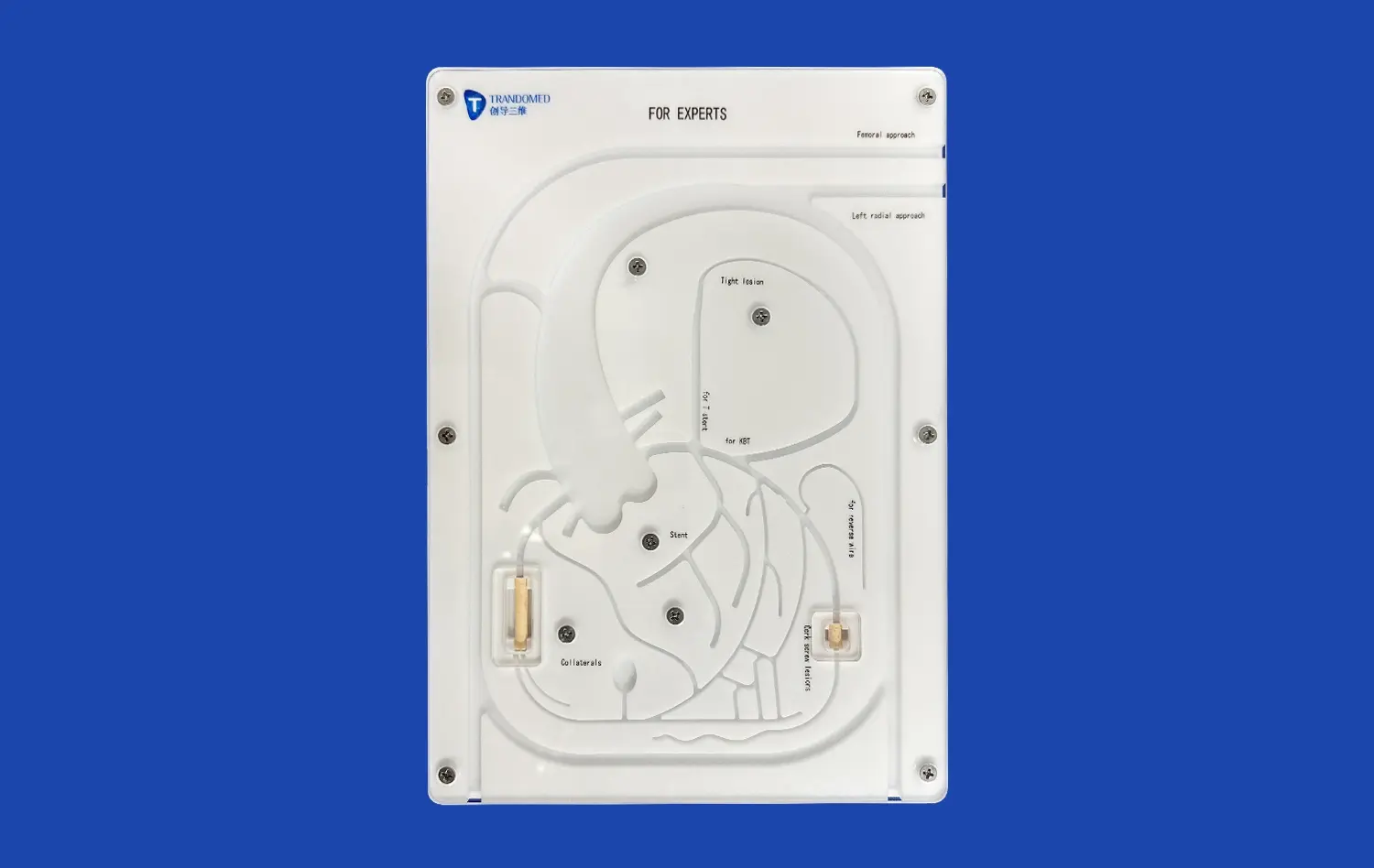
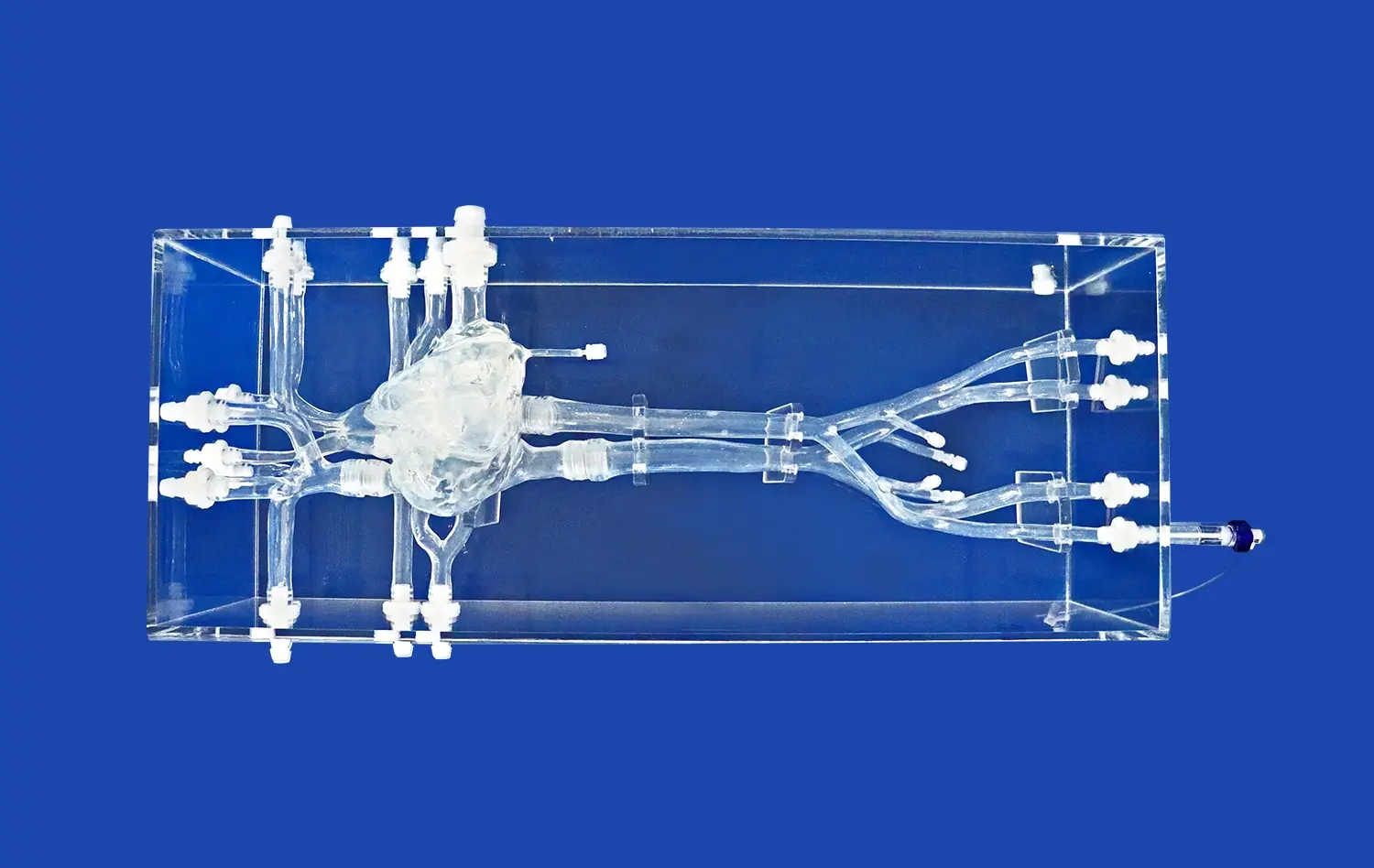
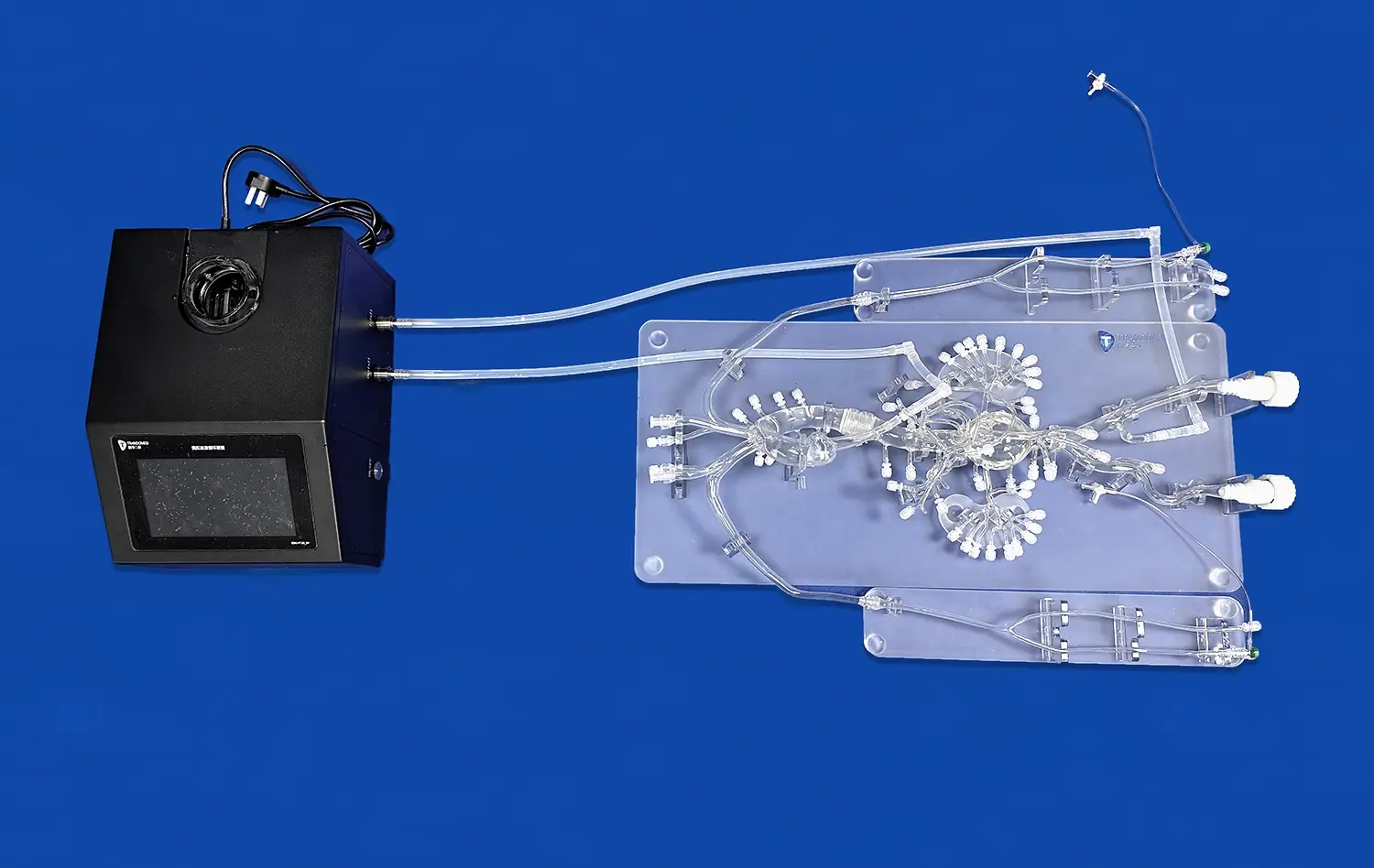
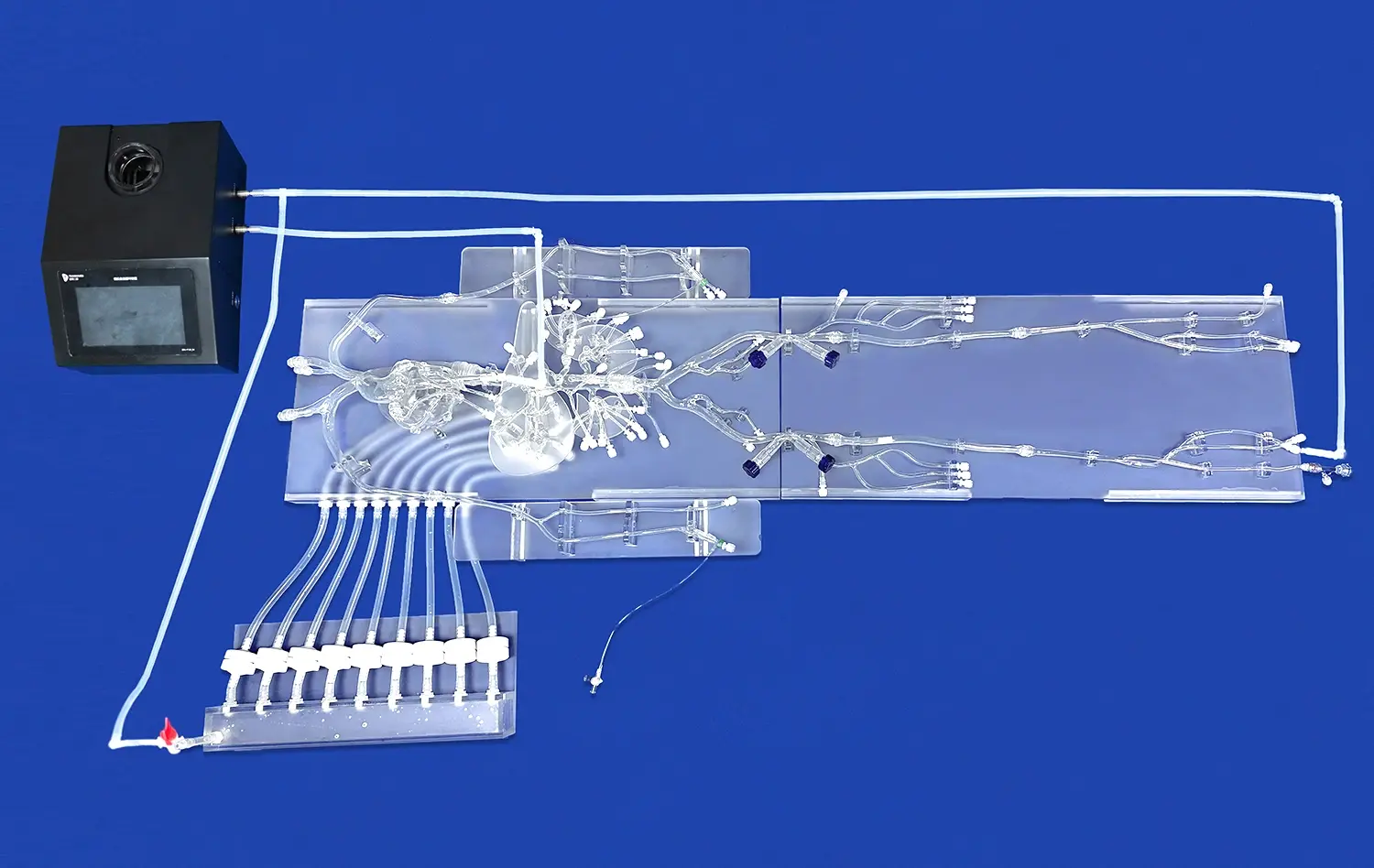
What Anatomical Features Are Best Studied with 3D Models?
Layered Structure of the Stomach Wall
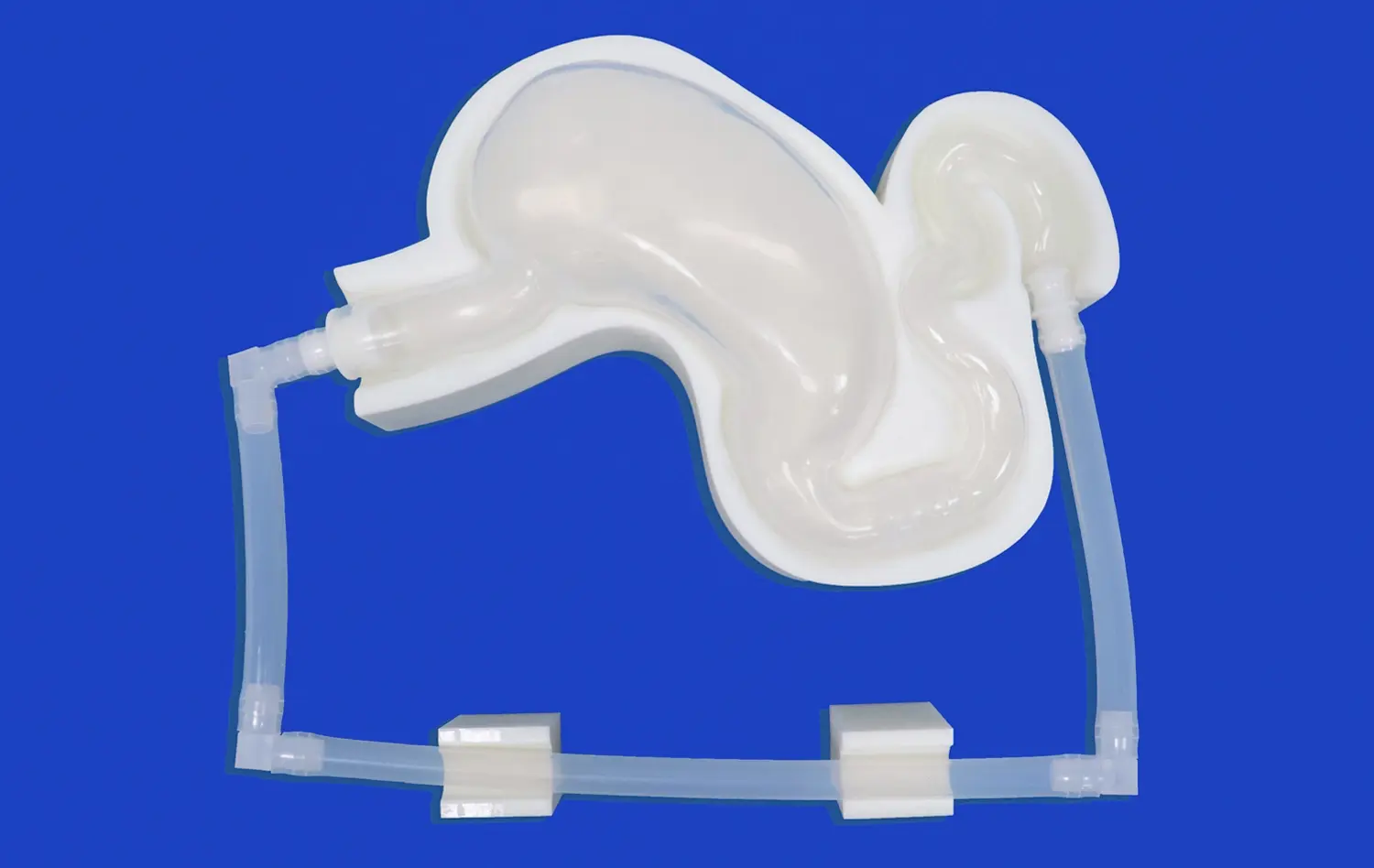
Three-dimensional stomach models excel at demonstrating the complex layered structure of the gastric wall. These models allow learners to examine the four main layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa. The mucosa, with its intricate folds called rugae, is particularly well-represented in 3D models, showcasing how this layer increases the stomach's surface area for optimal digestion. Transparent silicone models, like those produced by Trandomed, offer an exceptional view of these layers, enabling students to visualize how they interact during various digestive processes.
Gastric Vasculature and Innervation
The stomach's rich blood supply and intricate nervous system are best understood through 3D models. These representations can accurately depict the major blood vessels, such as the left and right gastric arteries, as well as the celiac plexus and vagus nerves. By studying these models, medical professionals can gain a clearer picture of how the stomach's blood flow and nerve supply influence its function, which is crucial for understanding various gastrointestinal disorders and planning surgical interventions.
Sphincter Anatomy and Function
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and pyloric sphincter are critical anatomical features that are often challenging to visualize in 2D images. Three-dimensional stomach models provide an excellent opportunity to examine these sphincters in detail. Learners can observe how the LES prevents reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, while the pyloric sphincter regulates the passage of chyme into the duodenum. This enhanced visualization aids in comprehending disorders like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and pyloric stenosis.
Hands-On Exploration of Stomach Structure and Function
Interactive Demonstrations of Gastric Motility
Advanced stomach models allow for dynamic demonstrations of gastric motility. These interactive features enable students to observe and manipulate the model to mimic peristaltic waves and mixing movements. By physically engaging with the model, learners can better understand how the stomach's muscular contractions facilitate the breakdown and movement of food. This hands-on experience is particularly valuable for grasping concepts related to gastric emptying and the mechanical aspect of digestion.
Simulating Gastric Secretions and pH Changes
Some sophisticated stomach models incorporate features that simulate gastric secretions and pH changes. These models may include removable inserts or color-changing elements to represent the production of hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes. By manipulating these components, students can visualize how the stomach's chemical environment changes during the digestive process. This interactive approach helps in understanding the role of gastric juice in protein digestion and the stomach's protective mechanisms against self-digestion.
Exploring Gastric Absorption and Nutrient Processing
While the stomach is not the primary site of nutrient absorption, it does play a role in the initial stages of digestion and the absorption of certain substances. Advanced stomach models can illustrate how the gastric mucosa facilitates the absorption of water, some electrolytes, and certain drugs. By examining these models, learners can gain insights into the stomach's role in the overall digestive process and its interaction with the small intestine. This exploration is particularly useful for pharmaceutical students studying drug absorption and bioavailability.
How Realistic Models Facilitate Mastery of Complex GI Concepts?
Bridging Theoretical Knowledge and Practical Application
Realistic stomach models serve as a crucial bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application in gastroenterology. These models, especially those created using advanced 3D printing techniques like those employed by Trandomed, offer an unprecedented level of detail and accuracy. By interacting with these lifelike representations, medical students and professionals can translate abstract concepts from textbooks into tangible, three-dimensional understanding. This hands-on experience is invaluable for reinforcing anatomical relationships and physiological processes that are difficult to grasp from two-dimensional images alone.
Enhancing Surgical Planning and Technique
In the realm of gastrointestinal surgery, realistic stomach models play a pivotal role in enhancing surgical planning and technique. Surgeons can use these models to visualize complex anatomical structures and practice intricate procedures before entering the operating room. For instance, when planning a gastrectomy or fundoplication, a high-fidelity stomach model allows surgeons to strategize their approach, anticipate potential challenges, and refine their techniques. This pre-operative preparation using realistic models can lead to improved surgical outcomes and reduced complications.
Facilitating Patient Education and Informed Consent
Realistic stomach models are powerful tools for patient education and obtaining informed consent. When explaining gastrointestinal conditions or proposed surgical procedures to patients, healthcare providers can use these models to provide clear, visual explanations. This tangible representation helps patients better understand their anatomy, the nature of their condition, and the proposed treatment. Consequently, patients are more likely to engage in their care decisions and provide truly informed consent. The use of realistic models in patient education can also alleviate anxiety and improve overall patient satisfaction with their healthcare experience.
Conclusion
Stomach models have revolutionized the way we approach gastroenterological education and research. By providing a tangible, three-dimensional representation of complex anatomical structures, these models significantly enhance our understanding of human digestive anatomy. From facilitating the study of intricate gastric layers to enabling interactive demonstrations of stomach function, these models bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. As medical education continues to evolve, the role of realistic stomach models in fostering a deeper comprehension of gastrointestinal concepts and improving surgical outcomes cannot be overstated. Their impact extends beyond the classroom, influencing patient care and advancing our collective knowledge of digestive health.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are committed to advancing medical education and research through our state-of-the-art 3D printed stomach models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of medical simulators, we offer customizable, high-precision stomach models that cater to diverse educational and research needs. Our models, crafted using advanced 3D printing technology and based on real human CT and MRI data, provide unparalleled anatomical accuracy. Whether you're an educational institution, research facility, or healthcare provider seeking to enhance your gastrointestinal training programs, Trandomed is your trusted partner. Experience the difference that our cutting-edge stomach models can make in your understanding of human digestive anatomy. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your educational and research objectives.
_1736215128474.webp)