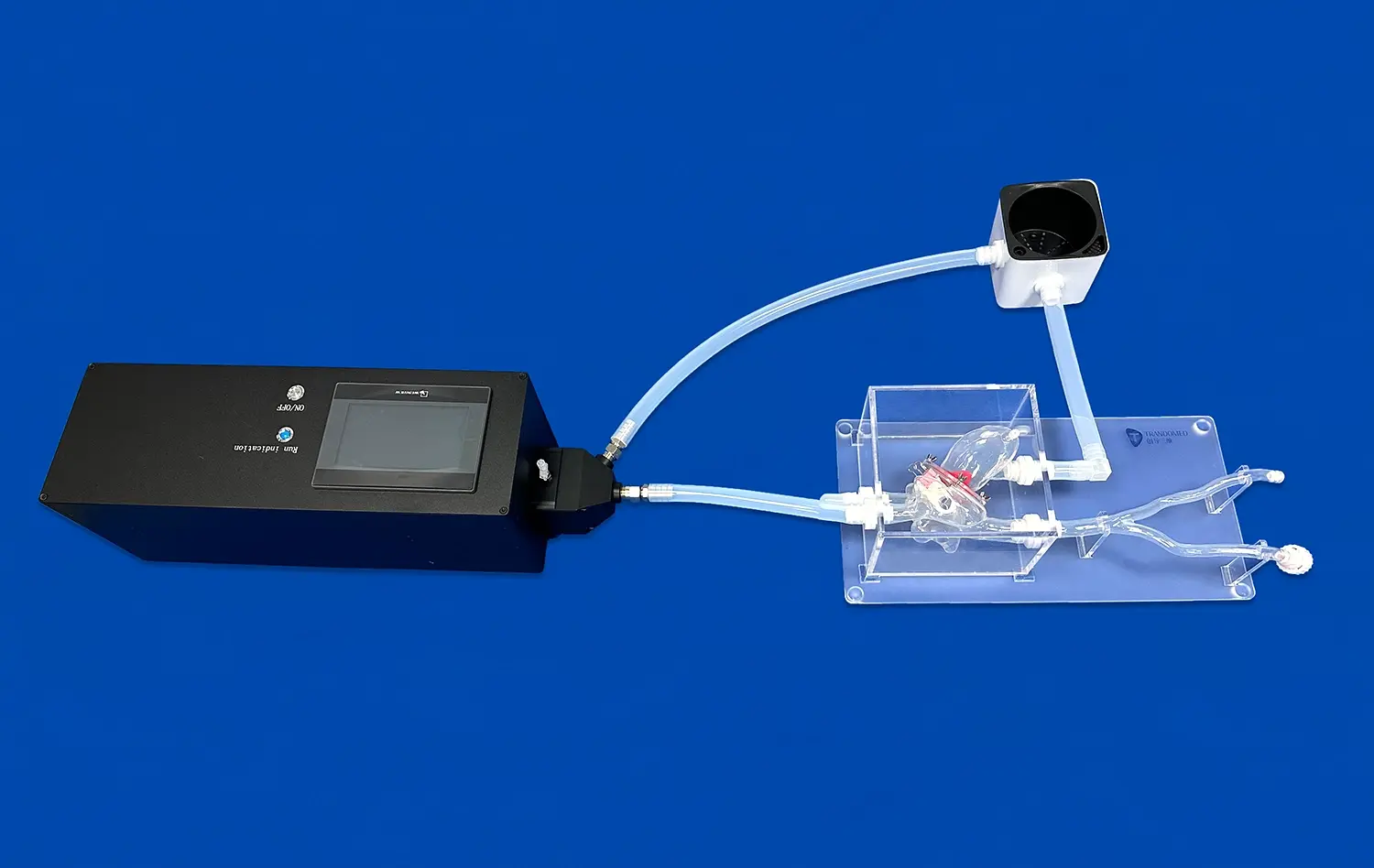
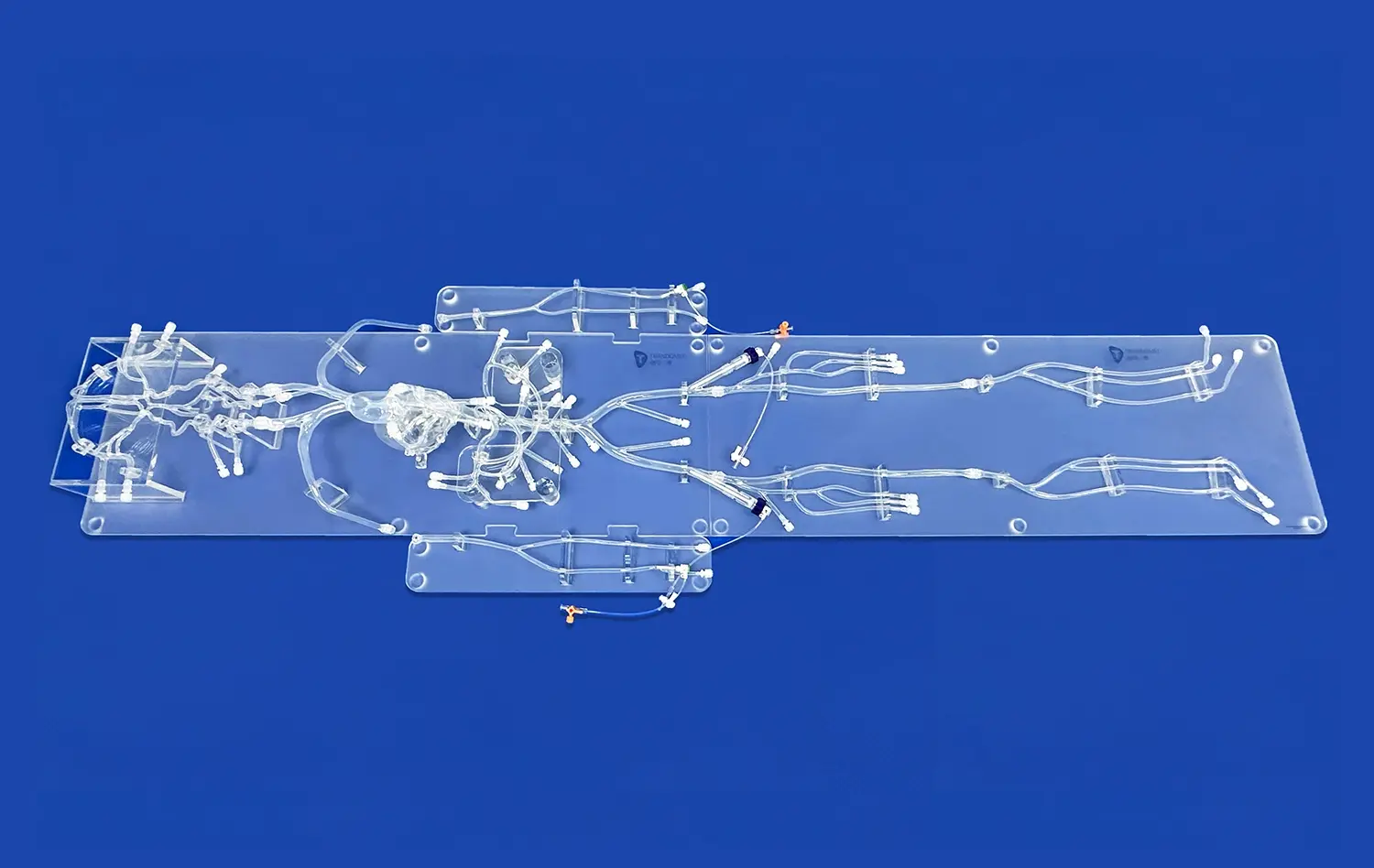
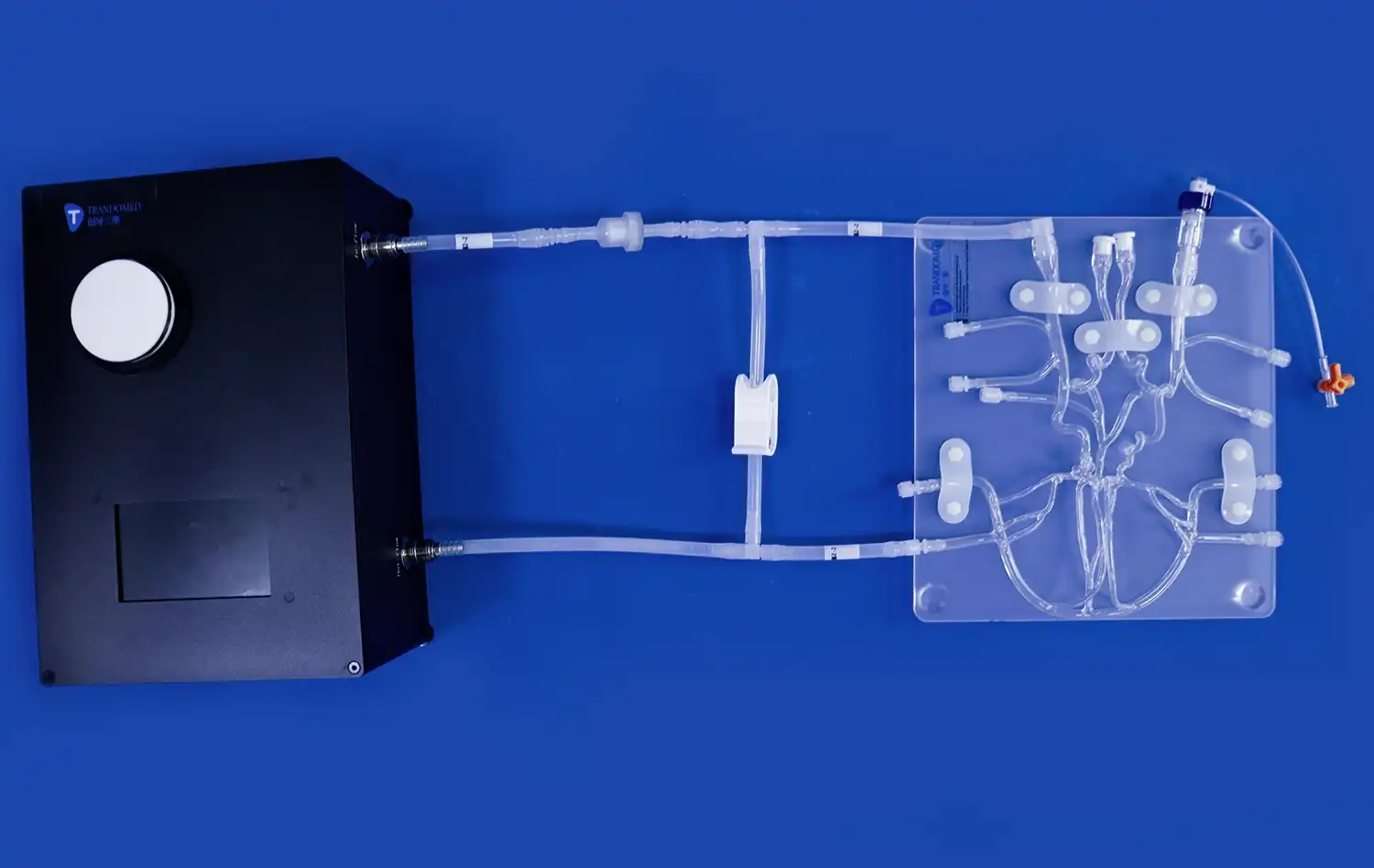
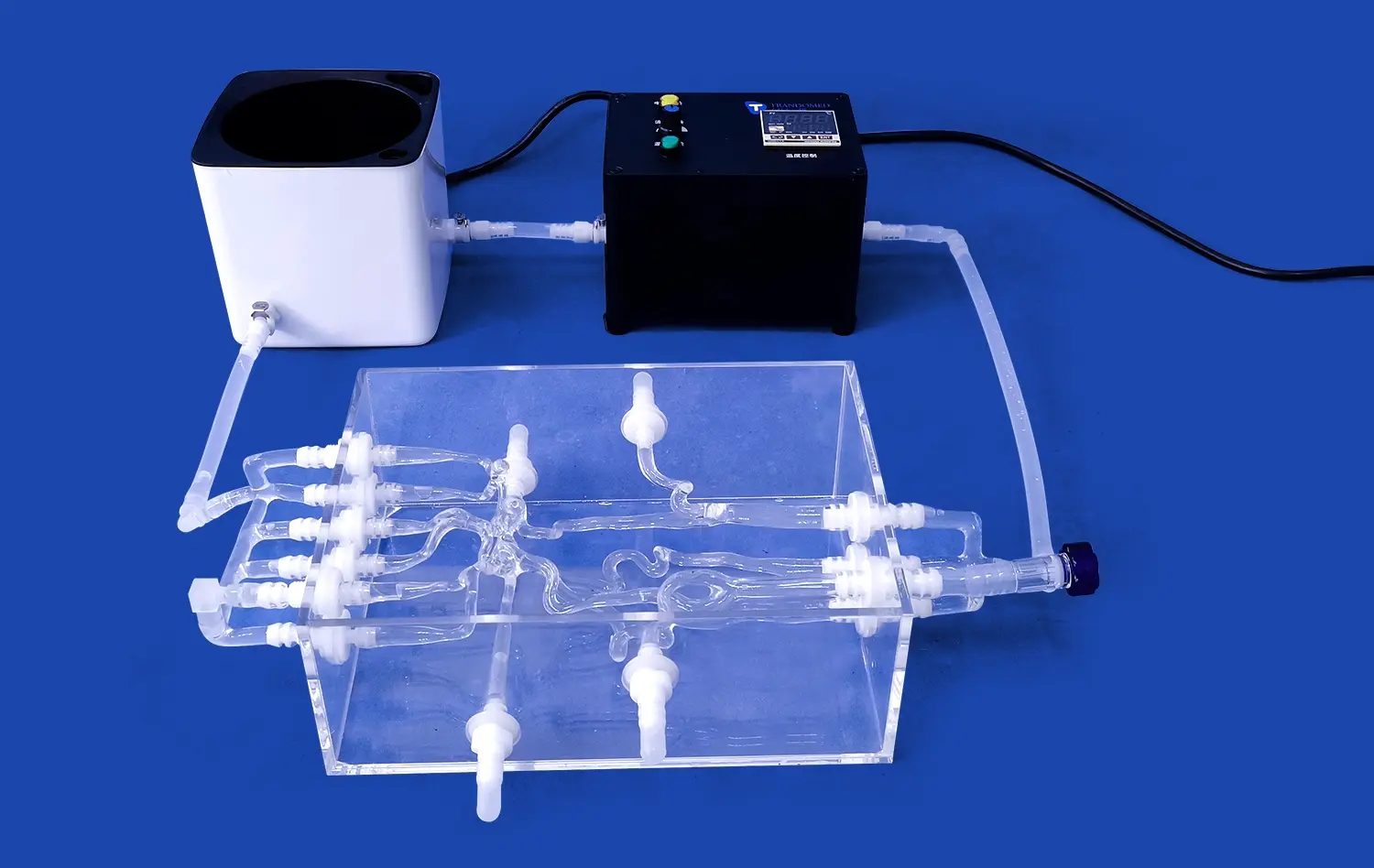
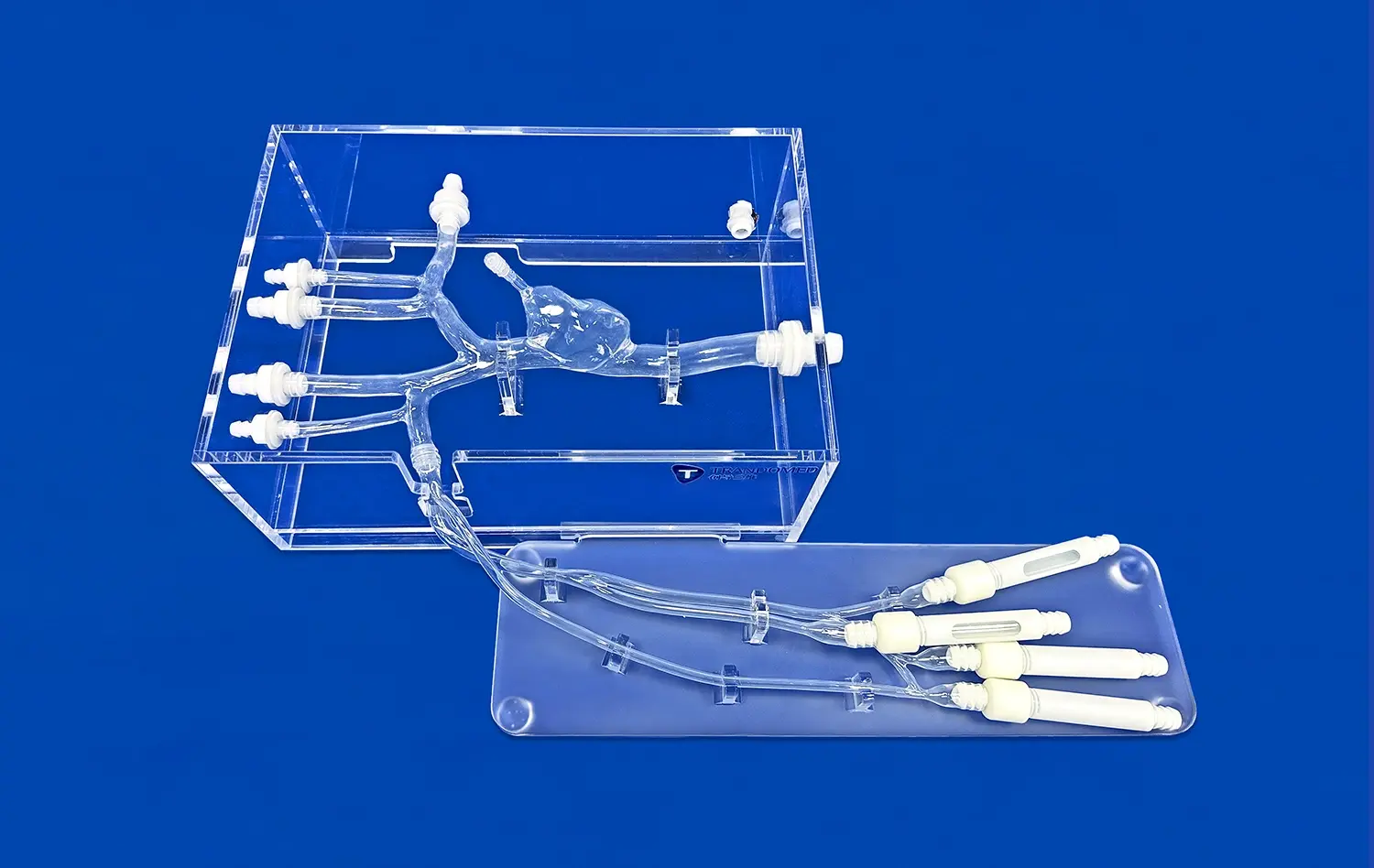
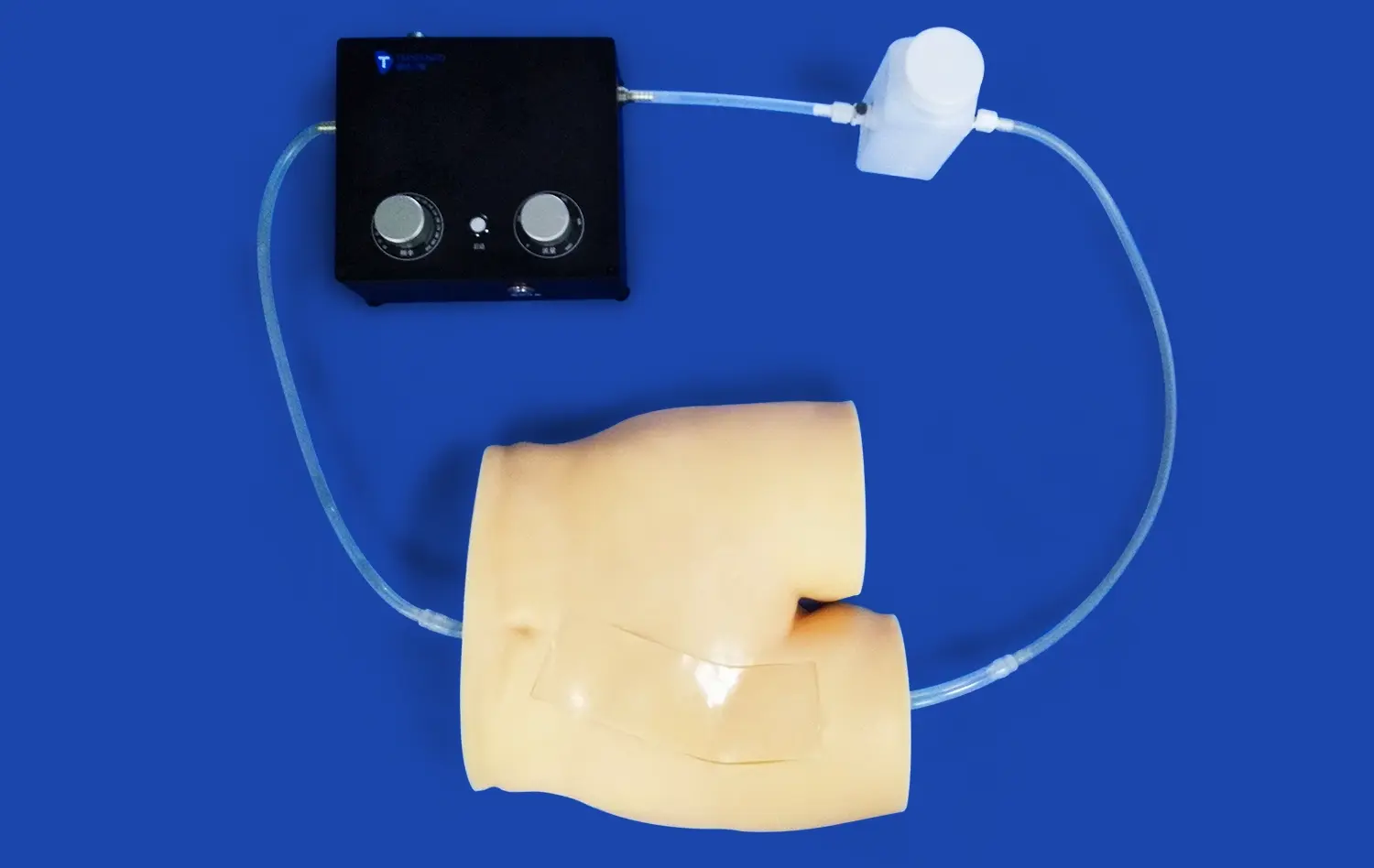
The human stomach model is a huge step forward in testing gastrointestinal devices because it allows for exact anatomical reproduction and lets makers do full tests without ethical issues or biological variability. Using real CT and MRI imaging data as a guide, these highly developed 3D prints have realistic structure layers. They include muscular outer jackets, thick muscle middle layers, and smooth mucosal linings that make the model's stomachs feel and act like real ones. This new thing lets makers of medical devices speed up the time it takes to build new products while still making sure that safety and effectiveness standards are met.
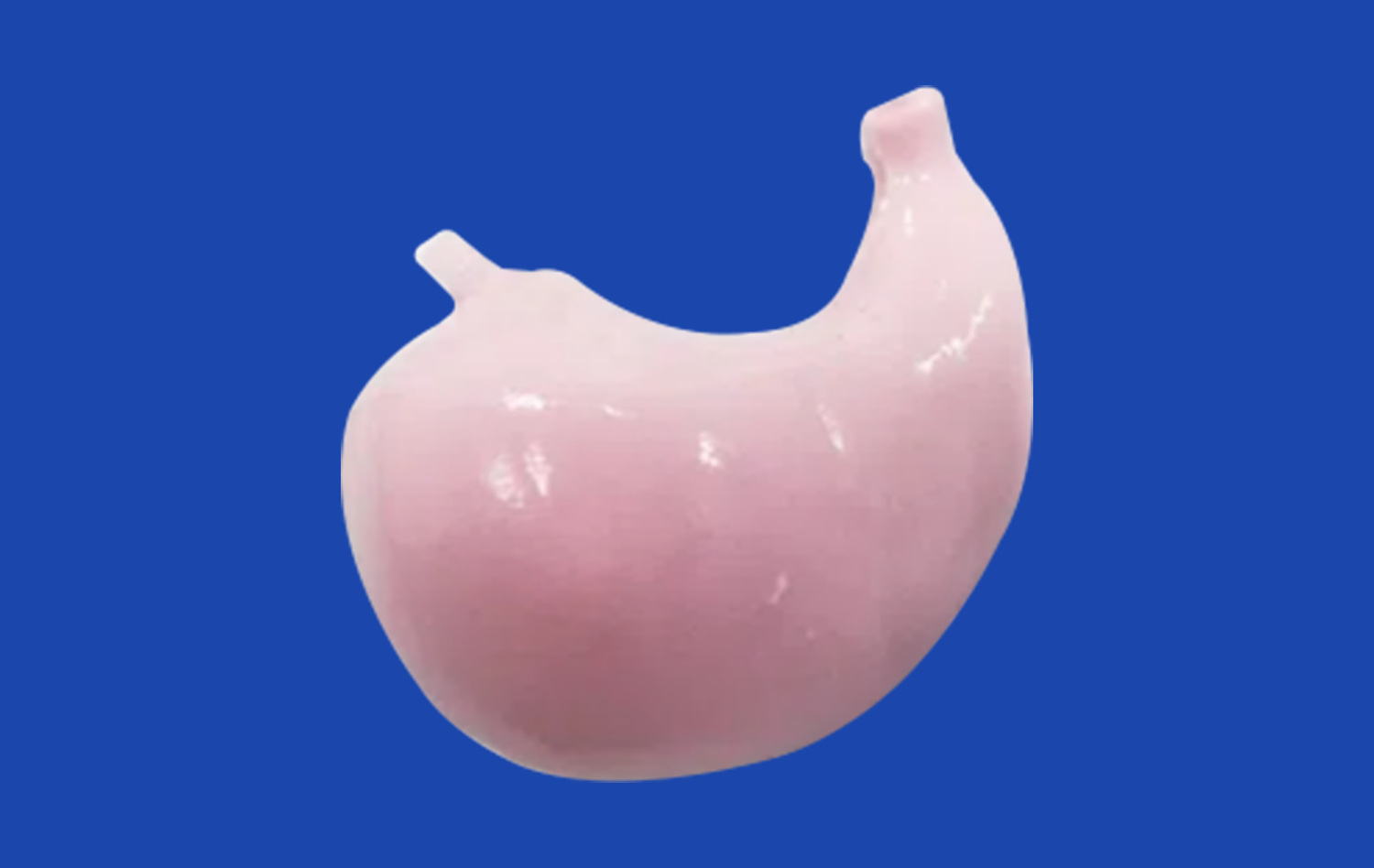
Understanding the Role of Human Stomach Models in Gastrointestinal Device Testing
Anatomical computer models are very important because they connect ideas about how to make something with real-world medical uses. The advanced engineering behind these stomach models makes it possible to do full device tests that could not be done before with other testing methods.
Anatomical Accuracy and Structural Precision
Today's stomach models have been made with care to include traits that look like real human bodies. These models have detailed structural parts, like anatomical sections that are identified and parts that can be taken off to allow for more in-depth study. The precision manufacturing method uses reverse 3D reconstruction technology to make sure that each model is exactly the right size based on imaging data from real patients.
The multi-layered build copies the natural make-up of the stomach, which gives a true testing space for a range of gastrointestinal devices. Engineers can study how devices work with different kinds of tissue, from the muscle walls on the outside to the inner mucosal surfaces, giving them a full picture of how they work.
Mechanical Properties and Functional Simulation
Advanced stomach models show mechanical qualities that are very similar to the way real tissue works. These features make it possible to realistically mimic the movements of the stomach, the forces that make things contract, and the interactions between the surface and other objects. These are all very important for making sure that the device is properly tested. The materials used keep the same properties after each test run, which guarantees that the results are reliable and can be repeated.
It can do more than just show a picture of the anatomy; it can also show how the digestive system works in real time, including changes in pH and the pressure that happens when the stomach is working normally. This all-inclusive method gives device makers detailed information about how their products work in situations that are realistic for the human body.
Challenges in Traditional Gastrointestinal Device Testing and How Models Solve Them
Standard ways of testing face a lot of problems that can have a big effect on how long it takes to make something new and on the results of the study. Knowing these limits makes it clear how much of a difference anatomical human stomach models have made in the medical device business.
Ethical and Regulatory Constraints
Using traditional tests means doing a lot of studies on live animals or samples from dead bodies, which raises a lot of ethics concerns and makes it harder to follow the rules. These methods have to get approved in a long, complicated process, need special buildings, and cost a lot of money, which can delay the development of new products for a long time.
Anatomical models get rid of these ethical issues and provide testing settings that are always the same and can be done again and again. Research teams can do long reviews without having to follow rules, which lets them make devices even better and make sure they work. This method encourages responsible progress while upholding strict testing rules.
Variability and Reproducibility Issues
Biological samples naturally show differences that can confuse the results of tests and make it harder to understand the data. Things like age, health, and differences in the bodies of the people being tested create factors that make standardized testing difficult.
Stomach models get around these issues by offering a uniform test tool that gets rid of biological differences. Each model has the same specs, which lets researchers figure out how the performance of each device varies and get results that can be repeated in different test sessions. This consistency speeds up the development stages and makes the data more reliable.
Cost and Logistical Considerations
Traditional testing methods often cost a lot because of the need to get samples, meet special keeping needs, and follow the rules. These costs can get out of hand, especially for smaller medical device companies or study groups that don't have a lot of money.
It is clear that skeletal models are good for the economy because they can be used more than once and don't need as much work to be used. One high-quality stomach model can be used for hundreds of tests. This keeps the test standards constant and lowers the cost per test by a lot.
Selecting the Best Human Stomach Model for Device Testing
Choosing the right anatomical models needs to be thought through carefully with specific testing needs, performance standards, and operating limits in mind. To make sure that they get the best value and performance, procurement managers and experts must look at a lot of different things.
Technical Specifications and Features
Good stomach models show a number of important traits that show how well they can be used for gadget testing. The materials used are very important; for example, advanced polymers make the product feel like tissue paper but keep it strong through many rounds of use.
The Trandomed Human Stomach Model (Product No. HSX006) is an example of these quality standards because it was made using data from real patients' CT and MRI scans. This model has real anatomy layering. The stomach is made up of thin muscular layers on the outside, thick layers of muscle in the middle, and smooth mucosal linings.
Customization and Integration Capabilities
These days, testing devices often needs to be set up in certain ways to meet certain study goals or to work with certain device features. Top manufacturers offer extensive customization services that make it possible to change models in exact ways without charging extra for design changes.
Trandomed offers a lot of different ways to customize things, like making models directly from a client's CT or MRI data, designs based on CAD, and the ability to make things right at the plant. This ability to adapt makes sure that each model can meet certain testing needs while still keeping high quality standards.
Procurement and Support Considerations
When businesses buy things, they need to know more about suppliers than just the general details about the products. Lead times, shipping options, technical support, and after-sales service are all important factors that affect the total value propositions.
Trustworthy suppliers usually send quickly, with a minimum of 7 to 10 days' notice for standard models. Many shipping choices, like FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT, make sure that the delivery can be planned in a way that works with urgent testing schedules and needs from around the world.
Integrating Human Stomach Models into the Device Development Process
Successful implementation of anatomical models requires strategic integration into existing development workflows and testing protocols. This process involves establishing standardized procedures, training personnel, and optimizing testing methodologies.
Protocol Development and Standardization
Effective integration begins with developing comprehensive testing protocols that leverage the unique capabilities of stomach models. These protocols should establish standardized procedures for model preparation, device installation, testing execution, and data collection.
The versatility of advanced models enables complex system integration, supporting comprehensive device evaluations that encompass multiple performance parameters simultaneously. This capability facilitates more efficient testing cycles and provides deeper insights into device behavior under various conditions.
Collaborative Testing and Innovation
Anatomical models facilitate enhanced collaboration between engineering teams, medical professionals, and regulatory specialists throughout the development process. The visual and tactile nature of these models enables more effective communication regarding design concepts and performance requirements.
Iterative testing cycles become more practical and cost-effective, enabling rapid prototyping and design optimization. Development teams can quickly evaluate multiple design variations and implement improvements based on comprehensive performance data.
Future Technology Integration
Emerging technologies promise to enhance the capabilities of anatomical models through digital integration and advanced materials. Future developments may include real-time sensor integration, digital feedback systems, and enhanced material properties that further improve testing accuracy.
These technological advances will position stomach models as increasingly sophisticated tools that support more comprehensive device evaluation and accelerate innovation in gastrointestinal medical devices.
Trandomed's Advanced Solutions for Medical Device Testing
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (Trandomed) specializes in developing high-fidelity anatomical human stomach models tailored specifically for medical device testing applications. With over 20 years of experience in medical 3D printing innovation, we provide comprehensive solutions that meet the demanding requirements of modern device development.
Manufacturing Excellence and Quality Control
Our manufacturing process utilizes advanced 3D printing technologies combined with rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent product excellence. Each model undergoes comprehensive inspection procedures that verify anatomical accuracy, material properties, and functional performance.
The company maintains complete control over the production process through factory-direct manufacturing capabilities, enabling rapid response to custom requirements while maintaining strict quality standards. This approach ensures reliable delivery schedules and consistent product quality across all orders.
Global Support and Service Network
Trandomed provides comprehensive after-sales support including technical guidance, maintenance assistance, and customization consultation. Our global reach enables us to serve institutions worldwide with scalable solutions appropriate for both small research projects and large-scale procurement requirements.
The company's commitment to customer success extends beyond initial product delivery, providing ongoing support that ensures optimal model performance throughout extended testing campaigns.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced stomach models into gastrointestinal device testing represents a significant advancement in medical device development methodologies. These sophisticated tools provide unprecedented accuracy, consistency, and flexibility that enable more effective device evaluation while reducing ethical concerns and operational costs. The combination of anatomical precision, mechanical authenticity, and operational convenience positions these models as essential resources for modern medical device development. As technology continues advancing, stomach models will play increasingly important roles in accelerating innovation and improving patient outcomes through more effective medical devices.
FAQs
What makes a human stomach model suitable for gastrointestinal device testing?
A suitable stomach model combines anatomical precision based on real patient imaging data, material durability for repeated testing cycles, and mechanical properties that closely mimic natural tissue behavior. The model should feature authentic structural layers and compatibility with complex testing systems to enable comprehensive device evaluation.
Can human stomach models reproduce the dynamic environment of a real stomach?
Yes, advanced stomach models simulate mechanical movements, surface interactions, and physiological conditions including pH variations and contractile forces. These dynamic capabilities enable realistic testing scenarios that closely approximate natural gastric environments during device operation.
How long does it typically take to receive a custom human stomach model order?
Standard delivery times range from 7-10 days for most configurations, while custom models based on specific CT or MRI data may require additional time depending on complexity. Established suppliers like Trandomed offer expedited shipping options through multiple carriers to accommodate urgent testing schedules.
Partner with Trandomed for Advanced Stomach Model Solutions
Trandomed stands ready to support your gastrointestinal device testing requirements with industry-leading anatomical models and comprehensive customization services. As a trusted human stomach model supplier with over two decades of medical 3D printing expertise, we provide reliable solutions that accelerate device development while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Our experienced team offers personalized consultation services to help select optimal model configurations for your specific testing requirements. Whether you need standard models for routine testing or custom solutions based on patient-specific imaging data, we provide flexible options that support your research objectives.
Take advantage of our factory-direct manufacturing capabilities and global shipping network to streamline your procurement process. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your requirements and discover how our advanced stomach models can enhance your device development programs.
References
Johnson, M.K., et al. "Advanced 3D Printing Technologies in Medical Device Development: Applications and Validation Methods." Journal of Medical Engineering Technology, Vol. 45, 2023, pp. 234-251.
Chen, L.W., and Rodriguez, A.P. "Anatomical Model Fidelity in Gastrointestinal Device Testing: Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Modern Approaches." Medical Device Innovation Quarterly, Vol. 18, No. 3, 2023, pp. 89-104.
Thompson, R.J., et al. "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Anatomical Simulation Models in Medical Device Development." Healthcare Technology Economics Review, Vol. 29, 2022, pp. 156-172.
Williams, S.D., and Park, K.H. "Regulatory Considerations for Medical Device Testing Using Anatomical Models: Current Guidelines and Future Directions." Regulatory Affairs in Medical Technology, Vol. 12, 2023, pp. 45-62.
Martinez, C.E., et al. "Material Science Advances in Anatomical Model Development for Medical Applications." Biomedical Materials Research Journal, Vol. 67, No. 4, 2023, pp. 445-461.
Anderson, P.L., and Kumar, V.S. "Integration of 3D Anatomical Models in Medical Device Validation Protocols: Best Practices and Implementation Strategies." Medical Device Development Review, Vol. 31, 2023, pp. 78-95.