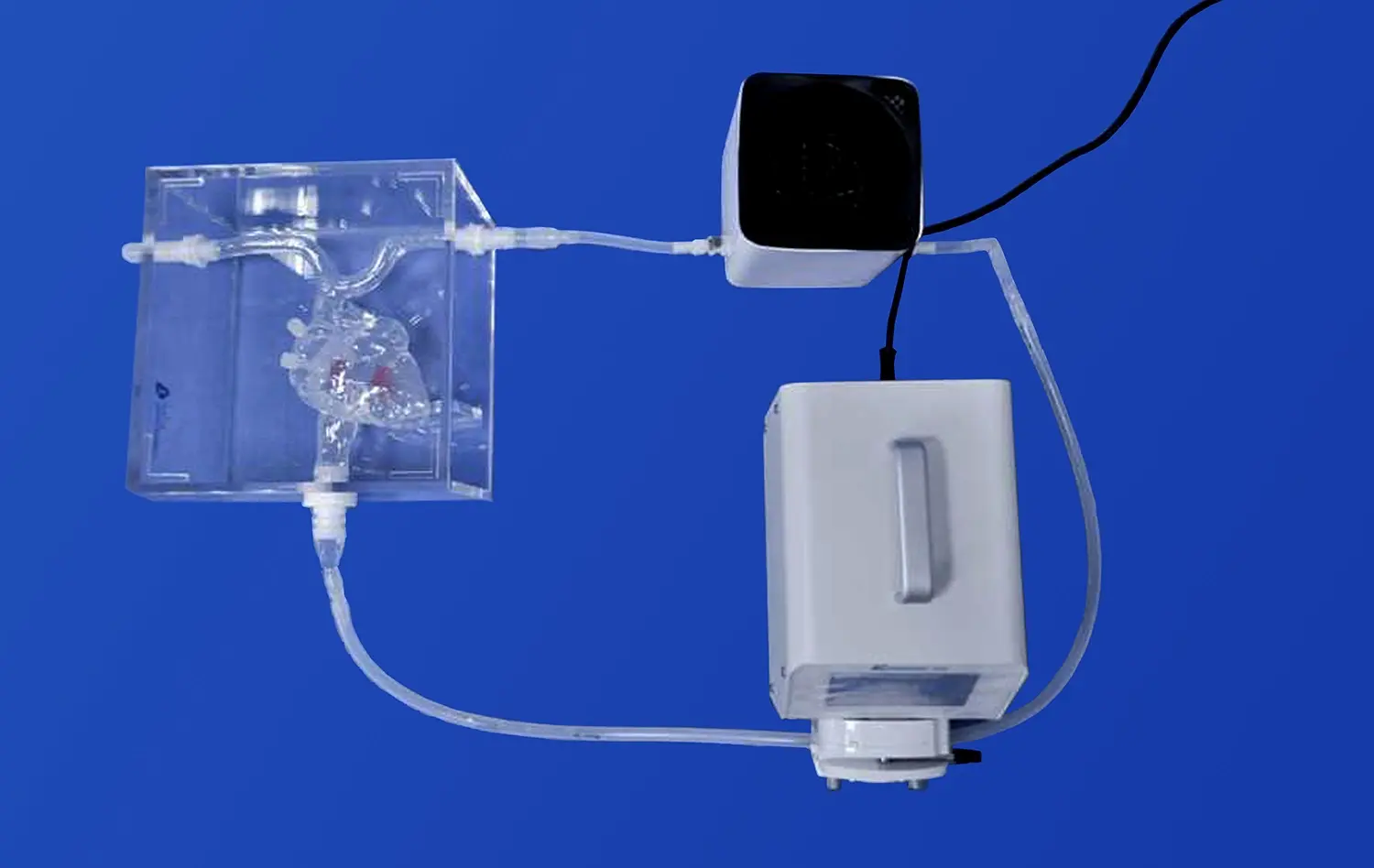
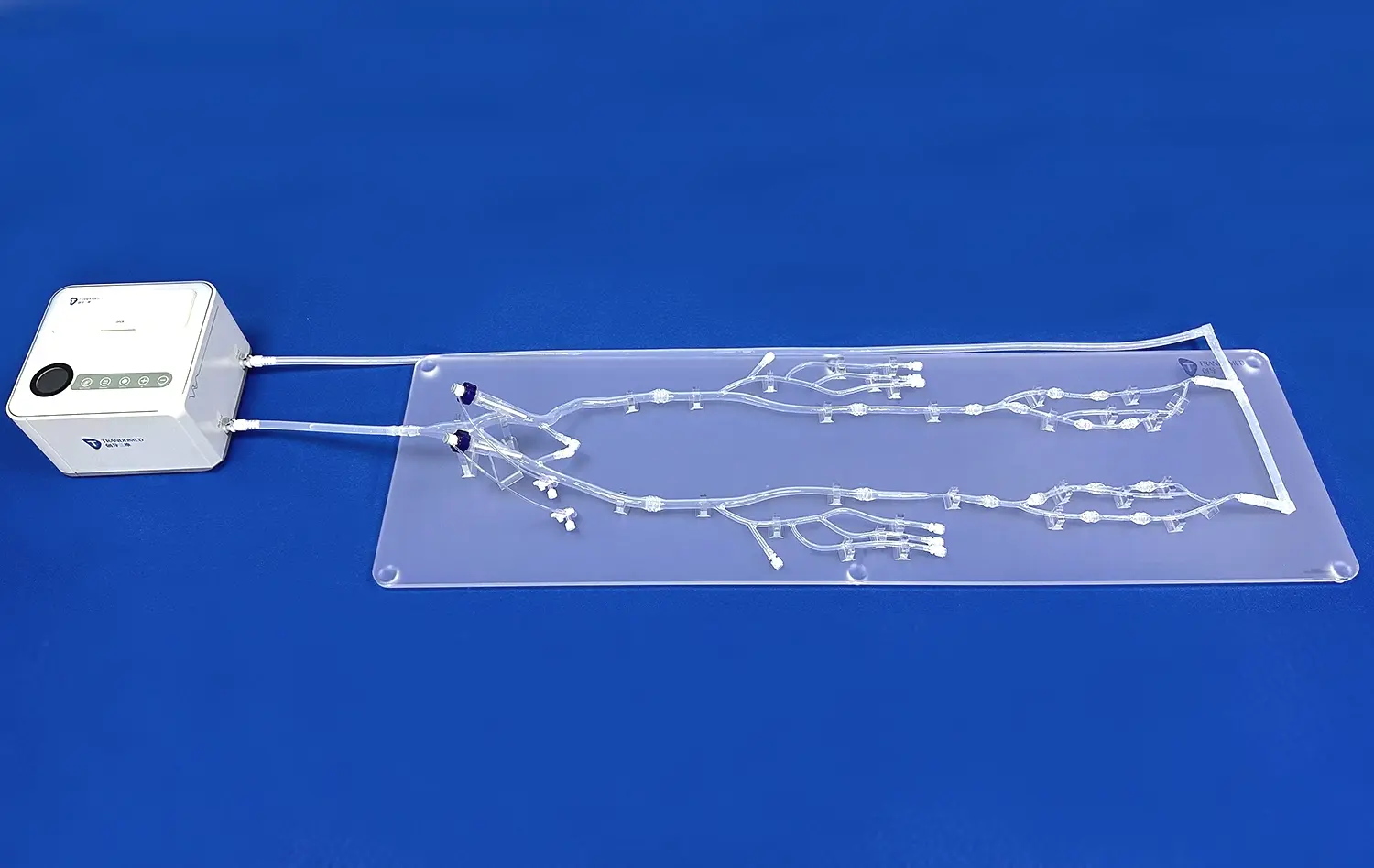
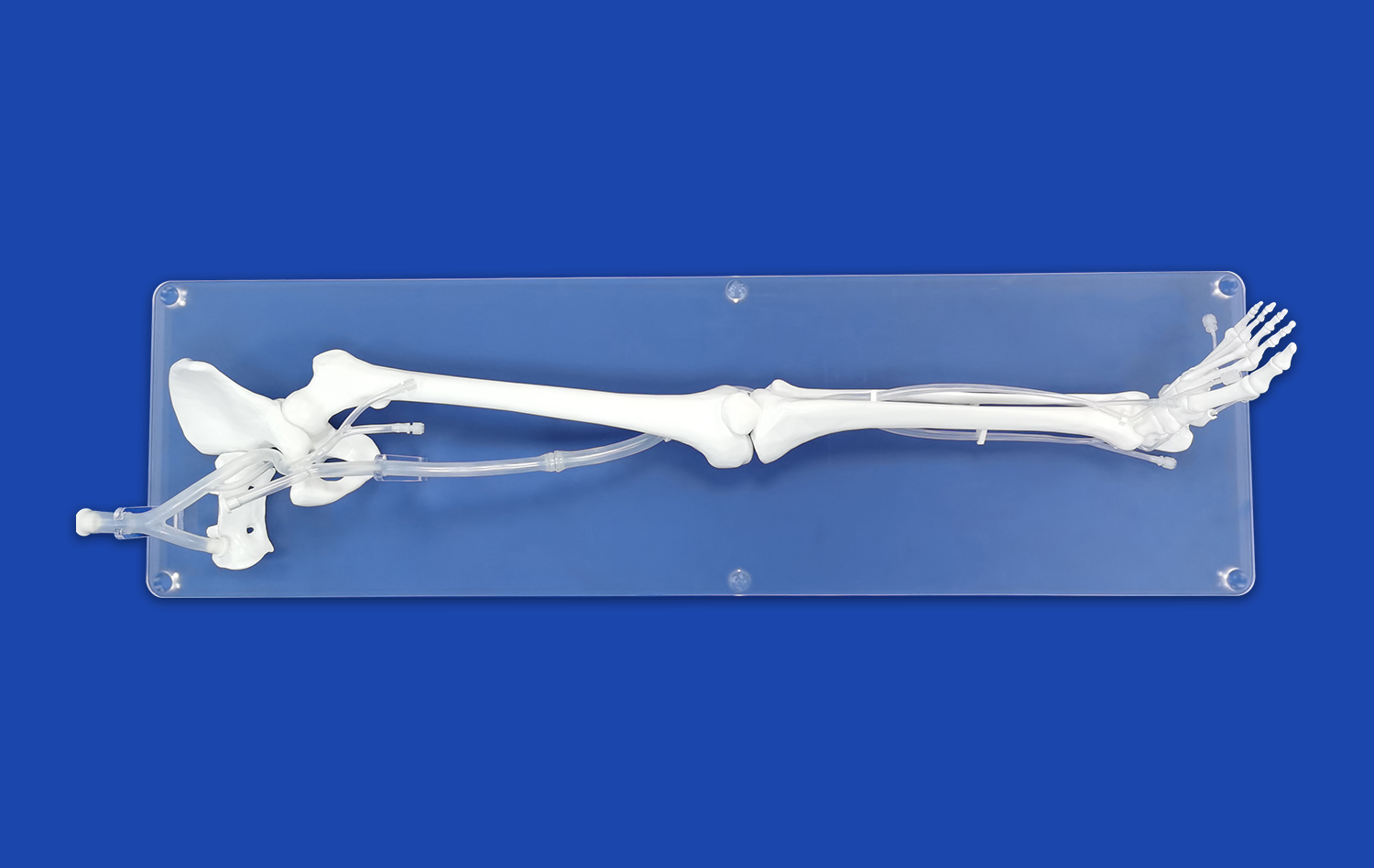
What Makes the Lower Extremity Artery Model Ideal for Endovascular Skill Development?
Anatomical Precision and Realism
The lower extremity artery model excels in anatomical precision, offering a lifelike representation of the vascular system. Crafted using advanced 3D printing technology and based on actual CT data, these models capture intricate details of arterial structures. This level of accuracy allows trainees to familiarize themselves with the complex network of vessels, including major arteries like the femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries, as well as their branches and variations.
The model's realism extends beyond visual aspects. The use of silicone with a Shore hardness of 40A closely mimics the texture and elasticity of human blood vessels. This tactile similarity enables practitioners to develop a genuine feel for navigating through arteries, encountering resistances, and managing vessel walls during simulated procedures.
Pathological Variability
One of the standout features of the lower extremity artery model is its ability to replicate various pathological conditions. Trainees can practice interventions on models simulating common vascular issues such as atherosclerosis, stenosis, and aneurysms. This pathological variability allows for a comprehensive training experience, preparing interventionalists for a wide range of clinical scenarios they may encounter in real practice.
The ability to customize models based on specific patient data further enhances this aspect. Institutions can request models that reflect rare or complex cases, ensuring that trainees are exposed to a diverse array of vascular conditions and anatomical variations.
Procedural Versatility
The lower extremity artery model supports a wide range of endovascular procedures, making it an invaluable tool for comprehensive skill development. Trainees can practice techniques such as guidewire navigation, catheter placement, balloon angioplasty, and stent deployment. The model's design allows for the use of actual medical devices, providing a realistic feel for tool manipulation and device deployment.
Moreover, the model's compatibility with imaging systems like fluoroscopy enhances the training experience. Practitioners can develop skills in image interpretation and navigation, crucial aspects of successful endovascular interventions. This integration of imaging with hands-on practice creates a holistic learning environment that closely mirrors real-world procedural settings.
Simulation-Based Learning for Vascular Intervention
Bridging Theory and Practice
Simulation-based learning using the lower extremity artery model serves as a crucial bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application in vascular intervention training. This approach allows trainees to apply their understanding of vascular anatomy and pathophysiology in a controlled, risk-free environment. By manipulating actual endovascular tools within the model, practitioners can translate conceptual knowledge into tangible skills.
The model facilitates a gradual progression from basic to advanced techniques. Novice practitioners can start with simple guidewire navigation and catheter placement, gradually advancing to more complex procedures like crossing chronic total occlusions or managing bifurcation lesions. This stepwise approach ensures a solid foundation of skills before tackling more challenging scenarios.
Repetitive Practice and Skill Retention
One of the key advantages of simulation-based learning with the lower extremity artery model is the opportunity for repetitive practice. Unlike real-world scenarios where each procedure is unique and irreversible, the model allows trainees to repeat techniques multiple times, refining their skills with each iteration. This repetition is crucial for developing muscle memory and improving procedural efficiency.
Studies have shown that skills acquired through simulation training have better retention rates compared to traditional learning methods. The hands-on nature of practicing with the lower extremity artery model creates stronger neural pathways, leading to improved long-term skill retention. This is particularly beneficial for procedures that may be encountered less frequently in clinical practice but require a high level of expertise when needed.
Team-Based Training and Communication
The lower extremity artery model is not limited to individual skill development; it also serves as an excellent platform for team-based training. Vascular interventions often involve multiple healthcare professionals working in concert. The model allows for the simulation of entire procedures, including pre-operative planning, intra-operative communication, and post-operative care.
Teams can practice scenarios that require coordinated efforts, such as managing complications or performing time-sensitive interventions. This collaborative approach improves not only technical skills but also enhances communication, leadership, and decision-making abilities within the team. By simulating high-stress situations in a controlled environment, healthcare professionals can develop the teamwork and crisis management skills essential for optimal patient care.
How 3D Anatomical Accuracy Improves Clinical Competence and Confidence?
Enhanced Spatial Awareness
The 3D anatomical accuracy of the lower extremity artery model significantly enhances spatial awareness among trainees. Unlike 2D images or textbook illustrations, the model provides a tangible, three-dimensional representation of vascular structures. This allows practitioners to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the spatial relationships between arteries, surrounding tissues, and potential anatomical variations.
Improved spatial awareness translates directly to better procedural skills. Trainees can visualize the path of guidewires and catheters through complex arterial networks, anticipating challenges and planning optimal approaches. This enhanced perception of depth and orientation is particularly crucial when navigating tortuous vessels or addressing lesions in hard-to-reach locations.
Realistic Procedural Feedback
The anatomical accuracy of the lower extremity artery model provides realistic procedural feedback, a critical component in developing clinical competence. The model's fidelity in replicating vessel elasticity, resistance, and response to interventions offers trainees immediate and accurate feedback on their actions. This tactile feedback is essential for developing the fine motor skills and tactile sensitivity required in endovascular procedures.
Trainees can experience the subtle nuances of different techniques, such as the feel of a guidewire crossing a stenosis or the resistance encountered during balloon inflation. This realistic feedback helps in building a repertoire of sensory cues that inform decision-making during actual procedures, enhancing overall clinical judgment and competence.
Confidence Building Through Familiarity
Regular practice with anatomically accurate models builds confidence by fostering familiarity with vascular structures and procedural steps. As trainees repeatedly interact with the lower extremity artery model, they become more comfortable with the intricacies of vascular anatomy and the challenges associated with different interventions.
This increased familiarity translates to greater confidence in clinical settings. Practitioners who have extensively trained on accurate models are better prepared to handle variations and complications they may encounter in real patients. The confidence gained through simulation training can lead to more assured decision-making, smoother procedure execution, and improved patient communication – all crucial aspects of successful vascular interventions.
Conclusion
The lower extremity artery model has emerged as a transformative tool in vascular intervention training, offering unparalleled benefits in skill development, procedural familiarity, and clinical confidence. Its anatomical accuracy, pathological variability, and procedural versatility provide a comprehensive platform for hands-on learning. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, facilitating repetitive training, and enhancing spatial awareness, the model significantly accelerates the learning curve for endovascular procedures. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of such high-fidelity simulation tools promises to elevate the standard of vascular intervention training, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and safer medical practices.
Contact Us
Elevate your institution's vascular intervention training program with Trandomed's cutting-edge lower extremity artery models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D printed medical simulators, we offer unmatched quality, customization options, and expert support. Experience the difference that anatomical accuracy and advanced simulation can make in developing skilled endovascular practitioners. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore how our innovative products can transform your training approach and contribute to better patient care outcomes.

_1734504221178.webp)
_1732863962417.webp)