How to Train for Carotid Artery Stenosis with an Endovascular Intervention Trainer?
2025-08-14 09:00:01
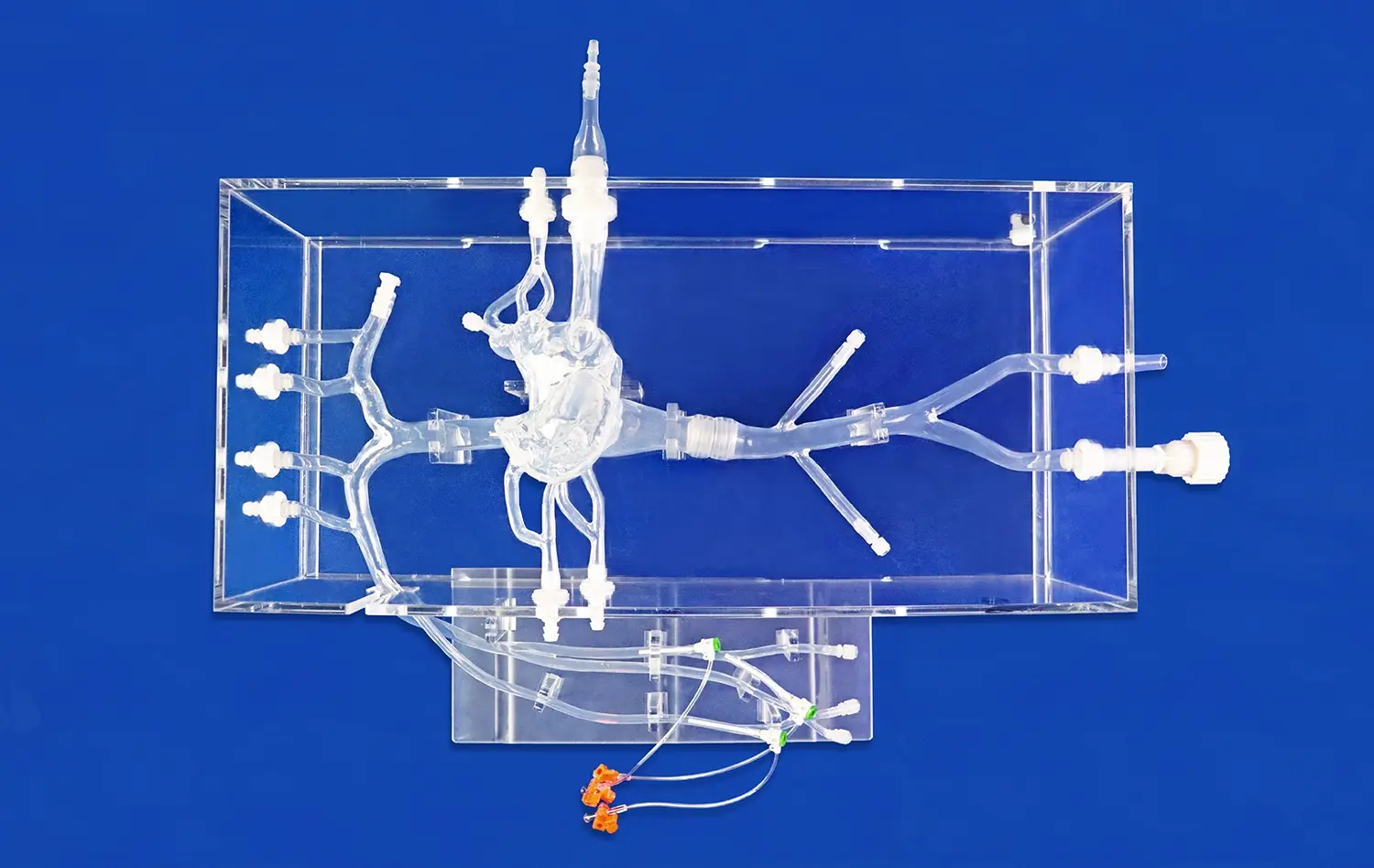
Training for carotid artery stenosis procedures using an endovascular intervention trainer offers medical professionals a safe, realistic environment to hone their skills. These advanced simulators replicate the intricate vascular anatomy and allow practitioners to practice critical techniques without risk to patients. By utilizing a high-fidelity endovascular simulator, interventionalists can repeatedly perform angioplasty, stenting, and embolic protection device placement - refining their abilities to navigate tortuous vessels, deploy devices accurately, and manage potential complications. The immersive training experience on an endovascular intervention trainer enhances procedural confidence, improves hand-eye coordination, and ultimately leads to better patient outcomes in real clinical scenarios involving carotid artery stenosis.
What Techniques Are Best Simulated in Carotid Artery Procedures?
Catheter Navigation and Wire Manipulation
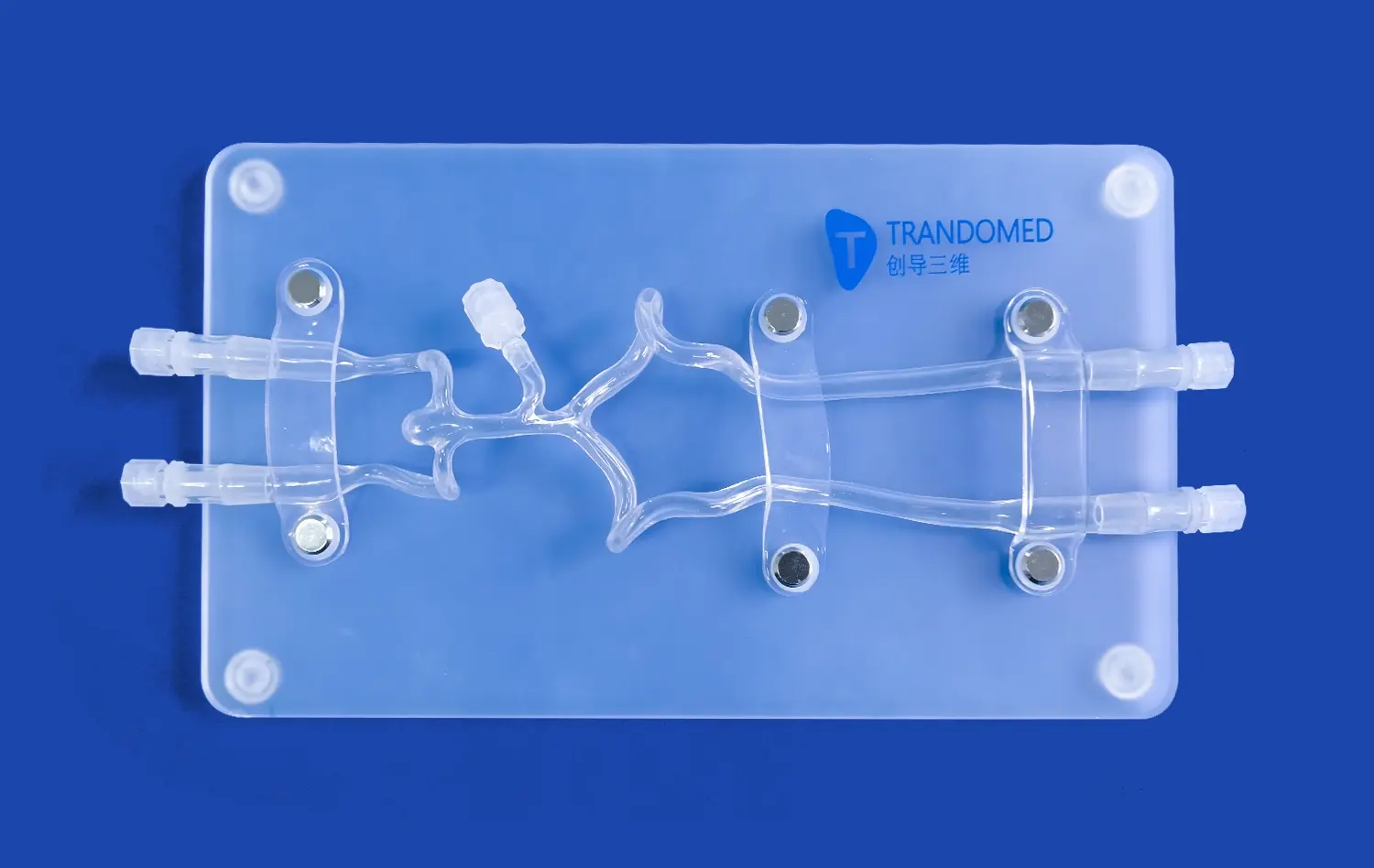
Mastering catheter navigation and wire manipulation is crucial for successful carotid artery interventions. An endovascular simulator allows trainees to practice these fundamental skills in a realistic vascular model. The silicone-based vessels in high-quality trainers like those offered by Trandomed replicate the elasticity and friction of actual arteries, providing authentic tactile feedback. Practitioners can refine their ability to navigate the aortic arch, select the common carotid artery, and advance guidewires and catheters through tortuous anatomy. This hands-on experience is invaluable for developing the dexterity and finesse required for challenging cases.
Angiographic Imaging Interpretation
Accurate interpretation of angiographic images is essential for diagnosing stenosis severity and guiding interventions. Advanced endovascular intervention trainers incorporate simulated digital subtraction angiography (DSA) systems that mimic real-time fluoroscopic imaging. Trainees can practice optimal C-arm positioning, contrast injection timing, and image capture techniques. By repeatedly performing angiograms on various simulated pathologies, interventionalists enhance their ability to assess lesion characteristics, vessel tortuosity, and collateral circulation. This imaging experience translates directly to improved decision-making in live cases.
Device Selection and Deployment
Choosing appropriate devices and deploying them precisely is critical in carotid artery procedures. Endovascular intervention trainers allow practitioners to experiment with a wide array of stents, balloons, and embolic protection devices. The modular design of advanced simulators enables customization of lesion types, allowing practice on eccentric stenoses, calcified plaques, and tortuous segments. Trainees can perfect their technique for precise stent sizing, positioning, and deployment. The ability to practice these skills repeatedly in a consequence-free environment builds confidence and proficiency that directly benefits patient care.
Step-by-Step Practice of Stenting and Angioplasty in Stenotic Segments
Pre-procedural Planning and Access
Effective training for carotid artery stenting begins with thorough pre-procedural planning. Using an endovascular intervention trainer, practitioners can analyze simulated CT or MRI data to assess lesion characteristics, vessel anatomy, and potential access routes. This planning phase is crucial for selecting appropriate devices and anticipating potential challenges. Trainees can then practice various access techniques, including femoral and radial approaches, honing their skills in achieving stable arterial access while minimizing complications. The realistic tactile feedback provided by high-quality simulators enhances the learning experience, closely mimicking the feel of actual patient procedures.
Lesion Crossing and Pre-dilation
Once access is established, the next critical step is navigating the stenotic lesion. Endovascular intervention trainers allow practitioners to refine their wire and catheter skills in crossing tight, eccentric, or calcified stenoses. The ability to practice this delicate maneuver repeatedly builds confidence and improves success rates in real procedures. After crossing the lesion, trainees can perfect their technique for pre-dilation angioplasty. This includes selecting appropriate balloon sizes, positioning the balloon precisely within the stenosis, and mastering inflation techniques to achieve optimal lumen gain while minimizing the risk of embolic complications.
Stent Deployment and Post-dilation
The cornerstone of carotid artery stenosis treatment is precise stent deployment. Using an endovascular intervention trainer, practitioners can practice selecting the correct stent size, positioning it accurately across the lesion, and deploying it with proper technique. Advanced simulators allow trainees to experience various stent designs and delivery systems, preparing them for the range of devices they may encounter in clinical practice. Following stent deployment, post-dilation is often necessary to ensure full expansion and apposition to the vessel wall. Trainees can perfect their post-dilation technique, learning to balance the need for optimal stent expansion with the risk of plaque disruption and embolization.
Evaluating Embolic Protection Devices Under Realistic Conditions
Device Selection and Deployment Strategies
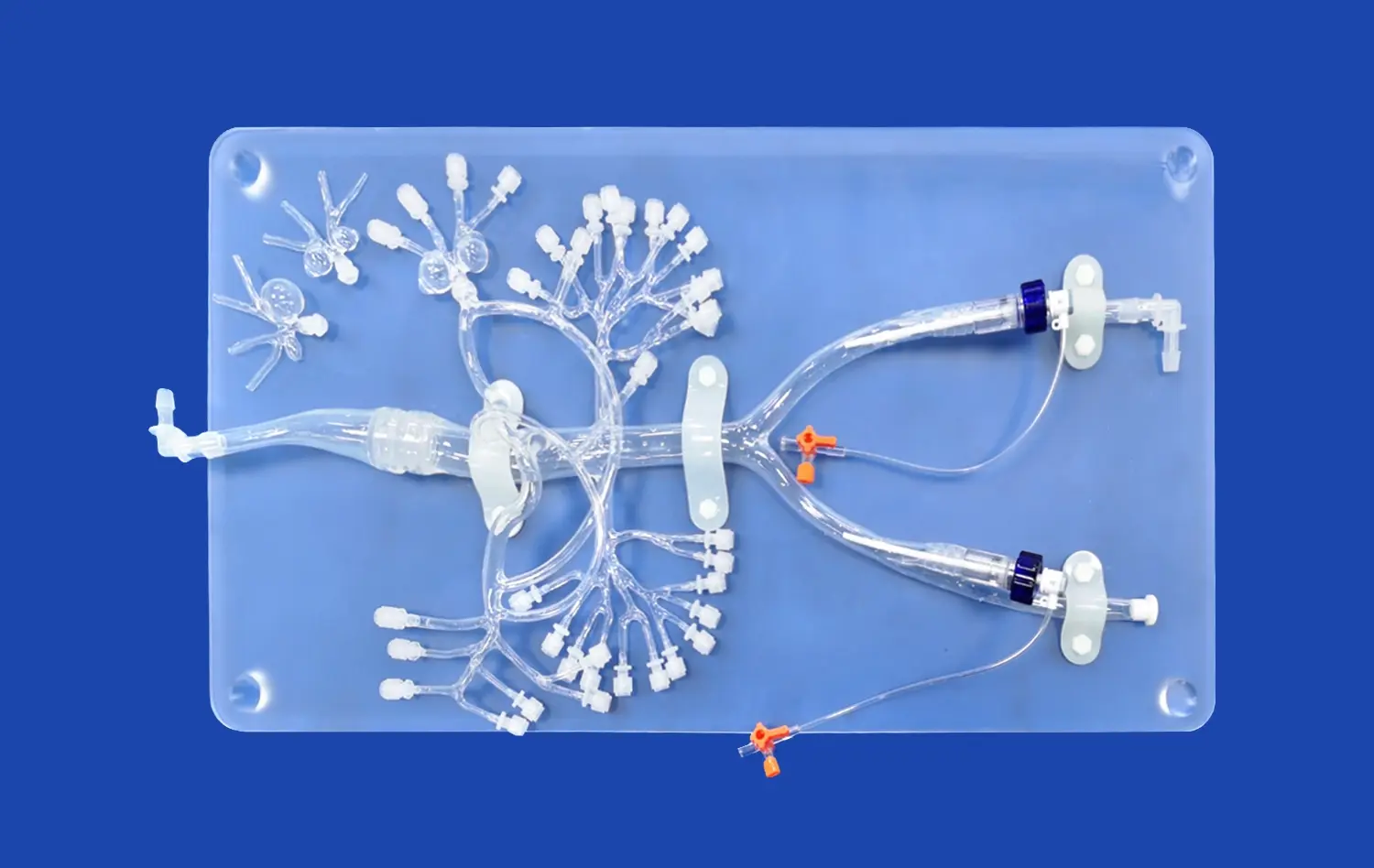
Embolic protection devices (EPDs) play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of stroke during carotid artery interventions. An endovascular intervention trainer provides an ideal platform for evaluating different types of EPDs and perfecting deployment techniques. Practitioners can compare proximal and distal protection strategies, practicing the nuances of filter placement, balloon occlusion systems, and flow reversal techniques. The ability to deploy these devices repeatedly in various anatomical configurations enhances proficiency and helps interventionalists select the most appropriate protection strategy for each patient scenario.
Assessing EPD Efficacy in Complex Anatomies
Advanced endovascular simulators allow for the creation of complex anatomies that challenge EPD effectiveness. Using an endovascular intervention trainer, trainees can practice deploying protection devices in tortuous vessels, at bifurcations, and in the presence of severe calcification. By simulating these challenging scenarios, practitioners can assess how different EPDs perform under various conditions. This hands-on experience is invaluable for developing the judgment needed to select the most appropriate device for each unique patient anatomy, potentially reducing procedural complications in real-world cases.
Complication Management and EPD Retrieval
Perhaps the most critical aspect of EPD training is learning to manage potential complications and perform safe device retrieval. Endovascular intervention trainers can simulate scenarios such as filter overload, incomplete stent expansion, or vessel spasm that may complicate EPD removal. Practitioners can practice techniques for safely collapsing and retrieving filters laden with debris, managing situations where the EPD becomes entangled with the stent, and troubleshooting instances of vasospasm or dissection. This focused training on complication management enhances procedural safety and prepares interventionalists to handle unexpected challenges during live cases.
Conclusion
Training for carotid artery stenosis interventions using an endovascular simulator is an invaluable tool for improving procedural skills and patient outcomes. These advanced trainers provide a realistic, risk-free environment for practicing critical techniques in catheter navigation, angiographic interpretation, and device deployment. By offering hands-on experience with various stenting techniques and embolic protection devices, endovascular intervention trainers help build the confidence and proficiency needed to tackle complex cases. As medical technology continues to advance, incorporating simulation-based training into interventional programs will be crucial for maintaining the highest standards of care in carotid artery procedures.
Contcat us
To explore how Trandomed's state-of-the-art endovascular intervention trainers can enhance your training program and improve procedural outcomes, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our customizable simulation solutions offer unparalleled realism and versatility, providing the tools you need to master carotid artery interventions and advance patient care.
References
1. Saratzis A, Calderbank T, Sidloff D, et al. Role of simulation in endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) training: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017;53(1):118-125.
2. Neequaye SK, Aggarwal R, Van Herzeele I, et al. Endovascular skills training and assessment. J Vasc Surg. 2007;46(5):1055-1064.
3. Maertens H, Aggarwal R, Desender L, et al. Development of a proficiency-based stepwise endovascular curricular training (PROSPECT) program. J Surg Educ. 2016;73(1):51-60.
4. Rudarakanchana N, Van Herzeele I, Desender L, et al. Virtual reality simulation for the optimization of endovascular procedures: current perspectives. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015;11:195-202.
5. Willaert WI, Aggarwal R, Van Herzeele I, et al. Recent advancements in medical simulation: patient-specific virtual reality simulation. World J Surg. 2012;36(7):1703-1712.
6. Desender LM, Van Herzeele I, Aggarwal R, et al. Training with simulation versus operative room attendance. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2011;52(1):17-37.
_1732863962417.webp)