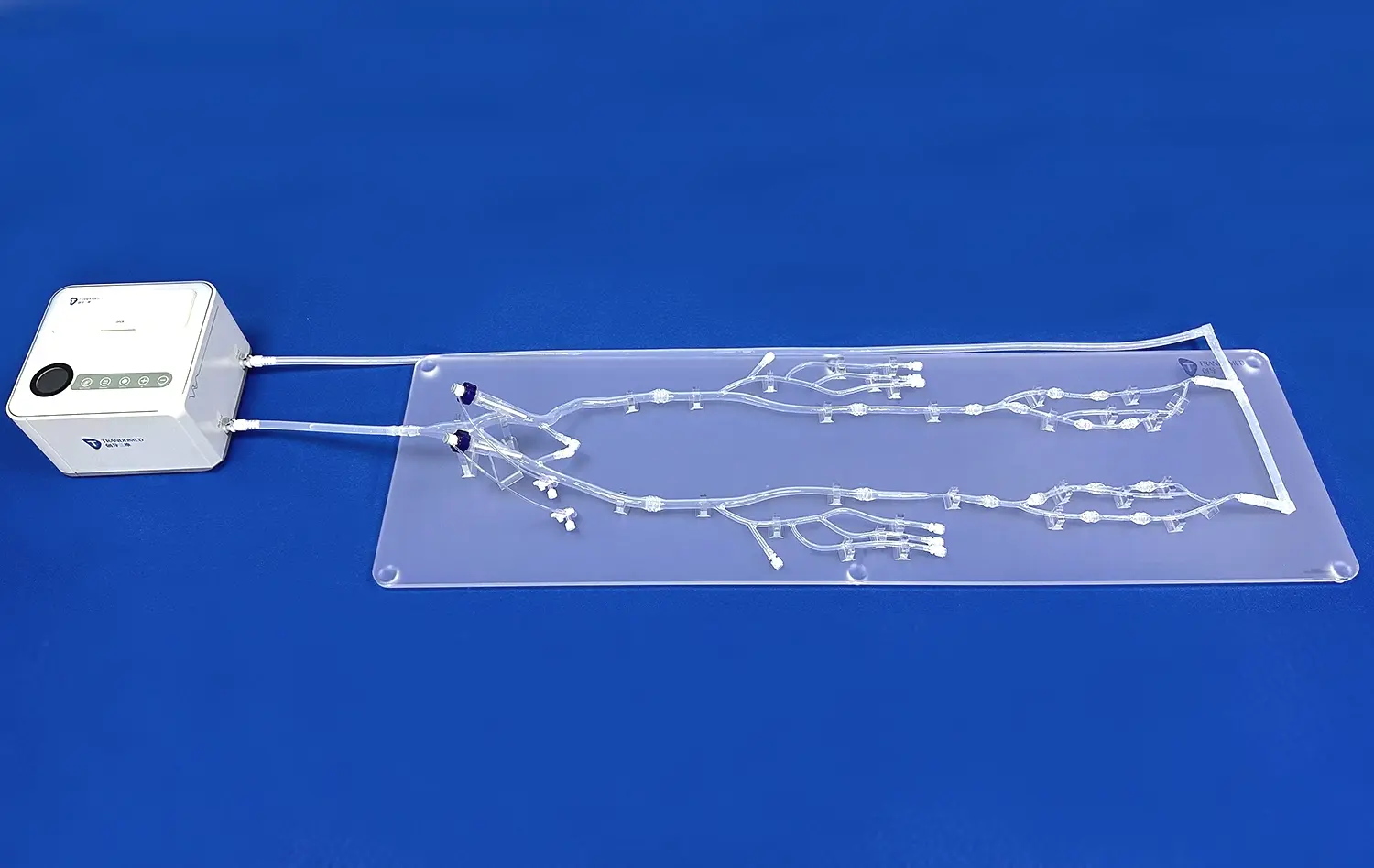
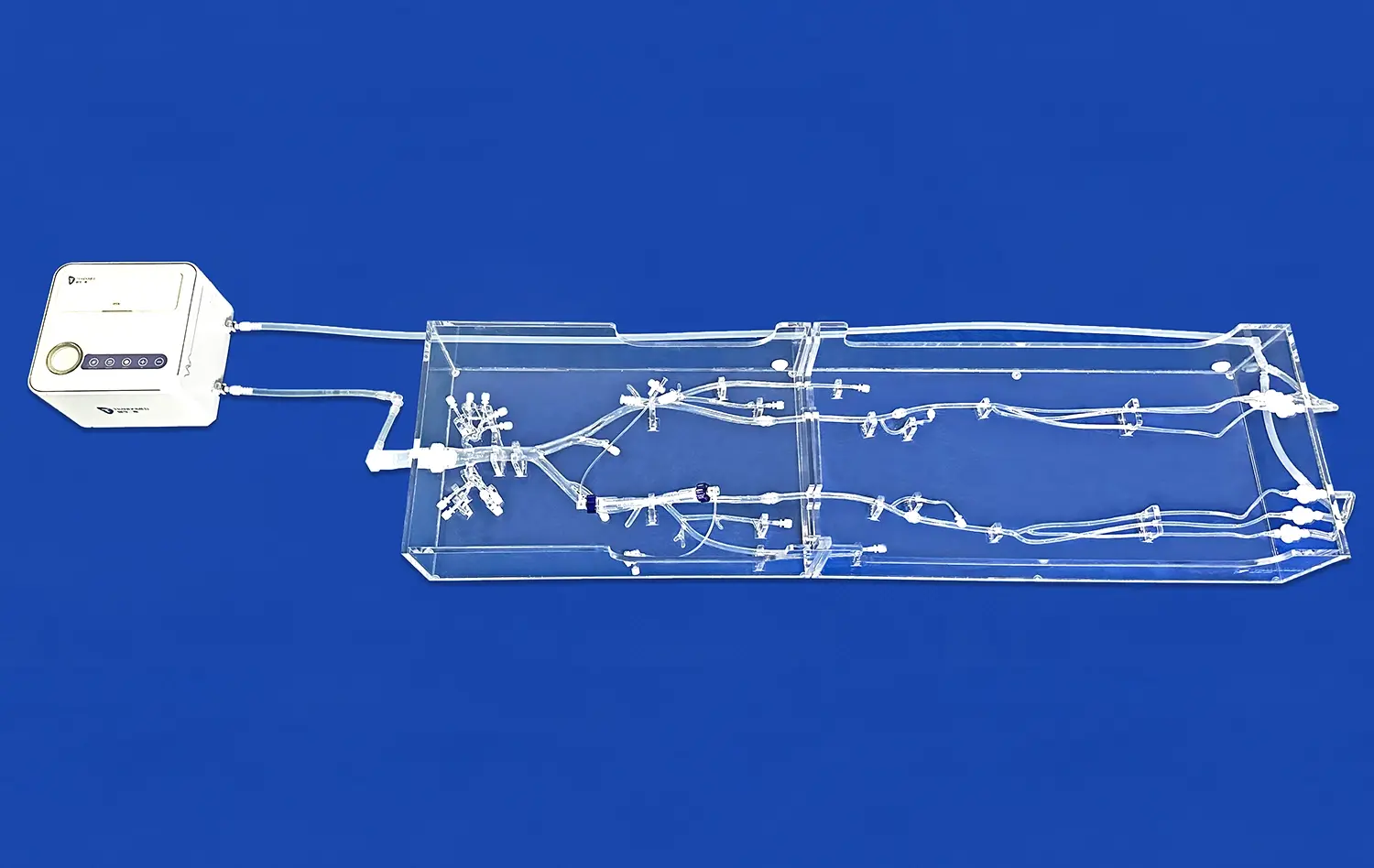
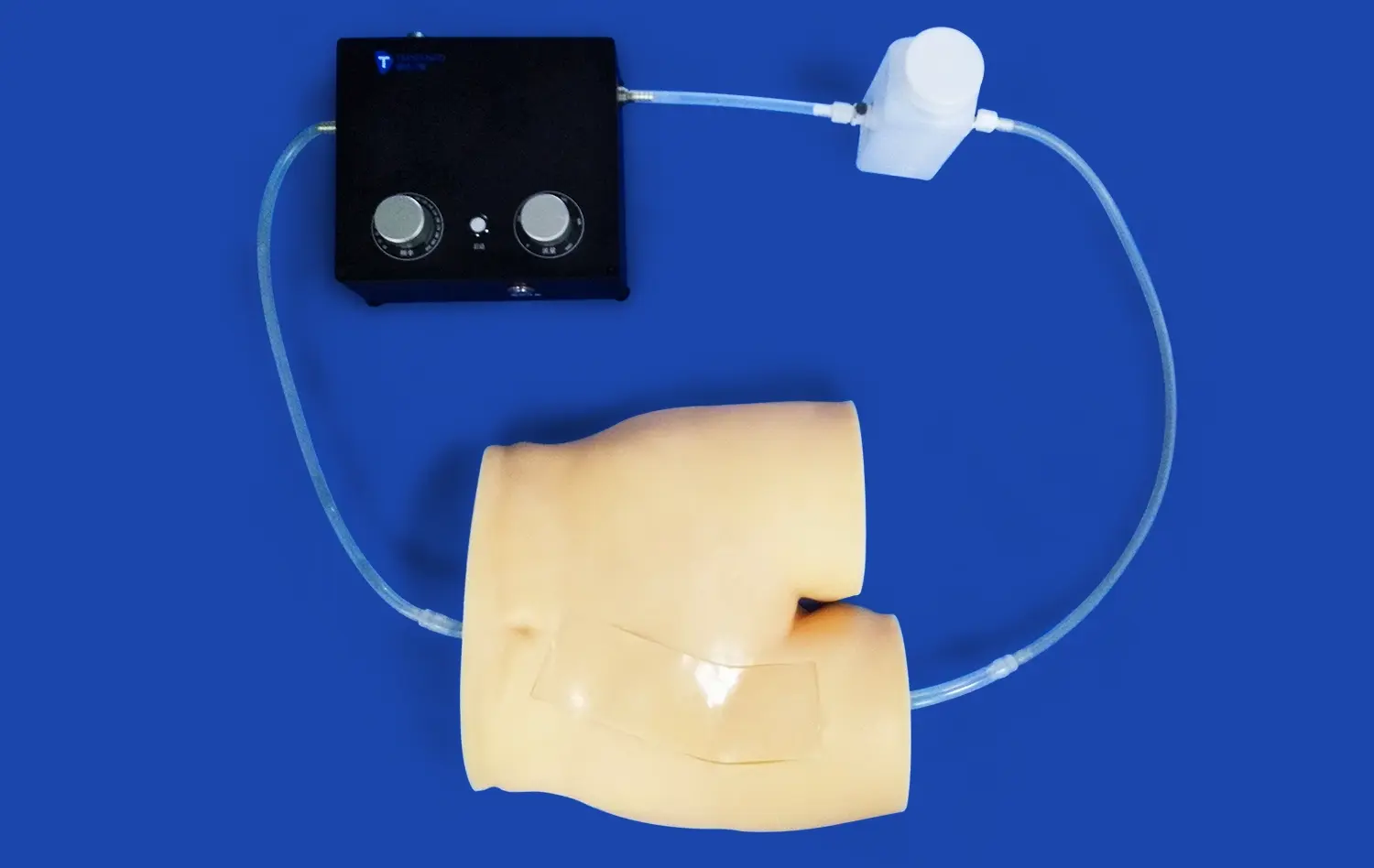
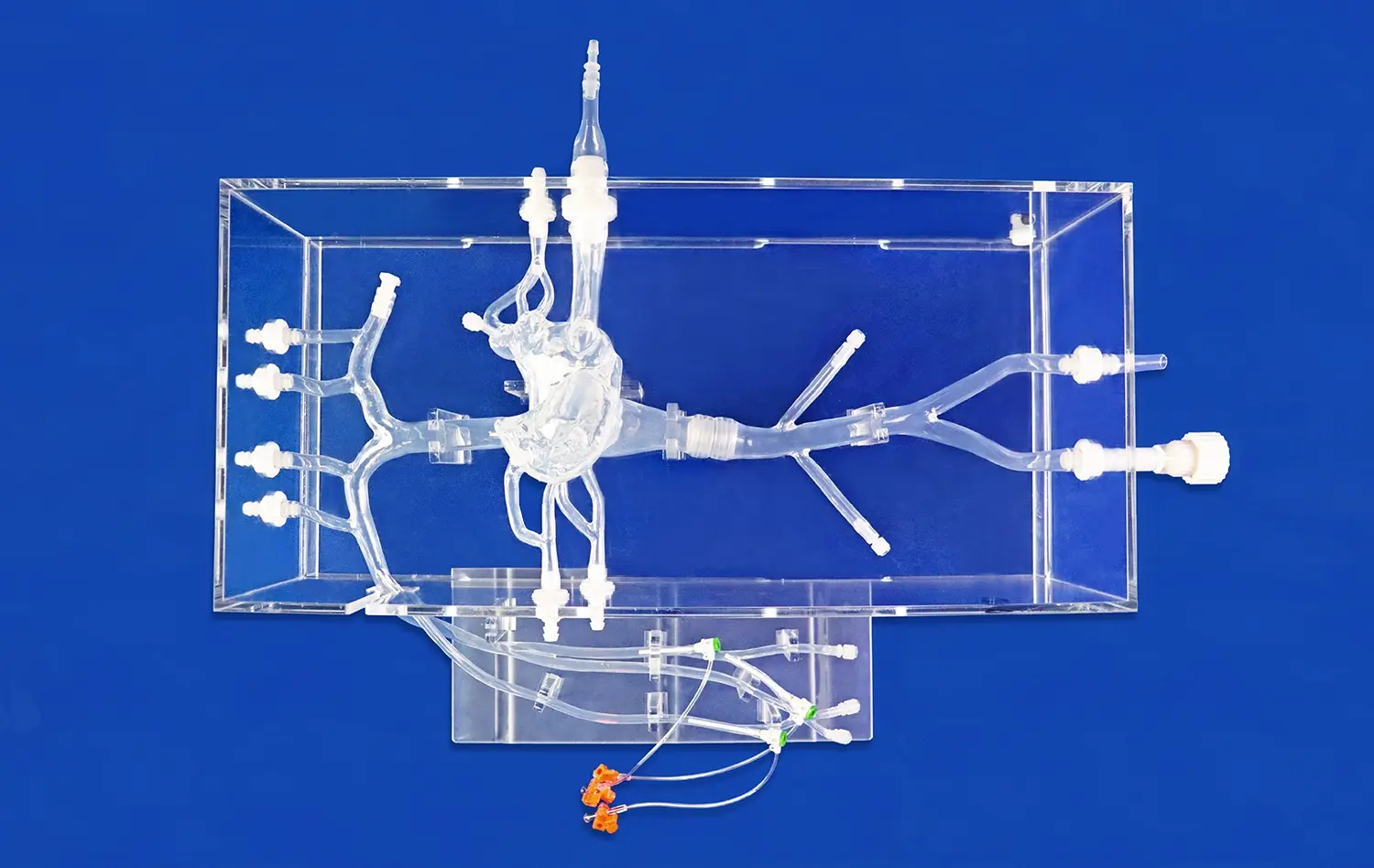
When old ways of teaching meet new technology, medical education reaches a very important point in its growth. Today's human stomach models are a huge improvement over older teaching tools. They are much more accurate and allow students to learn by interacting with them. These advanced models of the digestive system have changed the way medical workers, teachers, and students learn about gastric anatomy. In the past, classrooms have mostly used static charts and drawings from textbooks. Now, 3D-printed models of the body make it possible for students to learn by seeing, touching, and using them. This helps medical students connect the theory they learn with the practice they do.

Limitations of Traditional Teaching Models in Digestive System Education
Teaching about the digestive system has mostly used 2D images that don't show how complicated the human body really is. Medical schools and training programs around the United States are still having a hard time with traditional ways of teaching that make it harder for students to understand and be interested in what they're learning.
Spatial Representation Challenges
Anatomical charts and textbooks show the stomach as a flat, unchanging picture that doesn't show how the structures in the stomach relate to each other in three dimensions. It's hard for students to picture how the muscular layers, mucosal folds, and anatomical regions work together in real physiological situations. This problem is especially clear when teaching difficult subjects like gastric movement, acid production zones, and pathological changes that make stomach function worse.
Limited Interactive Learning Opportunities
Conventional teaching tools offer very little hands-on experience, which means students can only passively observe instead of actively exploring. Medical education study consistently shows that hands-on learning makes it easier for healthcare students to remember and understand what they have learned. Traditional models don't give students the chance to take them apart, change them, or look at them from different points. This stops students from building the spatial understanding that is necessary for clinical practice.
Procurement and Sustainability Issues
Schools and universities continue to have problems with standard teaching materials, such as having to pay a lot to replace them, not having many suppliers to choose from, and worrying about how long they will last. texts, charts, and plastic models all have problems: charts and texts eventually lose their relevance, and plastic models often break with repeated use. These things make hidden costs that affect the budgets of schools and decrease the level of education over time.
Introduction to Modern Human Stomach Models: Features and Innovations
Modern medical imaging tools and improved manufacturing methods that make very accurate models of the digestive system have completely changed how anatomy is taught. These new ideas fix the basic problems with old ways of teaching and provide more educational value for medical schools around the world.
Advanced 3D Printing Technology
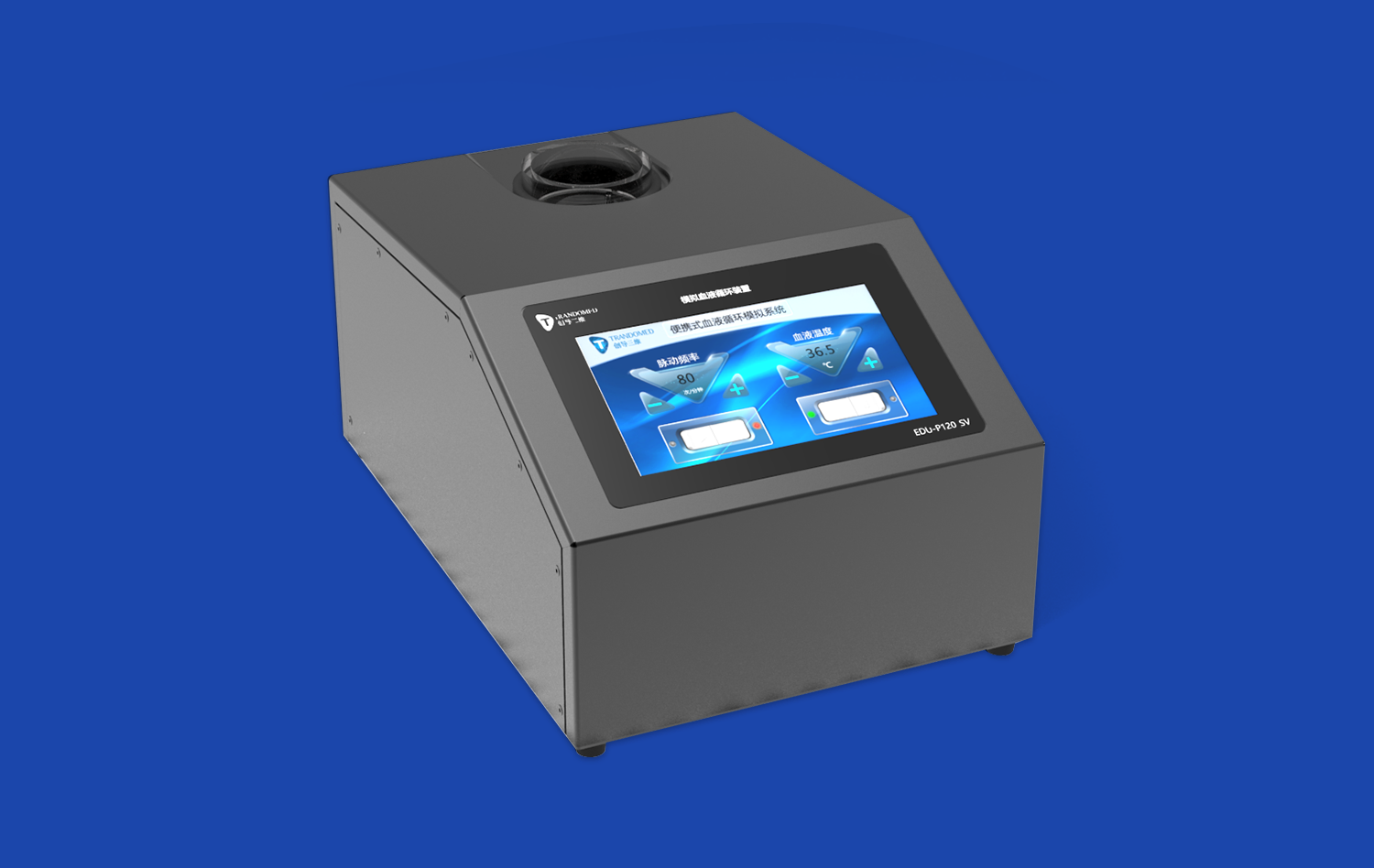
Today's stomach models use advanced 3D printing methods based on CT and MRI data from real patients. This makes sure that the shape and structure of the stomach is exactly right and similar to real human flesh. An example of this technology is Trandomed's Human Stomach Model (Product No. HSX006), which has three different layers: a thin muscular outer jacket, a thick middle layer of muscle, and a smooth inner lining. With this much information, students can look at body parts that couldn't be studied with regular teaching methods before.
Material Innovation and Durability
Newer versions of stomachs are made with advanced materials that feel very real and will last a long time even with heavy use in schools. These non-toxic, eco-friendly materials won't get worse even after being handled, cleaned, and changed around many times. The greater sturdiness means that the product is a better choice for schools that want long-lasting teaching tools that will continue to work well for several years.
Integration Capabilities
Anatomical models from today can be used with complicated educational systems that make it possible to run full simulations of the digestive system and test devices. This integration feature makes it possible for medical schools to build complex training spaces where students can safely see how the stomach works, practice medical procedures, and learn about how diseases affect the body.
Comparative Analysis: Human Stomach Models vs. Traditional Teaching Models
The stark differences between modern anatomical models and traditional teaching materials become apparent when examining their educational effectiveness, cost efficiency, and practical applications in medical training environments. This comparison reveals why leading institutions are transitioning to advanced stomach models for their educational programs.
Educational Effectiveness and Student Engagement
Research conducted at major medical universities shows that students using three-dimensional stomach models demonstrate significantly higher comprehension rates compared to those learning exclusively from textbooks and charts. The tactile nature of modern models enables students to explore anatomical relationships, identify pathological changes, and understand physiological processes through direct manipulation. This hands-on approach aligns with established learning principles that emphasize active participation in knowledge acquisition.
Anatomical Accuracy and Clinical Relevance
Traditional teaching materials often simplify complex anatomical structures to facilitate illustration, resulting in educational gaps that can impact clinical preparedness. Modern human stomach models based on actual patient imaging data provide authentic anatomical representation, including variations and pathological conditions that students will encounter in clinical practice. This accuracy ensures that educational experiences translate directly to real-world medical scenarios.
Long-term Value and Cost Considerations
While the initial investment in advanced stomach models may exceed traditional teaching material costs, the long-term value proposition strongly favors modern solutions. Institutions report extended product lifespans, reduced replacement frequency, and enhanced educational outcomes that justify the investment. Additionally, the ability to customize models for specific curriculum requirements provides flexibility that traditional materials cannot match.
Practical Procurement Tips for B2B Buyers: How to Choose the Right Human Stomach Model
Successful procurement of anatomical human stomach models requires careful consideration of institutional needs, supplier capabilities, and long-term educational objectives. Understanding these factors enables buyers to make informed decisions that maximize educational value while optimizing budget allocation.
Curriculum Alignment and Feature Assessment
Educational institutions should begin by clearly defining their specific curriculum requirements and learning objectives. Different programs may require varying levels of anatomical detail, pathological representations, or integration capabilities. Evaluating these needs against available model features ensures that the selected solution aligns with educational goals and provides maximum pedagogical value.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance
Choosing reliable suppliers with proven expertise in medical model manufacturing is crucial for ensuring product quality and ongoing support. Trandomed's 20+ years of experience in medical 3D printing and commitment to quality control exemplify the standards buyers should seek. Evaluating supplier credentials, manufacturing capabilities, and customer support services helps mitigate procurement risks while ensuring long-term satisfaction.
Customization and Scalability Options
Modern suppliers offer customization services that allow institutions to tailor models to their specific needs. This includes creating models from institution-provided CT/MRI data, incorporating specific pathological conditions, or developing custom configurations for unique educational requirements. Understanding these options enables buyers to maximize the educational value of their investment while addressing specialized training needs.
Future Trends in Educational Models for Digestive System Learning
The field of medical education is always changing as new tools make it possible to teach anatomy and clinical skills in new ways. These changes will affect how people buy things and teach in the next few years.
Technology Integration and Digital Enhancement
The coming together of physical models and digital technologies will, in theory, make learning more immersive and thorough. Apps that use augmented reality can add information to real-life models, and virtual reality systems can offer extra digital experiences that help people understand how dynamic bodily processes work.
Personalized Learning Solutions
As the need for personalized education rises, so do changeable human stomach model systems that can be changed to fit different ways of learning and educational levels. This move toward personalization helps schools make the most of teaching while also taking into account the different types of students and program needs.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Awareness of the environment is changing the way things are made. Suppliers are using more eco-friendly products and ways of making things. These changes are in line with the long-term goals of the school. At the same time, they keep up the quality and effectiveness that modern medical education needs.
Conclusion
A fundamental change in medical education methods can be seen in the transition from conventional teaching materials to modern human stomach models. Using real patient information to make 3D-printed models greatly improves the accuracy of how body parts are shown, gets students more interested in learning, and helps students learn better overall when compared to normal texts and charts. Modern gut models are an important investment for forward-thinking schools. They may be more expensive at first, but they help students learn better, last longer, and can be customized. As technology moves forward, the use of digital tools and eco-friendly manufacturing will open up even more opportunities for teaching anatomy. This makes it very important for procurement professionals to work with suppliers who know how to handle these changing needs and provide great solutions for education.
FAQs
How do modern stomach models compare to traditional anatomical charts in terms of educational effectiveness?
Modern stomach models provide three-dimensional, tactile learning experiences that significantly enhance student comprehension compared to two-dimensional charts. Students can physically manipulate the models, examine internal structures, and understand anatomical relationships that are impossible to convey through flat illustrations, resulting in improved retention rates and clinical preparedness.
What should institutions consider when transitioning from traditional teaching materials to advanced stomach models?
Institutions should evaluate their curriculum requirements, budget considerations, and long-term educational goals. Key factors include anatomical accuracy needs, student population size, integration with existing educational systems, and supplier support capabilities. The transition typically involves initial investment planning, staff training, and gradual implementation to maximize educational benefits.
Can modern stomach models be customized for specific educational programs or research requirements?
Yes, leading manufacturers like Trandomed offer comprehensive customization services including models based on specific CT/MRI data, pathological conditions, or unique anatomical variations. These customization options allow institutions to tailor models to their exact curriculum needs without additional design costs, ensuring optimal educational value for specialized training programs.
Discover Trandomed's Advanced Human Stomach Model Solutions
Trandomed stands at the forefront of medical education innovation, offering cutting-edge anatomical models that transform digestive system instruction. Our human stomach model manufacturer expertise, combined with over two decades of 3D printing experience, ensures that educational institutions receive superior products designed for excellence in medical training environments.
Our flagship stomach model (HSX006) represents the culmination of advanced manufacturing techniques and anatomical precision, featuring three distinct tissue layers based on real patient imaging data. The model's compatibility with complex testing systems and its environmentally safe construction make it ideal for intensive educational use across medical schools, hospitals, and research institutions.
We understand that each institution has unique requirements, which is why we offer comprehensive customization services without additional design costs. Whether you need models based on specific CT/MRI data or require particular anatomical variations, our expert team can deliver tailored solutions that meet your exact specifications. Our efficient production process ensures delivery within 7-10 days, while our global shipping capabilities through FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT guarantee reliable delivery worldwide.
Ready to revolutionize your digestive system education program? Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our advanced stomach models can enhance your educational outcomes. Visit trando-medical.com to explore our complete product range and download our comprehensive product brochure.
References
Anderson, J.M., & Thompson, K.L. (2023). "Effectiveness of Three-Dimensional Anatomical Models in Medical Education: A Systematic Review." Journal of Medical Education Technology, 45(3), 234-251.
Roberts, S.A., Chen, P.W., & Martinez, R.D. (2022). "Traditional vs. Modern Teaching Tools in Digestive System Education: A Comparative Study." Medical Education Research Quarterly, 18(4), 412-428.
Williams, E.T., Johnson, M.K., & Davis, L.R. (2023). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Advanced Anatomical Models in Healthcare Training." Healthcare Education Economics, 29(2), 156-174.
Brown, A.C., & Singh, P.K. (2022). "3D Printing Applications in Medical Education: Current Trends and Future Directions." International Journal of Educational Technology, 31(6), 289-305.
Taylor, M.J., Lee, S.H., & Wilson, K.A. (2023). "Student Learning Outcomes Using Interactive Anatomical Models: A Multi-Institutional Study." Academic Medicine Today, 98(7), 523-539.
Garcia, R.L., & Patel, N.M. (2022). "Procurement Strategies for Modern Medical Education Equipment: Best Practices for Institutional Buyers." Educational Procurement Review, 14(5), 78-92.
_1736216292718.webp)