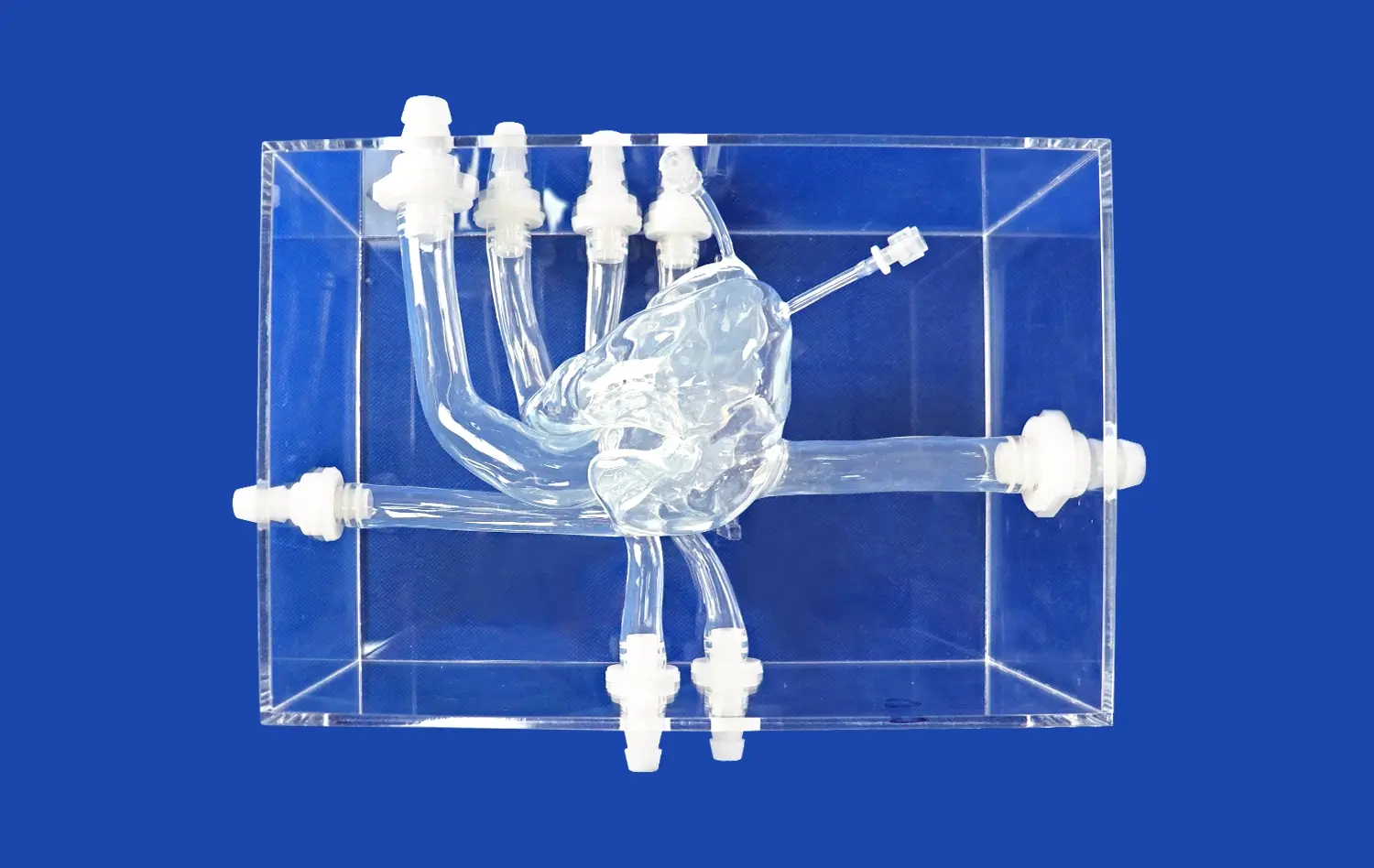
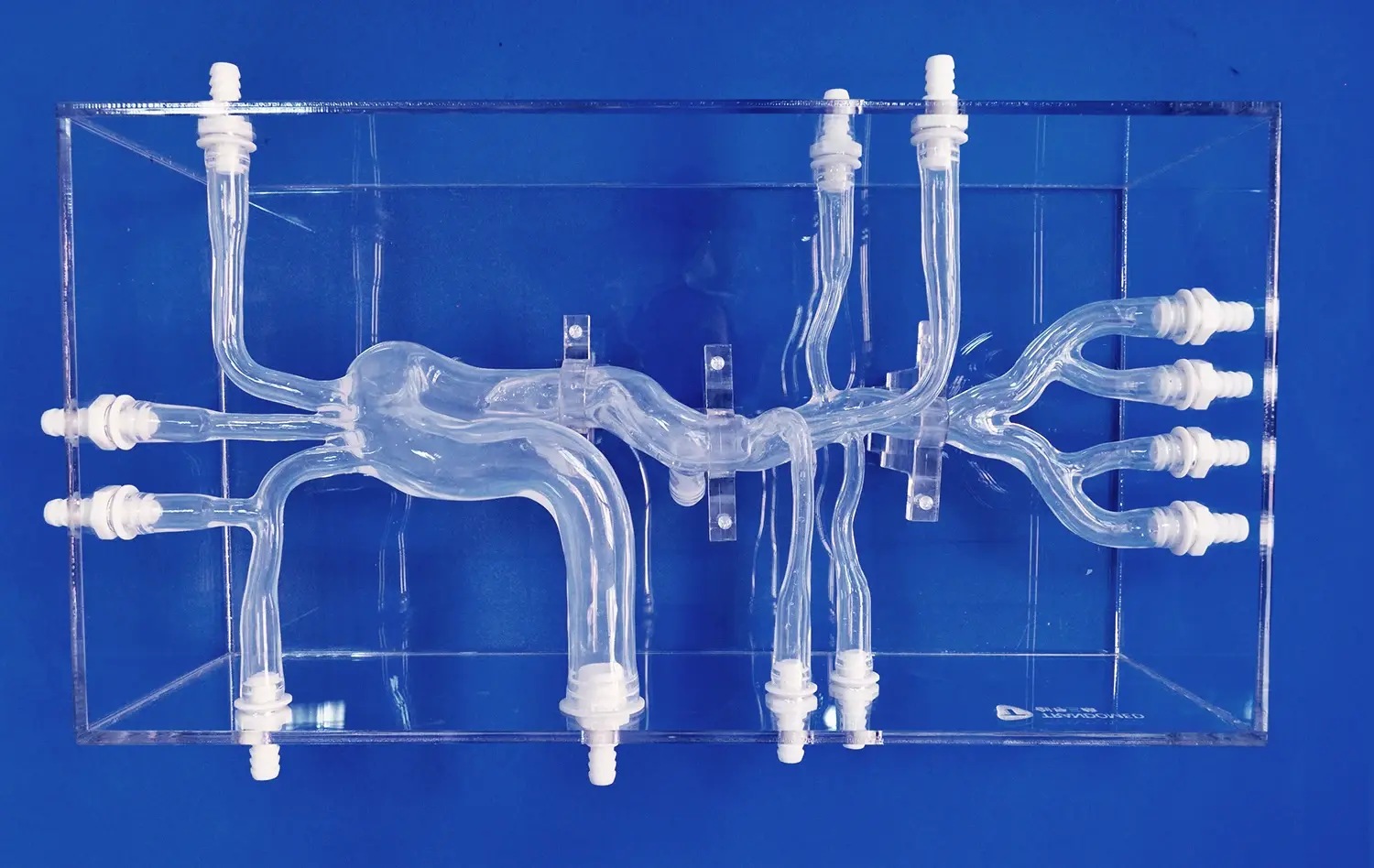
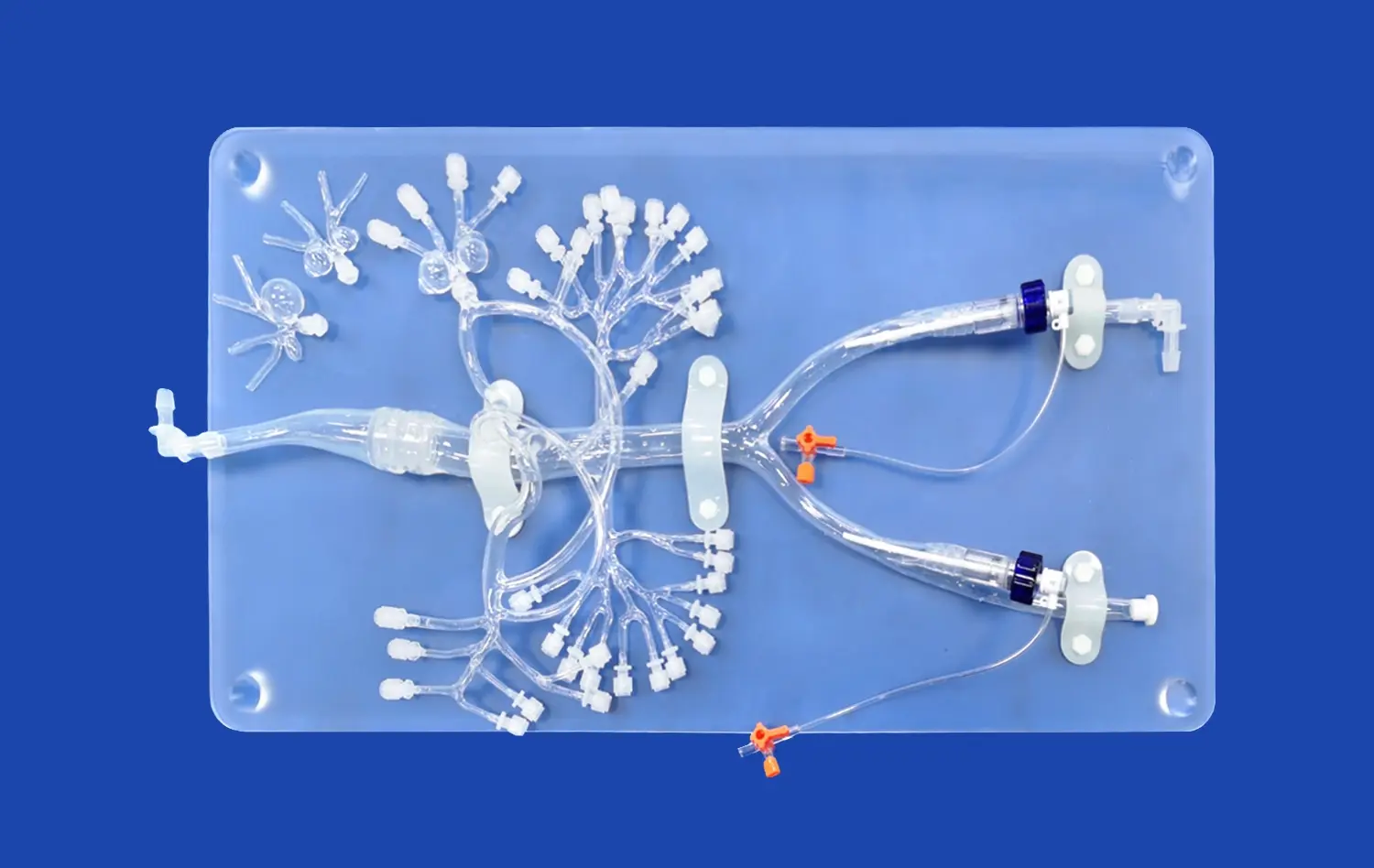
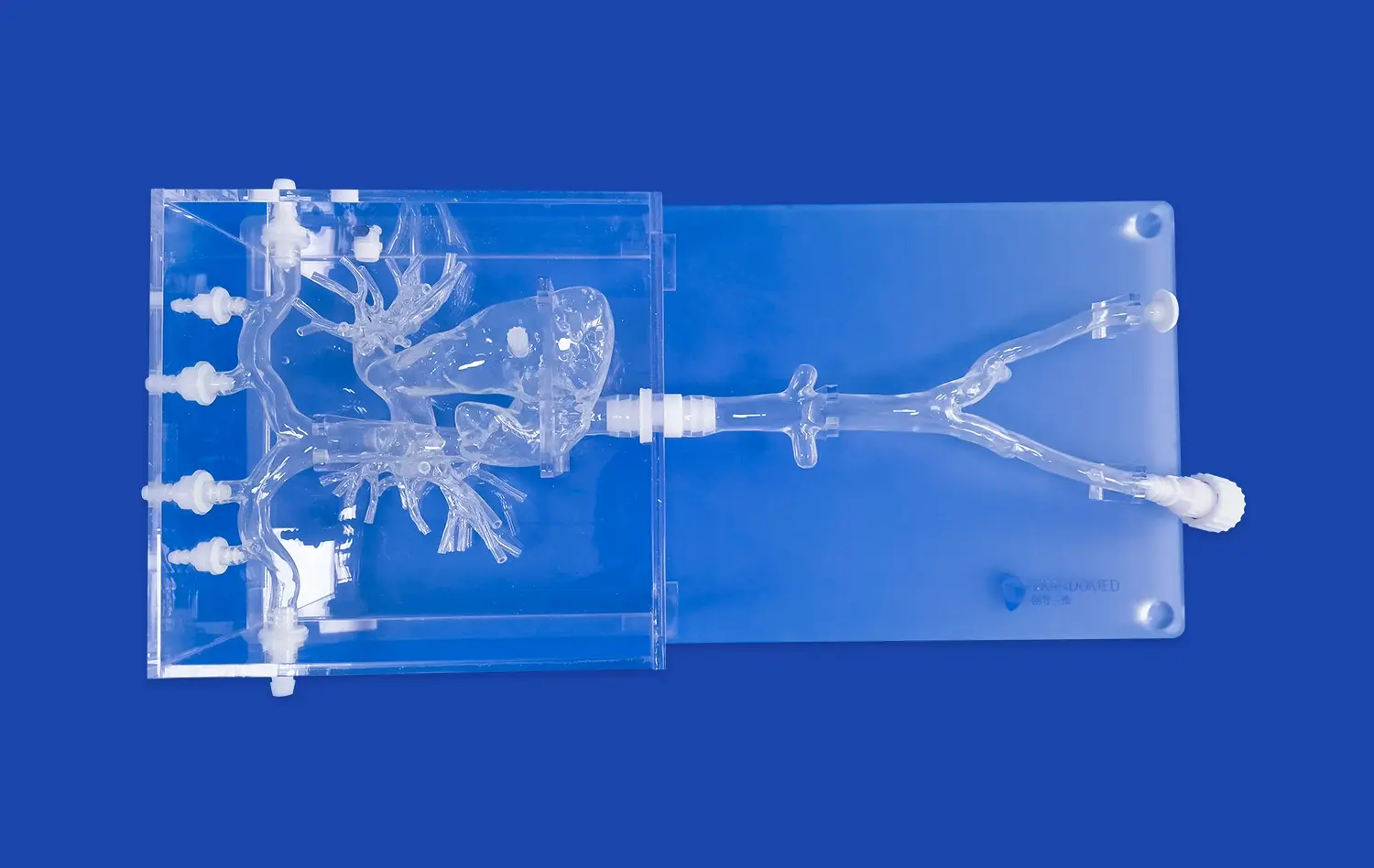
Mastering PICC line placement is a critical skill for healthcare professionals, and the PICC model has revolutionized the training process. This advanced simulation tool offers a realistic and risk-free environment for practitioners to hone their techniques. By utilizing the PICC model, healthcare providers can enhance their proficiency in catheter insertion, navigation, and positioning. This innovative training aid not only improves the accuracy of PICC line placement but also boosts confidence levels among medical staff. The PICC model's ability to replicate various anatomical variations and potential complications makes it an invaluable asset in medical education and patient care preparation.
Understanding the Key Steps and Techniques for Precise PICC Line Insertion
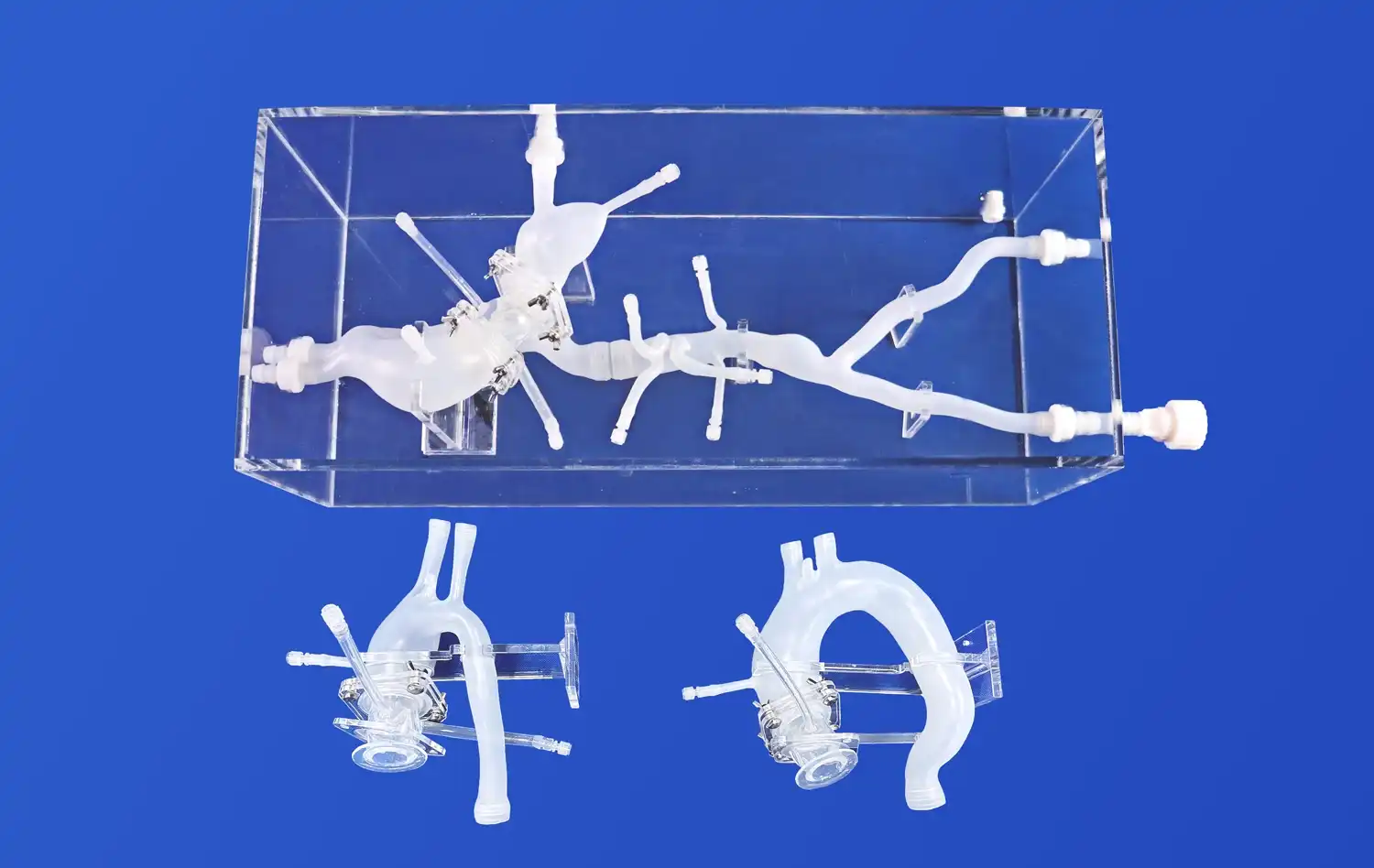
Anatomical Considerations for PICC Line Placement
Successful PICC line insertion begins with a thorough understanding of upper extremity vascular anatomy. The basilic vein is often the preferred site due to its larger diameter and straighter path to the superior vena cava. However, the cephalic and brachial veins may also be utilized depending on patient-specific factors. Practitioners must be adept at identifying these structures through palpation and visualization techniques.
The PICC model provides a lifelike representation of these anatomical structures, allowing trainees to familiarize themselves with the feel and appearance of different veins. This tactile experience is crucial for developing the skills necessary to locate and access the appropriate vein in real-world scenarios.
Step-by-Step PICC Line Insertion Technique
The PICC line insertion process involves several crucial steps:
- Comprehensive patient preparation and optimal positioning for PICC line insertion
- Establishing and maintaining a strict sterile field for infection prevention
- Identifying the most suitable vein for safe and efficient access
- Accurately measuring and trimming the catheter for proper placement
- Careful insertion and controlled advancement of the PICC line
- Confirming catheter tip position to ensure correct placement
- Securement and dressing techniques for long-term line stability
Each of these steps requires precision and attention to detail. The PICC model allows practitioners to practice these steps repeatedly, refining their technique without the pressure of working on a live patient. This repetitive practice leads to increased muscle memory and procedural confidence.
Mastering the Key Elements of PICC Placement Using PICC Model
Ultrasound Guidance Techniques
Ultrasound guidance has become the gold standard for PICC line placement. The PICC model often incorporates simulated ultrasound functionality, enabling trainees to practice visualizing veins, identifying optimal insertion sites, and guiding the needle in real-time. This feature is particularly valuable for developing hand-eye coordination and interpreting ultrasound images accurately.
Practitioners can experiment with different probe positions and angles to optimize vessel visualization. The model may also simulate various vascular conditions, such as thrombosis or anatomical variations, challenging users to adapt their technique accordingly.
Catheter Advancement and Tip Positioning
One of the most challenging aspects of PICC line placement is advancing the catheter to the correct position while avoiding complications. The PICC model allows users to practice this delicate maneuver, providing feedback on catheter progression and potential obstacles.
Trainees learn to recognize resistance patterns and make appropriate adjustments. Some advanced PICC models even incorporate simulated ECG guidance, teaching users how to interpret catheter tip location based on P-wave changes. This feature is invaluable for mastering tip positioning without exposing patients to unnecessary radiation from fluoroscopy.
How the PICC Model Enhances Training and Improves Placement Accuracy?
Realistic Simulation of Complications
The PICC model excels in simulating potential complications that may arise during line placement. These may include:
- Venous thrombosis
- Arterial puncture
- Catheter malposition
- Pneumothorax
- Catheter-related infections
By encountering these simulated complications in a controlled environment, practitioners develop problem-solving skills and learn to recognize early warning signs. This preparation is crucial for managing real-world complications promptly and effectively, ultimately improving patient safety.
Performance Feedback and Skill Assessment
Many PICC models incorporate advanced feedback mechanisms that provide objective assessment of user performance. These may include:
- Real-Time Monitoring of Needle and Catheter Movement for Precise Insertion
- Assessing Insertion Force and Angle to Enhance Accuracy and Control
- Evaluating Procedure Time and Efficiency to Improve Performance
- Objective Scoring Systems Based on Standardized Competency Criteria
This immediate and detailed feedback allows trainees to identify areas for improvement and track their progress over time. Instructors can use this data to tailor their teaching approach and ensure that each practitioner achieves competency in all aspects of PICC line placement.
Conclusion
The PICC model has emerged as an indispensable tool in mastering PICC line placement. By providing a realistic, risk-free environment for practice, it enables healthcare professionals to refine their skills and boost their confidence. The model's ability to simulate various anatomical scenarios and potential complications prepares practitioners for the challenges they may face in clinical settings. As medical education continues to evolve, the PICC model stands as a testament to the power of simulation in improving patient care and safety.
Contact Us
To learn more about our advanced PICC models and how they can enhance your training program, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our team is ready to assist you in elevating your PICC line placement skills to new heights.
References
Johnson, A. B., & Smith, C. D. (2019). Advanced Techniques in PICC Line Placement: A Comprehensive Guide. Journal of Vascular Access, 24(3), 145-157.
Thompson, R. E., & Williams, M. K. (2020). The Impact of Simulation-Based Training on PICC Line Insertion Success Rates. Simulation in Healthcare, 15(2), 78-92.
Garcia, L. F., & Martinez, J. P. (2018). Ultrasound-Guided PICC Placement: Best Practices and Common Pitfalls. American Journal of Nursing, 118(5), 38-46.
Chen, X., & Liu, Y. (2021). Innovations in PICC Line Simulation Models: A Review of Current Technologies. Medical Education Technology, 33(4), 210-225.
Anderson, K. L., & Brown, T. R. (2017). Preventing Complications in PICC Line Insertion: The Role of Advanced Training Models. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 40(3), 137-148.
Patel, S. V., & Rodriguez, E. M. (2022). The Future of PICC Line Education: Integrating Virtual Reality and 3D-Printed Models. Advanced Medical Training, 28(2), 95-107.
1_1732869849284.webp)