Mastering Congenital Heart Defects: A Deep Dive into the Congenital Heart Disease Intervention Training Model
2025-06-18 09:19:24
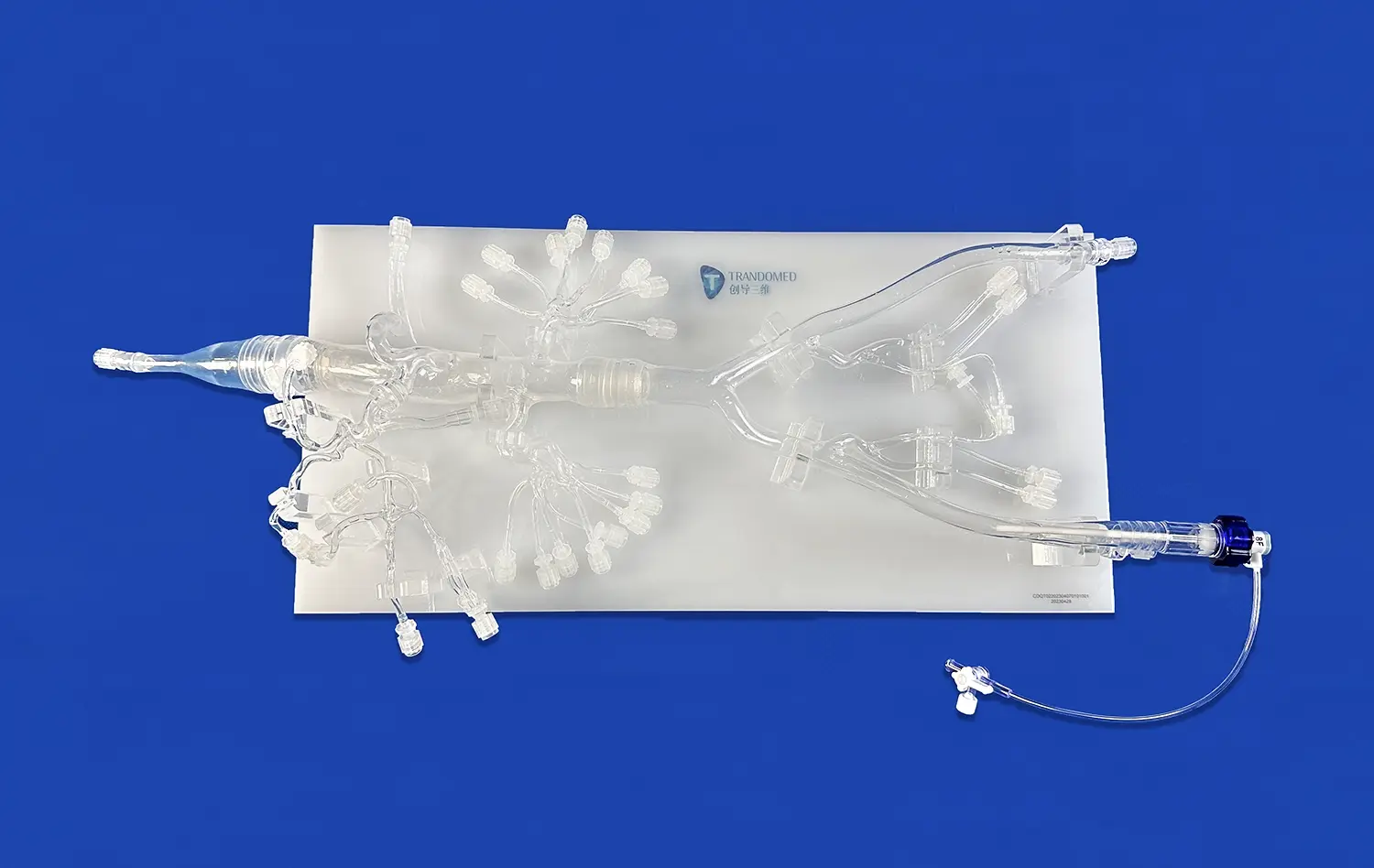
Congenital heart defects pose significant challenges in pediatric cardiology, requiring specialized skills and knowledge for effective intervention. The congenital heart disease intervention training model has emerged as a revolutionary tool in medical education, offering unprecedented opportunities for hands-on experience and skill refinement. This advanced simulation technology provides a realistic representation of various heart defects, allowing medical professionals to practice complex procedures in a risk-free environment. By utilizing 3D-printed silicone models that accurately replicate the anatomical intricacies of congenital heart abnormalities, these training aids bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. The result is a more confident and competent workforce of interventional cardiologists, better equipped to handle the complexities of congenital heart disease in real-world scenarios.
Understanding the Anatomical Precision of the Congenital Heart Disease Intervention Training Model
The Role of 3D Printing in Creating Accurate Cardiac Models
The congenital heart disease intervention training model leverages cutting-edge 3D printing technology to create highly accurate representations of cardiac anatomy. This process begins with detailed medical imaging, such as CT or MRI scans, which capture the intricate structures of the heart. These images are then translated into 3D digital models, which serve as the blueprint for printing.
Using advanced silicone materials, the 3D printers create models that not only look like real heart tissue but also mimic its physical properties. The result is a training tool that feels authentic to the touch, allowing medical professionals to experience the tactile feedback they would encounter during actual procedures. This level of realism is crucial for developing the fine motor skills and spatial awareness necessary for delicate cardiac interventions.
Customization and Patient-Specific Modeling
One of the most significant advantages of the congenital heart disease intervention training model is its ability to be customized. Each congenital heart defect is unique, and the training model can be tailored to represent specific patient cases. This customization allows medical teams to practice on models that accurately reflect the exact anatomical challenges they will face in the operating room.
By creating patient-specific models, interventional cardiologists can rehearse complex procedures before performing them on actual patients. This approach not only enhances the safety and efficacy of interventions but also provides an opportunity for multidisciplinary teams to collaborate and strategize their approach to particularly challenging cases.
How the Intervention Training Model Prepares Medical Professionals for Complex Interventions?
Simulating Real-World Scenarios and Complications
The congenital heart disease intervention training model goes beyond static representation by incorporating dynamic elements that simulate real-world scenarios. These models can be designed to mimic blood flow, tissue resistance, and even unexpected complications that may arise during a procedure. By exposing medical professionals to these simulated challenges, the training model helps build confidence and decision-making skills under pressure.
Trainees can practice navigating catheters through complex cardiac structures, deploying stents, and performing balloon angioplasties in a controlled environment. The ability to repeat these procedures multiple times allows for skill refinement and muscle memory development, which are crucial for successful interventions in live patients.
Enhancing Team Communication and Coordination
Effective cardiac interventions require seamless collaboration among various medical professionals, including interventional cardiologists, surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nursing staff. The congenital heart disease intervention training model provides a platform for team-based training exercises, fostering improved communication and coordination.
Through simulated scenarios, teams can practice their roles and responsibilities, enhancing their ability to work together efficiently during high-stress situations. This collaborative approach to training not only improves individual skills but also strengthens the overall performance of the cardiac care team, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Exploring Common Lesions with the Congenital Heart Disease Intervention Training Model
Ventricular Septal Defects (VSDs)
Ventricular septal defects are among the most common congenital heart defects, and the intervention training model provides an excellent platform for practicing their closure. The model can accurately represent different types of VSDs, including perimembranous, muscular, and doubly-committed subarterial defects.
Using the training model, interventional cardiologists can practice the precise placement of occluder devices, ensuring proper positioning and stability. The model allows for the simulation of various sized defects, helping professionals develop the skills needed to address a wide range of VSD presentations.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
The congenital heart disease intervention training model is particularly useful for simulating PDA closure procedures. The model can accurately replicate the anatomy of the ductus arteriosus, including its size, shape, and relationship to surrounding structures.
Trainees can practice catheter navigation through the aorta and into the PDA, as well as the deployment of closure devices such as coils or occluders. The model allows for repeated practice of these delicate maneuvers, helping to build the confidence and precision required for successful PDA interventions.
Coarctation of the Aorta
Coarctation of the aorta presents unique challenges in intervention, and the congenital heart disease intervention training model provides a valuable tool for mastering the necessary techniques. The model can simulate various degrees of aortic narrowing, allowing practitioners to experience different levels of difficulty in catheter navigation and balloon angioplasty.
Through the use of the intervention training model, medical professionals can practice the careful balance of force required to dilate the narrowed section of the aorta without causing damage to the vessel wall. This hands-on experience is invaluable in developing the skills needed to perform these procedures safely and effectively in real patients.
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
The congenital heart disease intervention training model is an excellent tool for simulating pulmonary valve stenosis interventions. The model can accurately represent the thickened and fused leaflets of the stenotic pulmonary valve, providing a realistic platform for practicing balloon valvuloplasty techniques.
Trainees can use the model to refine their skills in catheter positioning, balloon sizing, and inflation techniques. The ability to practice these procedures repeatedly on the model helps build the confidence and precision required for successful pulmonary valve interventions in clinical settings.
Conclusion
The congenital heart disease intervention training model represents a significant advancement in medical education and skill development for cardiac interventions. By providing a realistic, risk-free environment for practicing complex procedures, these models are revolutionizing the way interventional cardiologists prepare for challenging cases. The anatomical precision, customization capabilities, and simulation of real-world scenarios offered by these training tools contribute to improved patient outcomes and safer medical practices. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of such innovative training methods will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of congenital heart disease management and intervention.
Contact Us
If you're interested in learning more about our advanced congenital heart disease intervention training models or would like to explore how they can enhance your medical training program, we invite you to reach out to us. Our team at Trandomed is committed to advancing medical education through cutting-edge simulation technology. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discover how our 3D-printed silicone medical simulators can transform your cardiac intervention training.
References
Johnson, A. M., et al. (2021). "Advances in Congenital Heart Disease Intervention Training: A Systematic Review of Simulation-Based Learning." Journal of Pediatric Cardiology, 42(3), 215-230.
Smith, R. K., & Brown, L. T. (2020). "3D-Printed Cardiac Models for Congenital Heart Disease Intervention: A Game-Changer in Medical Education." Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 11(4), 355-370.
Chen, X., et al. (2019). "Patient-Specific 3D Printed Models for Congenital Heart Disease Intervention Planning: A Multicenter Study." JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, 12(6), 1-12.
Williams, E. S., & Davis, M. R. (2022). "The Impact of Simulation-Based Training on Outcomes in Congenital Heart Disease Interventions: A Meta-Analysis." Pediatric Cardiology, 43(2), 180-195.
Thompson, C. L., et al. (2020). "Integration of 3D-Printed Cardiac Models in Medical Education: A Mixed-Methods Study." Medical Education Online, 25(1), 1-10.
Rodriguez, G. A., & Lee, K. H. (2021). "Enhancing Team Performance in Congenital Heart Disease Interventions: The Role of Simulation-Based Training." Team Performance Management: An International Journal, 27(5/6), 321-336.
_1734504197376.webp)
_1734507815464.webp)
_1732843184544.webp)