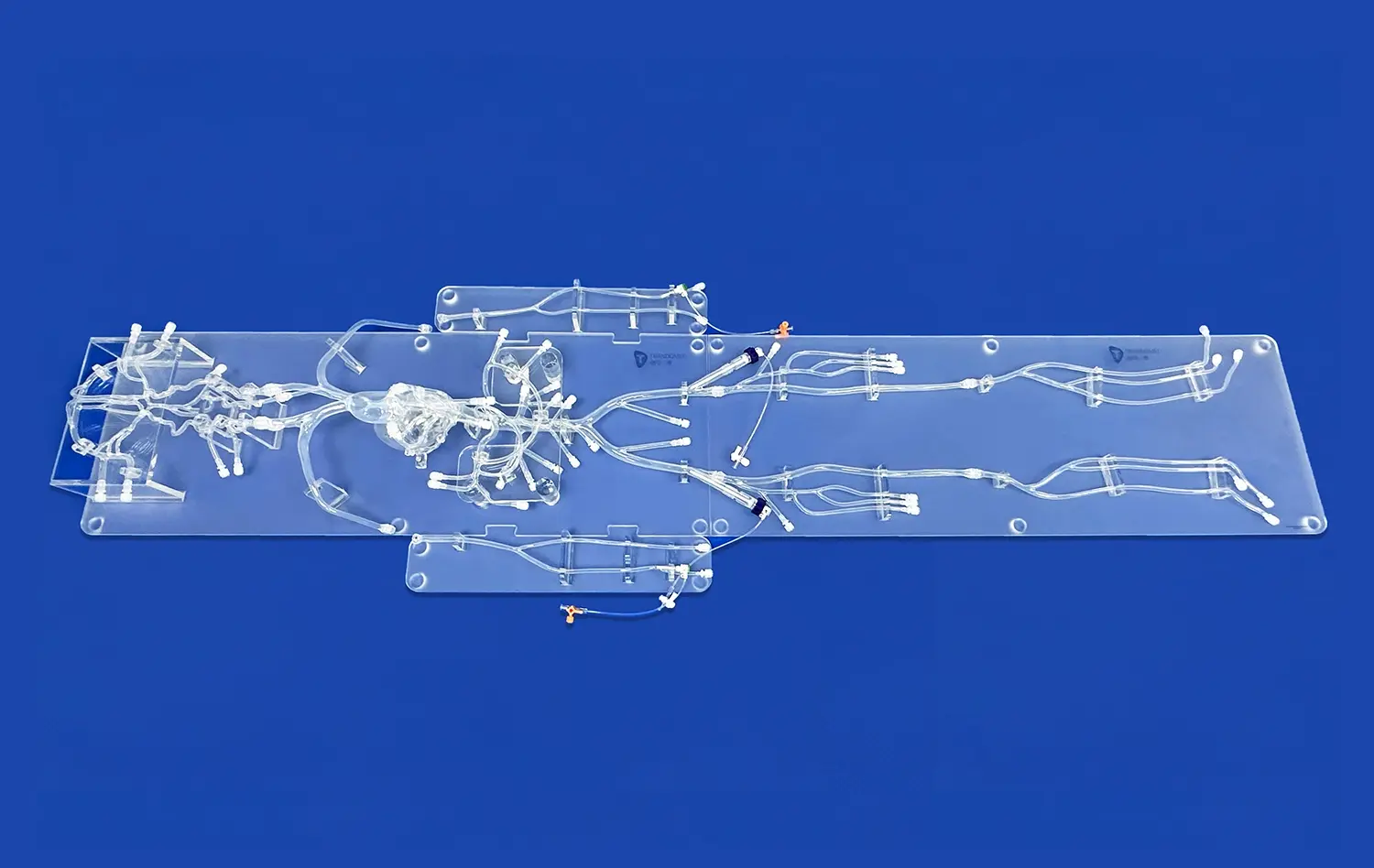
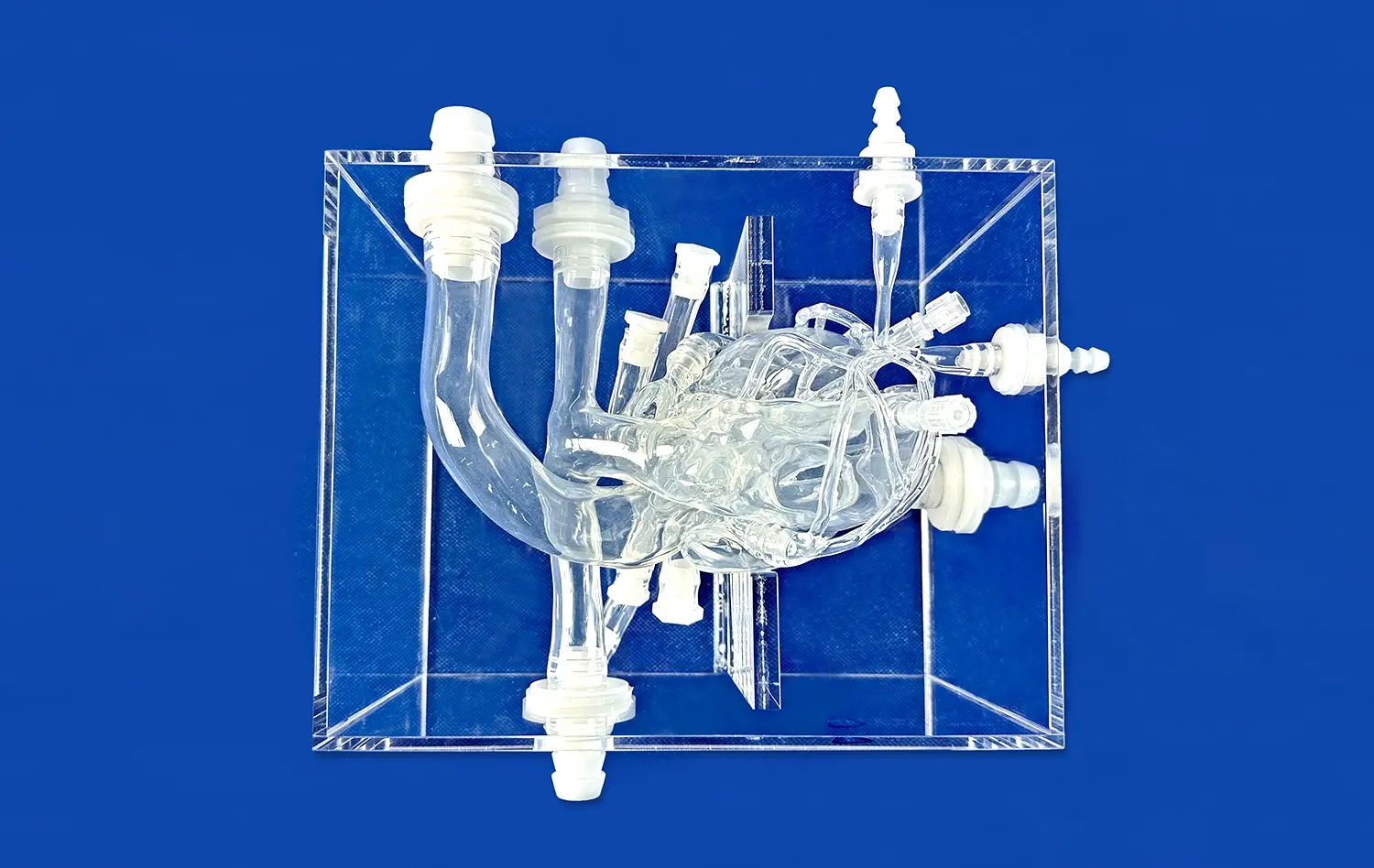
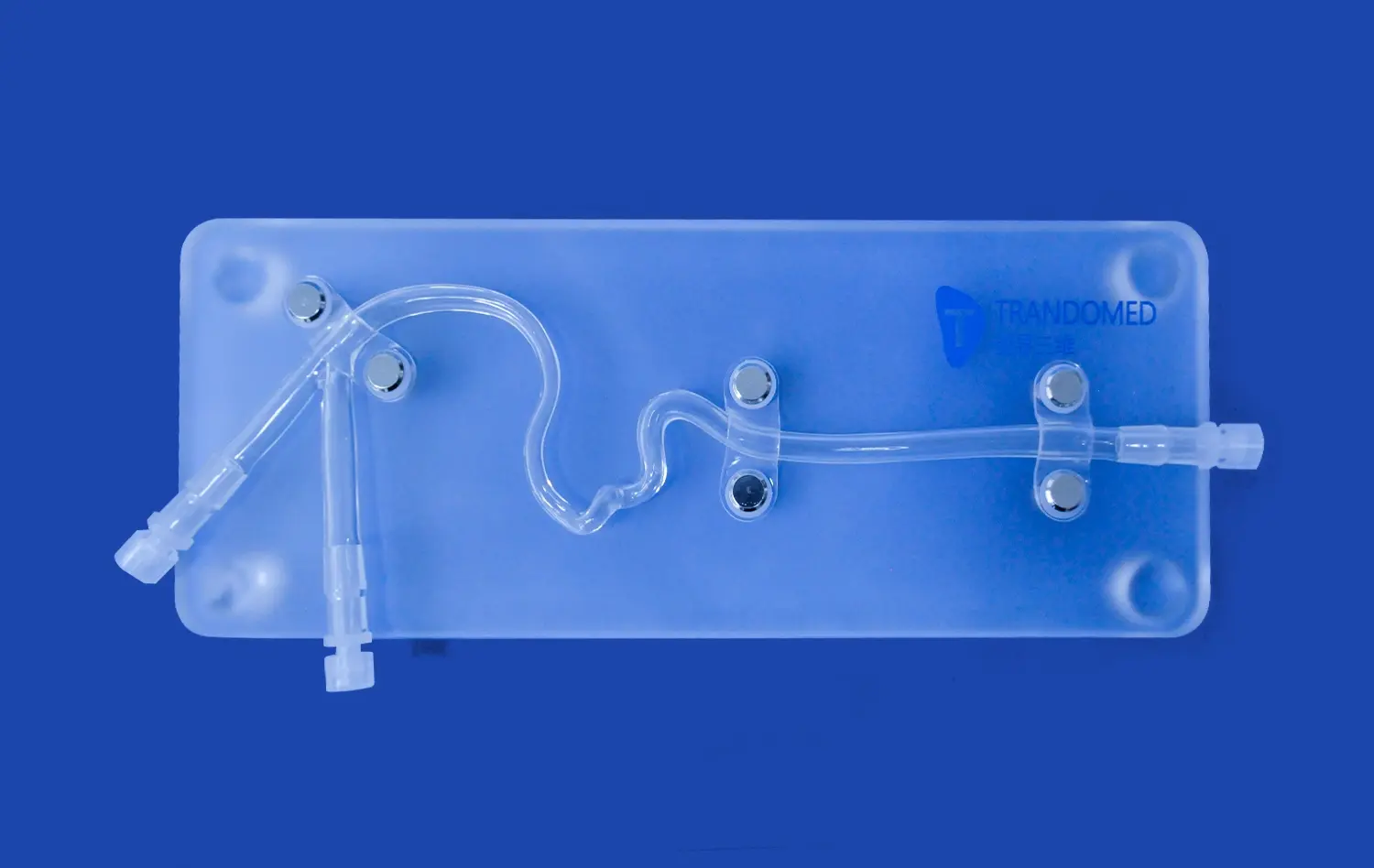
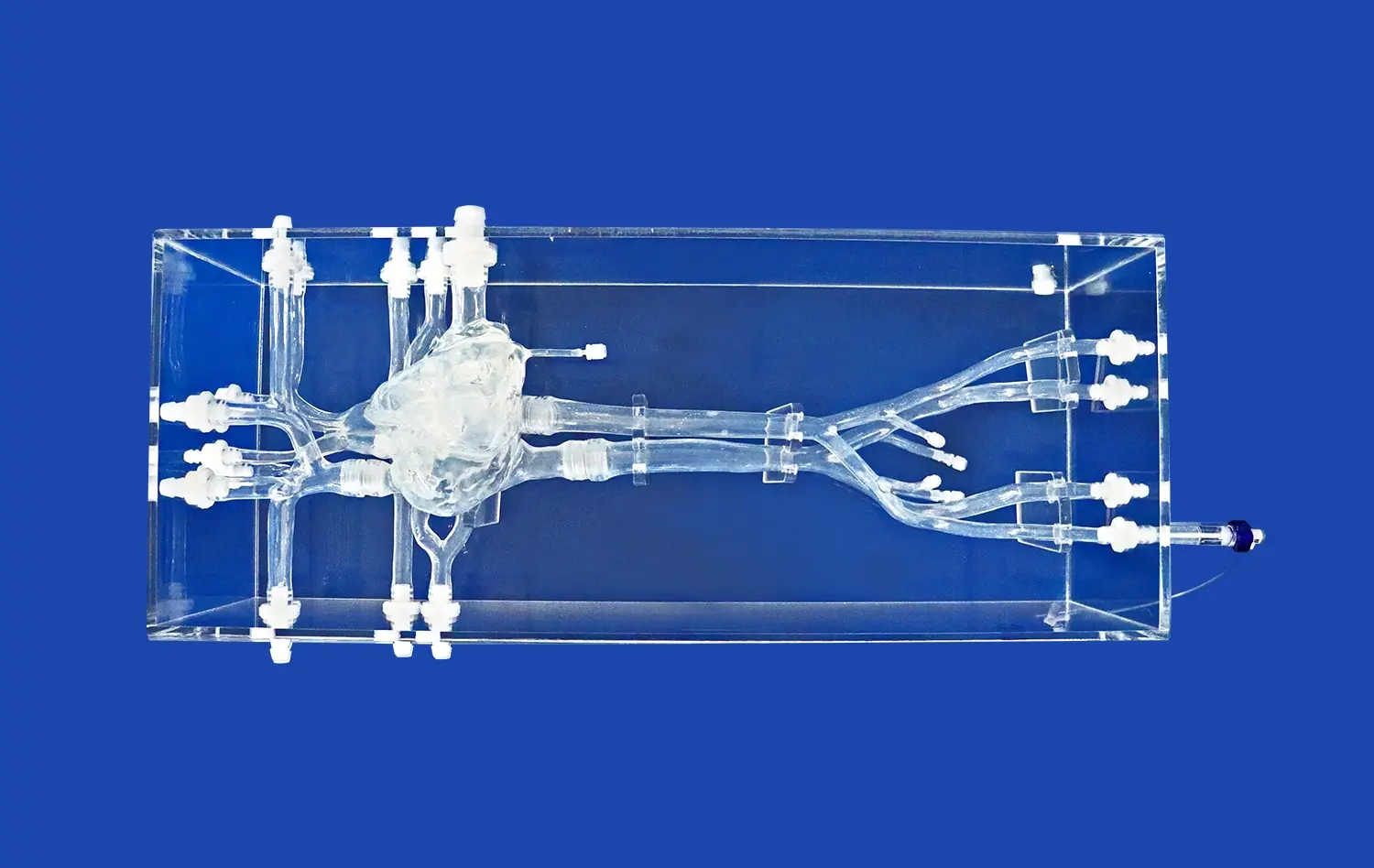
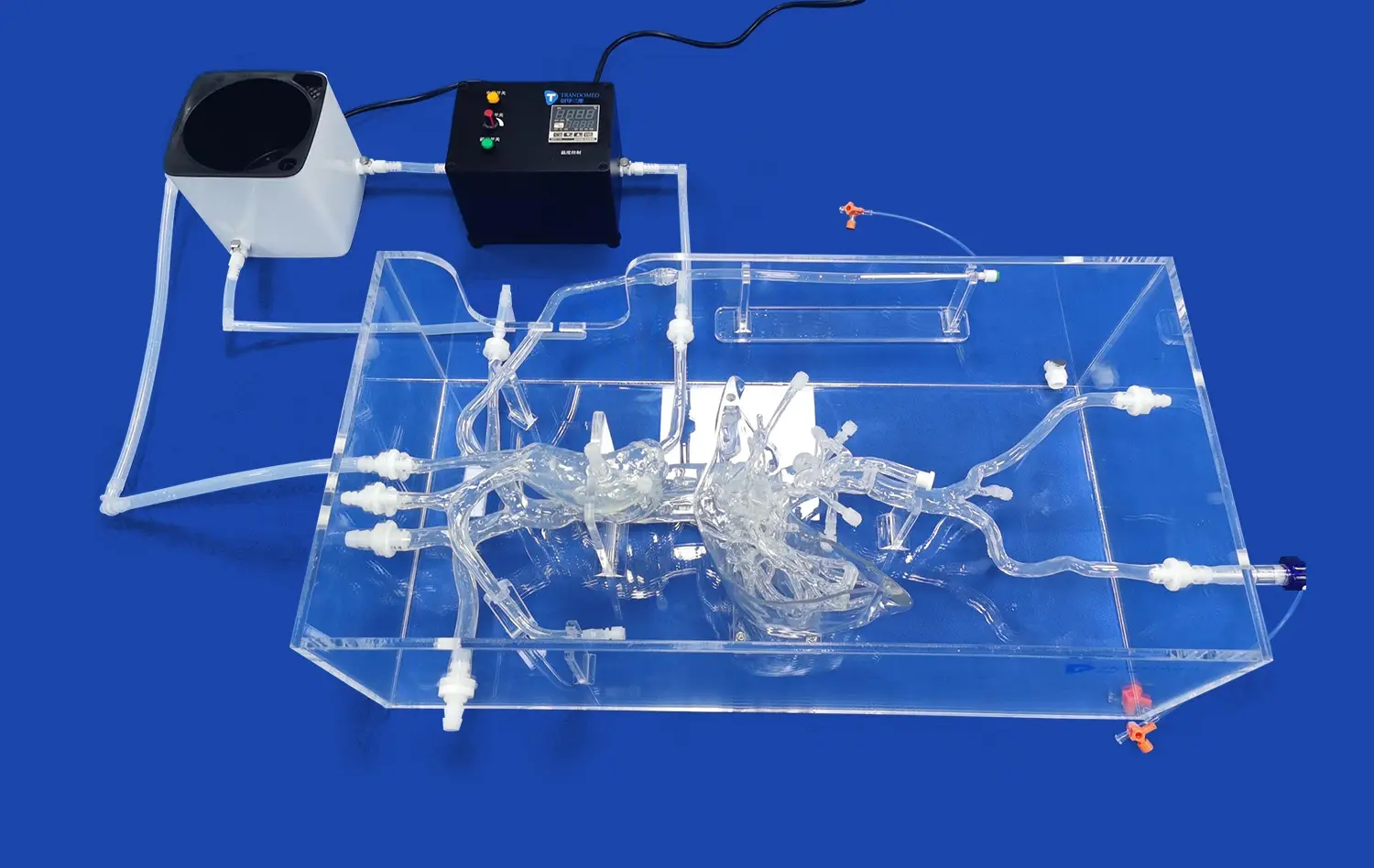
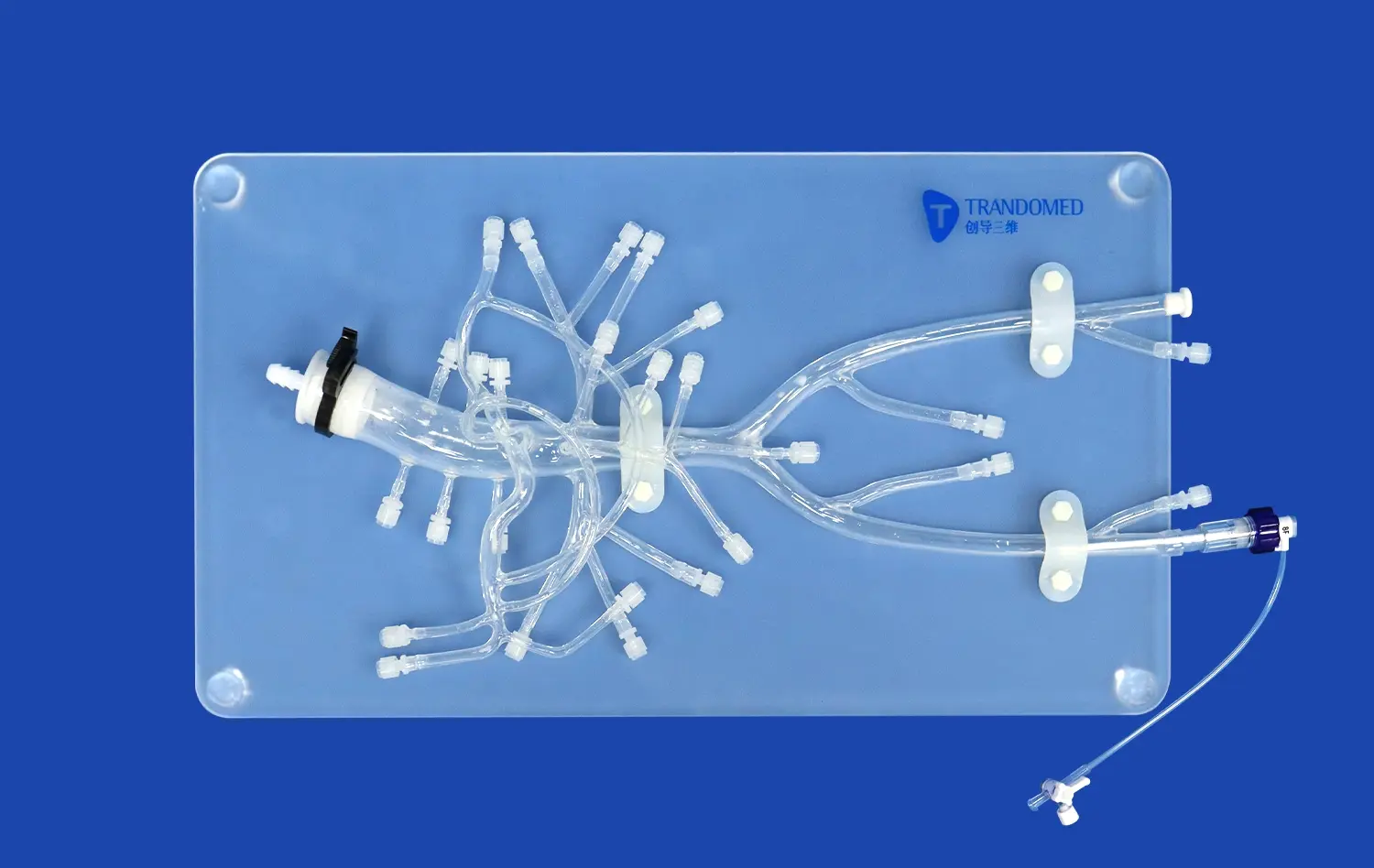
Realistic Peripheral Artery Intervention Training with Endovascular Intervention Trainer
2025-08-15 09:00:02
Endovascular intervention trainers have revolutionized the way medical professionals learn and perfect their skills in treating peripheral artery disease. These advanced simulators provide a risk-free environment for practitioners to hone their techniques in angioplasty, stenting, and other minimally invasive procedures. By offering a highly realistic replication of human vascular anatomy, endovascular trainers allow interventionists to practice complex cases, improve their hand-eye coordination, and enhance their decision-making abilities. The cutting-edge technology incorporated in these trainers, such as haptic feedback and real-time imaging, creates an immersive experience that closely mimics actual patient scenarios. As a result, healthcare providers can significantly improve their proficiency and confidence before performing procedures on real patients, ultimately leading to better outcomes and increased patient safety.
Which Peripheral Arteries Can Be Simulated Effectively?
Lower Extremity Arteries
Endovascular intervention trainers provide exceptionally realistic simulations of the critical lower extremity arterial network, which is a primary site for peripheral artery disease (PAD). These sophisticated models meticulously replicate the anatomy and common pathologies found in the iliac, femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries. Practitioners can encounter and manage a diverse range of simulated conditions, including significant stenoses (narrowings), complete occlusions, and potentially dangerous aneurysms. This high-fidelity environment allows clinicians to practice and refine a comprehensive suite of endovascular procedures essential for treating PAD, such as complex angioplasty, precise stent deployment, and effective atherectomy techniques within a safe, risk-free setting.
Upper Extremity Arteries
Although peripheral artery disease manifests less frequently in the upper extremities, modern endovascular intervention trainers effectively simulate these vital vascular territories. High-quality models accurately represent the anatomy of key arteries, including the subclavian, brachial, and radial vessels, which are crucial for access and specific pathologies. This capability provides essential opportunities for practitioners to develop and hone their skills in performing critical interventions like balloon angioplasty and stent placement in these regions. Training on these simulations ensures clinicians are proficient in managing upper extremity arterial diseases, such as subclavian steal syndrome or dialysis access complications, and familiar with the unique technical challenges they present.
Renal and Mesenteric Arteries
Advanced endovascular intervention trainers frequently incorporate detailed simulations of the renal and mesenteric arteries, recognizing their clinical significance. These models accurately replicate the often complex and tortuous anatomy of these visceral vessels and their associated pathologies. This realism is paramount for practicing essential interventions aimed at treating serious conditions like renovascular hypertension (caused by renal artery stenosis) and chronic mesenteric ischemia (resulting from mesenteric artery narrowing). Mastering techniques such as precise balloon dilatation and stent placement in these sensitive, anatomically challenging locations significantly enhances a trainee's overall procedural competency and confidence in managing complex visceral vascular disease.
Practicing Balloon Angioplasty and Atherectomy Techniques
Balloon Angioplasty Simulation
Endovascular trainers provide an ideal platform for mastering balloon angioplasty techniques. Users can practice selecting appropriate balloon sizes, positioning the balloon accurately within stenotic lesions, and inflating it to optimal pressures. The simulators often incorporate realistic resistance feedback, mimicking the sensation of balloon expansion against arterial plaque.
Atherectomy Device Handling
For more complex lesions, atherectomy is a valuable technique that can be practiced on endovascular trainers (endovascular intervention trainers). These simulators allow interventionists to familiarize themselves with various atherectomy devices, including rotational, directional, and laser atherectomy tools. Users can practice navigating these devices through tortuous vessels and removing simulated plaque effectively.
Complication Management
One of the key advantages of using endovascular intervention trainers is the ability to practice managing complications. Scenarios such as vessel dissection, perforation, or embolization can be simulated, allowing practitioners to develop their problem-solving skills and learn how to handle these critical situations without putting actual patients at risk.
Enhancing Device Navigation in Tortuous Vessel Paths
Guidewire and Catheter Manipulation
Navigating through tortuous vessels is a crucial skill in endovascular interventions. Endovascular trainers offer a safe environment to practice guidewire and catheter manipulation techniques. Users can improve their ability to navigate through complex anatomies, cross tight lesions, and maintain wire position during device exchanges.
Accessing Challenging Lesions
Some peripheral artery lesions can be particularly challenging to access due to their location or the surrounding vessel anatomy. Endovascular intervention trainers can simulate these difficult scenarios, allowing practitioners to develop strategies for accessing and treating lesions in bifurcations, heavily calcified segments, or chronically occluded vessels.
Optimizing Fluoroscopy Use
Efficient use of fluoroscopy is essential in endovascular procedures to minimize radiation exposure. Many trainers incorporate simulated fluoroscopy, enabling users to practice optimizing their imaging techniques. This includes learning to position the C-arm effectively, using collimation appropriately, and minimizing the overall fluoroscopy time while still obtaining the necessary visual information.
Conclusion
Endovascular intervention trainers have become indispensable tools in the training of vascular specialists. By providing a realistic and risk-free environment for practicing peripheral artery interventions, these simulators significantly enhance the learning curve and skill development of interventionists. The ability to replicate a wide range of arterial pathologies, practice various techniques, and manage complications in a controlled setting translates to improved patient outcomes and safety in real-world procedures. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and lifelike simulations, further bridging the gap between training and clinical practice.
Contact us
To learn more about our state-of-the-art endovascular intervention trainers and how they can benefit your training program, contact Trandomed today. Our expert team is ready to provide you with personalized solutions tailored to your specific training needs. Email us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com for more information on our cutting-edge medical simulation technology.
References
1. Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in Endovascular Simulation Training: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 33(5), 521-530.
2. Johnson, A. & Williams, R. (2021). "Impact of Simulation-Based Training on Endovascular Procedural Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis." European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 61(2), 285-293.
3. Lee, S.H. et al. (2023). "Virtual Reality in Peripheral Artery Intervention Training: Current Applications and Future Perspectives." Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, 46(3), 412-420.
4. Garcia, M.A. & Brown, T.L. (2022). "Optimizing Endovascular Skills Acquisition: The Role of High-Fidelity Simulators." Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 29(1), 102-110.
5. Wilson, K.R. et al. (2021). "Endovascular Simulation for Peripheral Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Training Efficacy." Annals of Vascular Surgery, 70, 295-305.
6. Chang, Y.H. & Kim, J.S. (2023). "Novel Approaches in Endovascular Intervention Training: Integrating 3D-Printed Models with Virtual Simulation." Journal of Vascular Surgery, 77(4), 1289-1297.