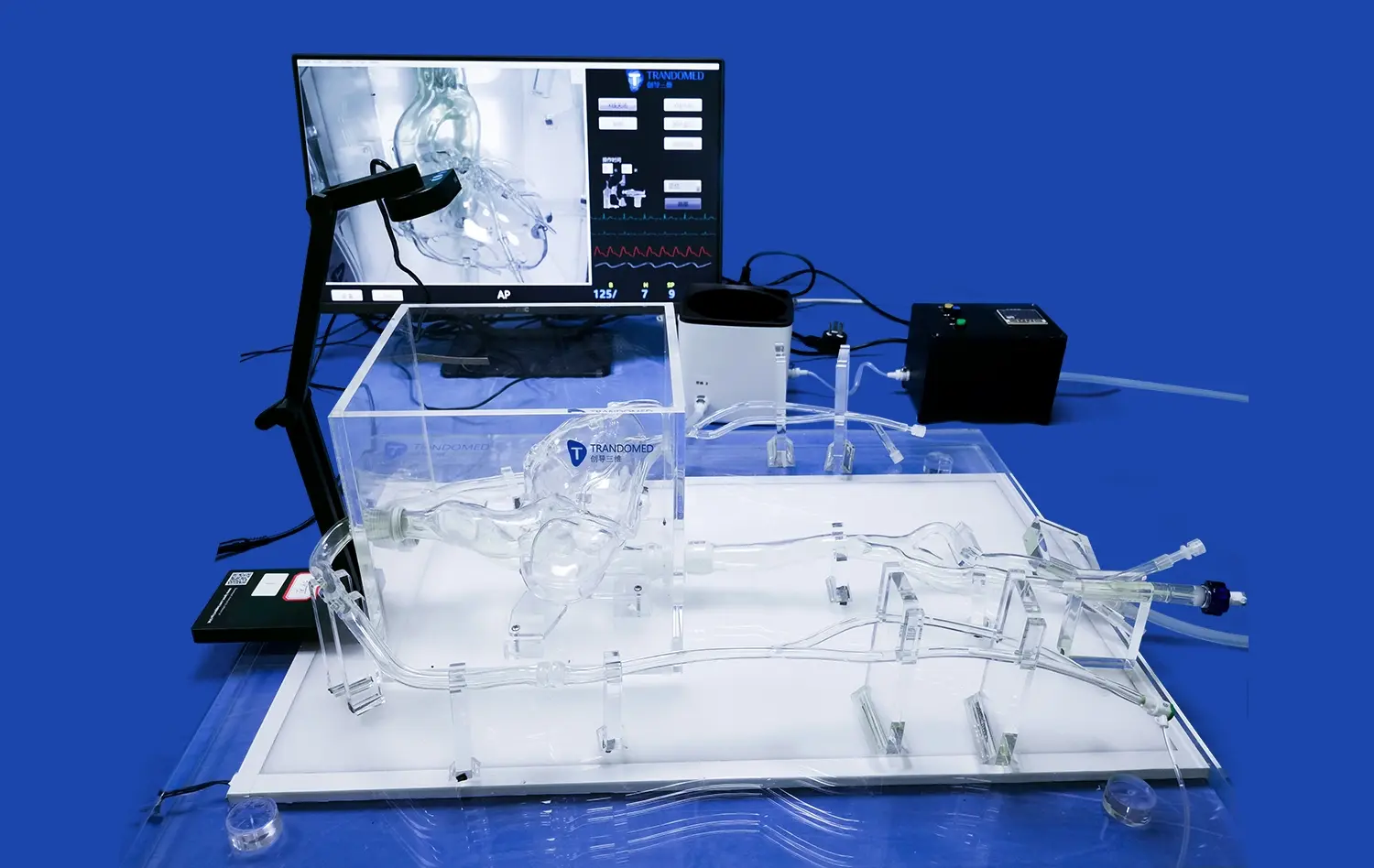
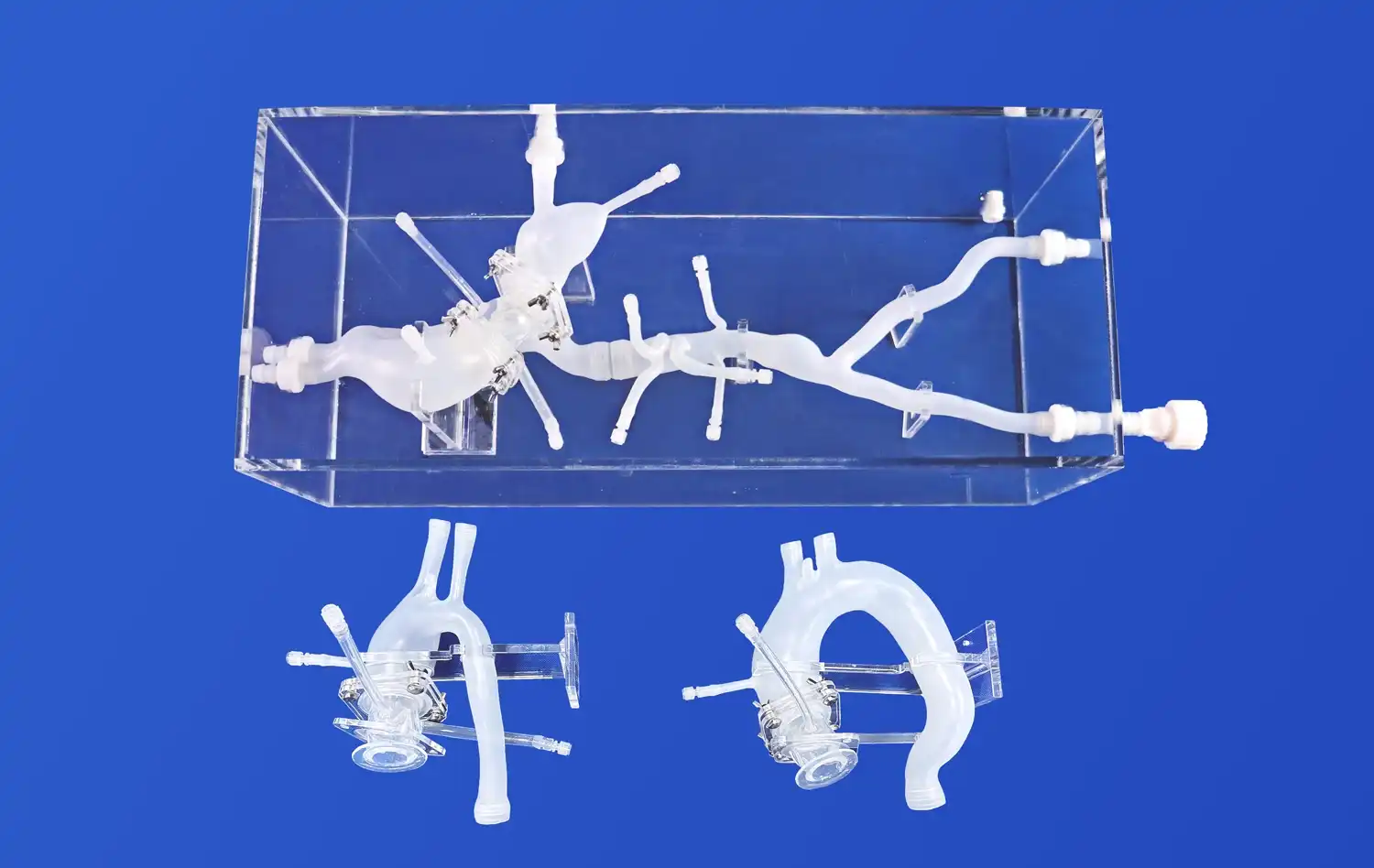
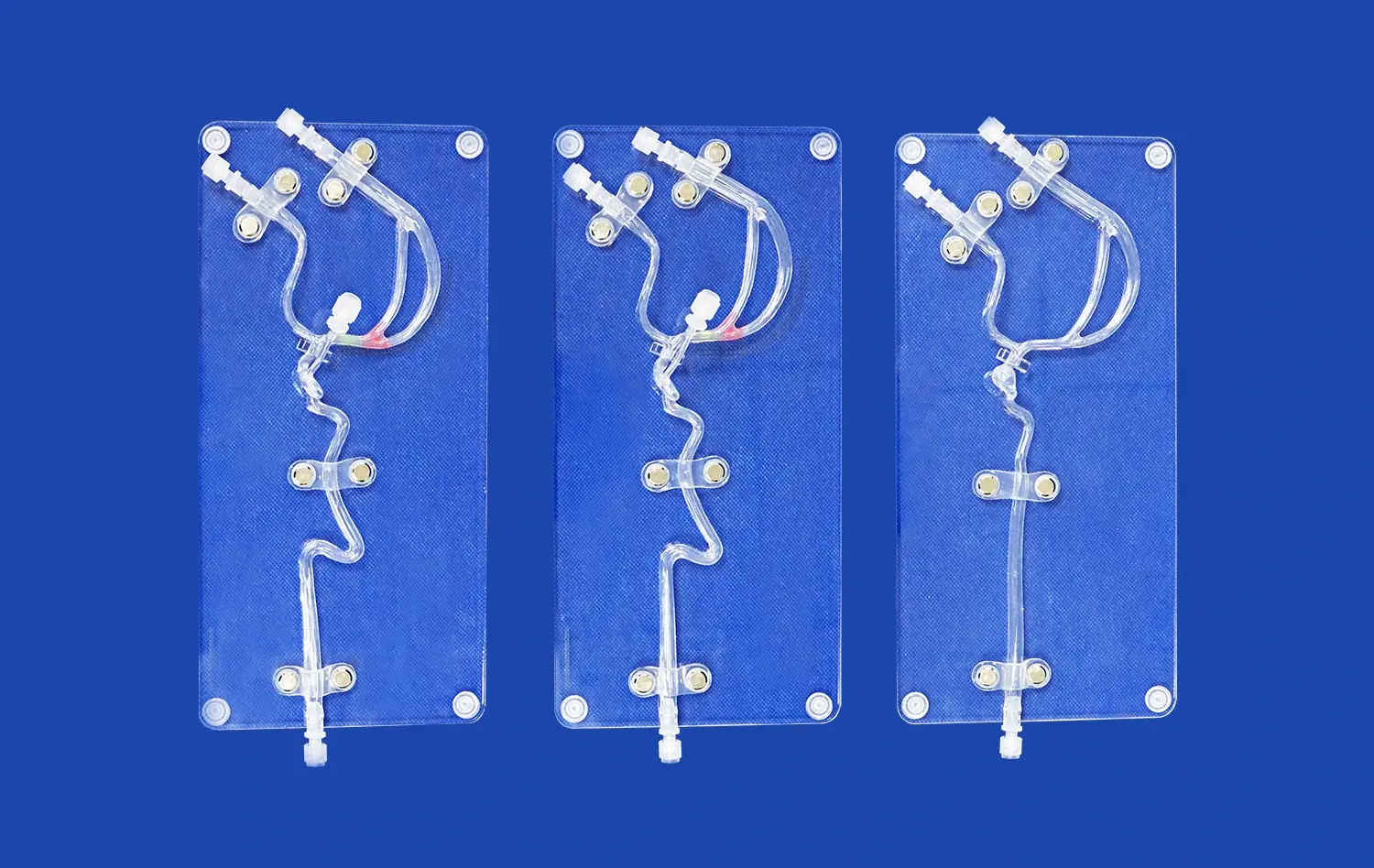
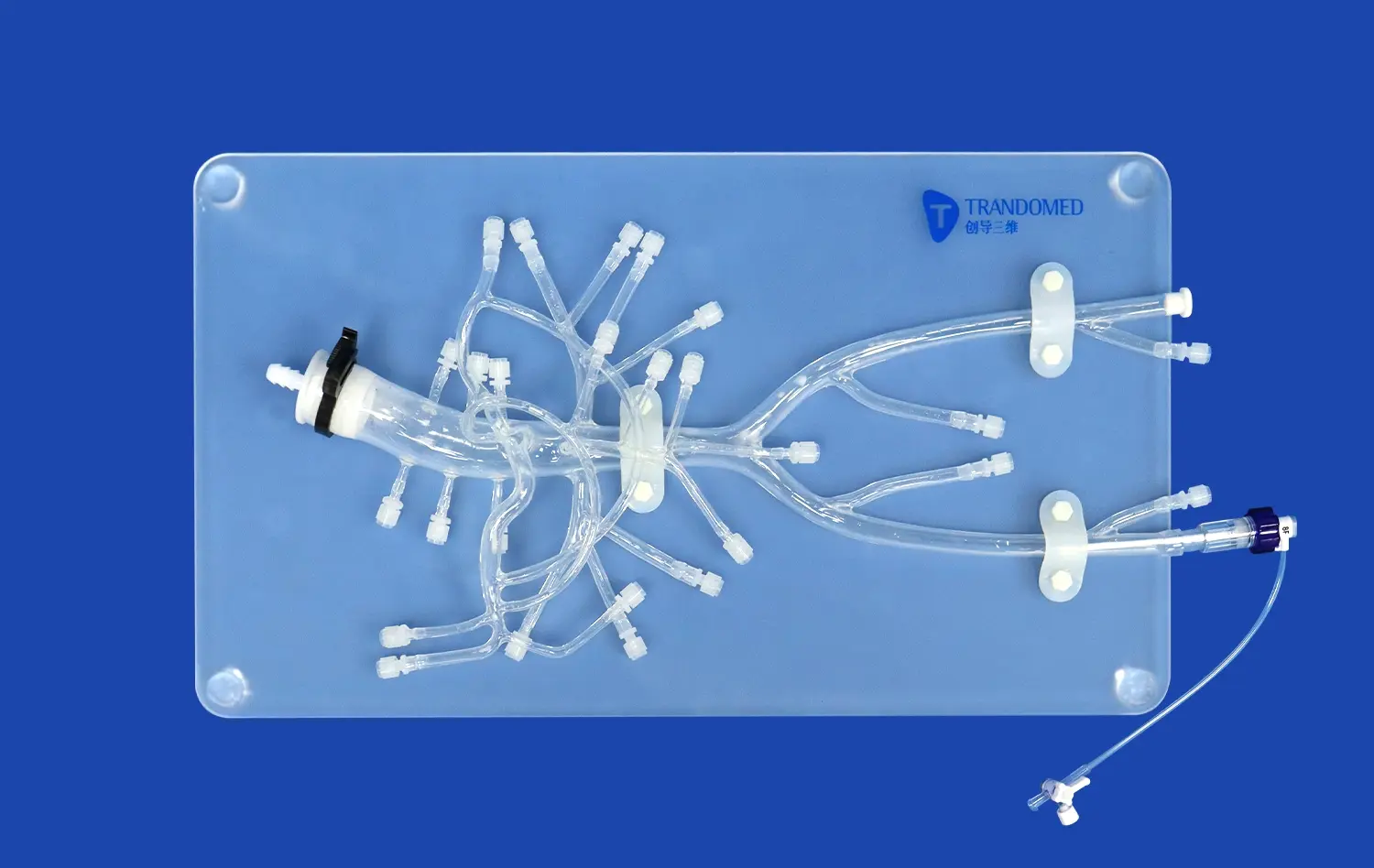
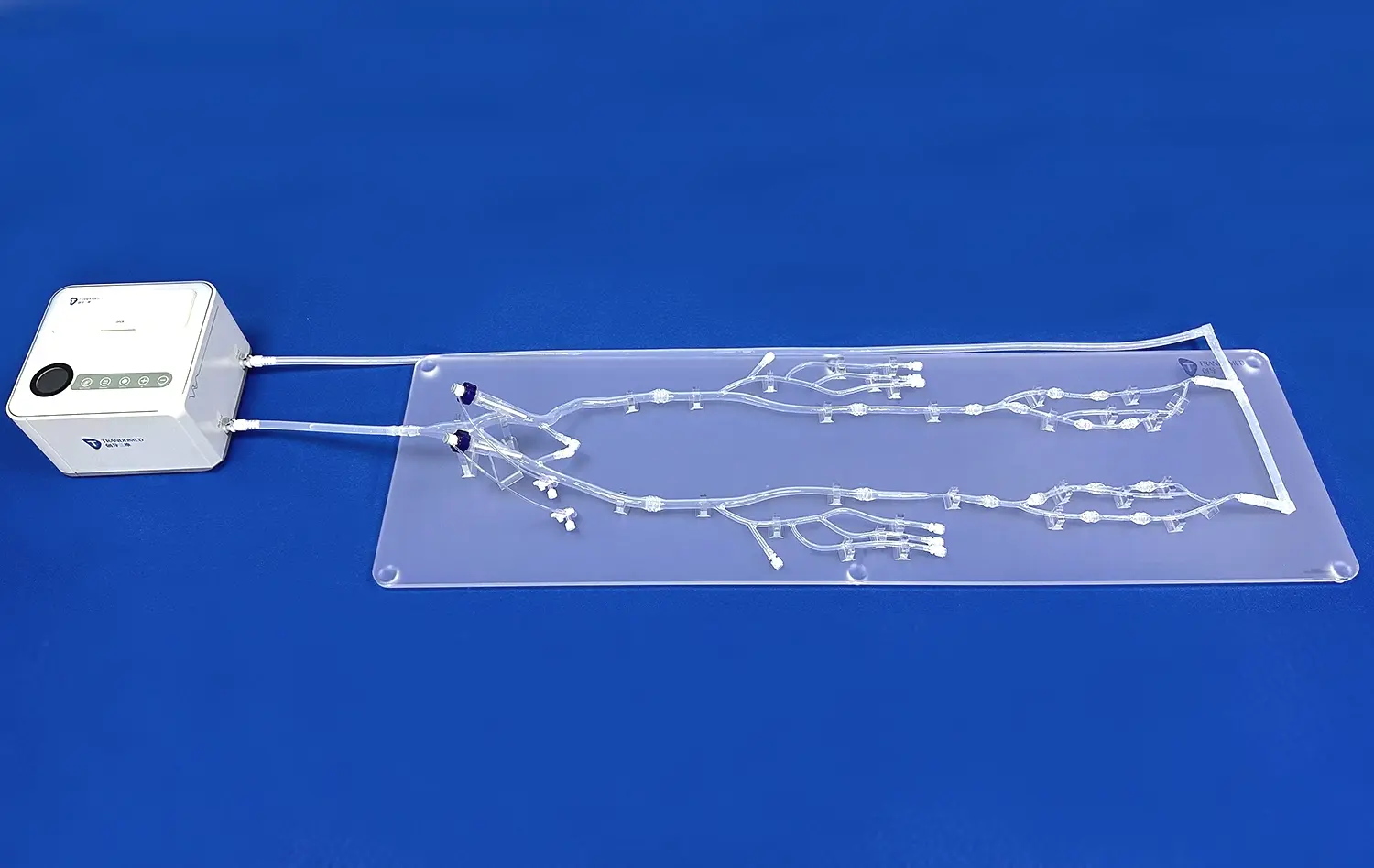
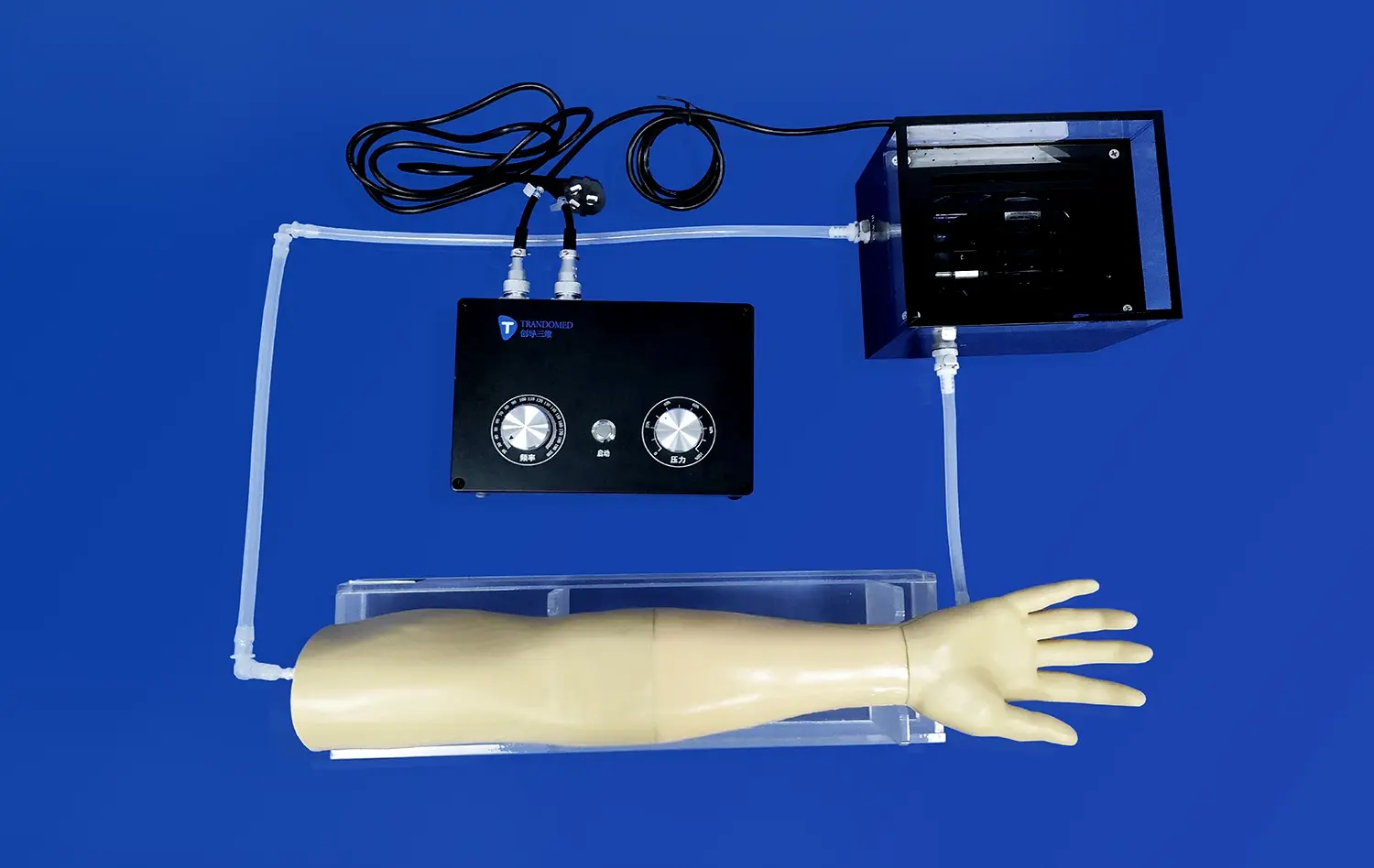
How Do Anatomically Correct Models Improve Surgical Precision?
Enhanced Spatial Awareness and Anatomical Understanding
Anatomically correct stomach models provide surgeons with a tangible representation of the complex three-dimensional structure of the gastrointestinal tract. By interacting with these lifelike replicas, medical professionals can develop a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships between different organs and tissues. This enhanced anatomical awareness translates directly to improved surgical precision, as surgeons can better visualize and navigate the intricate landscape of the stomach and surrounding structures during actual procedures.
Moreover, these models often incorporate various pathological conditions, allowing surgeons to familiarize themselves with abnormal anatomical variations they may encounter in real patients. This exposure to diverse scenarios helps build confidence and adaptability, crucial traits for achieving optimal surgical outcomes.
Realistic Tissue Handling and Instrument Manipulation
High-quality stomach simulators are designed to mimic the texture, elasticity, and resistance of actual stomach tissue. This realism enables surgeons to practice proper tissue handling techniques and develop the necessary tactile sensitivity required for delicate procedures. By repeatedly interacting with these lifelike materials, surgeons can refine their motor skills and improve their ability to apply appropriate force and pressure during surgical maneuvers.
Furthermore, these models allow for the use of real surgical instruments, providing an authentic experience in tool manipulation. Surgeons can practice techniques such as suturing, stapling, and dissection on the model, honing their dexterity and precision with the same instruments they'll use in the operating room.
Customizable Pathologies for Targeted Training
Advanced stomach models can be customized to represent specific pathologies or anatomical variations. This feature allows surgeons to practice on scenarios tailored to their particular needs or areas of specialization. For instance, a model might be designed to showcase a stomach tumor, enabling oncological surgeons to rehearse complex resection techniques.
By practicing on these customized models, surgeons can develop targeted skills and strategies for addressing specific challenges they may face in their clinical practice. This focused training approach significantly contributes to improved surgical precision and confidence when dealing with similar cases in real patients.
Simulation of Common and Complex GI Procedures
Endoscopic Techniques and Minimally Invasive Surgeries
Realistic stomach models serve as invaluable tools for simulating endoscopic procedures and minimally invasive surgeries. These models can be designed with hollow interiors and accessible entry points, allowing trainees to practice inserting and manipulating endoscopes and laparoscopic instruments. By simulating procedures such as gastroscopy, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), and laparoscopic fundoplication, surgeons can refine their techniques in a controlled environment.
The ability to repeatedly practice these procedures on anatomically accurate models helps surgeons overcome the learning curve associated with minimally invasive techniques. This leads to improved efficiency and reduced procedure times when performing actual surgeries, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
Complex Resections and Reconstructions
Advanced stomach models enable the simulation of complex gastrointestinal procedures, such as partial or total gastrectomy and subsequent reconstructions. These intricate surgeries require a high level of skill and precision, making practice on realistic models crucial for surgical success.
By incorporating features like variable tissue densities and simulated blood vessels, these models allow surgeons to practice delicate dissection techniques, vascular control, and anastomosis creation. The ability to rehearse these challenging procedures in a low-stakes environment helps surgeons refine their approach and anticipate potential complications before encountering them in live surgery.
Management of Gastrointestinal Emergencies
Stomach models can also be utilized to simulate emergency scenarios, such as gastrointestinal perforations or severe bleeding. These high-pressure situations require quick thinking and precise action, making simulation-based training essential for developing the necessary skills and decision-making abilities.
By practicing on models that can be manipulated to represent various emergency conditions, surgeons can improve their response times and develop effective strategies for managing critical situations. This type of training is particularly valuable for residents and fellows, as it provides a safe environment to learn and make mistakes without risking patient safety.
How Realistic Models Reduce Training Risks and Improve Outcomes?
Minimizing Patient Risk During the Learning Curve
One of the most significant advantages of using realistic stomach models in surgical training is the substantial reduction in patient risk during the learning process. Traditional surgical education often involves a "see one, do one, teach one" approach, which can potentially expose patients to complications arising from a surgeon's inexperience. By incorporating lifelike stomach simulators into the training curriculum, medical institutions can ensure that surgeons have ample opportunity to practice and refine their skills before operating on actual patients.
This approach not only protects patients from unnecessary risks but also allows surgeons to make mistakes and learn from them in a consequence-free environment. As a result, when surgeons do begin performing procedures on real patients, they are better prepared and more confident, leading to improved patient safety and outcomes.
Standardization of Surgical Techniques and Procedures
Realistic stomach models play a crucial role in standardizing surgical techniques and procedures across medical institutions. By providing a consistent platform for training and assessment, these models ensure that all surgeons receive uniform instruction in best practices and evidence-based approaches to gastrointestinal surgery.
Standardization through model-based training helps reduce variability in surgical outcomes and promotes the adoption of proven techniques. This consistency in approach not only improves overall patient care but also facilitates better communication and collaboration among surgical teams, as all members share a common foundation of knowledge and skills.
Objective Assessment and Continuous Improvement
High-fidelity stomach models offer an excellent opportunity for objective assessment of surgical skills and performance. Unlike real surgeries, where variables can be difficult to control, simulations using these models provide a standardized environment for evaluating a surgeon's technique, efficiency, and decision-making abilities.
Many advanced simulation systems incorporate sensors and tracking technologies that can measure various performance metrics, such as instrument movement, procedure time, and accuracy. This data can be used to provide detailed feedback to trainees, helping them identify areas for improvement and track their progress over time.
Furthermore, the ability to record and review simulated procedures allows for in-depth analysis and debriefing sessions, promoting a culture of continuous improvement in surgical practice. This iterative learning process, facilitated by realistic models, contributes significantly to the overall enhancement of surgical skills and, consequently, to better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Realistic stomach models have emerged as indispensable tools in gastrointestinal surgical training, offering a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By providing a safe, standardized environment for skill development and assessment, these models significantly contribute to improved surgical precision, reduced training risks, and enhanced patient outcomes. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of high-fidelity simulations will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping the next generation of skilled and confident gastrointestinal surgeons.
Contact Us
Elevate your gastrointestinal surgical training program with Trandomed's state-of-the-art stomach models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D printed medical simulators, we offer anatomically accurate, customizable solutions that meet the diverse needs of medical institutions worldwide. Experience the benefits of our innovative products, backed by over 20 years of expertise in medical 3D printing. Don't miss the opportunity to enhance your surgical education and improve patient outcomes. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our realistic stomach models and how they can revolutionize your training approach.