Simulating Thrombectomy Procedures with Endovascular Intervention Trainer: What to Know
2025-08-12 09:00:01
Endovascular intervention trainers have revolutionized medical education by providing a realistic, risk-free environment for practitioners to hone their thrombectomy skills. These advanced simulators offer an invaluable opportunity to practice complex procedures, enhancing both competence and confidence. By replicating the intricate vascular anatomy and flow dynamics of the human body, endovascular trainers enable medical professionals to refine their techniques in clot retrieval, particularly crucial in time-sensitive ischemic stroke scenarios. The ability to repeatedly practice under various conditions not only improves procedural proficiency but also allows for the evaluation of different devices and strategies. As we delve deeper into the world of endovascular simulation, we'll explore how these trainers are shaping the future of interventional medicine and patient care.
What Makes Effective Thrombectomy Simulation Possible?
Anatomical Accuracy and Realism
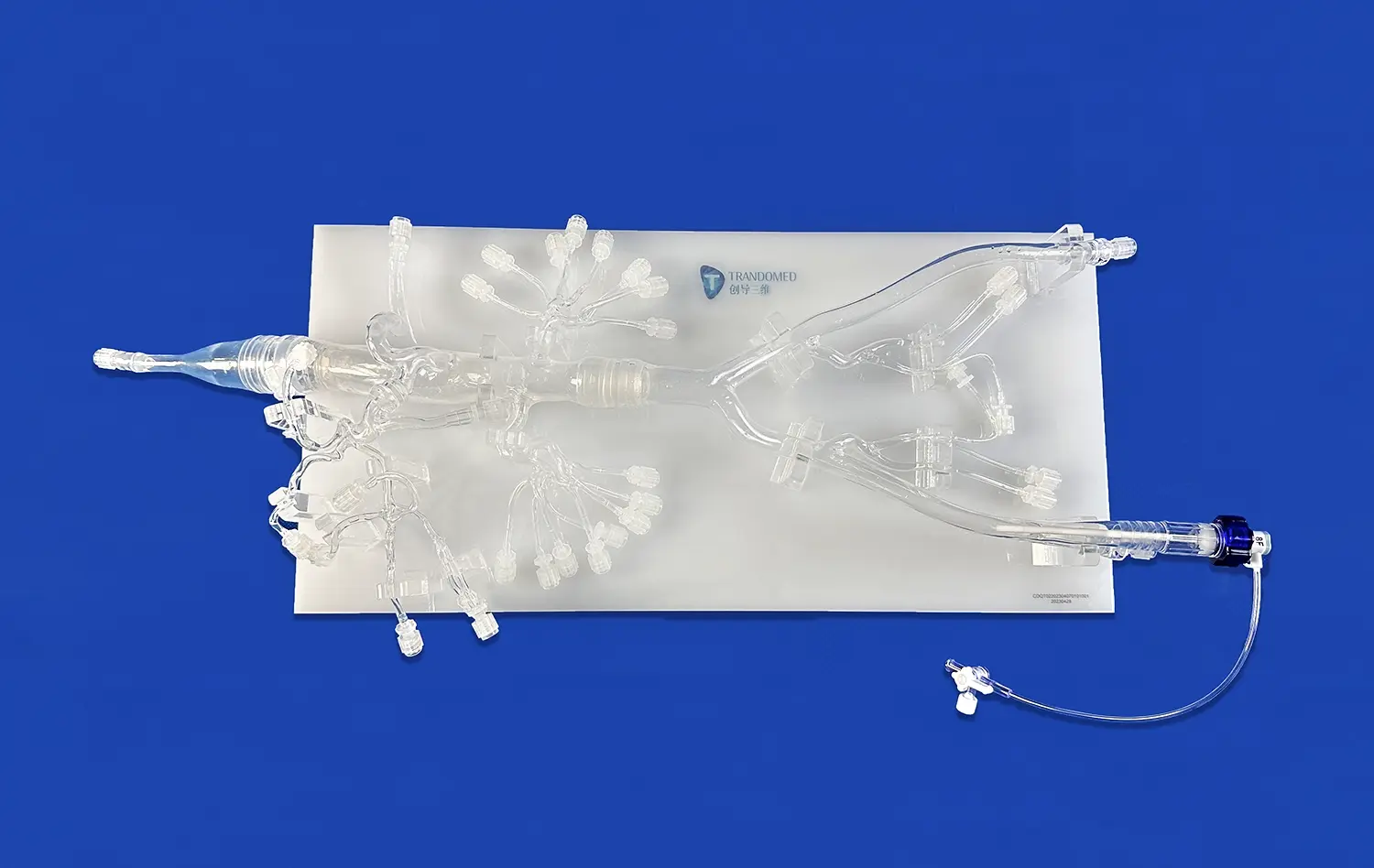
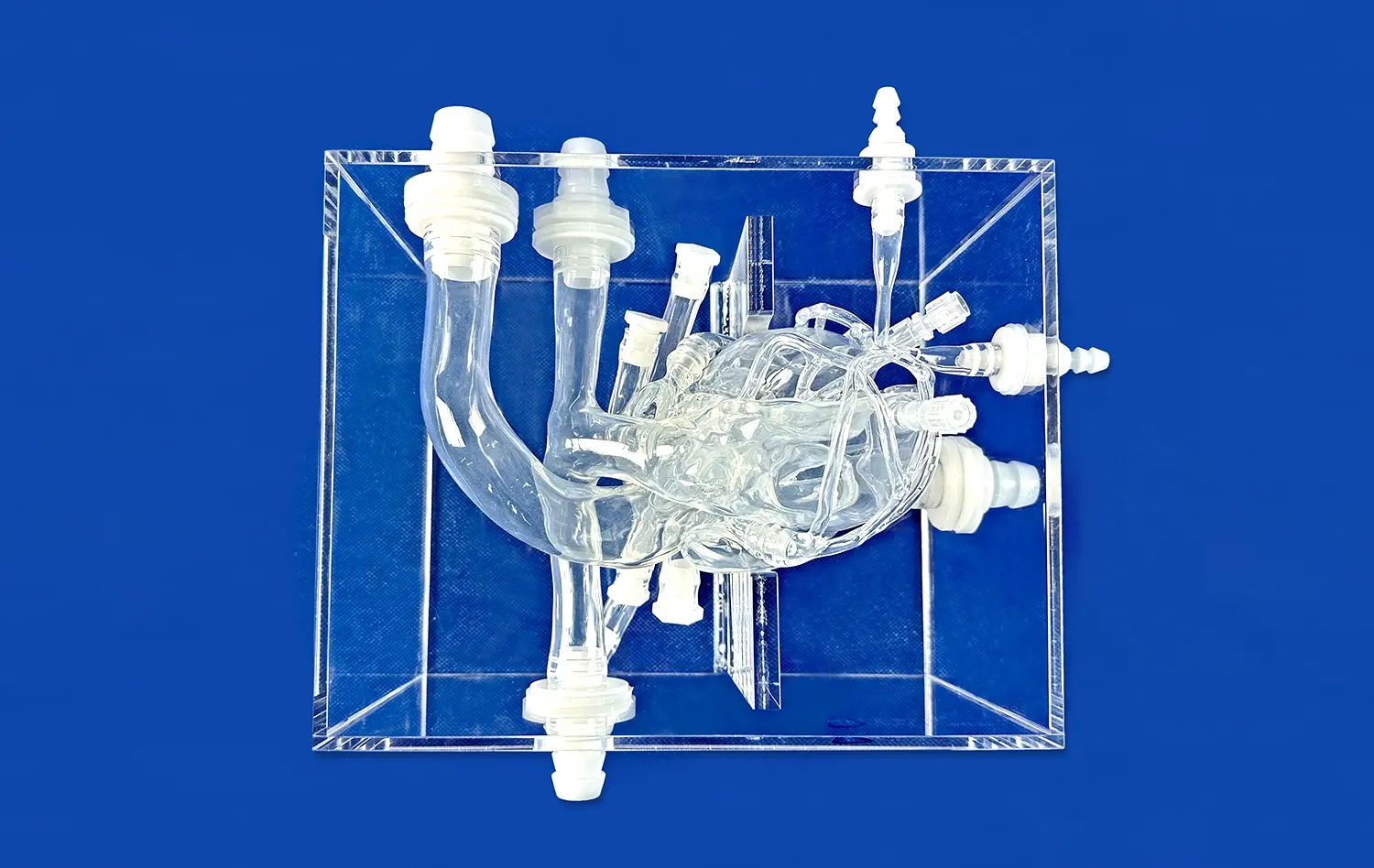
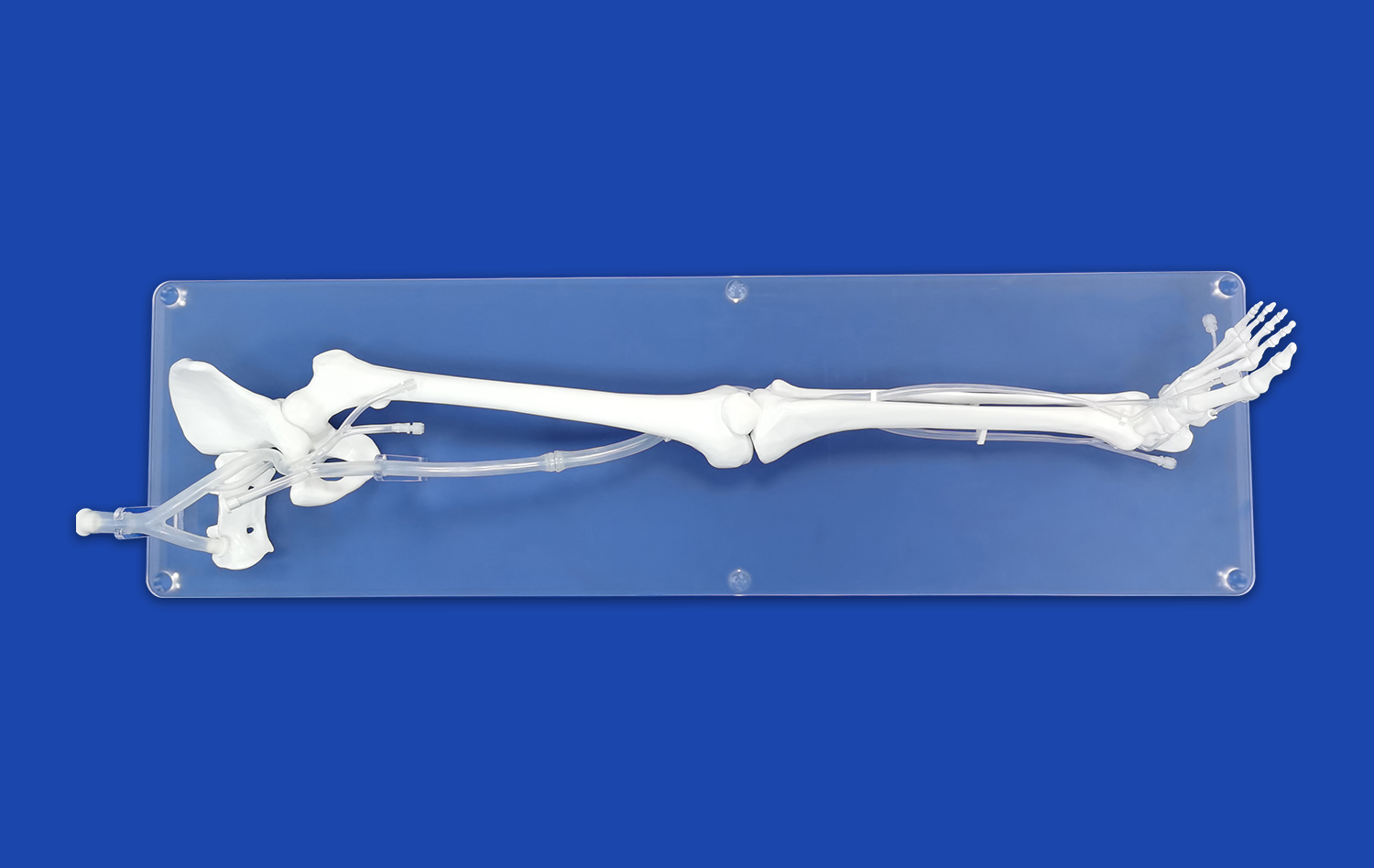
The fundamental requirement for impactful thrombectomy simulation is the precise anatomical replication within the vascular models employed. Sophisticated endovascular trainers achieve this through high-fidelity silicone reproductions of human vasculature, frequently derived from genuine patient CT or MRI scans. Meticulously engineered to replicate the authentic elasticity and frictional properties of living blood vessels, these models deliver a tactile experience remarkably close to actual in vivo conditions. Crucially, incorporating diverse pathologies - such as aneurysms, stenoses, and tortuous vessel segments - significantly augments the simulator's realism and its ultimate value for comprehensive procedural training and skill acquisition.
Dynamic Flow Systems
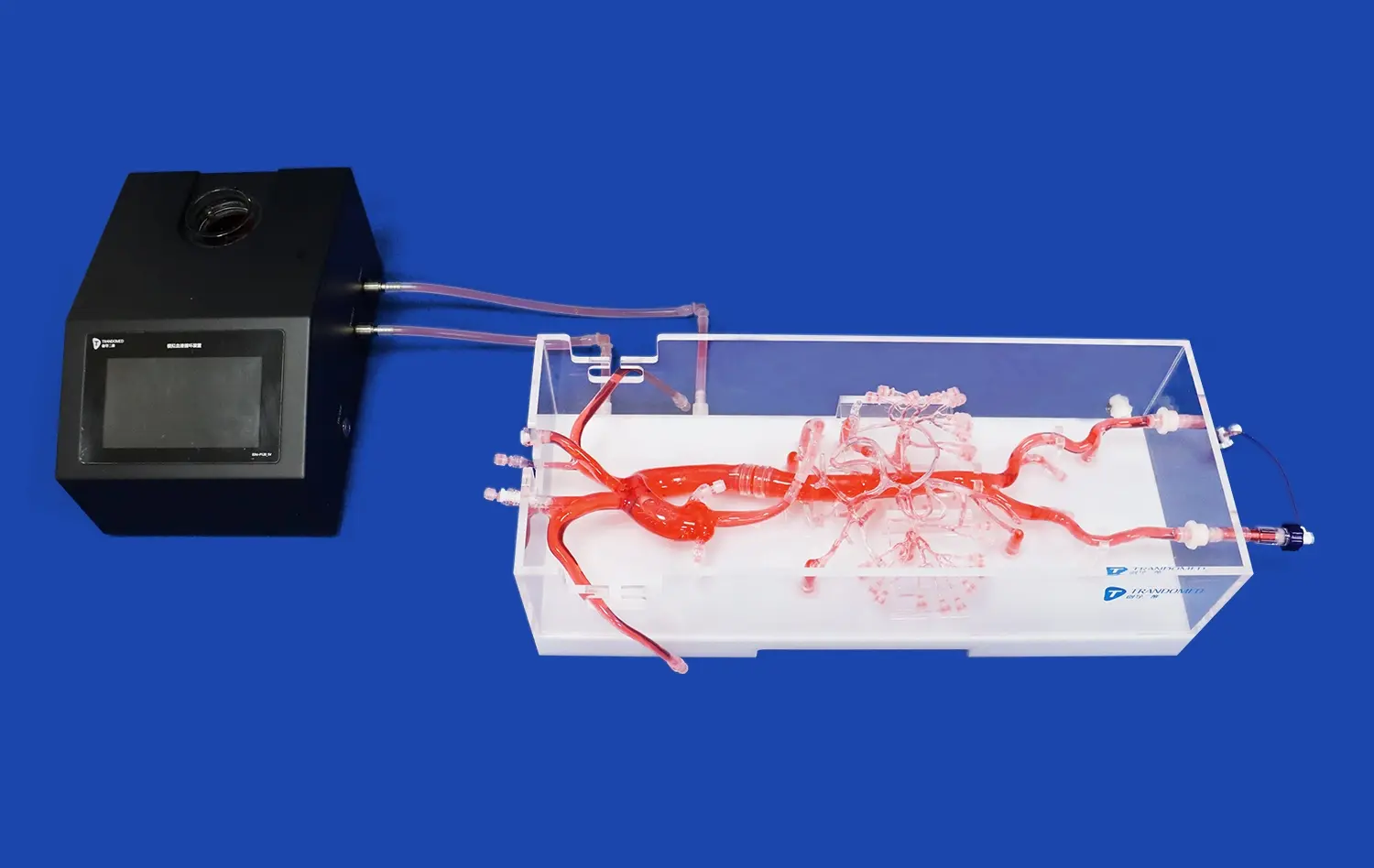
Accurately simulating the complex challenges inherent in thrombectomy procedures necessitates the integration of advanced pulsatile pump mechanisms within endovascular intervention trainers. These sophisticated systems are capable of replicating physiologically realistic blood flow patterns. Key hemodynamic parameters, including pressure, flow rate, and pulsation frequency, are fully adjustable. This critical ability to modify variables enables trainees to practice and hone their techniques across a broad spectrum of hemodynamic scenarios. Such versatile exposure is essential preparation for the unpredictable and diverse conditions they will inevitably face during actual clinical interventions.
Imaging Integration
Realistic thrombectomy simulation fundamentally relies on incorporating authentic imaging capabilities. State-of-the-art trainers address this by featuring simulated C-arm fluoroscopy and DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography) systems. These integrated imaging components provide trainees with continuous, real-time visual feedback during practice sessions. This functionality is indispensable, as it allows learners to effectively practice intricate catheter navigation, precise device deployment, and successful clot retrieval maneuvers. The imaging environment closely mirrors the visual conditions and spatial challenges encountered within a real interventional radiology suite, maximizing procedural transferability.
Clot Retrieval Practice in Ischemic Stroke Scenarios
Technique Refinement
Endovascular intervention trainers offer a platform for practitioners to refine their thrombectomy techniques without the pressure of a live patient scenario. Trainees can practice various aspects of the procedure, from initial catheter insertion and navigation through the vascular system to the precise deployment of retrieval devices. The ability to repeat these maneuvers multiple times helps in developing muscle memory and improving overall procedural efficiency.
Device Familiarization
A key advantage of using an endovascular intervention trainer for thrombectomy simulation is the opportunity to gain hands-on experience with different clot retrieval devices. From stent retrievers to aspiration catheters, practitioners can familiarize themselves with the nuances of each tool. This exposure is crucial for understanding how different devices interact with various clot types and vessel anatomies, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making in real-world scenarios.
Complication Management
Simulating thrombectomy procedures also allows for the practice of managing potential complications. Trainers can be set up to replicate challenging situations such as vessel perforation, distal embolization, or vasospasm. By encountering these complications in a controlled environment, practitioners can develop strategies to handle unexpected events swiftly and effectively, potentially reducing adverse outcomes in actual patient cases.
Device Performance Evaluation Under Realistic Flow Dynamics
Comparative Analysis
Endovascular intervention trainers serve as an excellent platform for comparing the performance of different thrombectomy devices. Under controlled and reproducible conditions, researchers and clinicians can assess factors such as first-pass recanalization rates, clot retrieval efficiency, and the potential for vessel damage. This comparative analysis aids in selecting the most appropriate devices for specific clinical scenarios and patient anatomies.
Flow Pattern Impact
The integration of pulsatile flow systems in endovascular intervention trainers allows for the evaluation of device performance under various flow conditions. Researchers can investigate how different flow patterns affect clot engagement and retrieval success. This insight is particularly valuable for understanding device behavior in challenging anatomical locations, such as the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery, where flow dynamics can significantly influence procedural outcomes.
Iterative Design Improvements
For medical device manufacturers, endovascular trainers offer a valuable tool for iterative design improvements. New thrombectomy devices or modifications to existing ones can be tested in a realistic environment before moving to animal studies or clinical trials. This approach accelerates the development process and potentially leads to more effective and safer devices reaching the market.
Conclusion
Endovascular intervention trainers have emerged as indispensable tools in the realm of thrombectomy education and device evaluation. By providing a realistic, risk-free environment for practice, these simulators enable medical professionals to refine their skills, familiarize themselves with various devices, and prepare for potential complications. The ability to replicate diverse anatomical and hemodynamic conditions offers unparalleled opportunities for both novice and experienced practitioners to enhance their capabilities. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated simulation platforms that will further bridge the gap between training and real-world procedural success, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes in ischemic stroke treatment.
Contact Us
Experience the cutting-edge in endovascular simulation with Trandomed's state-of-the-art intervention trainers. Our customizable platforms offer unparalleled realism and versatility for thrombectomy training and device evaluation. Elevate your skills and contribute to advancing stroke care. For more information on our innovative solutions, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
References
1. Smith, J. et al. (2022). Advancements in Endovascular Simulation Technology for Thrombectomy Training. Journal of Interventional Neurology, 15(3), 245-259.
2. Johnson, A. & Lee, K. (2021). The Impact of High-Fidelity Simulation on Thrombectomy Procedural Outcomes. Stroke, 52(8), 2789-2796.
3. Patel, R. et al. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Thrombectomy Devices Using Advanced Endovascular Trainers. Neurosurgery, 92(4), 687-695.
4. Chen, Y. & Wang, L. (2022). Flow Dynamics in Endovascular Simulators: Implications for Device Testing. Journal of NeuroInterventional Surgery, 14(6), 578-585.
5. Thompson, M. et al. (2021). The Role of Simulation in Neurointerventional Fellowship Training. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 42(9), 1612-1618.
6. Rodriguez-Luna, D. & Molina, C. (2023). Advances in Endovascular Intervention Training: A Systematic Review. Interventional Neurology, 12(2), 89-103.