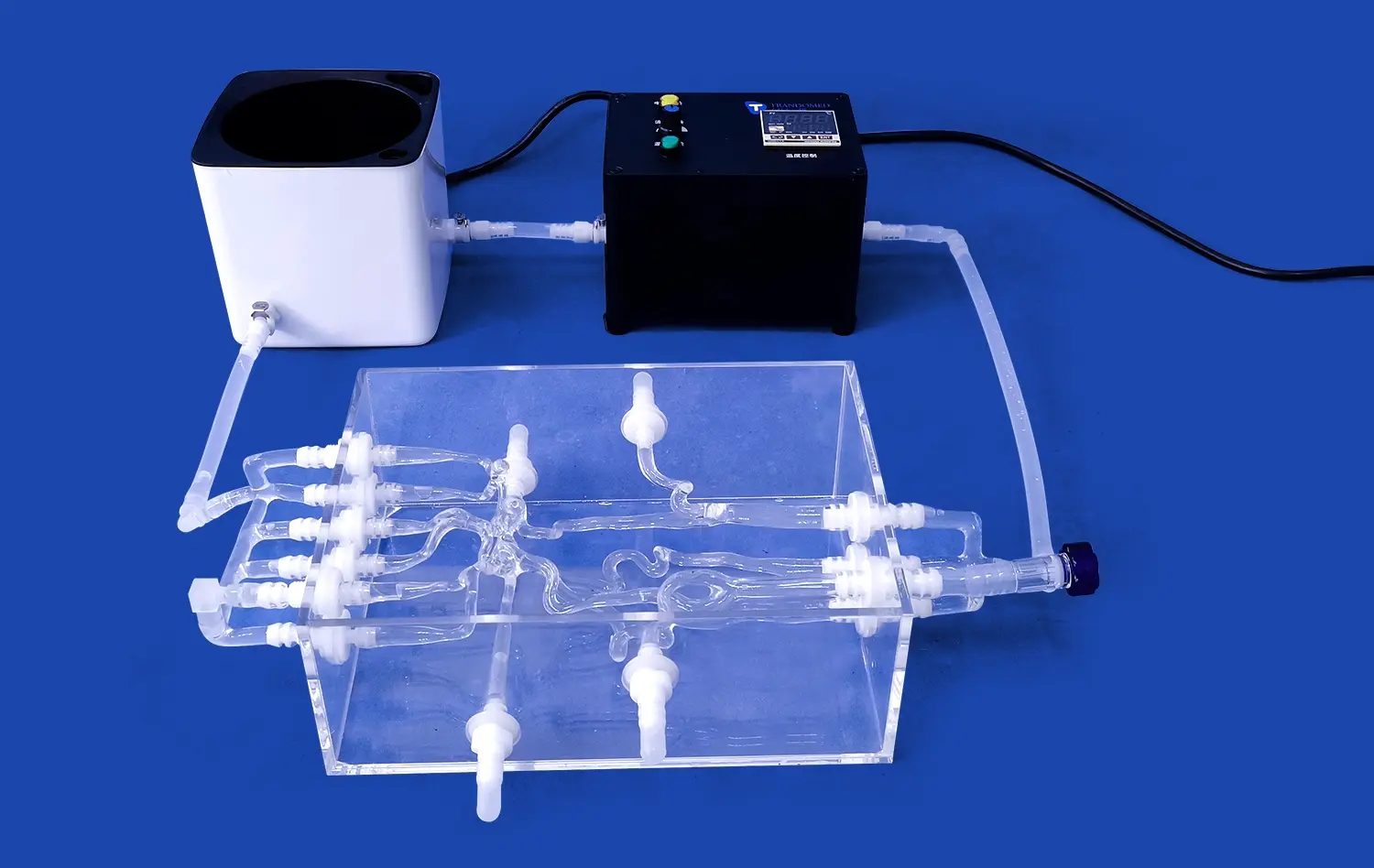
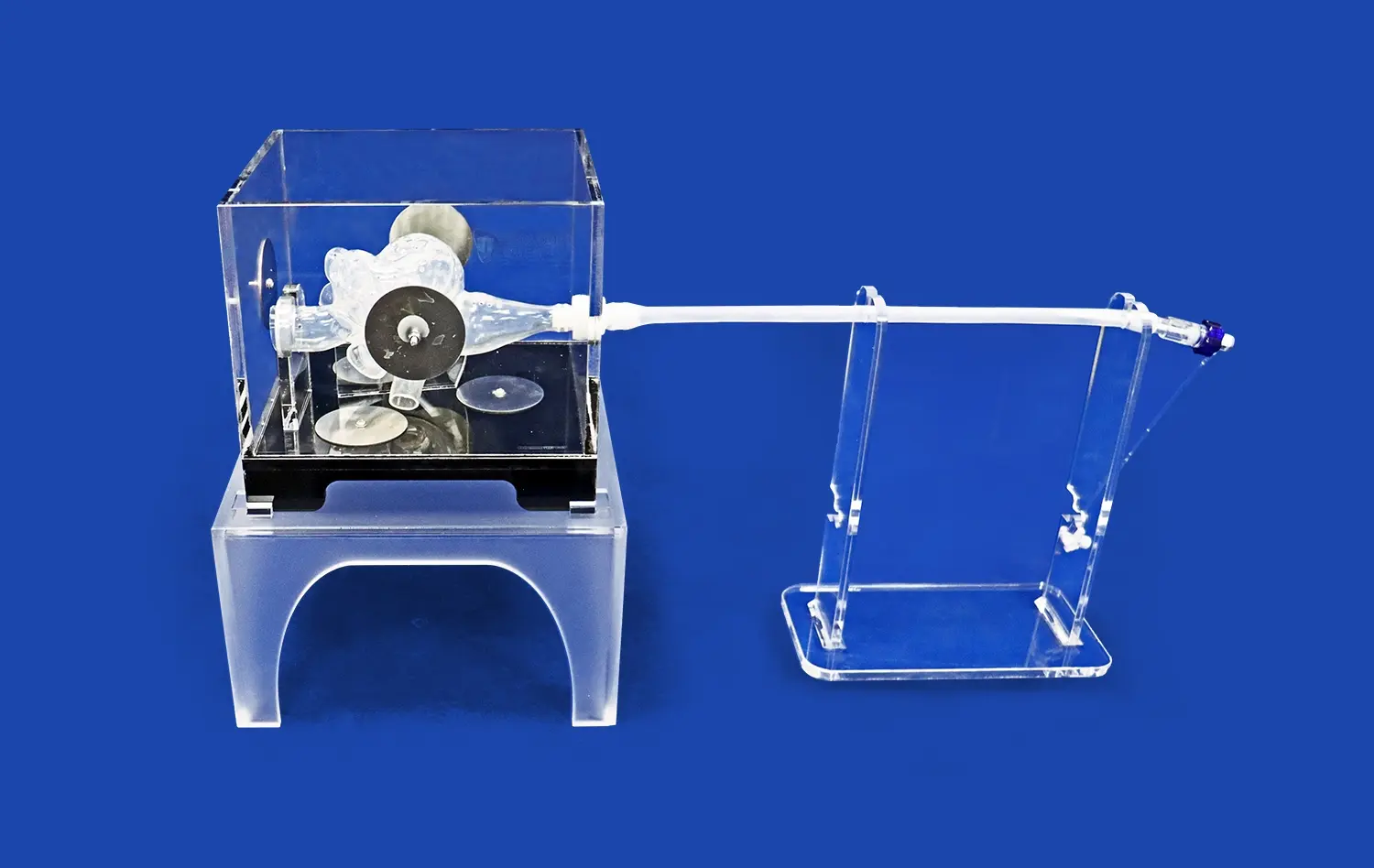
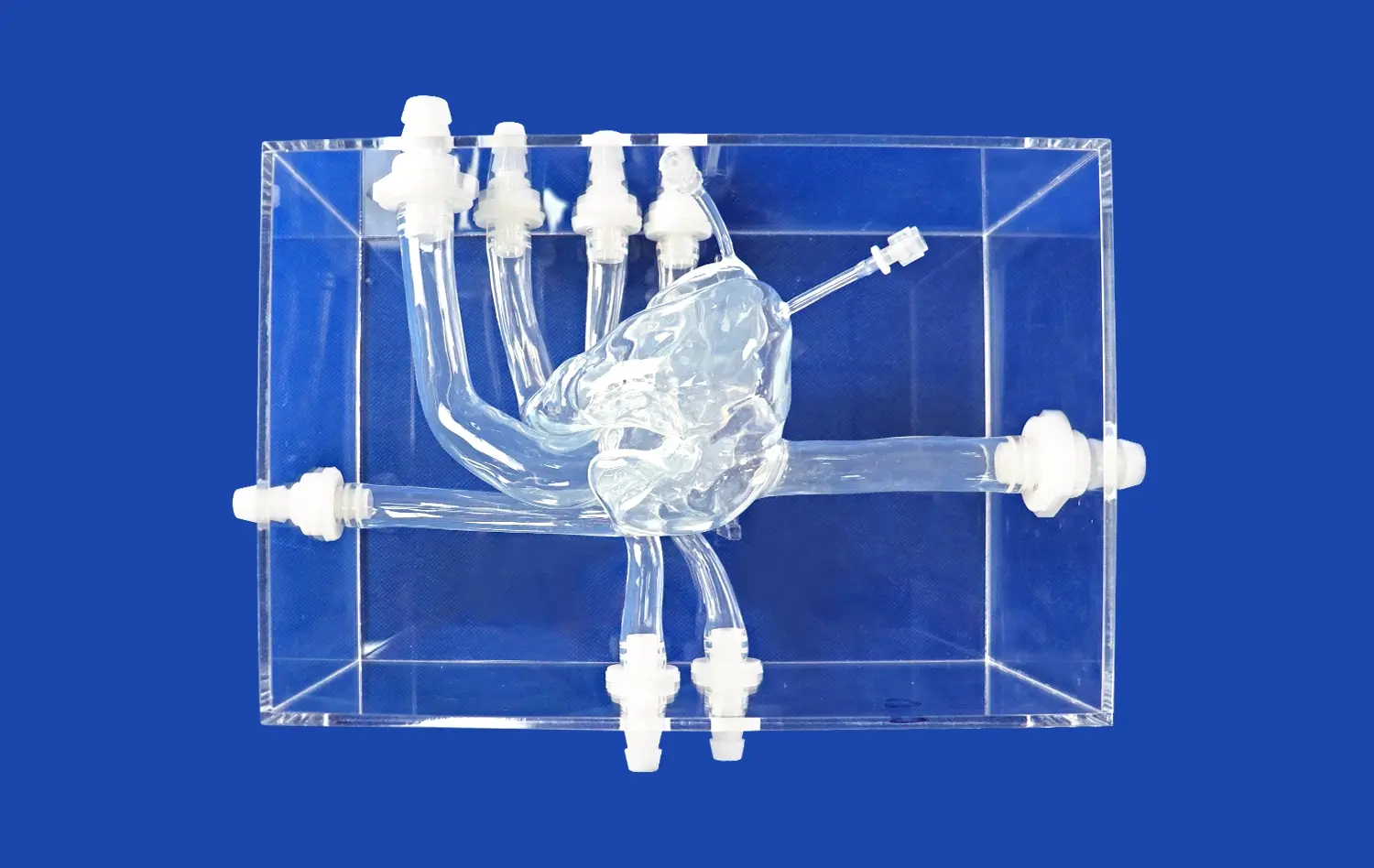
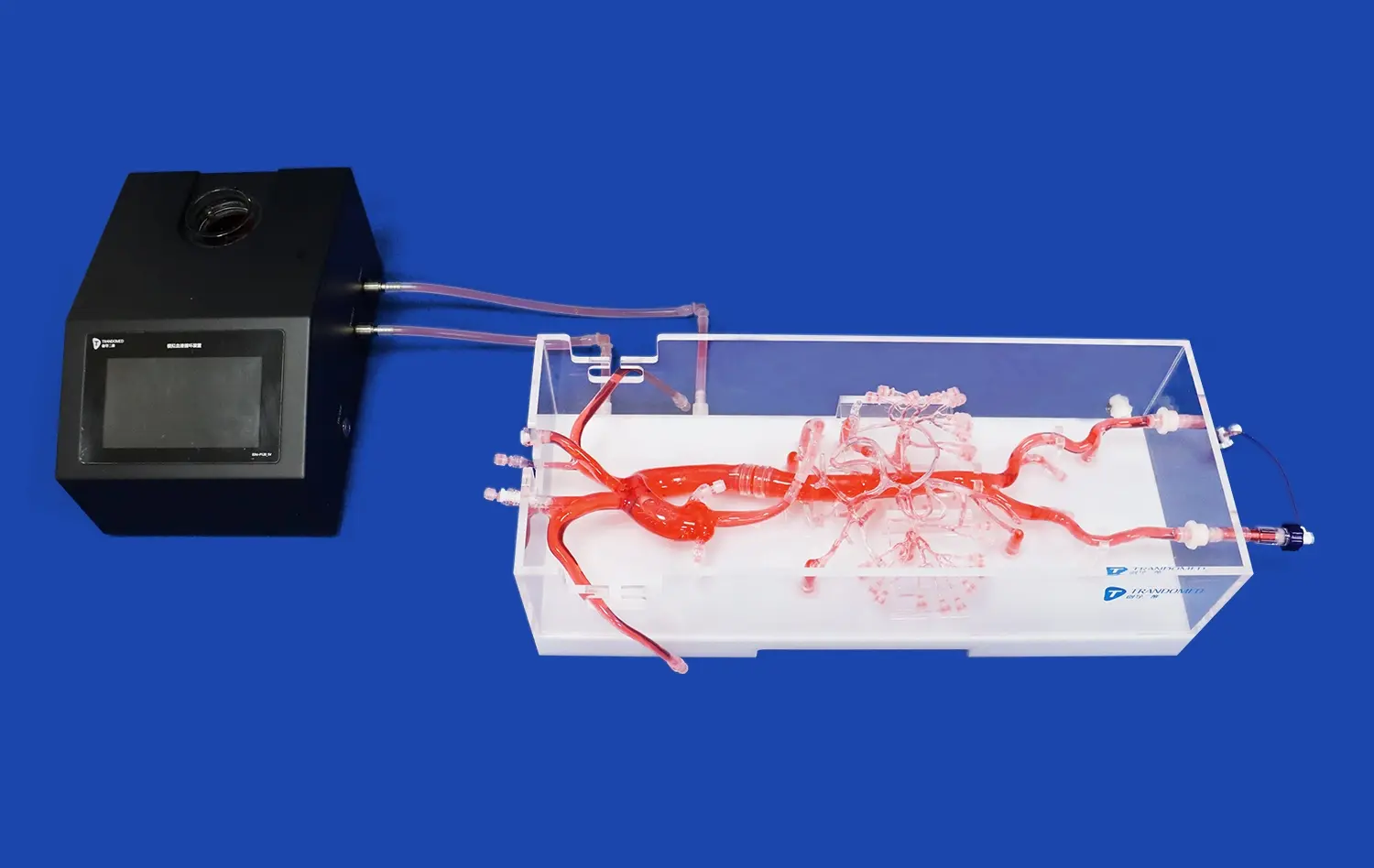
How Do Small Intestine Models Enable Precise Simulation?
Anatomical Accuracy and Detail
Small intestine models derived from real patient CT and MRI data capture the organ's intricate structure with exceptional precision. These models replicate the complex folds, villi, and microstructures that characterize the small intestine, allowing for a level of detail that was previously unattainable with traditional teaching methods. The anatomical accuracy of these models enables medical professionals to visualize and understand the organ's architecture in three dimensions, enhancing their spatial awareness and comprehension of its functions.
Tactile Learning Experience
Unlike 2D images or digital simulations, physical small intestine models provide a tactile learning experience that is crucial for developing hands-on skills. Medical students and residents can palpate the model, feeling the texture and consistency of the simulated tissue. This tactile feedback is invaluable for developing the sensory skills required in various medical procedures, such as endoscopies or surgeries involving the small intestine. The ability to interact physically with the model reinforces learning and helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Customizable Pathologies
Advanced small intestine models can be customized to represent various pathological conditions, allowing for targeted training and research. These models can simulate common disorders such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or intestinal obstructions, providing healthcare professionals with a realistic platform to study and practice diagnosing these conditions. By incorporating specific pathologies into the models, educators can create diverse learning scenarios that prepare students for the complexities they may encounter in clinical practice.
Controlled Environment for Medical Research and Testing
Standardized Research Platforms
Small intestine models offer researchers a standardized platform for conducting experiments and studies. These models provide consistent anatomical features and material properties, enabling scientists to perform repeatable experiments with reduced variability. This standardization is crucial for comparing results across different studies and institutions, ultimately accelerating the pace of medical research in gastrointestinal health. Researchers can use these models to investigate drug absorption, nutrient uptake, and the effects of various interventions on the small intestine with greater precision and reproducibility.
Ethical Alternative to Animal Testing
The use of small intestine models presents an ethical alternative to animal testing in many research applications. By utilizing these highly accurate replicas, researchers can reduce their reliance on animal subjects for initial stages of research and testing. This approach not only addresses ethical concerns but also provides a more human-relevant model for studying diseases and developing treatments. The ability to conduct preliminary studies on these models can help refine research protocols and potentially reduce the number of animal experiments required in later stages of research.
Long-term Studies and Environmental Factors
Small intestine models enable researchers to conduct long-term studies and investigate the effects of various environmental factors on intestinal health. These models can be exposed to different conditions, such as simulated digestive fluids or specific bacterial populations, over extended periods without the ethical concerns associated with human or animal subjects. This capability allows for the exploration of chronic conditions, the long-term effects of dietary changes, or the impact of environmental toxins on intestinal function. The insights gained from such studies can contribute significantly to our understanding of gastrointestinal health and disease prevention.
How Realistic Models Enhance Device Validation and Procedure Planning?
Accelerated Medical Device Testing
Realistic small intestine models play a crucial role in accelerating the development and validation of medical devices. Manufacturers can use these models to test the performance, safety, and efficacy of new devices in a controlled environment that closely mimics human anatomy. This approach allows for rapid iterations and refinements in device design, potentially reducing the time and cost associated with bringing new medical technologies to market. By identifying and addressing potential issues early in the development process, companies can improve the overall quality and reliability of their products before human trials.
Surgical Planning and Training
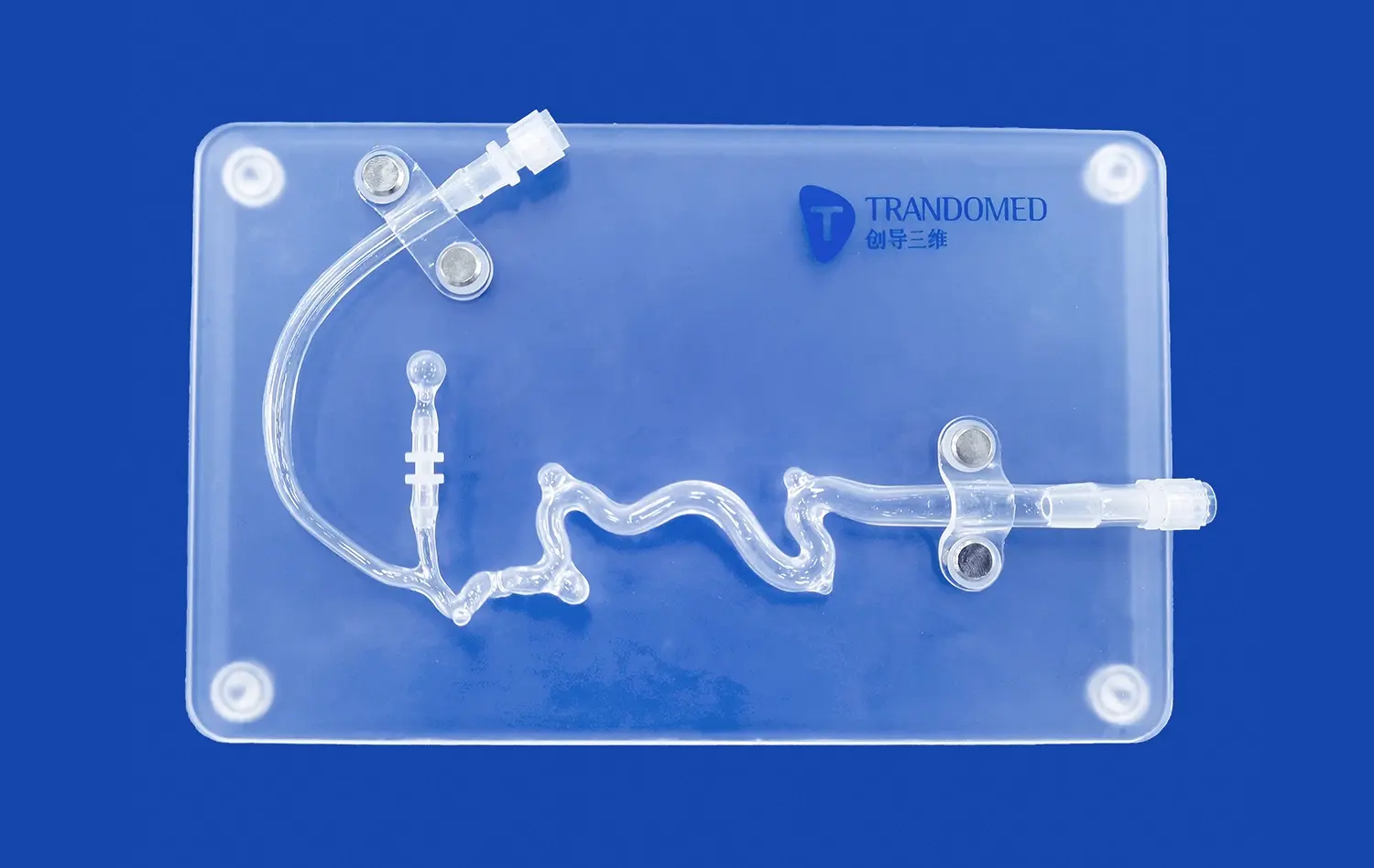
Advanced small intestine models serve as invaluable tools for surgical planning and training. Surgeons can use patient-specific models to rehearse complex procedures, develop new surgical techniques, or plan intricate interventions before operating on actual patients. This pre-operative planning can lead to improved surgical outcomes, reduced operating times, and enhanced patient safety. Additionally, these models provide a risk-free environment for surgeons to practice and refine their skills, particularly for rare or challenging cases that they may not frequently encounter in clinical practice.
Endoscopic Procedure Simulation
Small intestine models are particularly useful for simulating endoscopic procedures, allowing gastroenterologists and endoscopists to hone their skills in a realistic setting. These models can be designed with varying degrees of difficulty, simulating different pathologies or anatomical variations that practitioners might encounter. By practicing on these models, healthcare professionals can improve their dexterity, decision-making skills, and familiarity with endoscopic equipment. This targeted training can lead to more efficient and safer endoscopic procedures in clinical settings, ultimately benefiting patient care and outcomes.
Conclusion
Small intestine models have emerged as indispensable tools in medical education, research, and device development. By providing highly accurate representations of this complex organ, these models enable precise simulations, facilitate controlled research environments, and enhance medical device validation processes. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and versatile small intestine models to further revolutionize gastrointestinal medicine, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes in the field of gastroenterology.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are at the forefront of developing cutting-edge small intestine models for medical simulation and research. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D-printed medical simulators, we offer customizable solutions to meet your specific needs. Our advanced manufacturing processes and commitment to quality ensure that you receive the most realistic and durable small intestine models available. Whether you're a medical institution, research facility, or device manufacturer, partner with Trandomed to elevate your training, research, and development capabilities. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discuss how our small intestine models can benefit your organization.


1_1732869849284.webp)