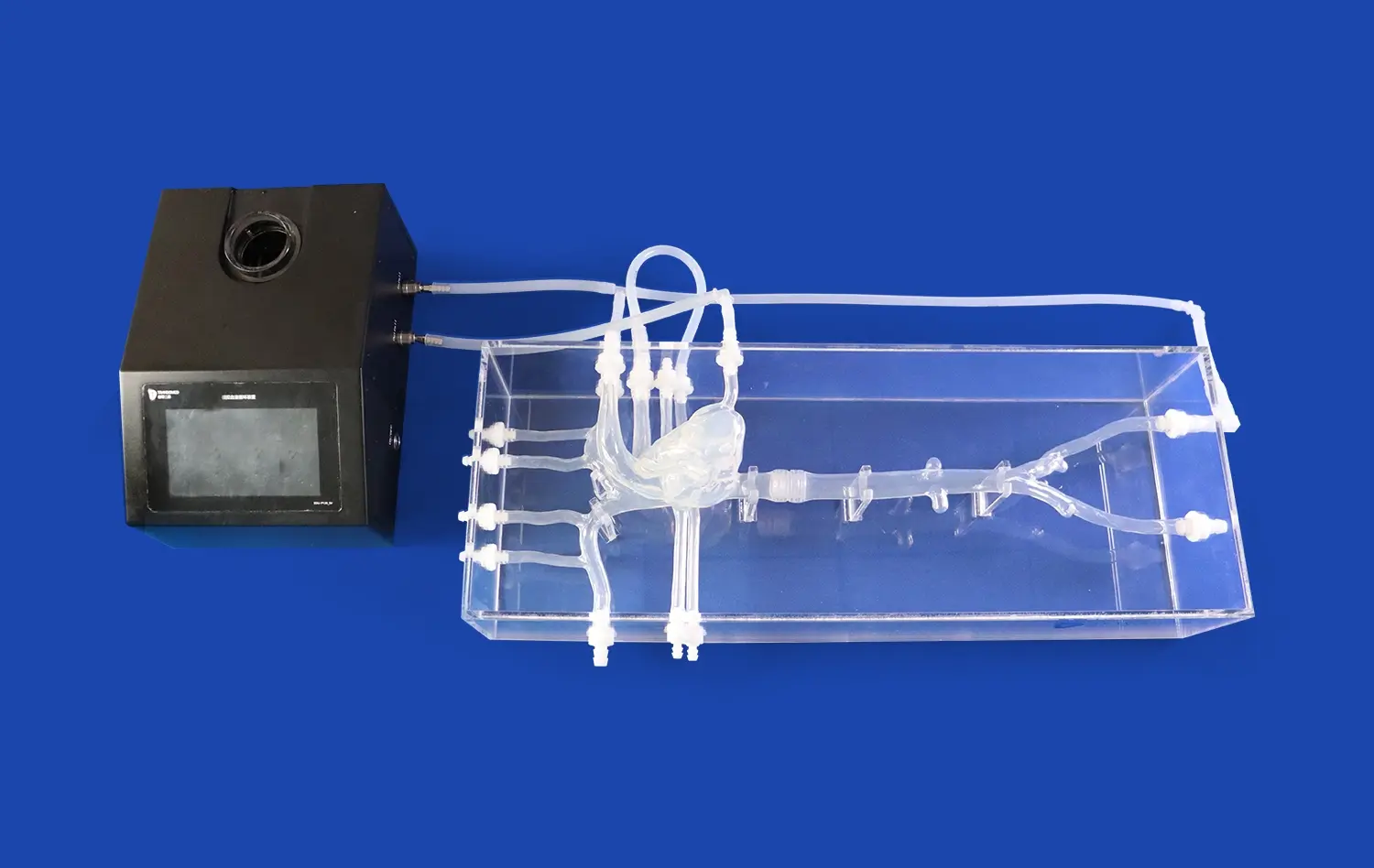
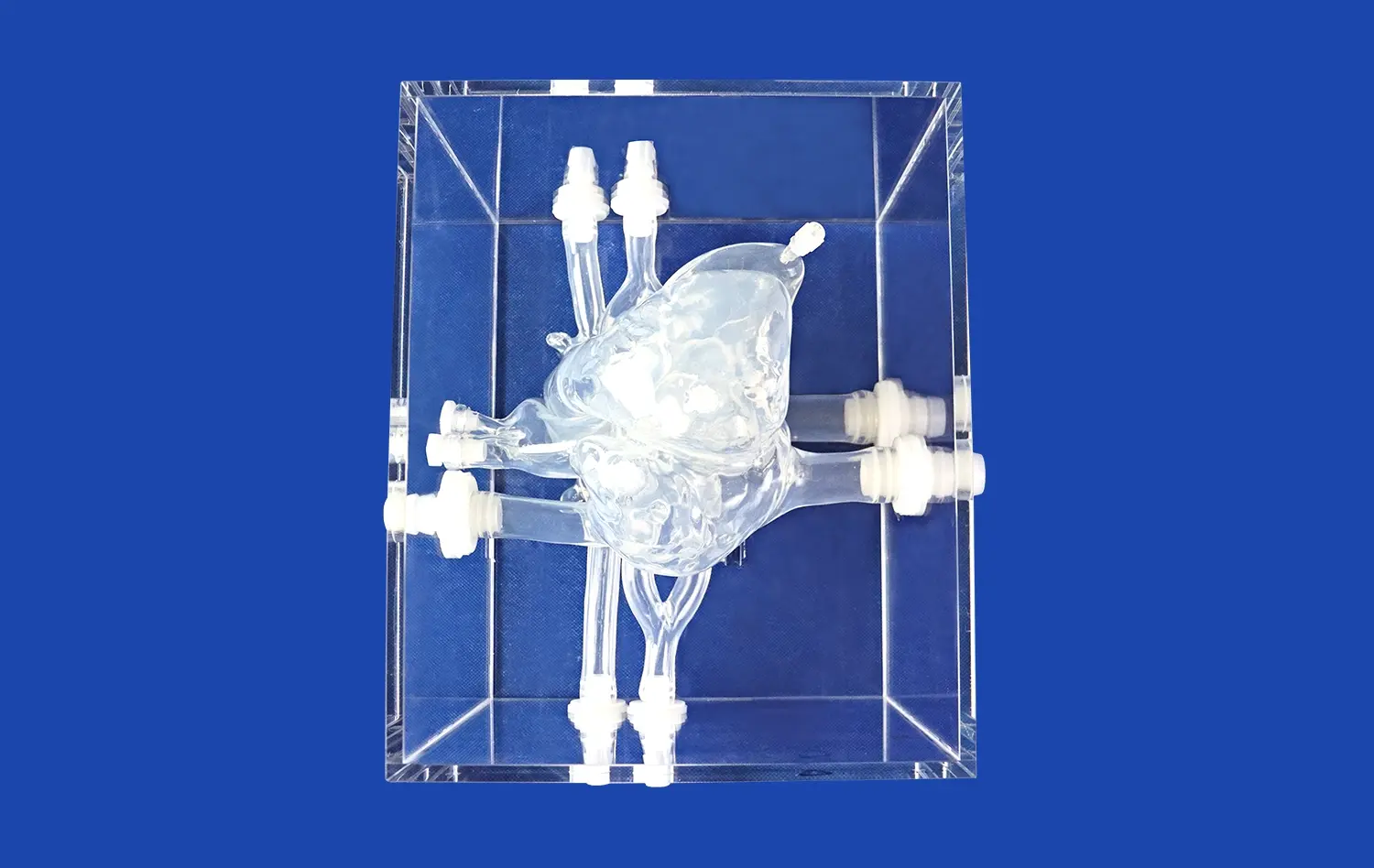
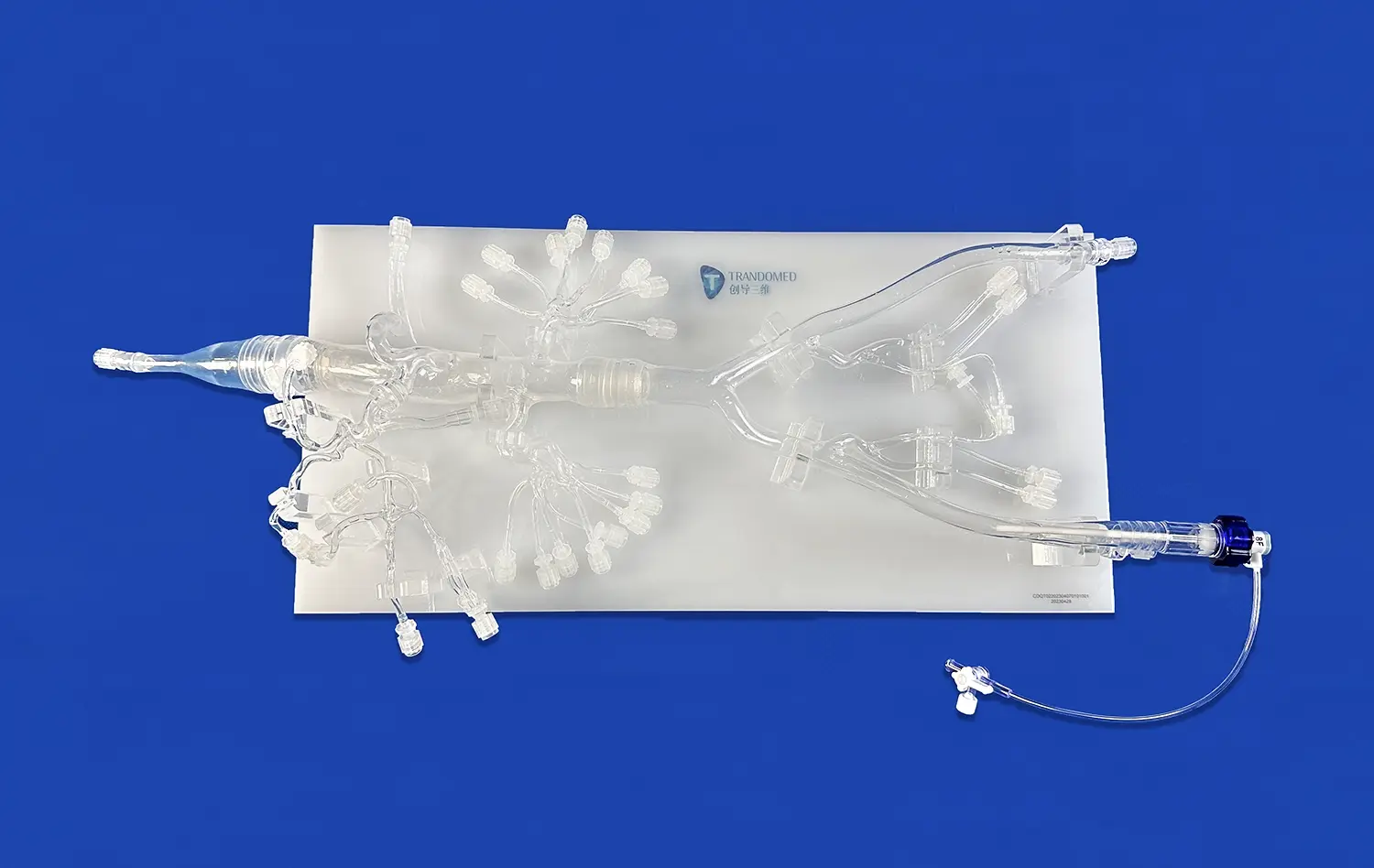
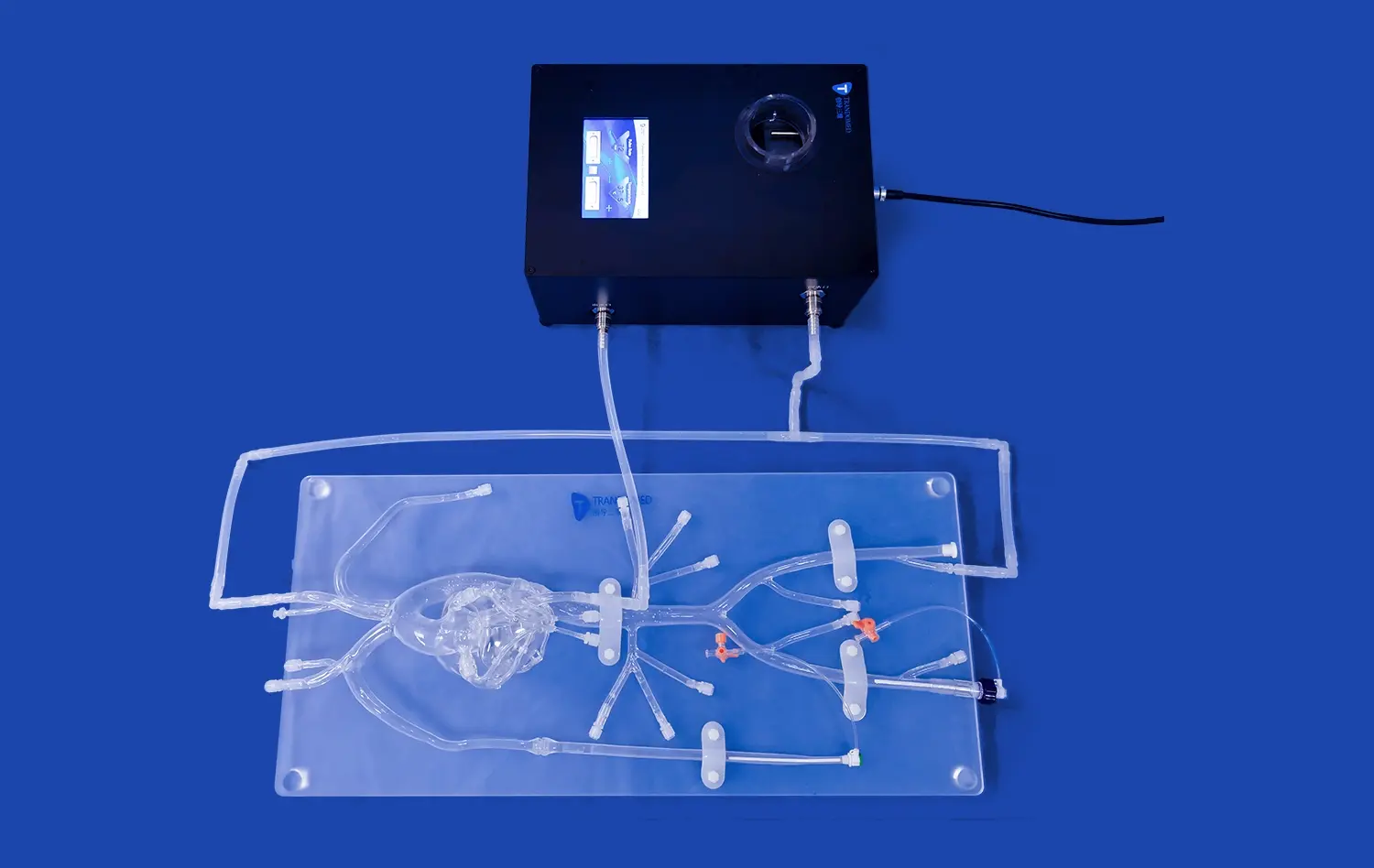
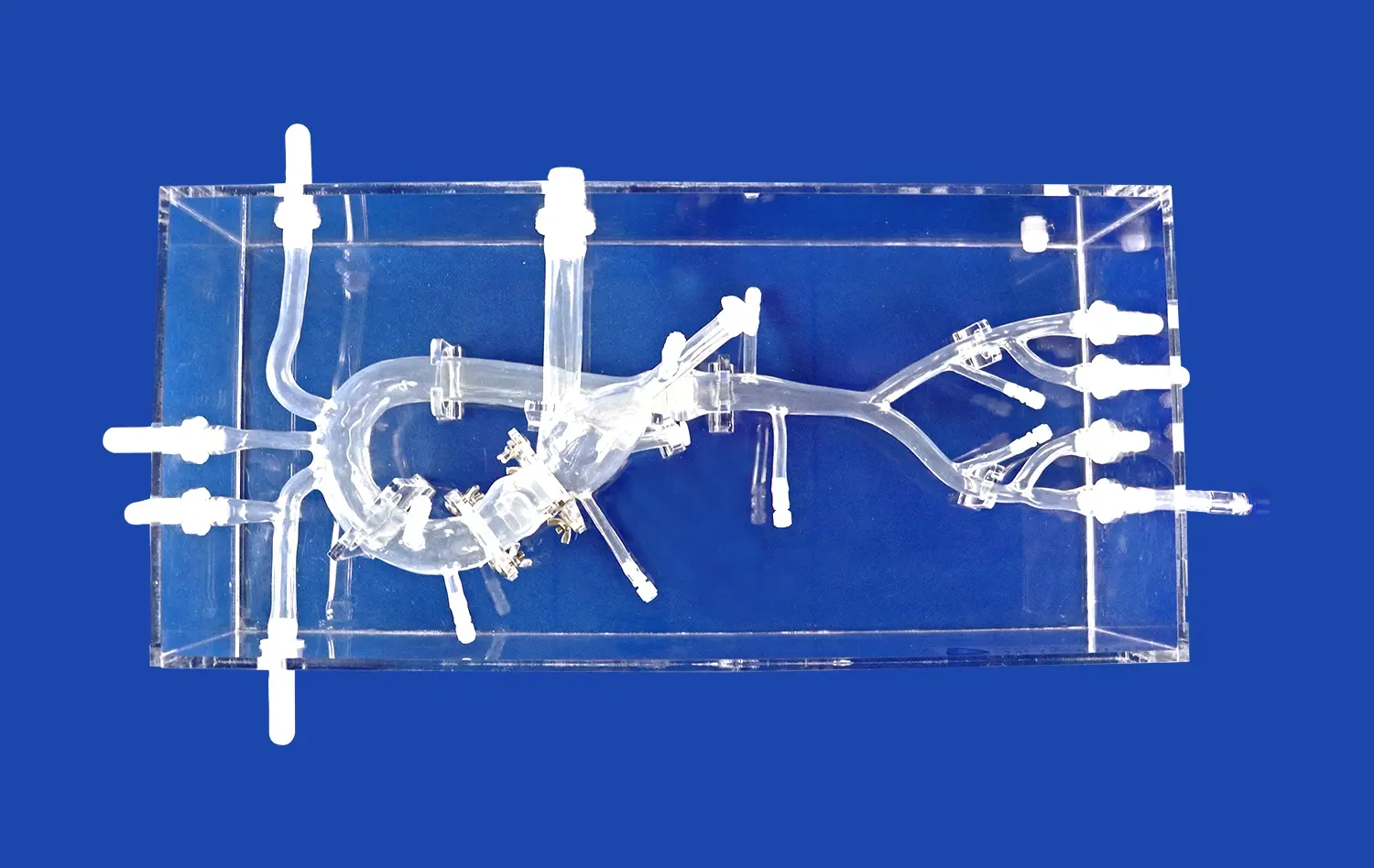
How Do 3D Models Integrate into Medical Curricula?
Enhancing Anatomical Understanding
3D stomach models serve as invaluable tools in medical education, offering students a tactile and visual representation of gastric anatomy. Unlike traditional 2D illustrations, these models allow learners to examine the stomach from various angles, providing a comprehensive view of its structure. Students can explore the different layers of the stomach wall, from the mucosa to the serosa, gaining a deeper appreciation for the organ's complexity. This hands-on approach helps solidify anatomical knowledge, making it easier for students to recall and apply this information in clinical settings.
Facilitating Procedural Training
Medical curricula increasingly incorporate 3D stomach models to simulate various gastroenterological procedures. These models enable students to practice techniques such as endoscopy, gastric biopsies, and even laparoscopic surgeries in a risk-free environment. By manipulating realistic stomach replicas, learners can develop the necessary hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness required for these delicate procedures. This practical experience builds confidence and competence, preparing future physicians for the challenges they'll face in real patient care scenarios.
Bridging Theory and Practice
The integration of 3D stomach models into medical curricula creates a seamless connection between theoretical knowledge and practical application. As students learn about gastric physiology and pathology, they can simultaneously observe and interact with accurate representations of healthy and diseased stomach tissues. This multisensory approach reinforces learning, helping students to better understand concepts such as gastric motility, secretion processes, and the effects of various gastrointestinal disorders. By bridging theory and practice, 3D models contribute to a more holistic and effective medical education experience.
Visualizing Anatomy Beyond Textbooks and 2D Images
Unveiling Complex Structures
3D stomach models offer an unparalleled view of the organ's intricate architecture, surpassing the limitations of traditional textbooks and 2D images. These models allow students to visualize the stomach's curvatures, folds, and sphincters with remarkable clarity. By examining a three-dimensional representation, learners can better understand the spatial relationships between different gastric regions, such as the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. This enhanced visualization aids in grasping concepts like the angle of His and the importance of the gastroesophageal junction in preventing reflux.
Exploring Layers and Blood Supply
Advanced 3D stomach models often feature dissectible layers, enabling students to peel back the organ's various strata. This feature provides an in-depth look at the mucosal folds, submucosal layer, and muscular architecture responsible for the stomach's unique functions. Additionally, these models can incorporate detailed representations of the stomach's rich vascular network, including the left and right gastric arteries, short gastric arteries, and gastroepiploic vessels. Visualizing this complex blood supply enhances students' understanding of gastric perfusion and potential complications in surgical interventions.
Demonstrating Dynamic Processes
Unlike static textbook illustrations, some 3D stomach models are designed to demonstrate dynamic physiological processes. These interactive models can simulate peristaltic movements, illustrating how the stomach mixes and propels food. They may also feature removable sections to show the gradual breakdown of food particles and the secretion of gastric juices. By visualizing these processes in three dimensions, students gain a more intuitive understanding of gastric function, aiding in their comprehension of concepts like gastric emptying and the role of the pyloric sphincter in regulating chyme passage into the duodenum.
How Interactive Models Enhance Knowledge Retention and Application?
Multisensory Learning Experience
Interactive 3D stomach models engage multiple senses, creating a rich learning environment that promotes better knowledge retention. As students manipulate these models, they simultaneously activate visual, tactile, and kinesthetic learning pathways. This multisensory approach helps to create stronger neural connections, making it easier for learners to recall complex anatomical details. For instance, feeling the rugae (folds) of the stomach lining while visually examining their distribution can lead to a more lasting understanding of the stomach's internal structure compared to simply viewing a diagram.
Problem-Based Learning Scenarios
Advanced 3D stomach models can be integrated into problem-based learning scenarios, enhancing students' ability to apply their knowledge to real-world situations. Educators can use these models to present case studies involving various gastric pathologies, such as ulcers, tumors, or inflammatory conditions. Students can then use the models to explore the affected areas, discuss potential diagnostic approaches, and propose treatment strategies. This hands-on problem-solving not only reinforces anatomical knowledge but also develops critical thinking skills essential for clinical practice.
Personalized Learning Pace
Interactive 3D models allow students to learn at their own pace, accommodating different learning styles and speeds. Learners can spend extra time examining areas they find challenging or revisit specific structures as needed. This self-directed exploration fosters a deeper understanding and helps students build confidence in their knowledge. Moreover, the ability to manipulate and explore the model independently encourages active learning, which has been shown to significantly improve long-term retention and the ability to apply knowledge in diverse clinical contexts.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D stomach models into modern medical teaching represents a significant leap forward in anatomical education. These innovative tools offer unparalleled opportunities for students to visualize, interact with, and comprehend complex gastric structures and functions. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, 3D models enhance learning outcomes, improve knowledge retention, and better prepare future healthcare professionals for clinical challenges. As medical education continues to evolve, the role of these interactive, three-dimensional teaching aids will undoubtedly expand, fostering a new generation of physicians equipped with a deeper, more intuitive understanding of gastric anatomy and physiology.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we're committed to advancing medical education through cutting-edge 3D printing technology. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of anatomical models, we offer high-quality, customizable 3D stomach models that meet the diverse needs of medical institutions worldwide. Our factory-direct pricing ensures you receive top-tier educational tools without breaking your budget. Experience the difference that precision-engineered, interactive models can make in your teaching curriculum. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our innovative products and how we can support your educational goals.

_1734504197376.webp)