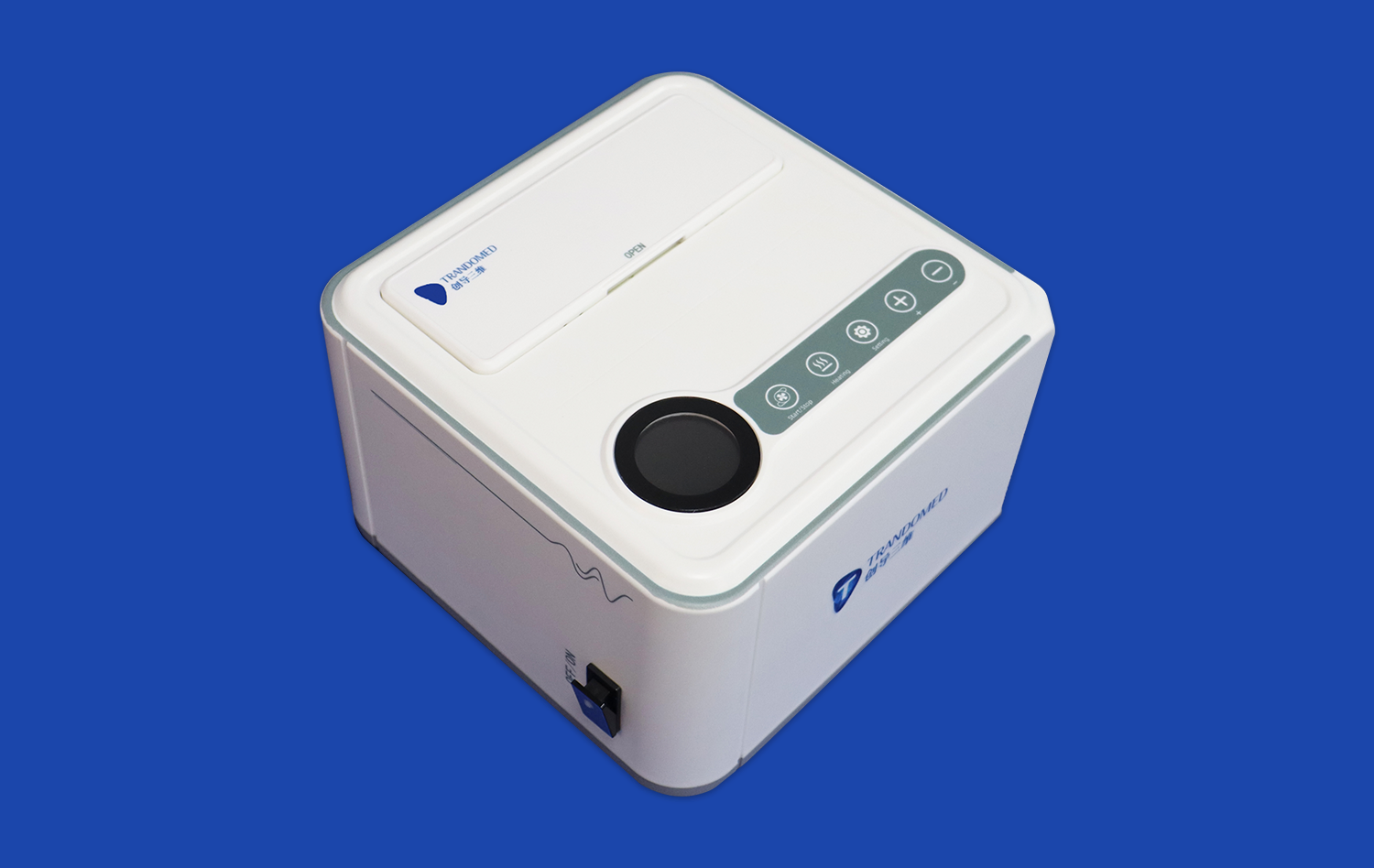
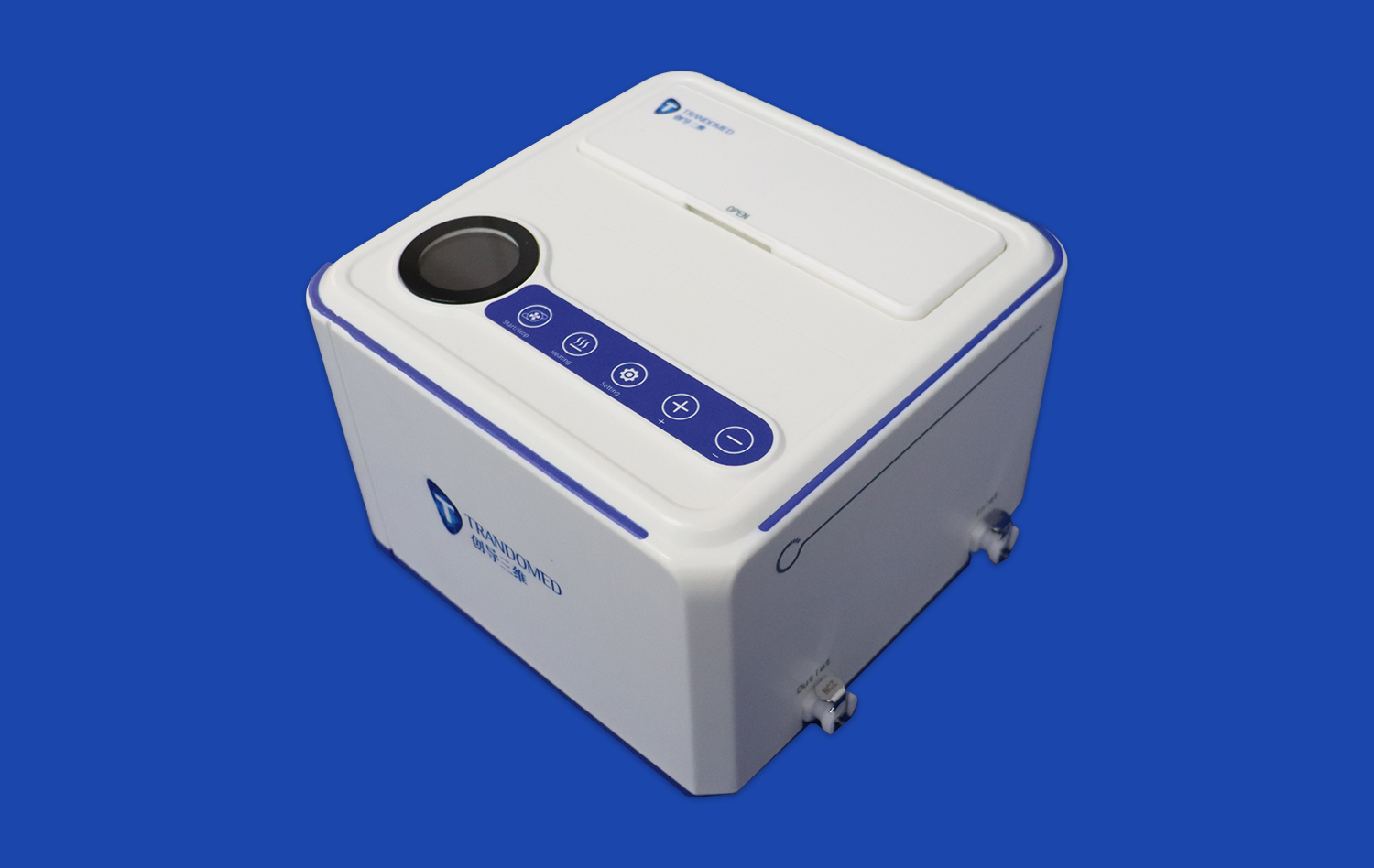
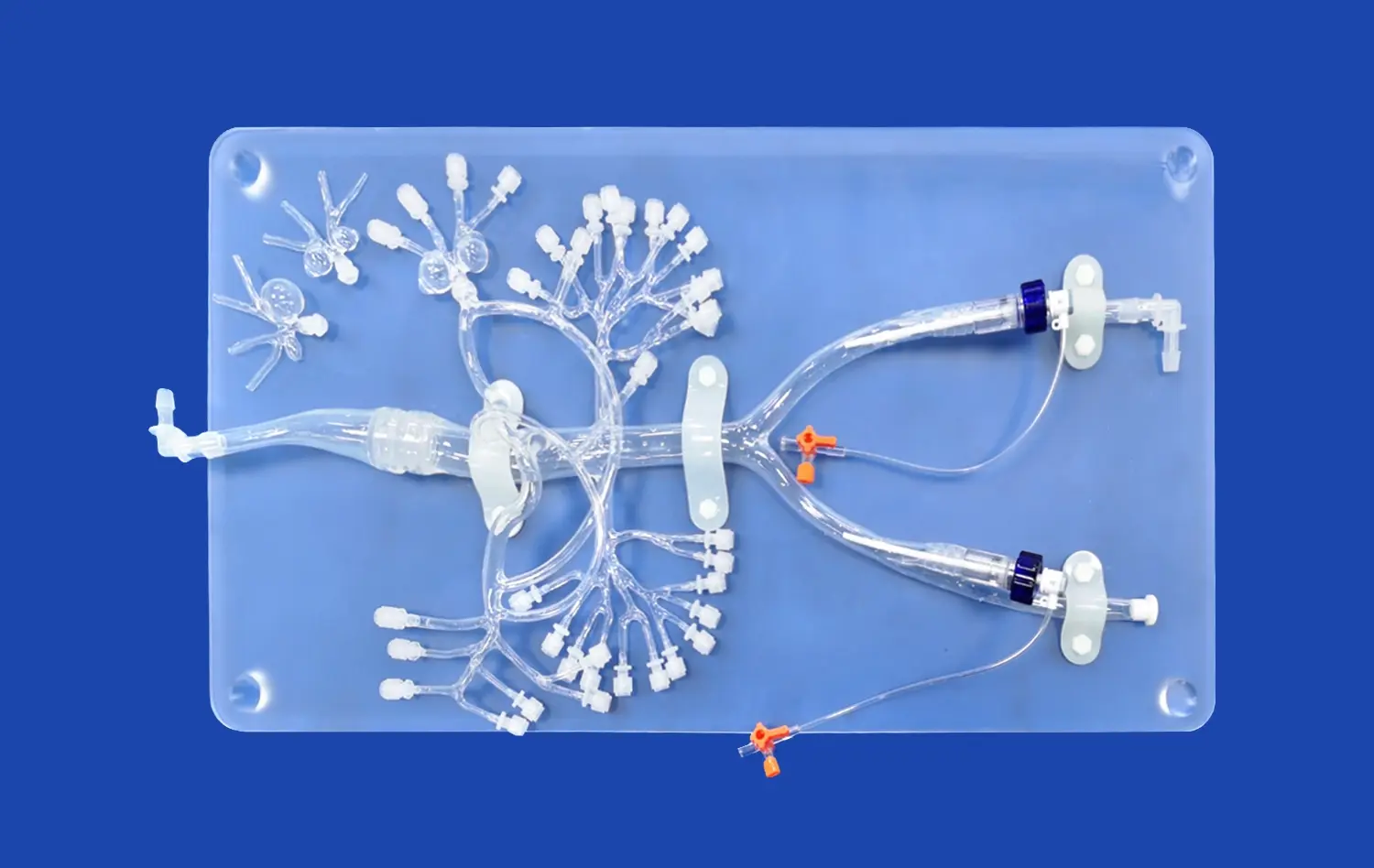
Why are Atrial Septal Puncture Training Models Essential for Interventional Learning?
Enhancing Procedural Proficiency
Atrial septal puncture training models serve as invaluable tools for enhancing procedural proficiency among interventional cardiologists and electrophysiologists. These sophisticated simulators offer a lifelike representation of cardiac anatomy, allowing practitioners to refine their techniques in a controlled environment. By replicating the tactile feedback and visual cues encountered during actual procedures, these models enable learners to develop muscle memory and spatial awareness crucial for successful interventions.
Mitigating Patient Risk
One of the primary advantages of utilizing atrial septal puncture simulators is the significant reduction in patient risk during the learning process. Trainees can practice complex procedures repeatedly without the fear of causing harm to real patients. This risk-free environment encourages experimentation and allows for the exploration of various techniques, ultimately leading to more confident and competent practitioners when they transition to clinical practice.
Accelerating the Learning Curve
The incorporation of atrial septal puncture models in training programs has been shown to accelerate the learning curve for interventional procedures. By providing immediate feedback and allowing for repetitive practice, these simulators help trainees quickly identify areas for improvement and refine their skills. This accelerated learning process translates to shorter training periods and faster acquisition of essential competencies, benefiting both healthcare providers and patients alike.
Stepwise Practice of Venous Access and Transseptal Techniques Using the Model
Mastering Vascular Navigation
Atrial septal puncture models offer a comprehensive platform for mastering vascular navigation techniques. Trainees can practice guiding catheters through the intricate venous system, from the femoral vein to the right atrium. The model's anatomically accurate representation of the iliac veins, inferior vena cava, and superior vena cava allows learners to develop a keen sense of catheter manipulation and overcome common challenges encountered during vascular access procedures.
Perfecting Transseptal Puncture Technique
The core focus of these simulation models, such as the atrial septal puncture model, lies in perfecting the transseptal puncture technique. Learners can practice locating the fossa ovalis, positioning the transseptal needle, and executing the puncture with precision. The ability to interchange between normal atrial septum and atrial septal defect (ASD) inserts provides exposure to various anatomical scenarios, preparing practitioners for the diverse patient cases they may encounter in clinical practice.
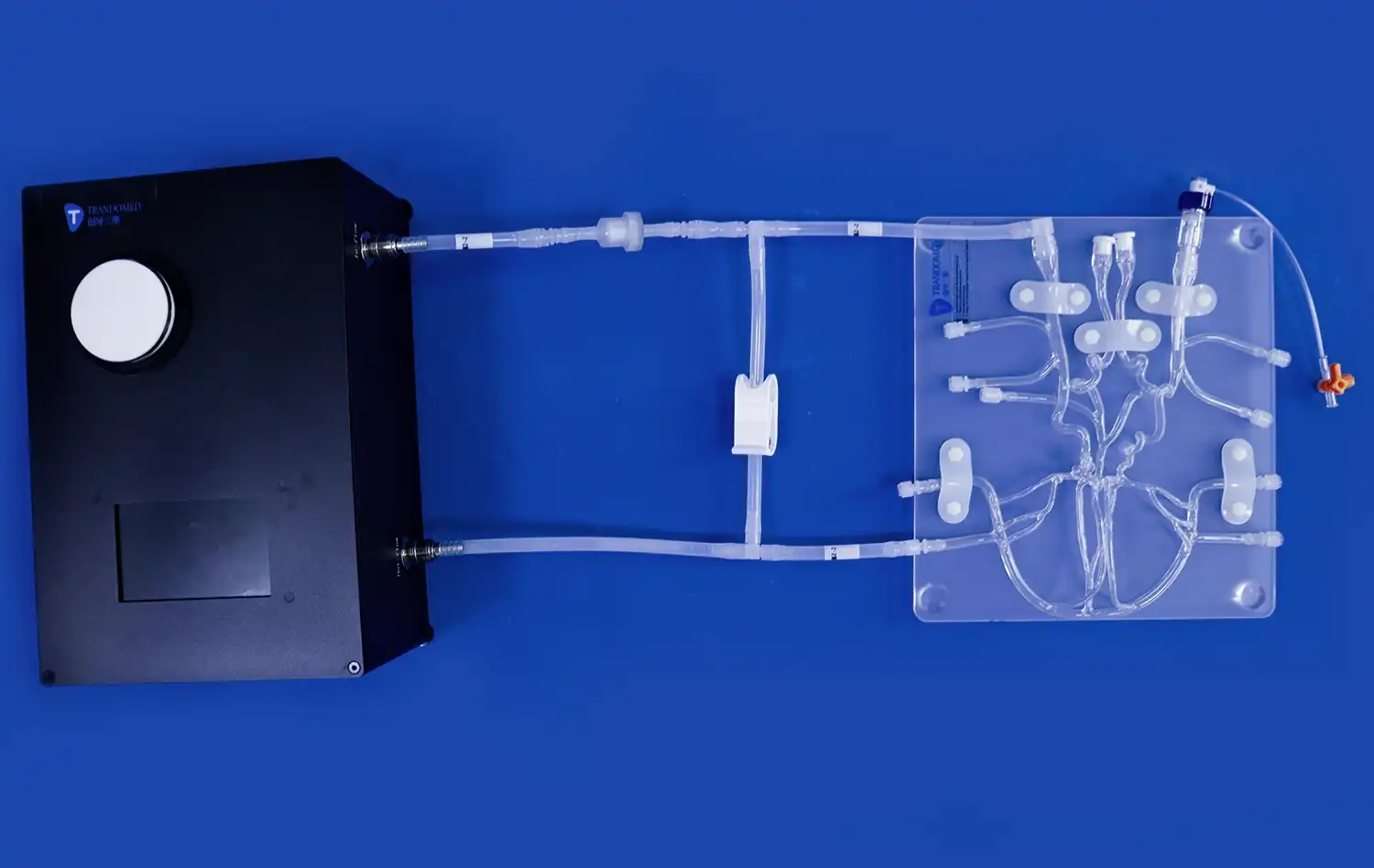
Advancing to Complex Interventions
As trainees gain proficiency in basic techniques, atrial septal puncture models allow for progression to more complex interventions. Practitioners can simulate procedures such as cryoballoon ablation of pulmonary veins and radiofrequency ablation for pulmonary vein isolation. The modular design of these models, featuring detachable upper and lower sections, enables customization of training scenarios to match specific learning objectives and procedural requirements.
Advancing Competency in Complex Interventional Pathways with Simulation
Integrating Advanced Imaging Techniques
Simulation using atrial septal puncture models facilitates the integration of advanced imaging techniques into interventional training. Practitioners can enhance their skills in interpreting fluoroscopic images and echocardiographic guidance during procedures. This multi-modal approach to learning ensures that trainees develop a comprehensive understanding of the spatial relationships within the heart, crucial for successful navigation and intervention in complex cases.
Addressing Anatomical Variations
One of the key advantages of using sophisticated atrial septal puncture simulators is the ability to address anatomical variations. These models can be customized to represent different patient anatomies, including variations in septal thickness, atrial size, and pulmonary vein configurations. Exposure to such diverse scenarios prepares interventionalists to adapt their techniques to individual patient characteristics, enhancing their versatility and effectiveness in clinical practice.
Fostering Team-based Learning
Atrial septal puncture models play a crucial role in fostering team-based learning environments. These simulators allow for collaborative training sessions involving interventional cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and supporting staff. By simulating real-world scenarios, teams can practice communication, coordination, and decision-making skills essential for efficient and safe procedure execution. This team-oriented approach to training ultimately translates to improved patient care and outcomes in the catheterization laboratory.
Conclusion
Atrial septal puncture models have revolutionized interventional pathway training, offering an unparalleled platform for skill development and procedural mastery. These advanced simulators provide a safe, realistic environment for practitioners to refine their techniques, from basic vascular access to complex ablation procedures. By accelerating the learning curve, mitigating patient risk, and addressing diverse anatomical scenarios, these models play a pivotal role in shaping competent, confident interventional specialists. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of such sophisticated simulation tools will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of interventional cardiology and electrophysiology training programs, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient care and improved clinical outcomes.
Contact Us
Experience the future of interventional training with Trandomed's cutting-edge atrial septal puncture models. Our anatomically accurate, customizable simulators offer unparalleled realism and versatility for your training needs. Elevate your skills and confidence in a risk-free environment. For more information on how our advanced simulation solutions can transform your interventional pathway training program, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
_1734507205192.webp)
_1732843184544.webp)