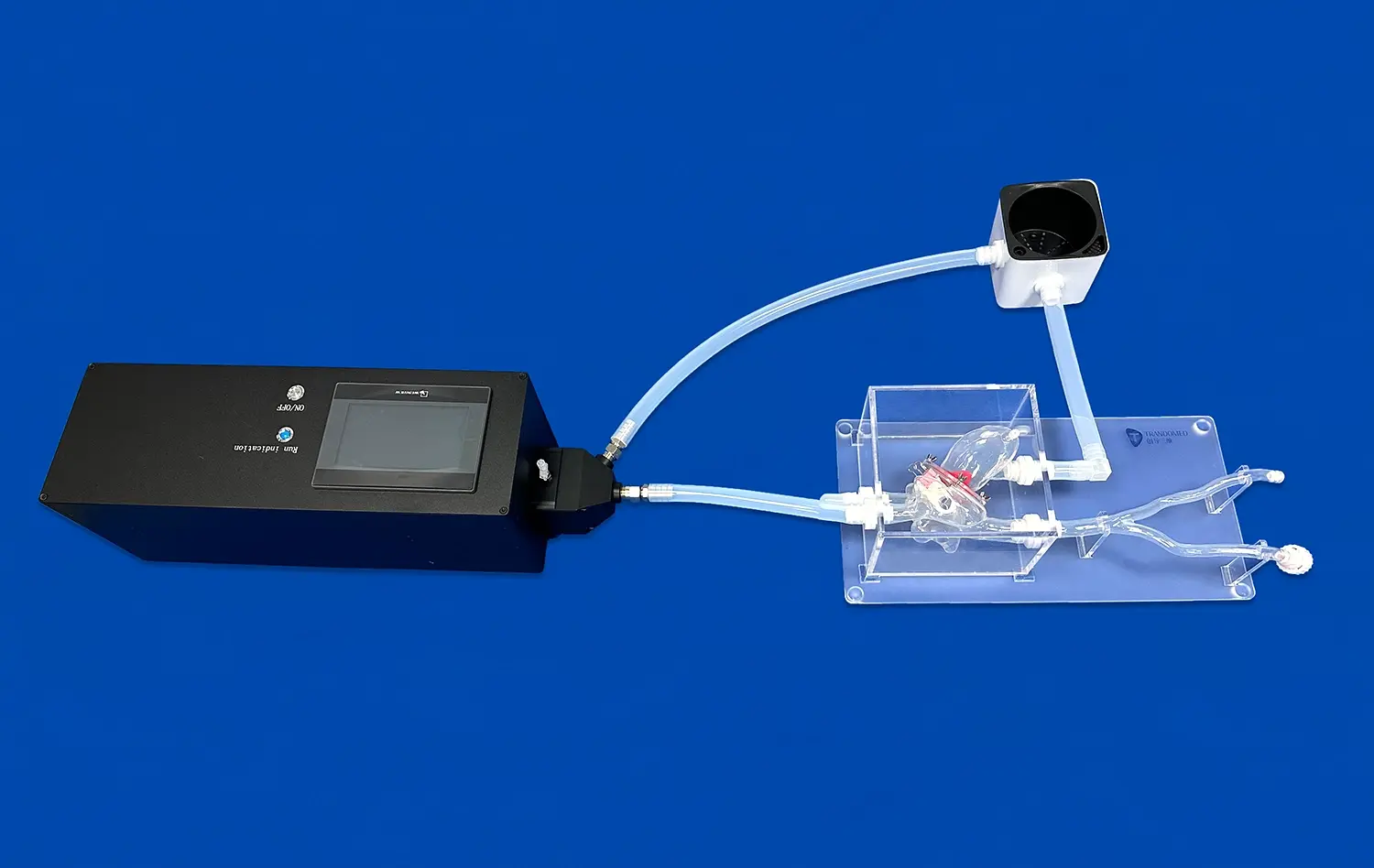
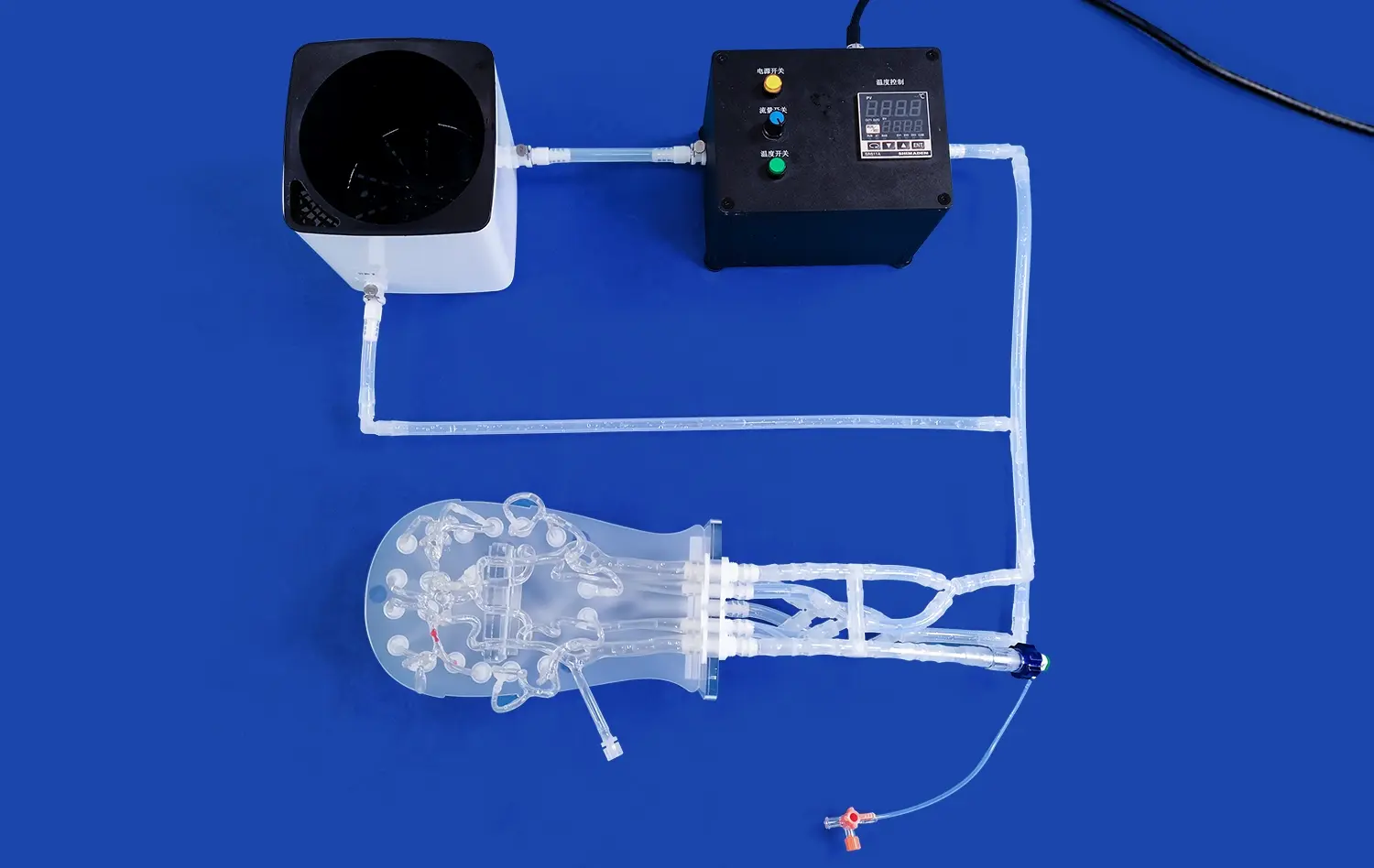
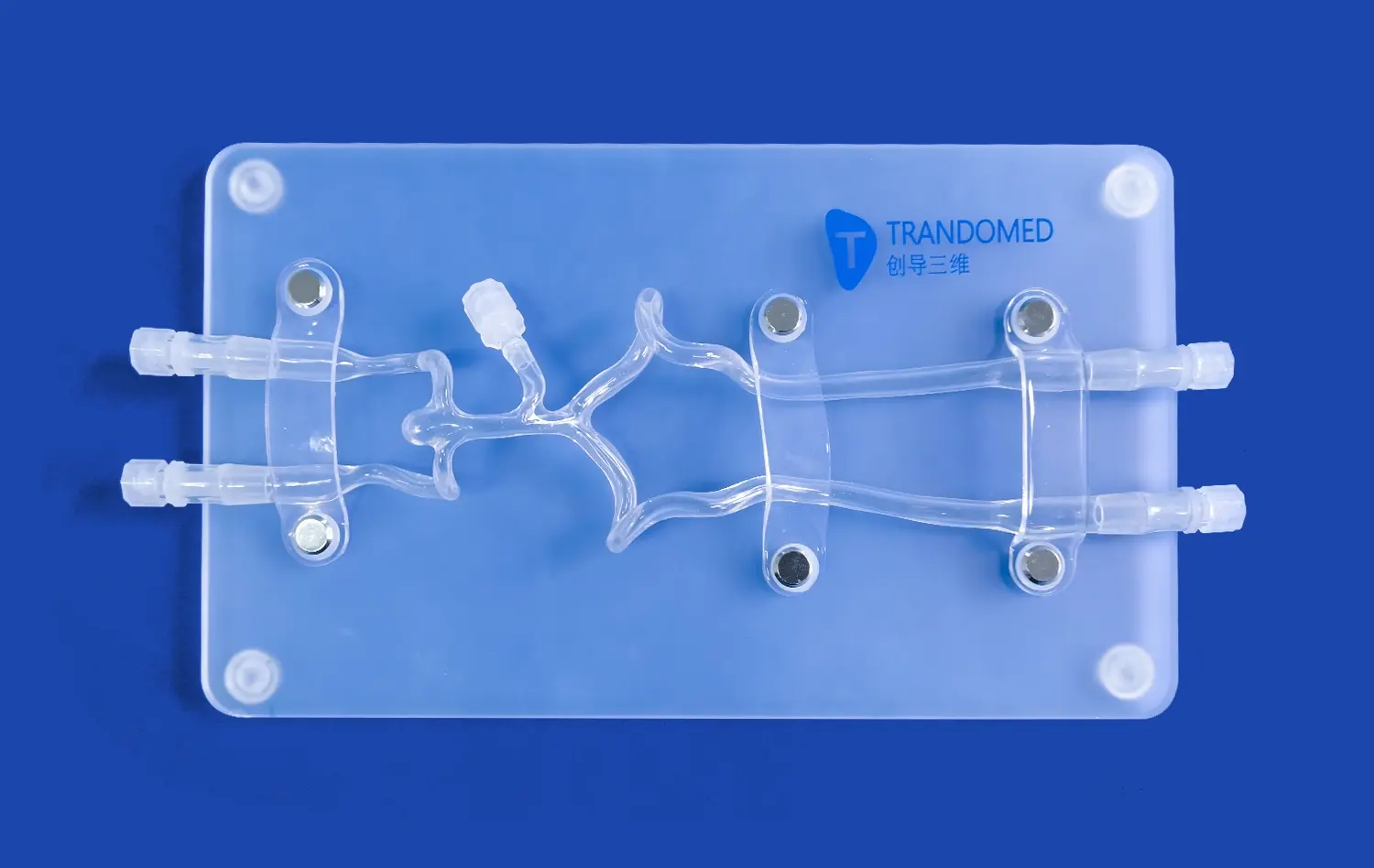
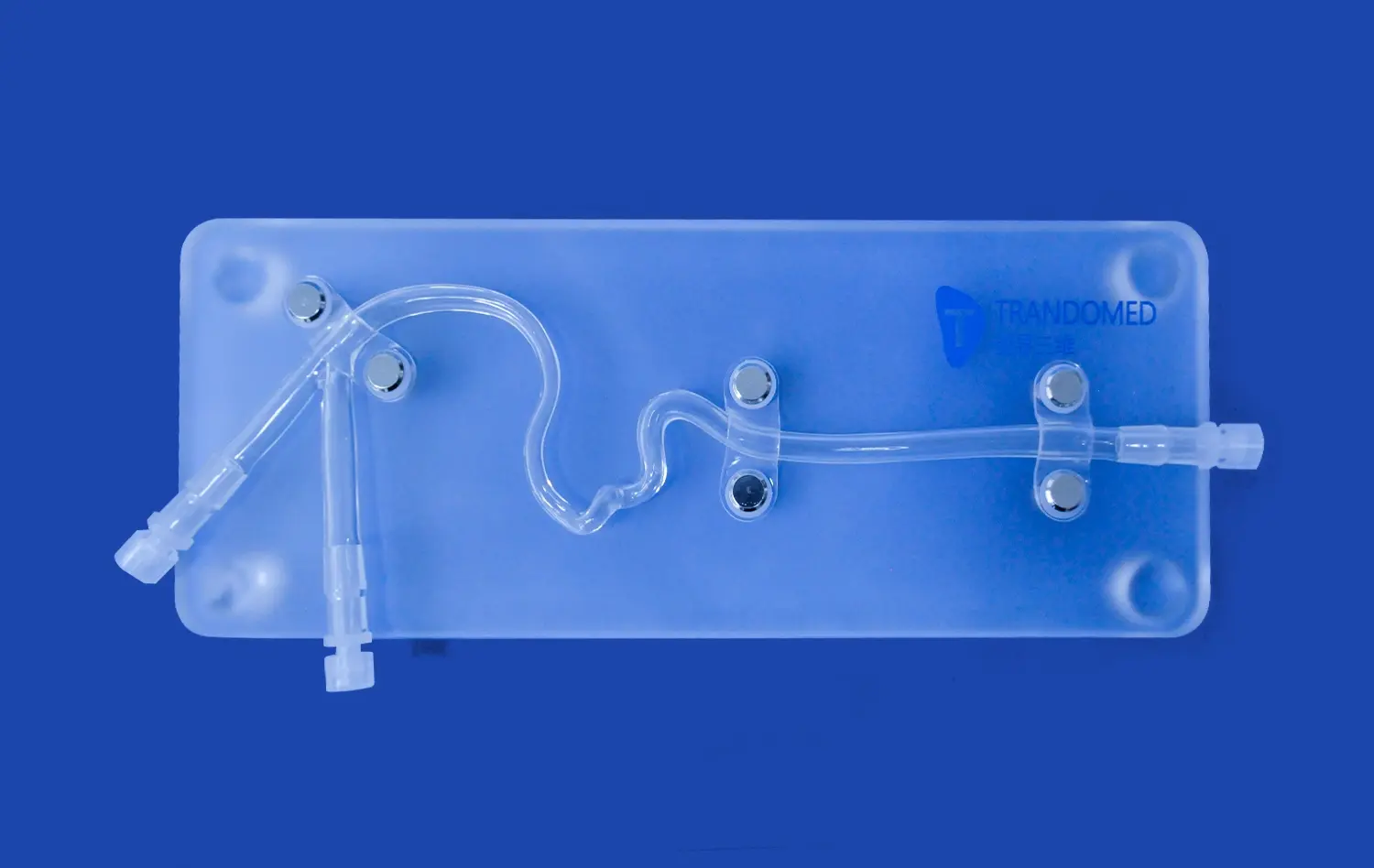
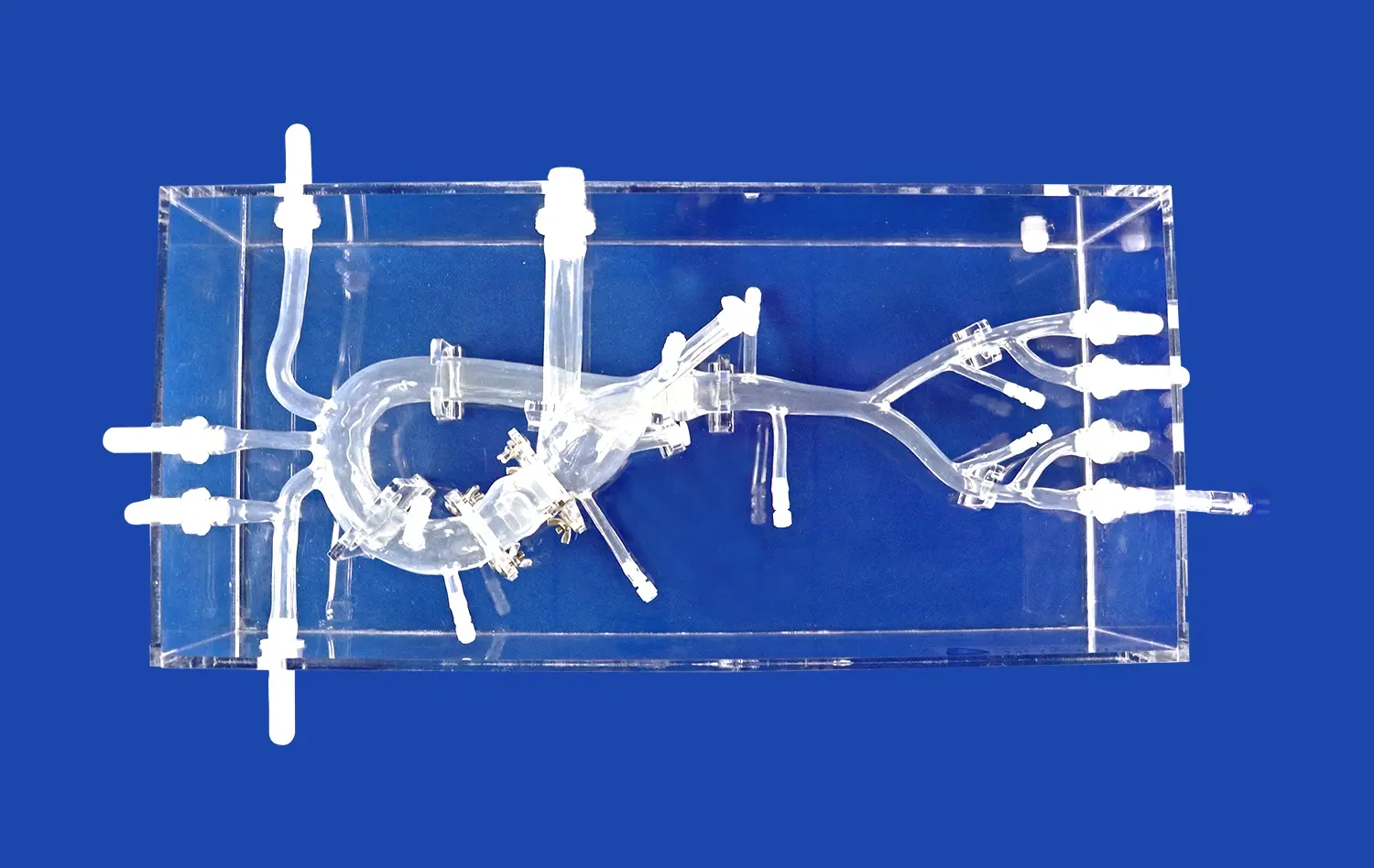
How Do Artery Models Support Advanced Vascular Research?
Enhancing Visualization and Understanding
Lower extremity artery models provide researchers with tangible representations of complex vascular structures. Unlike 2D imaging, these models offer a three-dimensional perspective, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of arterial anatomy. Researchers can examine intricate details, such as vessel bifurcations, stenoses, and aneurysms, with unprecedented clarity. This enhanced visualization aids in identifying potential areas of concern and developing targeted research questions.
Facilitating Experimental Design
The use of anatomically accurate artery replicas, such as the lower extremity artery model, enables researchers to design more sophisticated experiments. These models serve as consistent, reproducible platforms for testing hypotheses related to blood flow dynamics, plaque formation, and the efficacy of various treatment modalities. By providing a standardized environment, lower extremity vascular models help eliminate variables that might otherwise confound results in live subject studies.
Advancing Computational Fluid Dynamics
Arterial simulations play a crucial role in validating and refining computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models. Researchers can compare theoretical predictions with physical observations using these detailed replicas. This synergy between computational and physical modeling enhances our understanding of hemodynamics in the lower extremities, leading to more accurate predictions of disease progression and treatment outcomes.
Bridging Experimental Design and Clinical Application
Translating Research Findings to Clinical Practice
Lower extremity artery models serve as a vital link between laboratory findings and bedside care. By replicating patient-specific vascular conditions, these models allow researchers to test novel treatment approaches in a controlled environment before moving to clinical trials. This intermediate step helps refine techniques, identify potential complications, and optimize treatment protocols, ultimately improving patient safety and outcomes.
Enhancing Medical Device Development
The development of new vascular interventional devices greatly benefits from the use of anatomically accurate artery simulations. Engineers and designers can prototype and iterate on stents, catheters, and other endovascular tools using these models. The ability to test devices in realistic arterial geometries helps identify design flaws, assess deployment mechanisms, and evaluate device performance under various physiological conditions. This accelerates the development cycle and increases the likelihood of successful clinical implementation.
Improving Surgical Planning and Training
Patient-specific lower extremity vascular models have revolutionized surgical planning and training. Surgeons can rehearse complex procedures on exact replicas of a patient's anatomy, allowing them to anticipate challenges and optimize their approach. For trainees, these models provide a safe environment to practice techniques and develop skills without risk to patients. The tactile feedback and visual fidelity offered by high-quality silicone models enhance the learning experience, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Why the Lower Extremity Artery Model Accelerates Medical Innovation?
Facilitating Collaborative Research
Lower extremity artery models foster collaboration across medical disciplines. Vascular surgeons, interventional radiologists, biomedical engineers, and material scientists can converge around these tangible representations of complex anatomies. This interdisciplinary approach sparks innovation, as diverse perspectives contribute to solving challenges in vascular health. The models serve as a common language, enabling specialists to communicate ideas more effectively and develop integrated solutions.
Accelerating Clinical Trials
The use of accurate vascular replicas in preclinical testing can significantly streamline the clinical trial process. By identifying potential issues early in the development phase, researchers can refine protocols and device designs before human trials begin. This not only saves time and resources but also enhances patient safety by minimizing risks associated with untested interventions. The ability to conduct thorough bench testing on realistic models builds confidence in new treatments, potentially expediting regulatory approval processes.
Driving Personalized Medicine
Patient-specific lower extremity artery models are at the forefront of personalized medicine in vascular care. By creating exact replicas of an individual's vascular anatomy, clinicians can tailor treatments to the unique characteristics of each patient. This personalized approach allows for the selection of optimal interventional strategies, custom-fitted devices, and individualized risk assessments. As 3D printing technology advances, the potential for on-demand production of patient-specific models opens new avenues for precision medicine in vascular health.
Conclusion
Lower extremity artery models have emerged as indispensable tools in vascular research and clinical innovation. By providing realistic, patient-specific simulations, these models enhance our understanding of vascular diseases, facilitate the development of new treatments, and improve surgical outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the role of these models in driving medical innovation will only grow, promising a future of more effective, personalized vascular care. The integration of lower extremity artery models into research and clinical practice represents a significant leap forward in our ability to address complex vascular challenges and improve patient outcomes.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we're at the forefront of medical simulation technology, providing high-quality lower extremity artery models that drive innovation in vascular research and clinical practice. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D-printed medical simulators, we offer customizable solutions to meet your specific research or training needs. Experience the difference that anatomically accurate, silicone-based vascular models can make in your work. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your medical innovation journey.