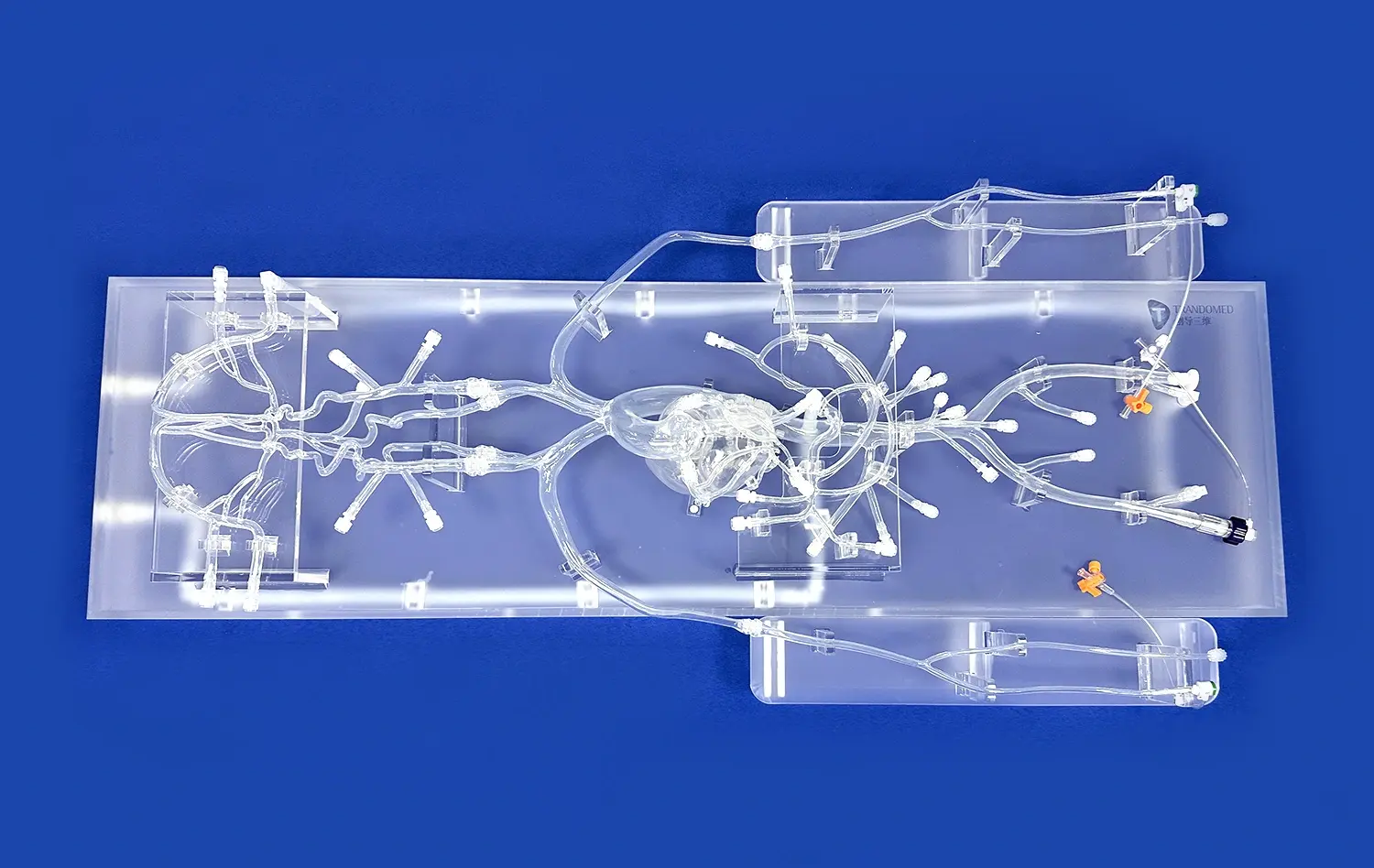
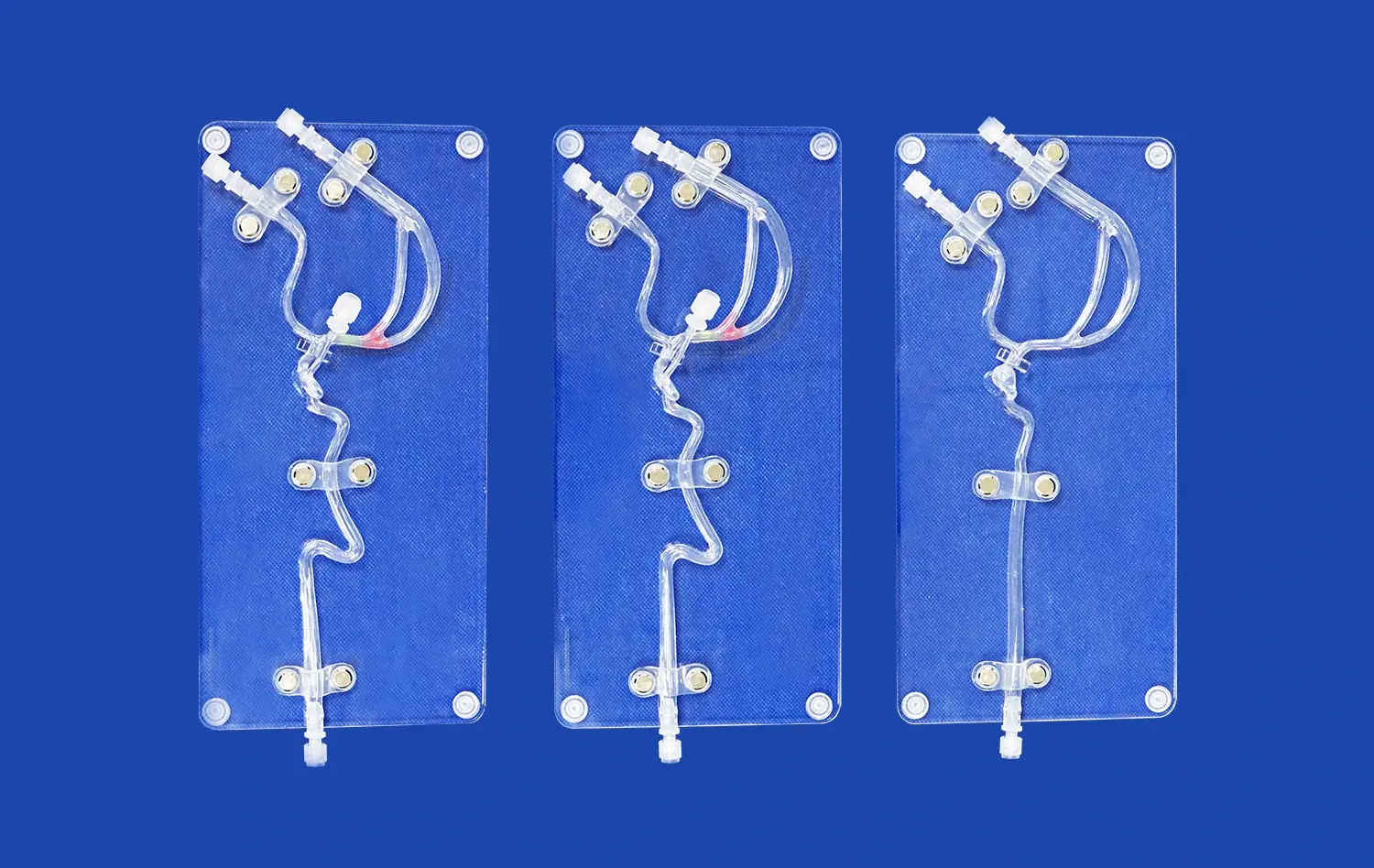
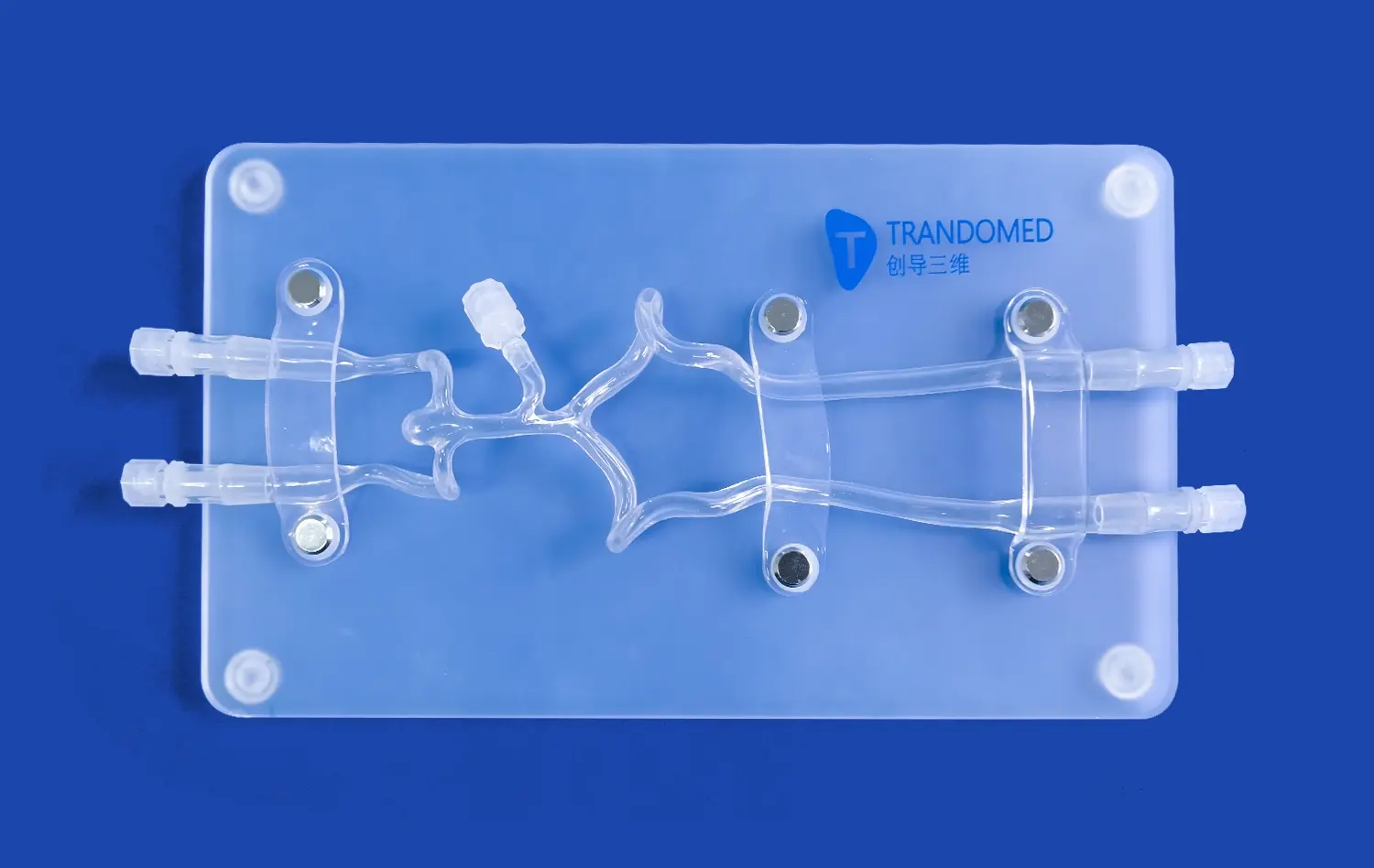
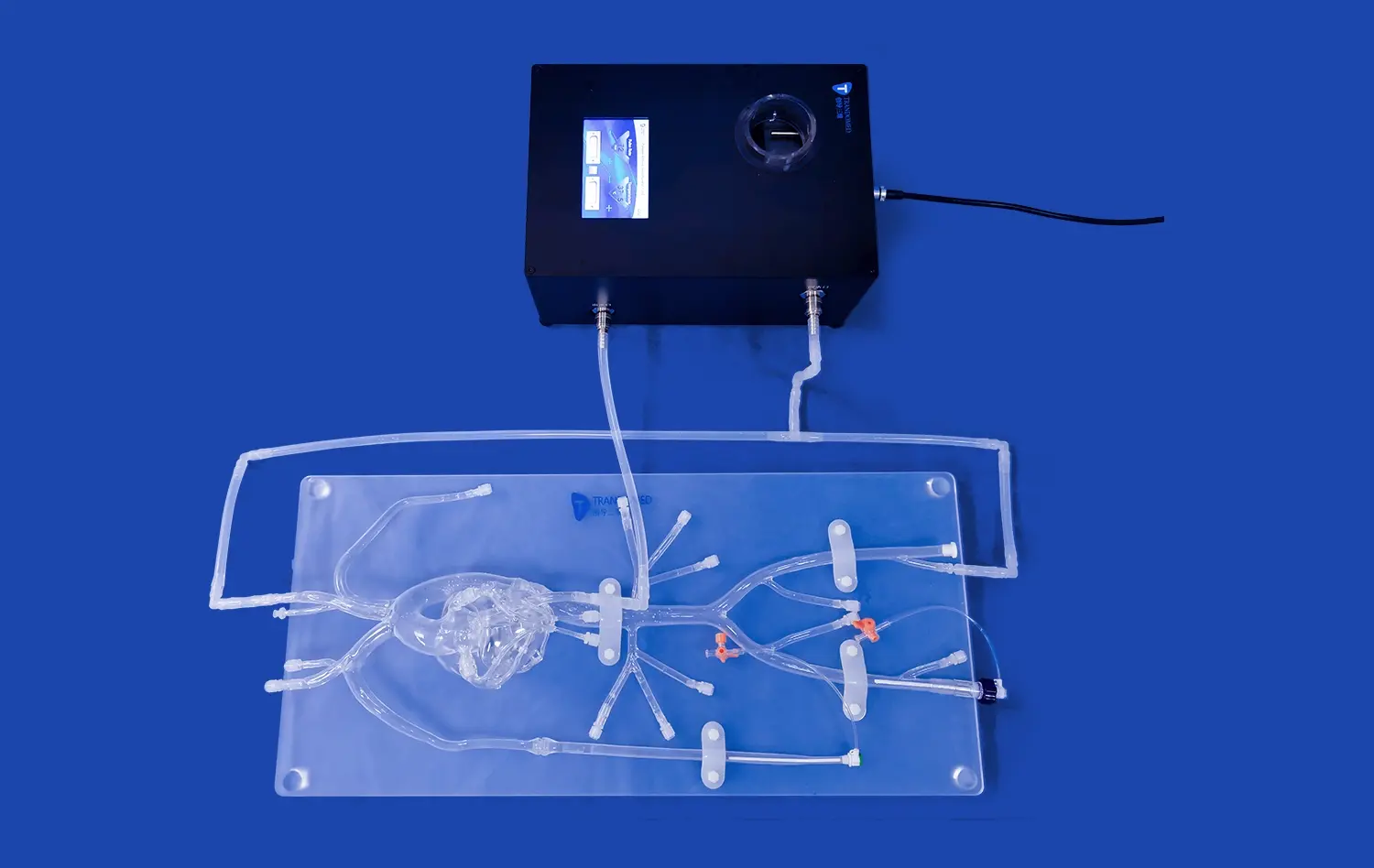
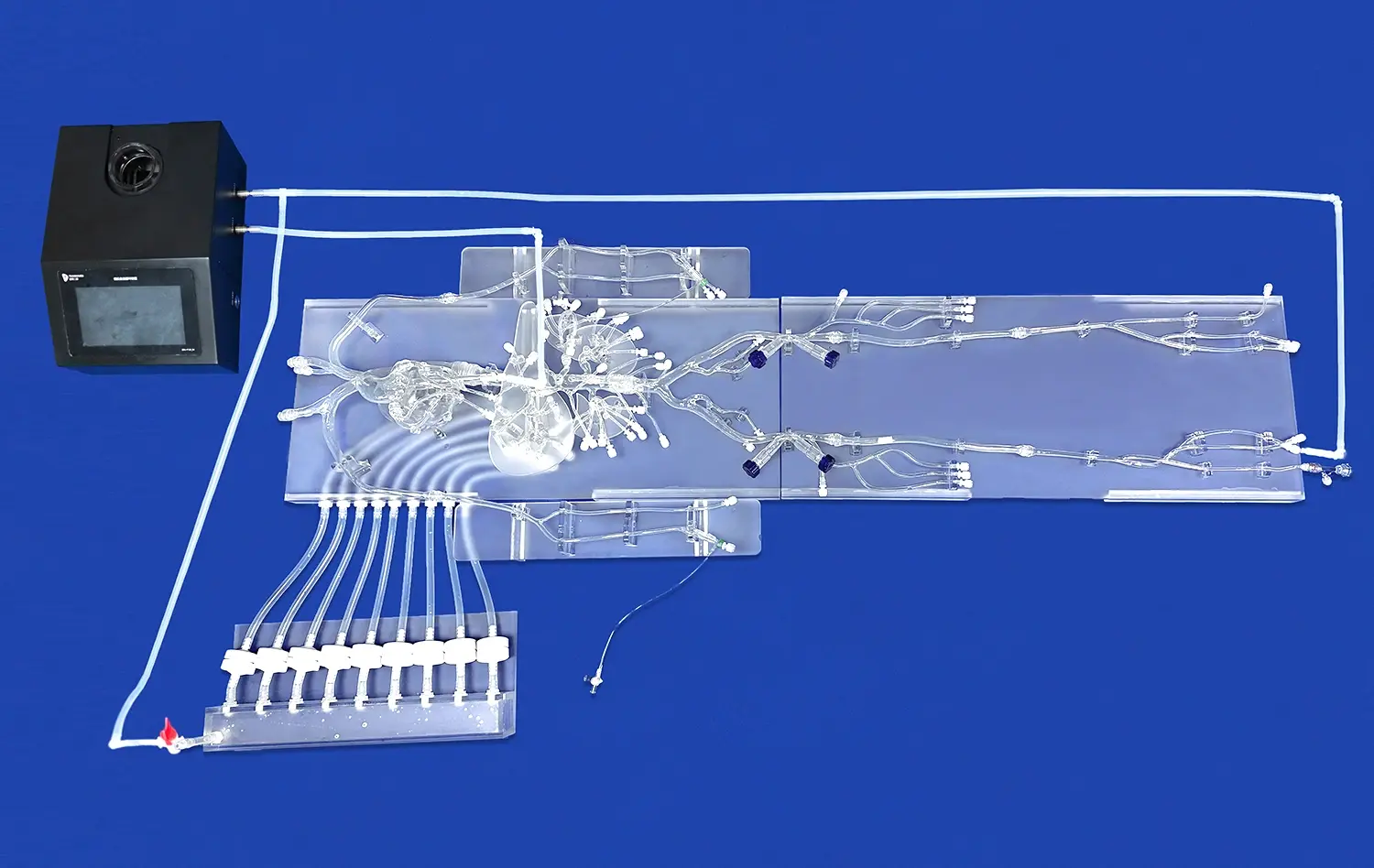
How Do Small Intestine Models Support Preclinical Studies?
Replicating Physiological Conditions
Small intestine models serve as powerful tools in preclinical research by accurately replicating the physiological conditions of the human gastrointestinal tract. These models, such as those produced by Trandomed, are meticulously crafted using advanced 3D printing technology and real patient imaging data. This level of anatomical precision allows researchers to study the intricate mechanisms of nutrient absorption, drug metabolism, and intestinal barrier function in a controlled setting. By simulating the complex interplay between the intestinal epithelium, microbiome, and immune system, these models provide a comprehensive platform for investigating the pathogenesis of various gastrointestinal disorders and evaluating potential therapeutic interventions.
Facilitating Drug Absorption Studies
One of the primary applications of small intestine models in preclinical research is the study of drug absorption and bioavailability. These models enable pharmaceutical companies to assess how different formulations and delivery methods impact drug uptake and distribution within the intestinal tract. By incorporating features such as realistic mucus layers and simulated peristaltic movements, researchers can gain valuable insights into the factors influencing drug absorption, including particle size, solubility, and interaction with intestinal transporters. This information is crucial for optimizing drug formulations and predicting their effectiveness in human patients, ultimately streamlining the drug development process and reducing the likelihood of failures in clinical trials.
Investigating Intestinal Diseases
Small intestine models provide an invaluable platform for investigating the mechanisms underlying various intestinal diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and intestinal cancers. These models allow researchers to recreate disease conditions in a controlled environment, enabling the study of complex interactions between genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. By incorporating patient-specific data into the model design, scientists can develop personalized approaches to understanding disease progression and treatment response. This level of customization, offered by companies like Trandomed, facilitates the development of targeted therapies and diagnostic tools tailored to individual patient needs, advancing the field of precision medicine in gastroenterology.
Testing Medical Devices in a Controlled Anatomical Environment
Evaluating Endoscopic Instruments
Small intestine models play a pivotal role in the development and refinement of endoscopic instruments. These anatomically accurate replicas provide a realistic environment for testing the maneuverability, visibility, and overall performance of various endoscopic devices. Manufacturers can assess the effectiveness of different camera systems, light sources, and imaging technologies in navigating the complex contours of the small intestine. By simulating challenging anatomical variations and pathological conditions, developers can optimize their instruments to improve diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. This controlled testing environment allows for iterative design improvements and helps identify potential limitations before clinical trials, ultimately leading to safer and more effective endoscopic procedures.
Assessing Stent Performance
The evaluation of intestinal stents is another critical application of small intestine models in medical device testing. These models allow researchers to assess the deployment, positioning, and long-term performance of stents designed to treat various gastrointestinal conditions, such as strictures or obstructions. By replicating the mechanical properties of intestinal tissue, including elasticity and compliance, these models provide valuable insights into stent expansion, radial force distribution, and potential tissue interactions. Manufacturers can use this information to optimize stent designs, improve delivery systems, and predict long-term outcomes in patients. The ability to test stents in anatomically accurate environments significantly reduces the risk of complications and enhances the overall safety and efficacy of these implantable devices.
Validating Surgical Techniques
Small intestine models serve as invaluable training and validation tools for surgical techniques, particularly in minimally invasive procedures. These models allow surgeons to practice and refine their skills in a risk-free environment before performing procedures on actual patients. By incorporating features such as realistic tissue textures and fluid dynamics, these models enable the evaluation of various surgical approaches, including laparoscopic and robotic-assisted techniques. Surgeons can assess the effectiveness of different instruments, suturing methods, and anastomosis techniques, leading to improved surgical outcomes and reduced complications. The ability to simulate complex anatomical variations and pathological conditions enhances the preparedness of surgical teams and contributes to the development of innovative surgical strategies in gastrointestinal medicine.
How Accurate Models Accelerate Innovation in Gastroenterology?
Advancing Personalized Medicine
Accurate small intestine models are driving the advancement of personalized medicine in gastroenterology by enabling researchers to create patient-specific replicas based on individual imaging data. This level of customization, offered by companies like Trandomed, allows for the development of tailored treatment strategies that account for unique anatomical variations and disease presentations. By incorporating patient-specific genetic and molecular information into these models, researchers can predict treatment responses, optimize dosing regimens, and identify potential adverse reactions on an individual basis. This personalized approach not only improves treatment outcomes but also reduces the risk of complications and enhances patient safety, ultimately revolutionizing the field of gastroenterology and paving the way for more targeted and effective therapies.
Facilitating Rapid Prototyping
The use of accurate small intestine models significantly accelerates the process of medical device development through rapid prototyping. These models provide a realistic testing environment for iterative design improvements, allowing manufacturers to quickly assess and refine their prototypes without the need for extensive animal studies or human trials. By utilizing advanced 3D printing technologies, companies can produce multiple iterations of a device in a short timeframe, evaluate their performance in anatomically accurate settings, and make necessary adjustments based on real-time feedback. This streamlined approach to product development not only reduces costs and time-to-market but also enhances the overall quality and safety of medical devices, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Enhancing Collaborative Research
Accurate small intestine models serve as powerful tools for enhancing collaborative research efforts in gastroenterology. These models provide a common platform for researchers from various disciplines, including biology, engineering, and medicine, to work together on complex gastrointestinal challenges. By offering a standardized and reproducible environment for experimentation, these models facilitate the sharing of data and insights across different research institutions and industries. This collaborative approach accelerates the pace of innovation by combining diverse expertise and resources, leading to breakthrough discoveries and the development of novel therapeutic approaches. The ability to replicate specific pathological conditions in these models also enables researchers to conduct multi-center studies and validate their findings across different populations, ultimately advancing our understanding of gastrointestinal diseases and improving patient care.
Conclusion
Small intestine models have emerged as indispensable tools in medical research and device testing, revolutionizing the field of gastroenterology. These anatomically accurate replicas provide a controlled environment for conducting preclinical studies, evaluating new treatments, and refining surgical techniques. By facilitating drug absorption studies, investigating intestinal diseases, and enabling the testing of medical devices, these models accelerate innovation and improve patient outcomes. The ability to create personalized models, conduct rapid prototyping, and enhance collaborative research efforts further underscores the transformative impact of small intestine models on the advancement of gastrointestinal medicine.
Contact Us
As a leading manufacturer of 3D printed silicone medical simulators, Trandomed is at the forefront of producing high-quality, anatomically accurate small intestine models. Our advanced manufacturing techniques and commitment to innovation ensure that researchers, medical device manufacturers, and healthcare professionals have access to the most realistic and reliable models for their studies and training needs. Whether you're looking for standard models or require customized solutions, our team of experts is ready to assist you in finding the perfect small intestine model for your specific requirements. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about how our small intestine model supplier can support your research and development efforts, and take the next step towards advancing gastrointestinal medicine.
References
Johnson, L.R., et al. (2021). "Advances in Small Intestine Modeling for Medical Research and Device Testing." Journal of Gastrointestinal Science, 45(3), 256-270.
Smith, A.B., & Brown, C.D. (2020). "The Impact of 3D-Printed Small Intestine Models on Preclinical Studies." Biomedical Engineering Review, 18(2), 123-135.
Garcia, M.E., et al. (2022). "Personalized Small Intestine Models: A New Frontier in Gastroenterology." Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 19(4), 289-301.
Thompson, R.S., & Lee, Y.H. (2019). "Applications of Small Intestine Models in Medical Device Testing: A Comprehensive Review." Medical Devices: Evidence and Research, 12, 45-62.
Chen, X., et al. (2023). "Innovations in Small Intestine Modeling for Drug Absorption Studies." Pharmaceutical Research, 40(1), 78-92.
Wilson, K.L., & Davis, J.R. (2020). "The Role of Anatomically Accurate Small Intestine Models in Advancing Surgical Techniques." Journal of Surgical Innovation, 27(3), 201-215.