How Do Aneurysm Models Help Students Understand Neurovascular Anatomy?
Enhancing Spatial Awareness of Cerebral Vasculature
Aneurysm models play a crucial role in developing students' spatial awareness of cerebral vasculature. Unlike 2D images or textbook illustrations, these three-dimensional representations allow learners to grasp the intricate relationships between various blood vessels in the brain. Students can observe how the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), middle cerebral artery (MCA), and internal carotid artery interact within the confined space of the skull. This enhanced spatial understanding is vital for future neurosurgeons and interventional radiologists who must navigate these complex structures during procedures.
Demonstrating Variability in Aneurysm Morphology
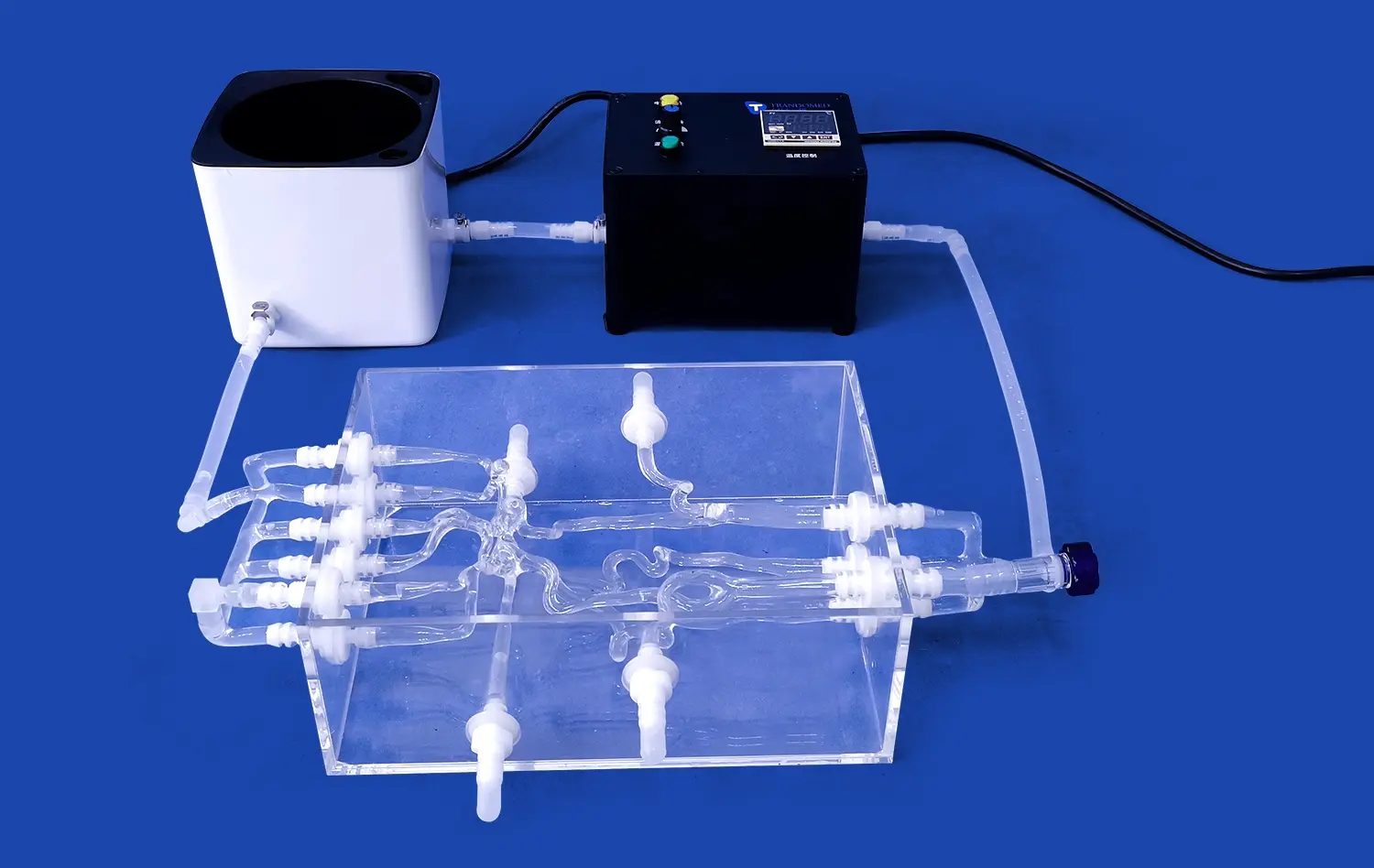
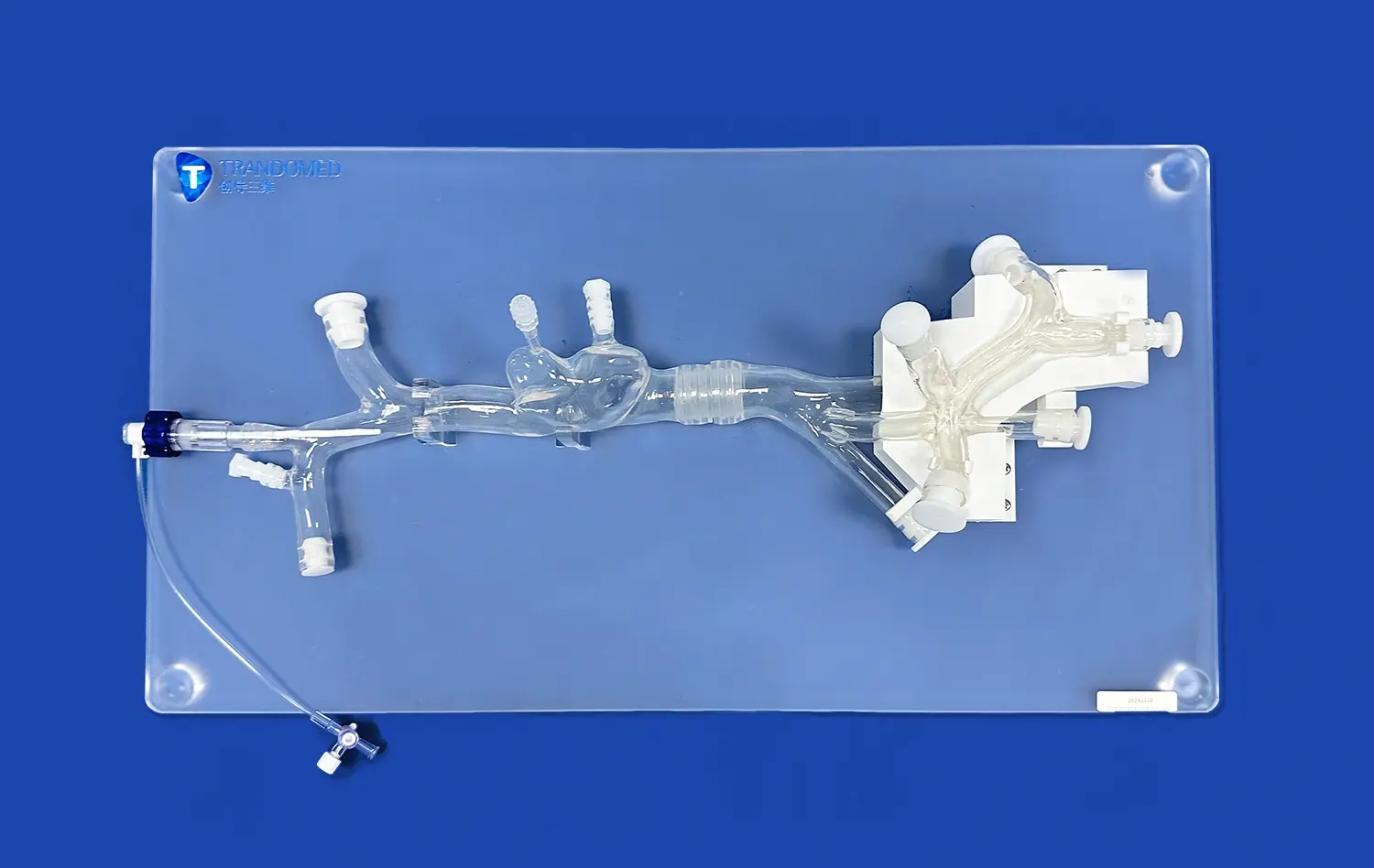
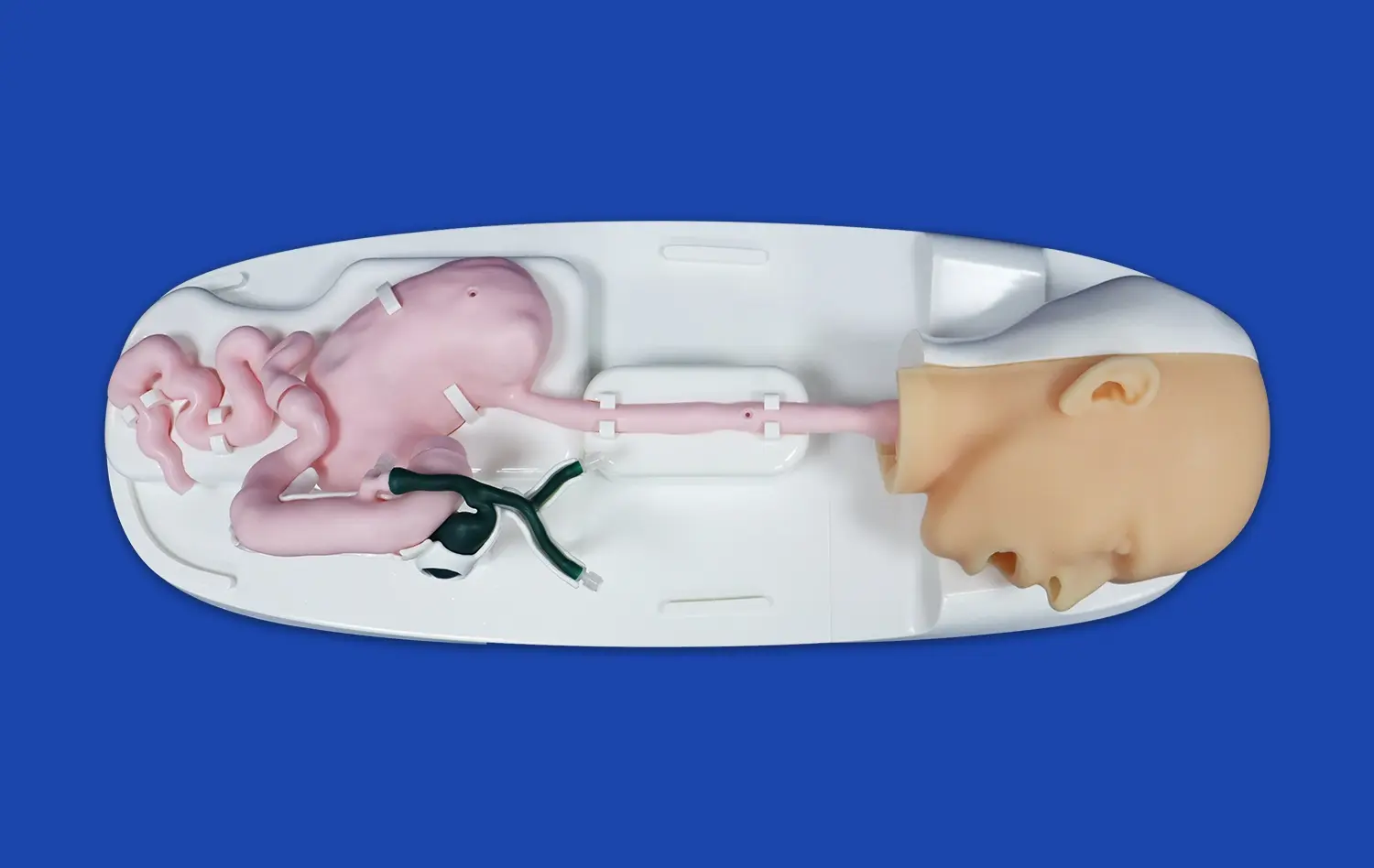
One of the key benefits of using aneurysm models is their ability to showcase the wide variety of aneurysm morphologies. These models can be customized to display different types of aneurysms, such as saccular, fusiform, or dissecting, in various locations throughout the cerebral vasculature. This exposure helps students recognize the diverse presentations of aneurysms they may encounter in clinical practice. For instance, the SJX011 model by Trandomed features four distinct aneurysms on the internal carotid artery, providing a comprehensive view of potential variations.
Facilitating Tactile Learning Experiences
Aneurysm models offer a tactile learning experience that is unmatched by traditional educational methods. Students can physically manipulate the models, feeling the texture and flexibility of the simulated blood vessels. This hands-on approach is particularly beneficial for kinesthetic learners and helps reinforce the concepts of vessel wall integrity and the potential weak points where aneurysms may form. The ability to touch and feel these structures creates a lasting impression that aids in long-term retention of anatomical knowledge.
Visualizing Cerebral Aneurysms Through 3D Simulation Models
Replicating Real-world Aneurysm Scenarios
Advanced 3D simulation models, like those produced by Trandomed, excel in replicating real-world aneurysm scenarios. These models are often based on actual patient data, ensuring a high degree of accuracy and relevance. The inclusion of features such as the tortuous internal carotid artery in the SJX011 model provides students with a realistic representation of the challenges they may face in clinical settings. By practicing on these true-to-life models, learners can develop the skills necessary to navigate complex vascular structures and identify potential risks associated with different aneurysm locations.
Enhancing Diagnostic Skills Through Visual Inspection
Visualizing cerebral aneurysms through 3D models significantly enhances students' diagnostic skills. These models allow learners to observe the subtle variations in aneurysm shape, size, and position that can impact treatment decisions. For example, students can learn to distinguish between wide-neck and narrow-neck aneurysms, understanding how these characteristics influence the choice between endovascular coiling and surgical clipping. The ability to inspect these features in a tangible, three-dimensional format helps students develop a more intuitive grasp of aneurysm morphology and its clinical implications.
Simulating Angiographic Views for Procedural Planning
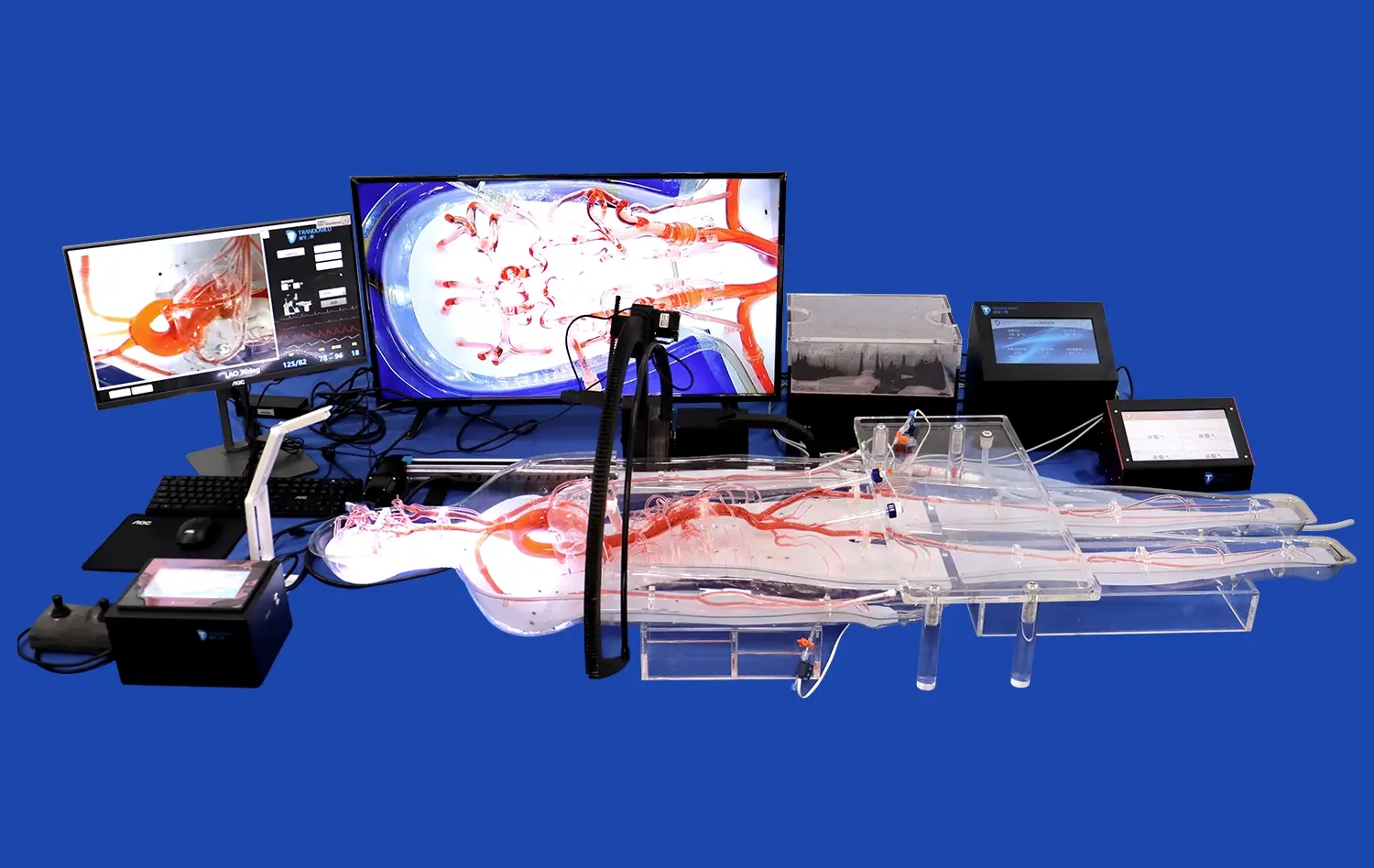
3D aneurysm models can be used to simulate angiographic views, providing students with valuable experience in procedural planning. By manipulating the model and viewing it from different angles, learners can practice identifying the optimal projection for visualizing an aneurysm during an endovascular procedure. This skill is crucial for successful aneurysm treatment, as proper visualization is essential for accurate device placement and assessment of treatment efficacy. The ability to practice these skills on a physical model before encountering them in a clinical setting can significantly improve students' confidence and competence.
Integrating Anatomical Models into Medical Curricula
Complementing Traditional Teaching Methods
Integrating anatomical models like the SJX011 into medical curricula serves as a powerful complement to traditional teaching methods. While lectures and textbooks provide essential theoretical knowledge, these 3D models offer a tangible, interactive element that reinforces learning. For instance, after studying the Circle of Willis in a lecture, students can examine a detailed aneurysm model to see how this vascular structure appears in three dimensions. This multi-modal approach to learning caters to different learning styles and helps solidify understanding of complex neurovascular concepts.
Facilitating Case-Based Learning Scenarios
Aneurysm models are invaluable tools for creating case-based learning scenarios. Educators can use these models to present students with realistic patient cases, challenging them to apply their knowledge in a practical context. For example, a model with multiple aneurysms can be used to simulate a complex case where students must decide on the optimal treatment strategy. This approach not only tests students' understanding of aneurysm morphology and treatment options but also encourages critical thinking and clinical decision-making skills.
Providing a Platform for Interdisciplinary Education
The integration of aneurysm models into medical curricula provides an excellent platform for interdisciplinary education. These models can be used to bring together students from various specialties, including neurosurgery, interventional radiology, and neurology. By examining the same model from different perspectives, students can gain insights into how their future colleagues approach aneurysm diagnosis and treatment. This collaborative learning environment fosters a holistic understanding of patient care and prepares students for the team-based approach that is essential in modern healthcare settings.
Conclusion
The integration of aneurysm models into teaching institutions offers a multitude of benefits that significantly enhance medical education. These sophisticated tools provide an unparalleled hands-on learning experience, improving students' understanding of neurovascular anatomy, aneurysm morphology, and treatment planning. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, aneurysm models prepare future healthcare professionals to tackle complex clinical scenarios with confidence and competence. As medical education continues to evolve, the role of these innovative teaching aids in shaping the next generation of skilled neurovascular specialists cannot be overstated.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are committed to advancing medical education through our state-of-the-art aneurysm models. Our SJX011 Intracranial Vascular with Aneurysm Model offers unparalleled realism and customization options to meet the diverse needs of teaching institutions. Experience the future of neurovascular education and enhance your training programs with our cutting-edge solutions. For more information or to discuss how our models can benefit your institution, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.
_1734507815464.webp)
_1732863962417.webp)