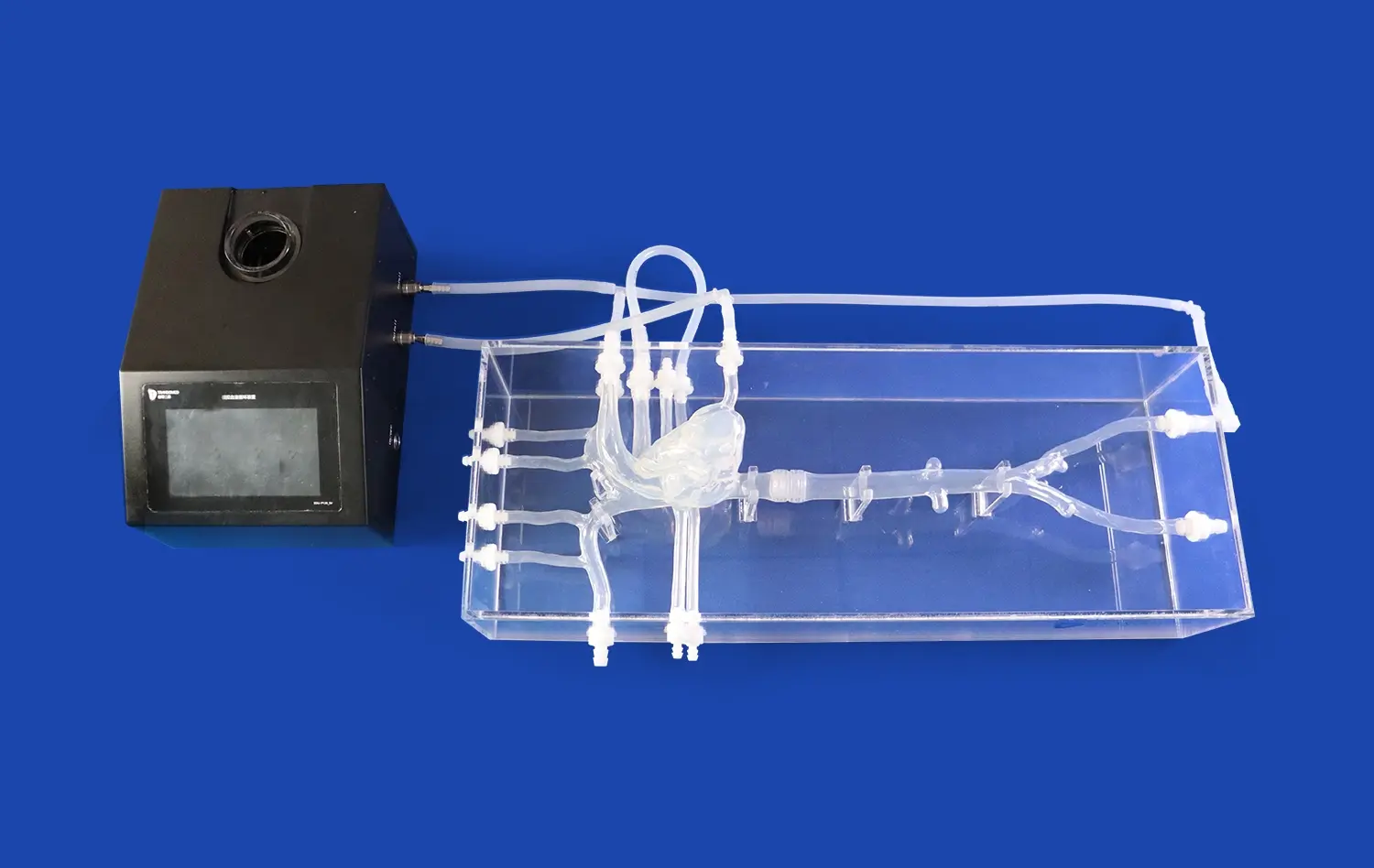
How Do Simulators Improve Clot Retrieval Techniques?
Replicating Complex Vascular Anatomy
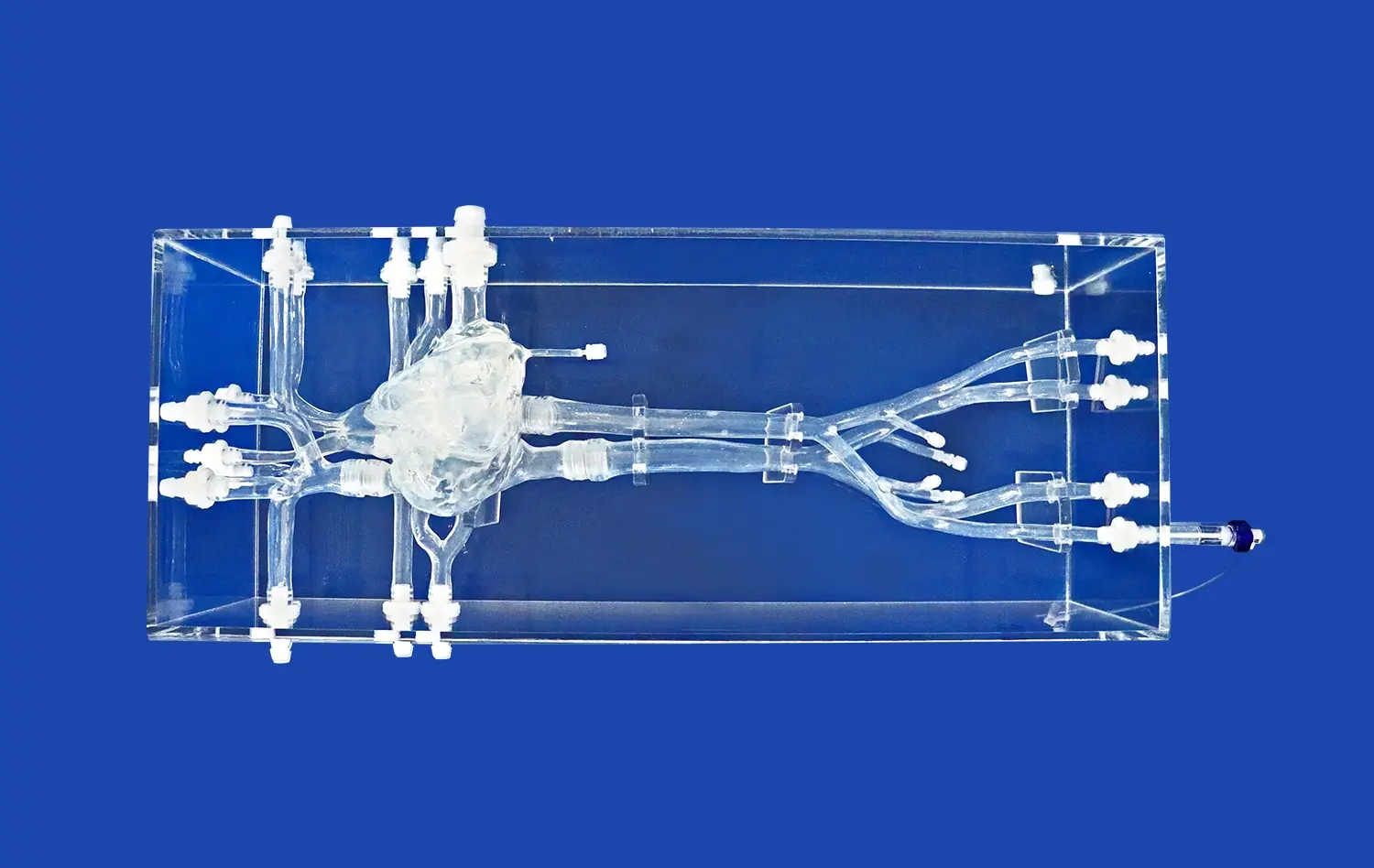
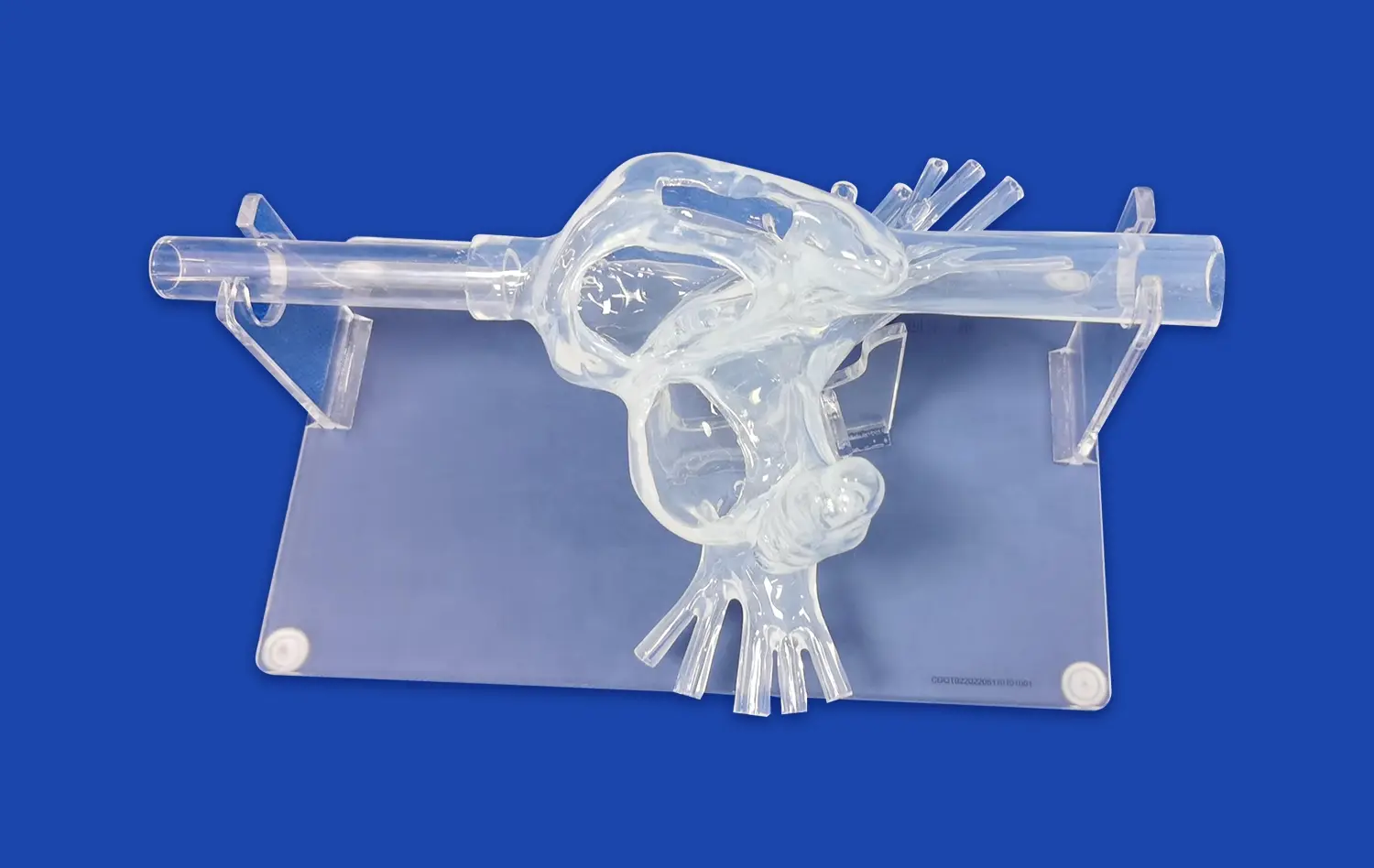
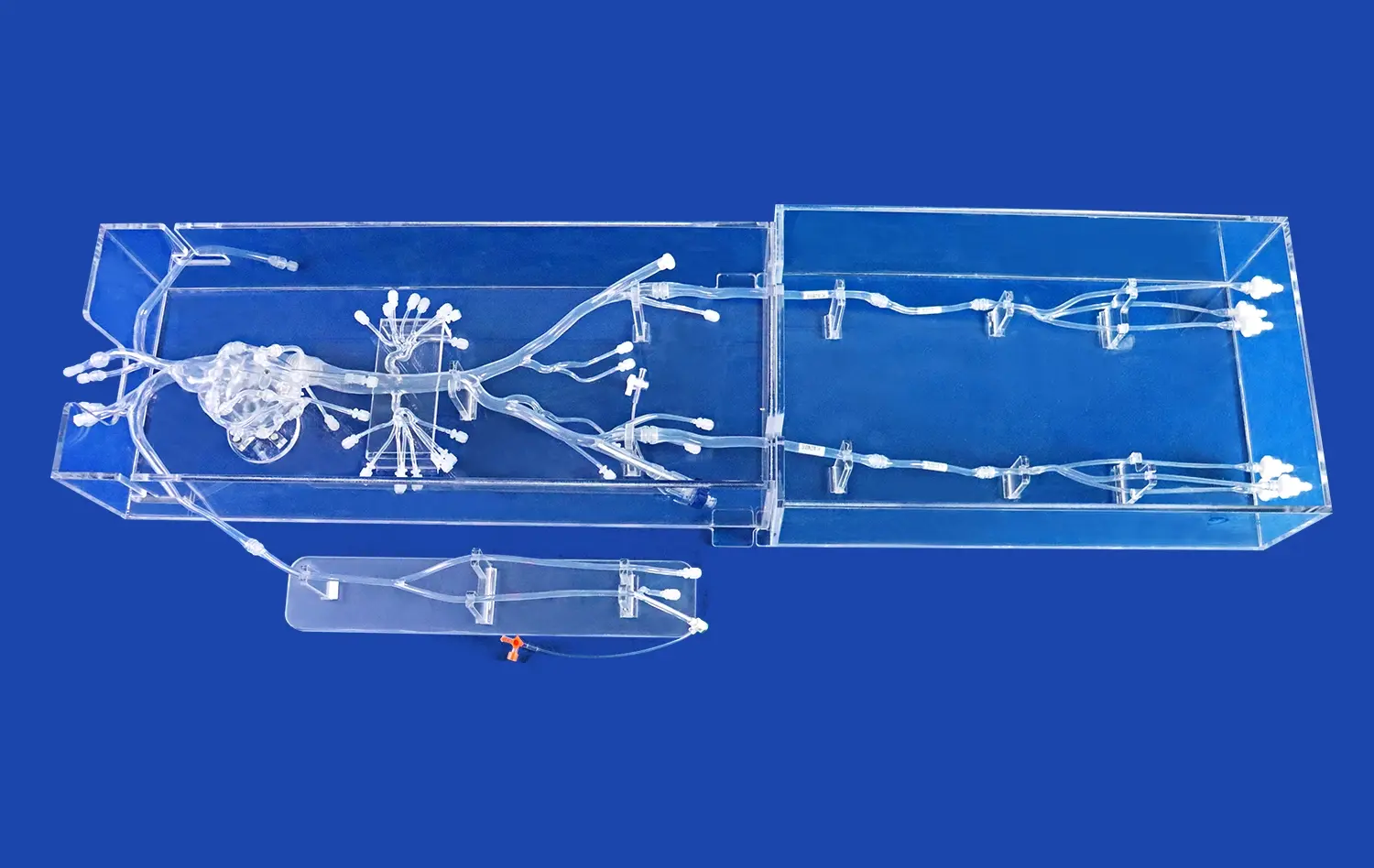
Neuro vascular simulators excel in reproducing intricate cerebral vasculature, from the femoral access point to the distal branches of the cerebral arteries. These models, often based on real patient data, incorporate various anatomical variations and pathologies, allowing trainees to encounter and navigate through challenging scenarios. The ability to practice in a setting that closely mimics human anatomy enhances the transferability of skills to real-world procedures.
Customizable Pathological Scenarios
Advanced simulation systems, which are neuro vascular simulators, offer the flexibility to create diverse thrombotic occlusions in different locations within the cerebral vasculature. This customization allows practitioners to experience a wide range of clinical scenarios, from straightforward cases to complex occlusions in tortuous vessels. By repeatedly practicing these varied situations, operators can develop adaptive strategies for efficient clot retrieval across different patient presentations.
Perfecting Device Selection and Manipulation
Neurovascular simulators provide an ideal platform for familiarizing oneself with various thrombectomy devices. Trainees can experiment with different stent retrievers, aspiration catheters, and combination techniques without the pressure of a live patient scenario. This hands-on experience is crucial for understanding the nuances of each device, optimizing selection based on clot characteristics and vascular anatomy, and mastering the fine motor skills required for successful deployment and retrieval.
Real-Time Feedback on Device Maneuverability and Clot Removal
Immediate Visual Feedback
One of the key advantages of neuro vascular simulators is the provision of real-time visual feedback. Many systems incorporate transparent vessel models or fluoroscopic simulation, allowing operators to observe the behavior of devices and clots in real-time. This immediate visualization helps in understanding the interactions between the device, the clot, and the vessel wall, fostering a deeper comprehension of the mechanical principles behind successful thrombectomy.
Tactile Sensation and Force Feedback
Neuro vascular simulators are designed to provide realistic tactile sensations, mimicking the feel of navigating through vessels and encountering resistance from clots. Some systems even incorporate force feedback mechanisms, allowing trainees to experience the subtle changes in resistance during device advancement, clot engagement, and retrieval. This haptic feedback is crucial for developing the fine motor control and intuition necessary for safe and effective thrombectomy procedures.
Performance Metrics and Analysis
Many neurovascular simulation platforms come equipped with sophisticated tracking and analysis tools. These features can measure various performance metrics such as procedure time, number of passes, successful recanalization rates, and potential complications like vessel perforation or distal embolization. By providing objective data on performance, these simulators enable trainees to track their progress over time and identify specific areas for improvement in their thrombectomy technique.
Enhancing Operator Confidence Before Live Thrombectomy Procedures
Gradual Skill Progression
Neuro vascular simulators facilitate a structured learning approach, allowing trainees to progress from basic catheterization skills to complex thrombectomy maneuvers. This step-wise skill acquisition helps build confidence systematically. Beginners can start with simple vessel navigation and gradually advance to challenging scenarios involving tortuous anatomy or resistant clots. As proficiency increases, the simulator can be adjusted to present more complex cases, ensuring that operators are well-prepared for the variability encountered in clinical practice.
Stress-Free Environment for Experimentation
The risk-free nature of neuro vascular simulator training creates an ideal environment for experimentation and learning from mistakes. Operators can try different approaches and techniques without the fear of causing harm to a patient. This freedom encourages innovation and helps develop problem-solving skills crucial for handling unexpected situations during live procedures. The ability to repeat scenarios multiple times also allows for refinement of technique and strategy, further boosting operator confidence.
Team Training and Communication
Advanced neurovascular simulators can be utilized for team-based training scenarios, mimicking the collaborative nature of real thrombectomy procedures. This approach allows not only for individual skill development but also for enhancing team communication and coordination. Practicing with other team members, including nurses and technicians, in a simulated environment helps streamline workflows and improves overall procedural efficiency. The confidence gained from these team exercises translates directly to improved performance and reduced stress levels during actual patient care.
Conclusion
The integration of neuro vascular simulators in intracranial thrombectomy training represents a significant advancement in medical education. These sophisticated tools provide a realistic, safe, and customizable environment for healthcare professionals to refine their skills and build confidence. By offering hands-on experience with various devices and scenarios, simulators bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. As technology continues to evolve, the role of neurovascular simulation in improving procedural outcomes and patient safety is likely to expand, making it an indispensable component of comprehensive stroke care education.
Contact Us
To explore how Trandomed's state-of-the-art neuro vascular simulators can enhance your thrombectomy training program and improve patient outcomes, contact us today. Our expert team is ready to provide personalized solutions tailored to your specific educational needs. Reach out to us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our innovative simulation technology and take the next step in advancing your interventional skills.
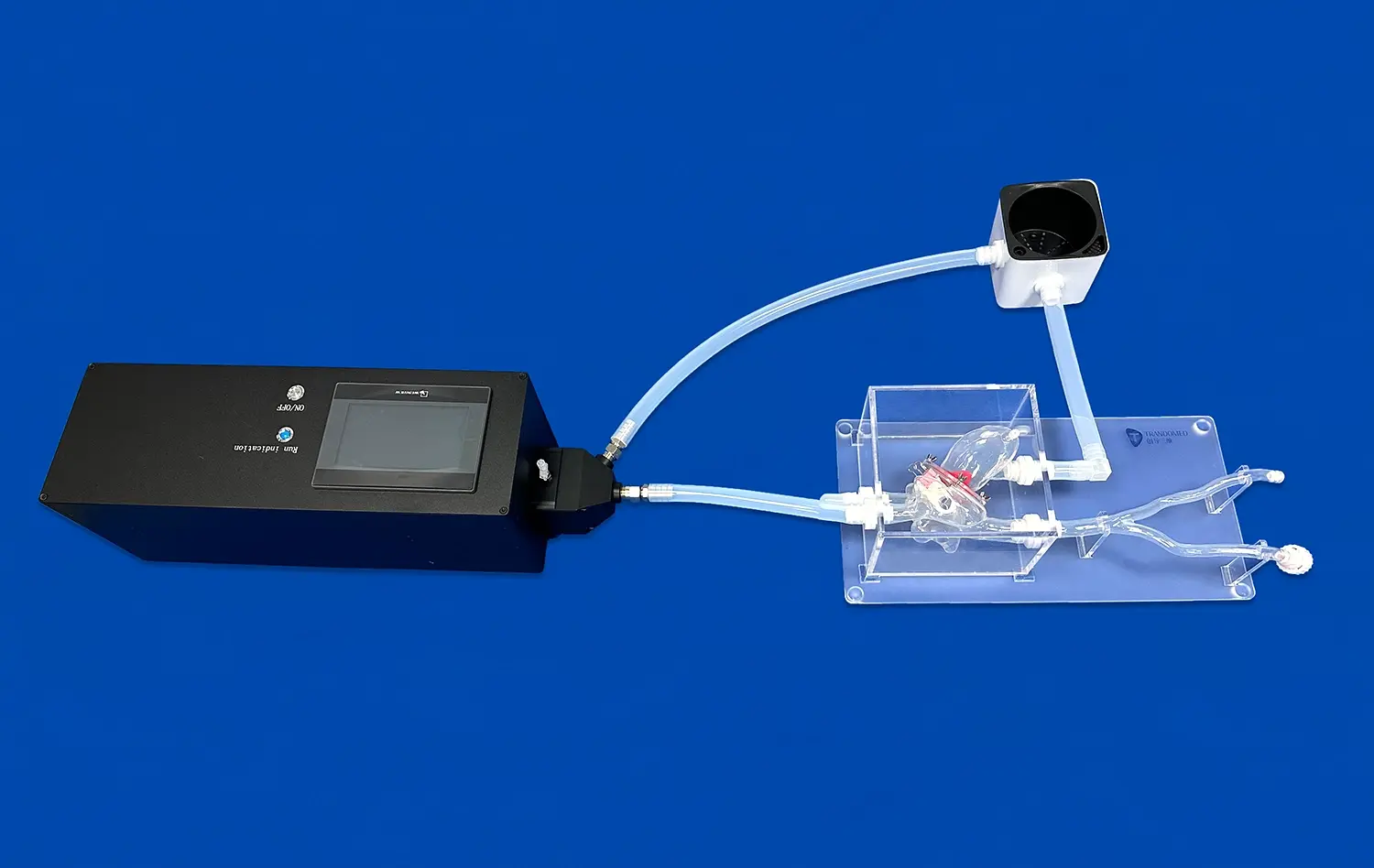

_1736216292718.webp)