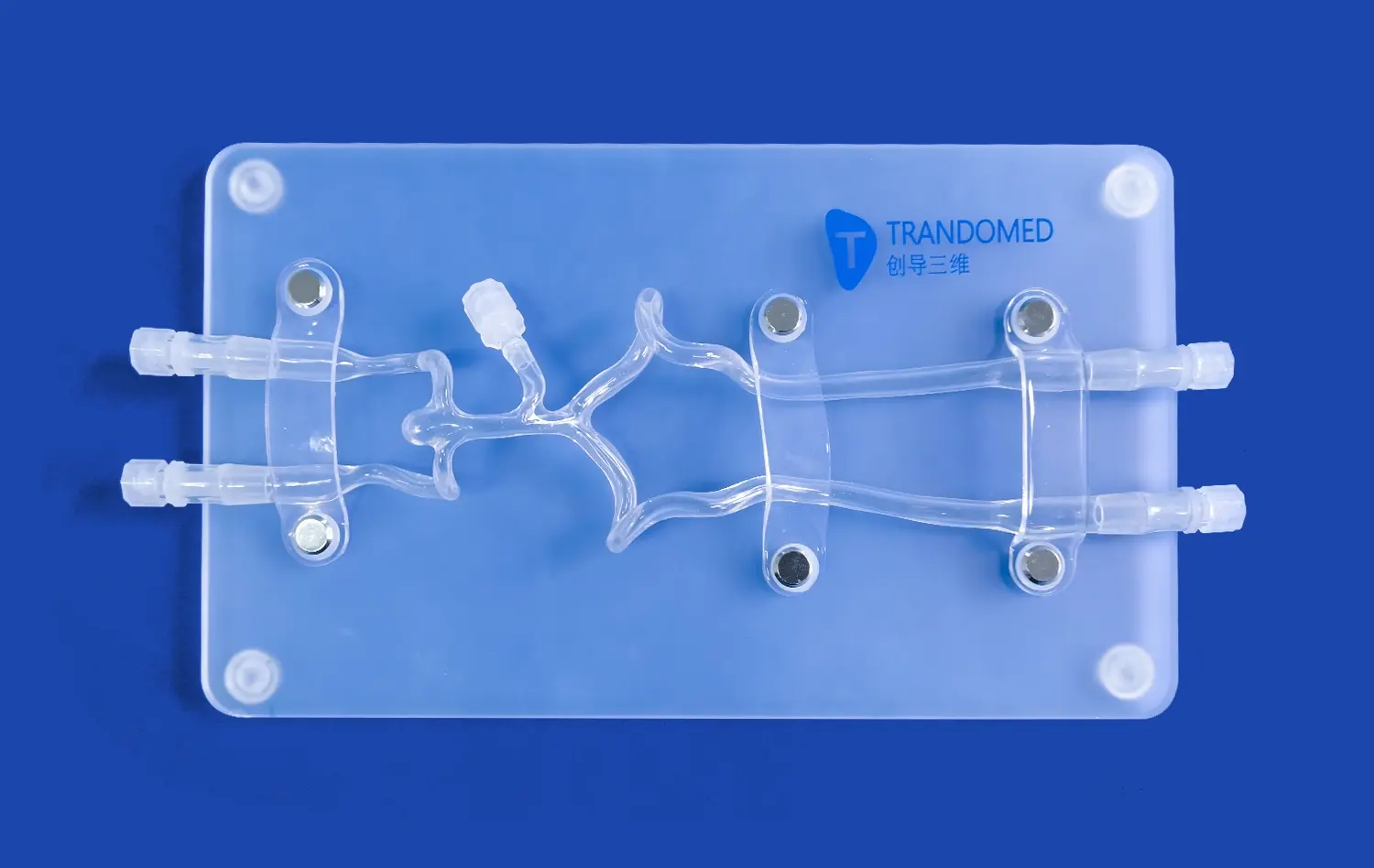
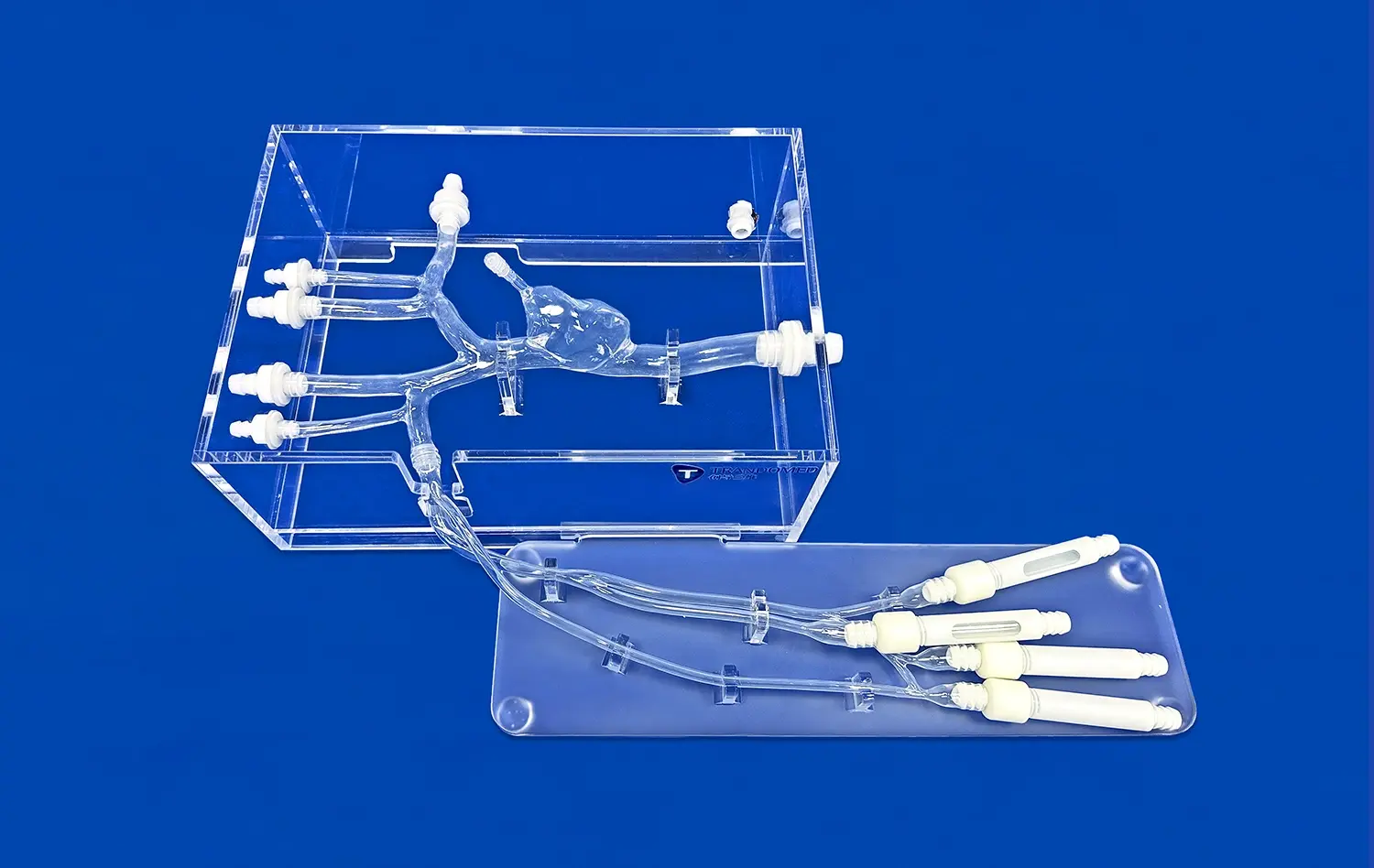
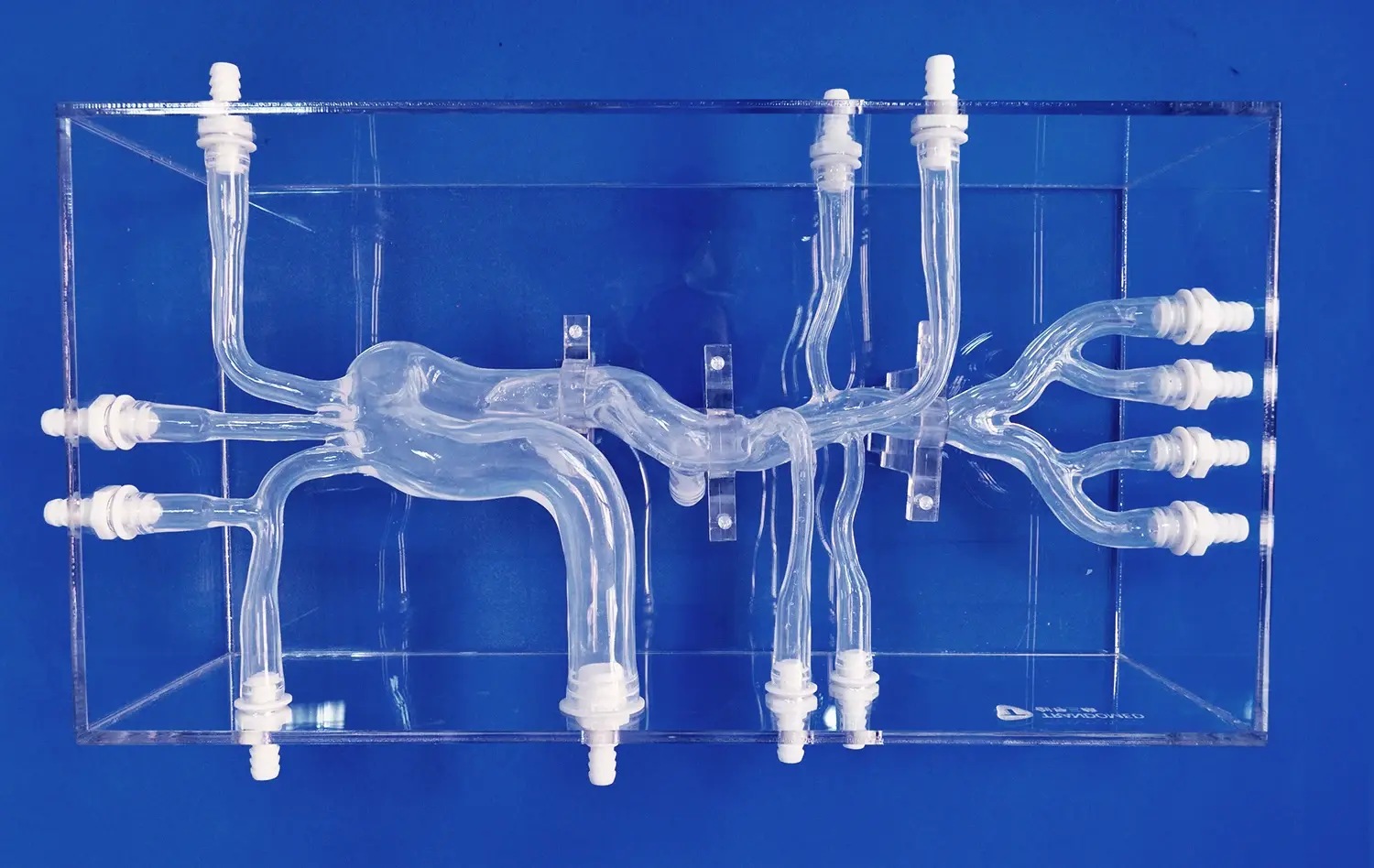
How Can Visual Models Simplify Understanding of Aortic Dissection?
Enhancing Spatial Awareness
Visual models of aortic dissection provide an unparalleled opportunity for learners to grasp the spatial relationships within the cardiovascular system. Unlike two-dimensional images or textbook descriptions, these models allow students to examine the aorta from multiple angles, gaining a comprehensive understanding of its structure and the impact of dissection on surrounding tissues. This enhanced spatial awareness is crucial for medical professionals, particularly those involved in interventional procedures or surgical planning.
Illustrating Complex Anatomical Features
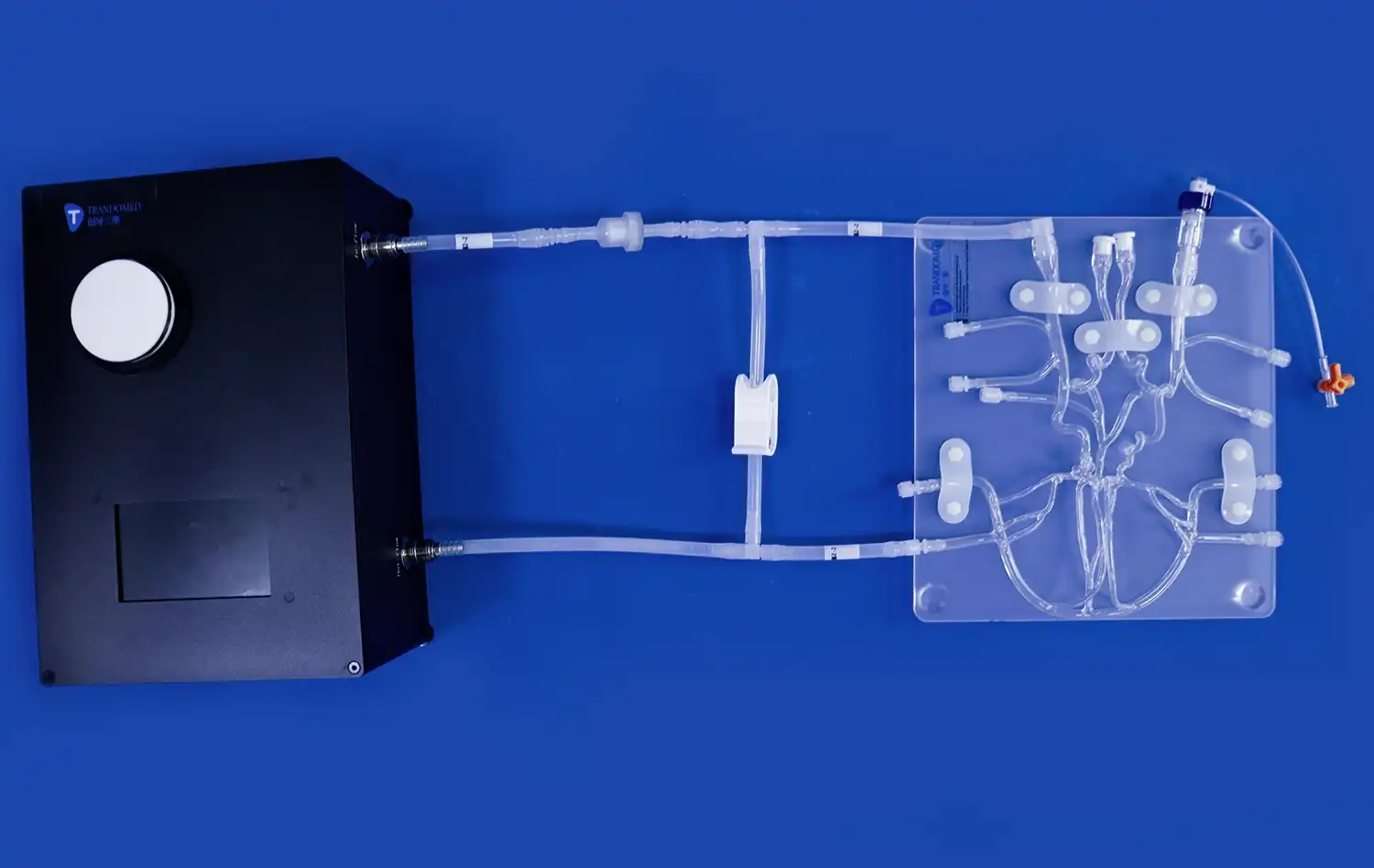
The intricacy of aortic anatomy can be challenging to convey through traditional teaching methods. Aortic dissection simulators, such as the XXK004D model, offer a detailed representation of major arteries involved in dissection scenarios. From the femoral artery to the ascending aorta, these models illustrate the interconnectedness of the vascular system, helping learners appreciate how a localized dissection can have far-reaching consequences throughout the body.
Demonstrating Pathological Changes
Perhaps the most significant advantage of using aortic dissection models is their ability to demonstrate pathological changes in a clear, accessible manner. The realistic depiction of dissection lesions in the thoracic aorta segment allows students to observe the separation of aortic wall layers, the formation of false lumens, and the potential complications that can arise. This visual representation helps solidify abstract concepts, making them more memorable and applicable in clinical settings.
Stepwise Exploration of True and False Lumens
Identifying Key Anatomical Landmarks
Aortic dissection models facilitate a stepwise approach to understanding the condition, beginning with the identification of key anatomical landmarks. Learners can trace the path of blood flow from the heart through the aorta, noting important structures such as the aortic valve, sinuses of Valsalva, and branches of the aortic arch. This foundational knowledge is essential for recognizing the normal anatomy before delving into the pathological changes associated with dissection.
Visualizing the Intimal Tear
The initiating event in aortic dissection - the intimal tear - is vividly illustrated in high-quality aortic dissection models. Students can examine the precise location and extent of the tear, understanding how it serves as the entry point for blood to separate the layers of the aortic wall. This visualization helps learners appreciate the importance of early detection and the potential for rapid progression of the dissection.
Tracing Blood Flow Patterns
One of the most challenging aspects of teaching aortic dissection is explaining the complex blood flow patterns that develop as a result of the condition. Advanced models allow for a hands-on exploration of both the true and false lumens. Learners can trace the path of blood as it flows through the true lumen and enters the false lumen through the intimal tear. This physical demonstration helps clarify concepts such as antegrade and retrograde dissection propagation, which are crucial for understanding the potential complications and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
Clarifying Disease Progression Through Physical Demonstration
Showcasing Different Types of Dissection
Aortic dissection models are invaluable tools for demonstrating the various classification systems used to describe the condition. For instance, the Stanford classification, which divides dissections into type A (involving the ascending aorta) and type B (limited to the descending aorta), can be easily illustrated using these physical representations. Learners can observe the differences in anatomical involvement and potential complications associated with each type, enhancing their ability to make accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions in clinical practice.
Illustrating Potential Complications
The progression of aortic dissection can lead to a range of serious complications, which are often difficult to conceptualize without visual aids. Advanced simulation models can depict scenarios such as aortic rupture, organ malperfusion, and the development of aneurysms. By physically demonstrating these complications, educators can help students understand the urgency of proper management and the potential consequences of delayed or inappropriate treatment.
Exploring Treatment Options
Aortic dissection models serve as excellent platforms for discussing and demonstrating various treatment approaches. From conservative medical management to complex surgical interventions, these models allow learners to visualize the rationale behind different treatment strategies. For example, the placement of endovascular stent grafts can be simulated, helping students understand the principles of excluding the false lumen and promoting aortic remodeling. This hands-on approach to exploring treatment options enhances clinical decision-making skills and prepares healthcare professionals for real-world patient care scenarios.
Conclusion
The use of aortic dissection models in medical education represents a significant advancement in teaching complex cardiovascular pathologies. These innovative tools bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical understanding, offering learners a tangible, interactive experience that enhances their comprehension of aortic dissection. By simplifying spatial relationships, illustrating anatomical features, and demonstrating disease progression, these models empower healthcare professionals to develop the skills and confidence necessary for effective diagnosis and treatment of this life-threatening condition. As medical education continues to evolve, the integration of such advanced simulation tools will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the next generation of competent and well-prepared cardiovascular specialists.
Contact Us
To learn more about how Trandomed's advanced aortic dissection models can enhance your medical education program and provide hands-on learning experiences, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Our team is dedicated to supporting your educational goals with cutting-edge simulation technology and personalized solutions.
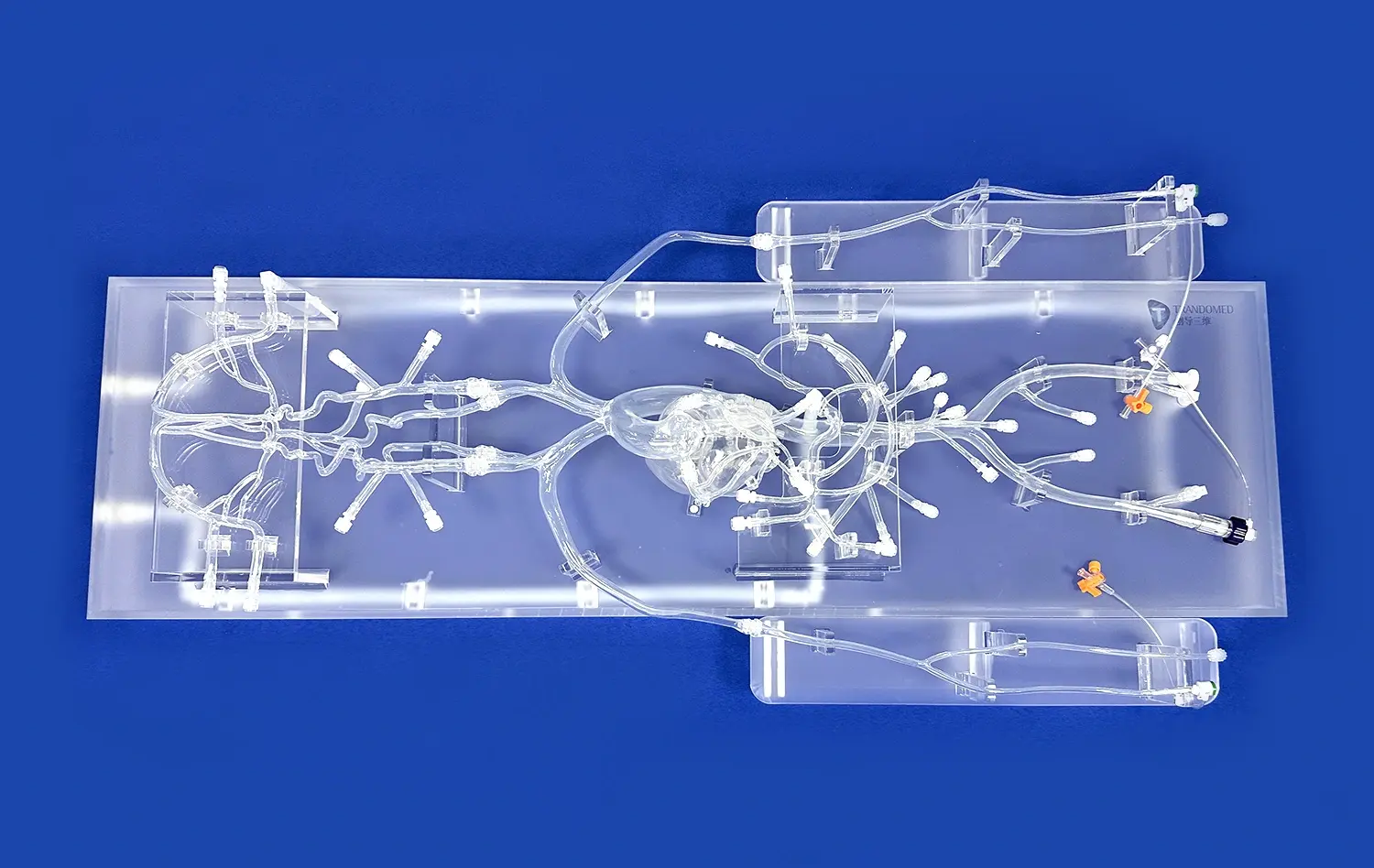
_1734504197376.webp)