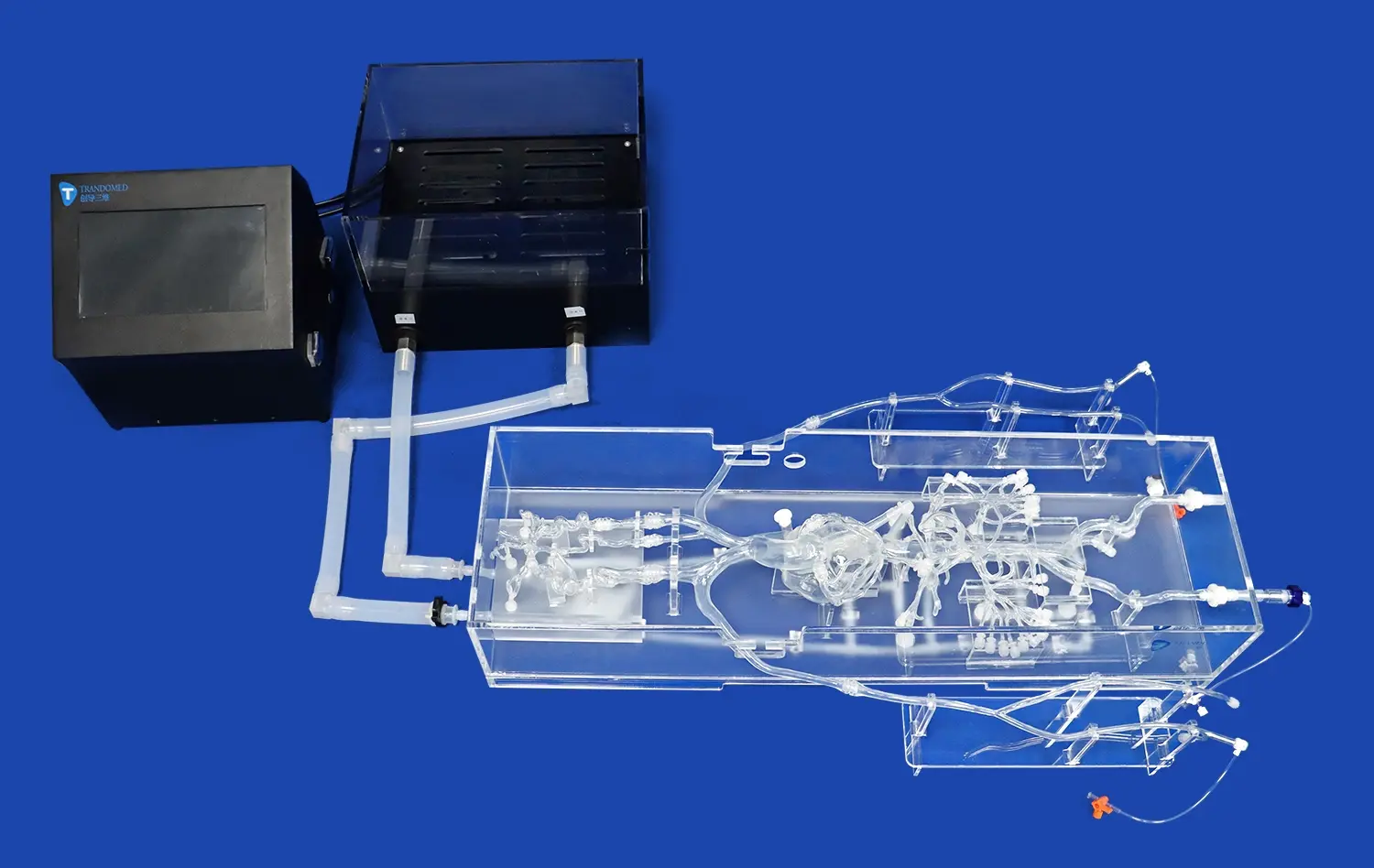
As medical education changes, new methods are needed that connect what students learn with how they should use it. A human stomach model is an important part of this teaching shift because it helps students learn about difficult body parts by doing them. It is often hard to learn all about gastric anatomy with traditional training methods because they don't use enough hands-on activities. The arrival of 3D printing has changed the way that anatomy models are made. This has opened up a lot of new possibilities for better medical training. These advanced models provide anatomically correct depictions that very closely resemble the properties of real human tissue. This gives educators powerful tools to boost student interest and learning in gastroenterology education.
Understanding the Limitations of Traditional Human Stomach Models
Material and Construction Deficiencies
Traditional models of anatomy often use hard plastics that don't look or feel like the real gastric flesh. These materials don't have the subtle qualities that are needed for actual palpation training. This makes it harder for students to build up their diagnostic skills. The inflexible setup stops the kind of hands-on learning that today's medical schools need.
Limited Educational Scope
Conventional stomach models usually only show healthy body parts and don't show unhealthy ones that are important for complete medical training. Because of this problem, teachers can't teach students about ulcers, tumors, and other stomach issues that they will see in clinical practice. The lack of parts that can be taken off makes it even harder to explore the object by hand.
Cost and Accessibility Challenges
Institutions often can't afford high-quality traditional types because they are so expensive. The limited supply and long lead times for procurement of teaching tools make it even harder for medical schools to find ones that work well. All of these play a role in the standard and accessibility of gastric anatomy education in different training schools.
How 3D-Printed Human Stomach Models Overcome These Challenges?
Advanced Material Innovation
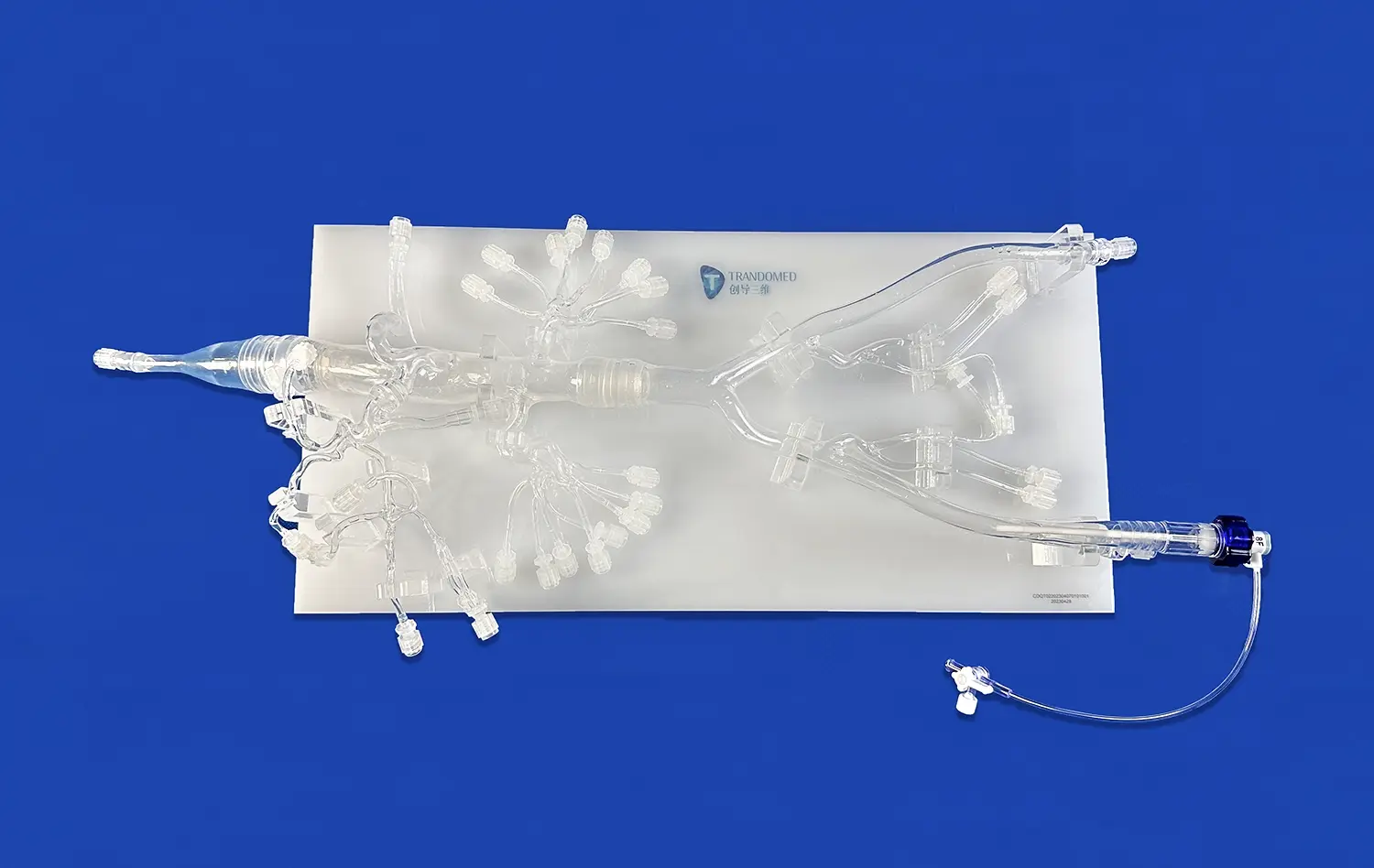
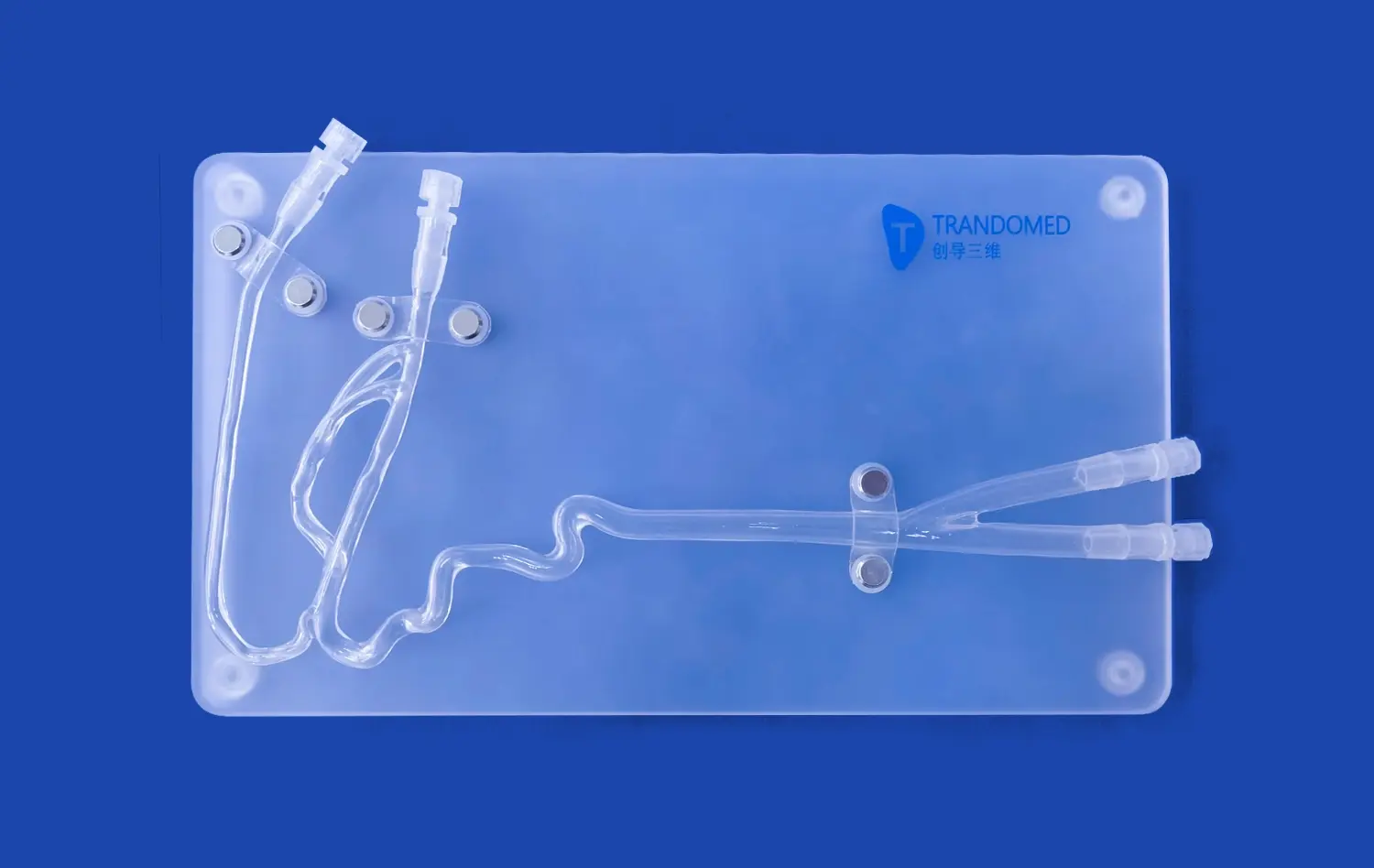
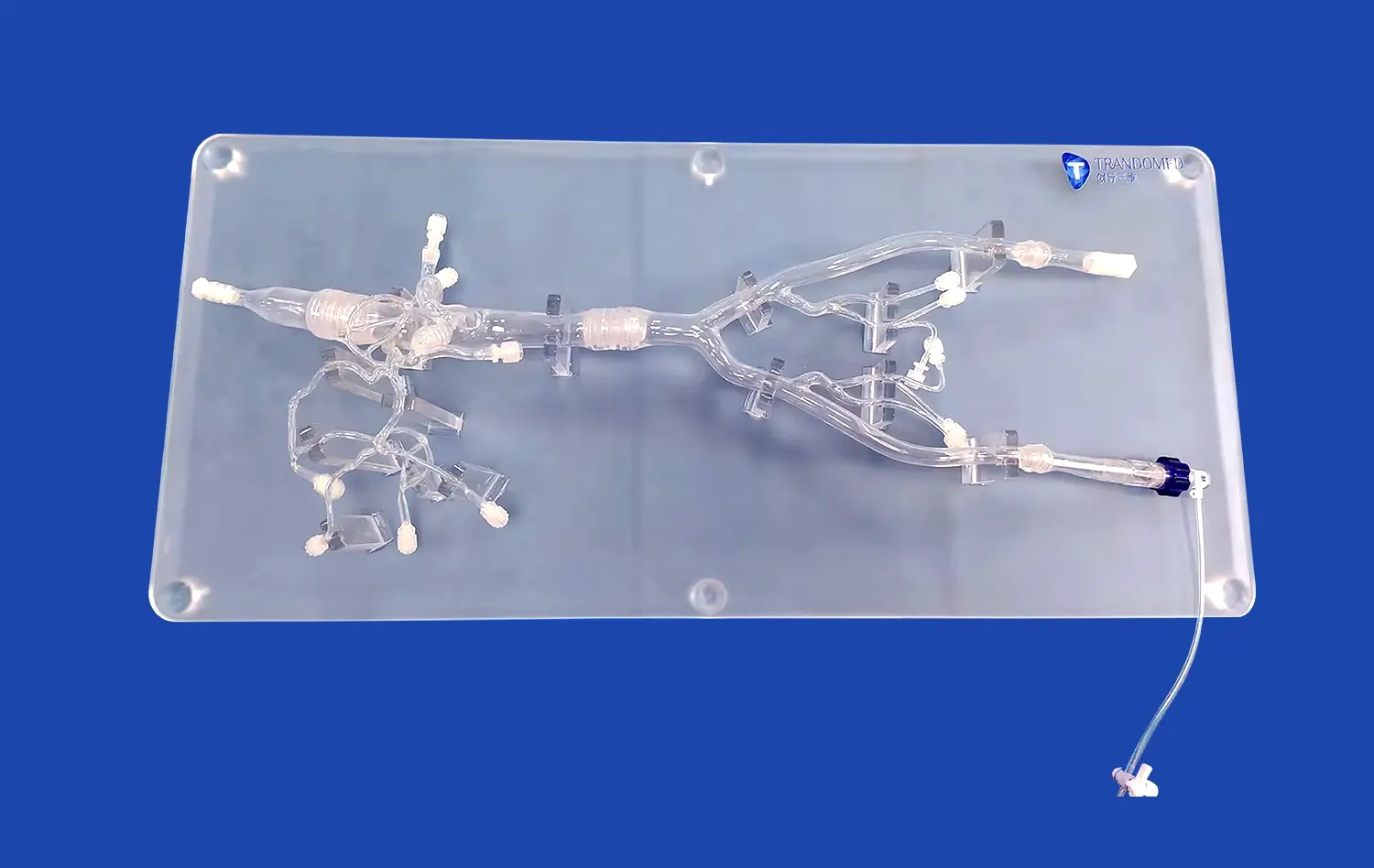
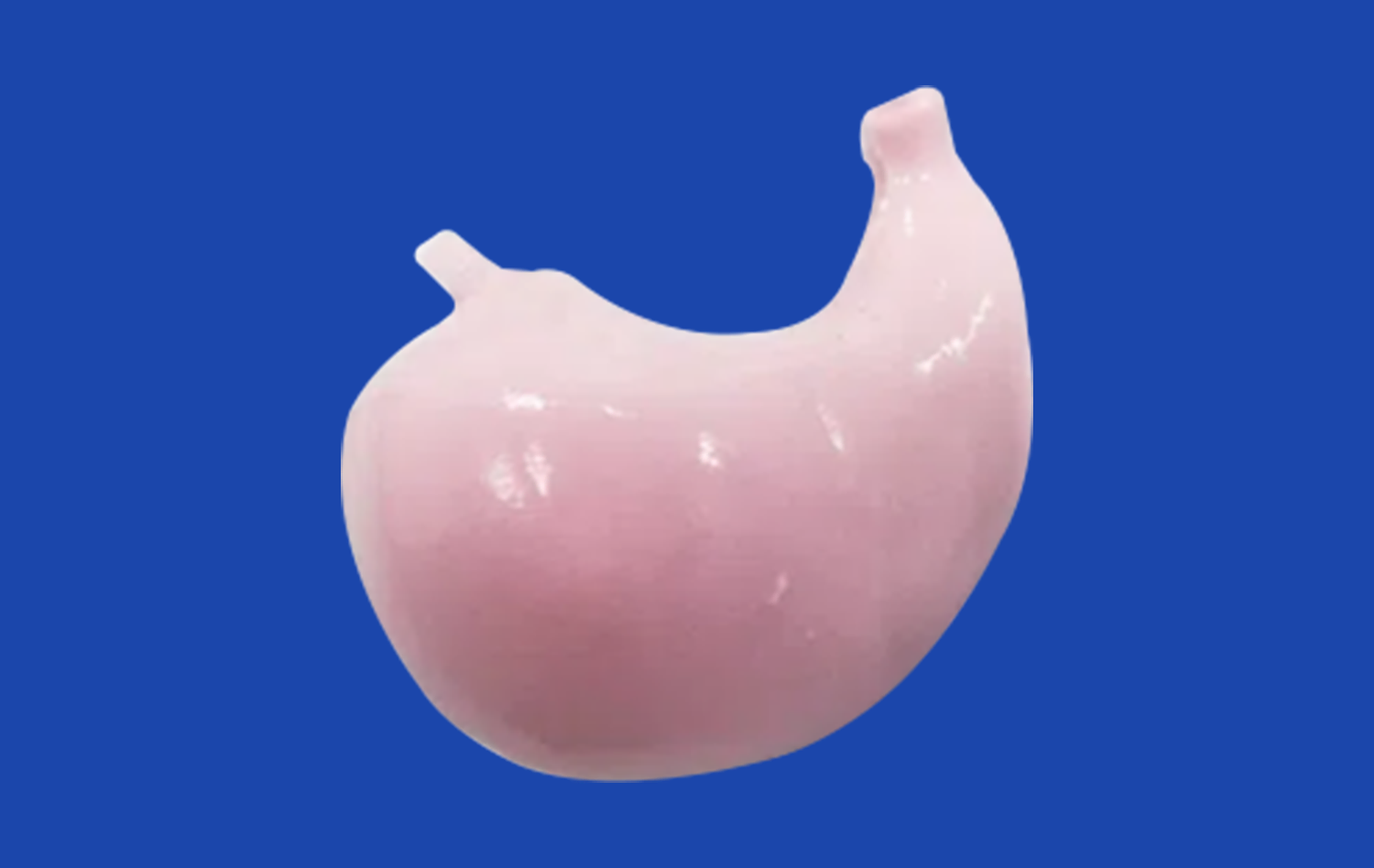
With new 3D printer technology and advanced materials that are a lot like human tissue, it's now possible to make models of stomachs. At Trandomed, our Human Stomach Model (Product No.: HSX006) is an example of this new type of product. It has three different layers: a thin muscular outer jacket, a thick muscled layer in the middle, and a smooth, slippery covering on the inside. This design with multiple layers makes it feel like you are really touching it, which makes learning better.
Anatomical Precision Through Medical Imaging
Modern 3D-printed models use CT and MRI data from real patients to make sure that they are as accurate as possible. This method gets rid of the guesswork that comes with standard model design and gives students real-life examples of human gastric anatomy. The reverse 3D reconstruction method keeps the exact size and shape of the relationships between anatomical structures.
Customizable Educational Solutions
Because 3D-printed stomach models are flexible, teachers can adapt training sessions to meet the needs of different students or classes. You can add pathological changes to show how diseases affect the body, and you can also take off the parts to see the internal structures more closely. This ability to adapt helps a wide range of teaching styles and learning goals.
Comparing 3D-Printed Models with Other Educational Tools
Superior Durability and Longevity
3D-printed stomach models don't break down with repeated handling like regular models do. The advanced materials and production methods make sure that the performance is always the same across many training sessions. This gives schools great long-term value.
Cost-Effective Educational Investment
While the costs to buy them may differ, 3D-printed models are more durable, customizable, and useful for teaching, making them a better deal. When institutions spend money on these models instead of traditional ones, they get better learning results per dollar, so these models are better for the economy.
Integration with Modern Technology
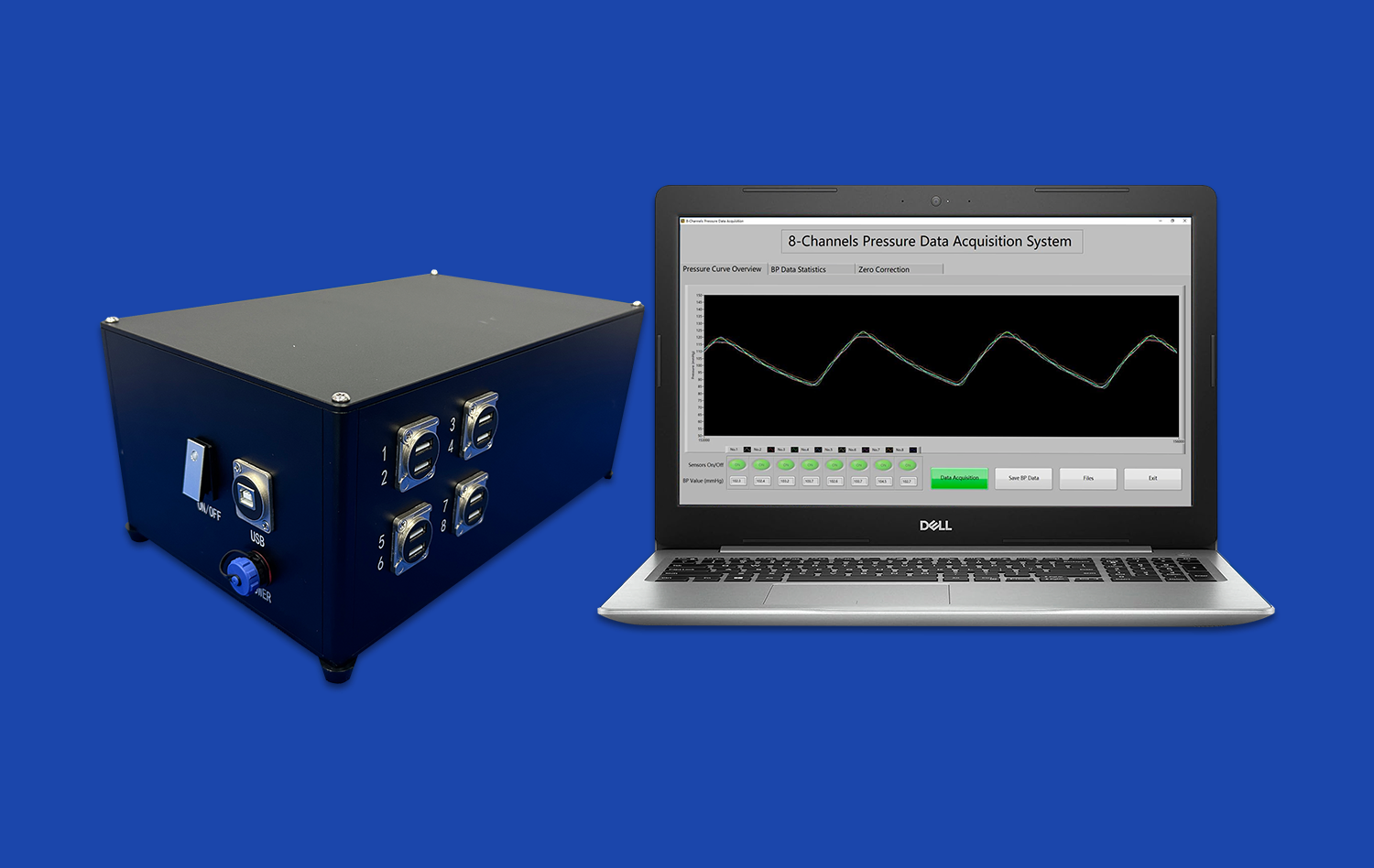
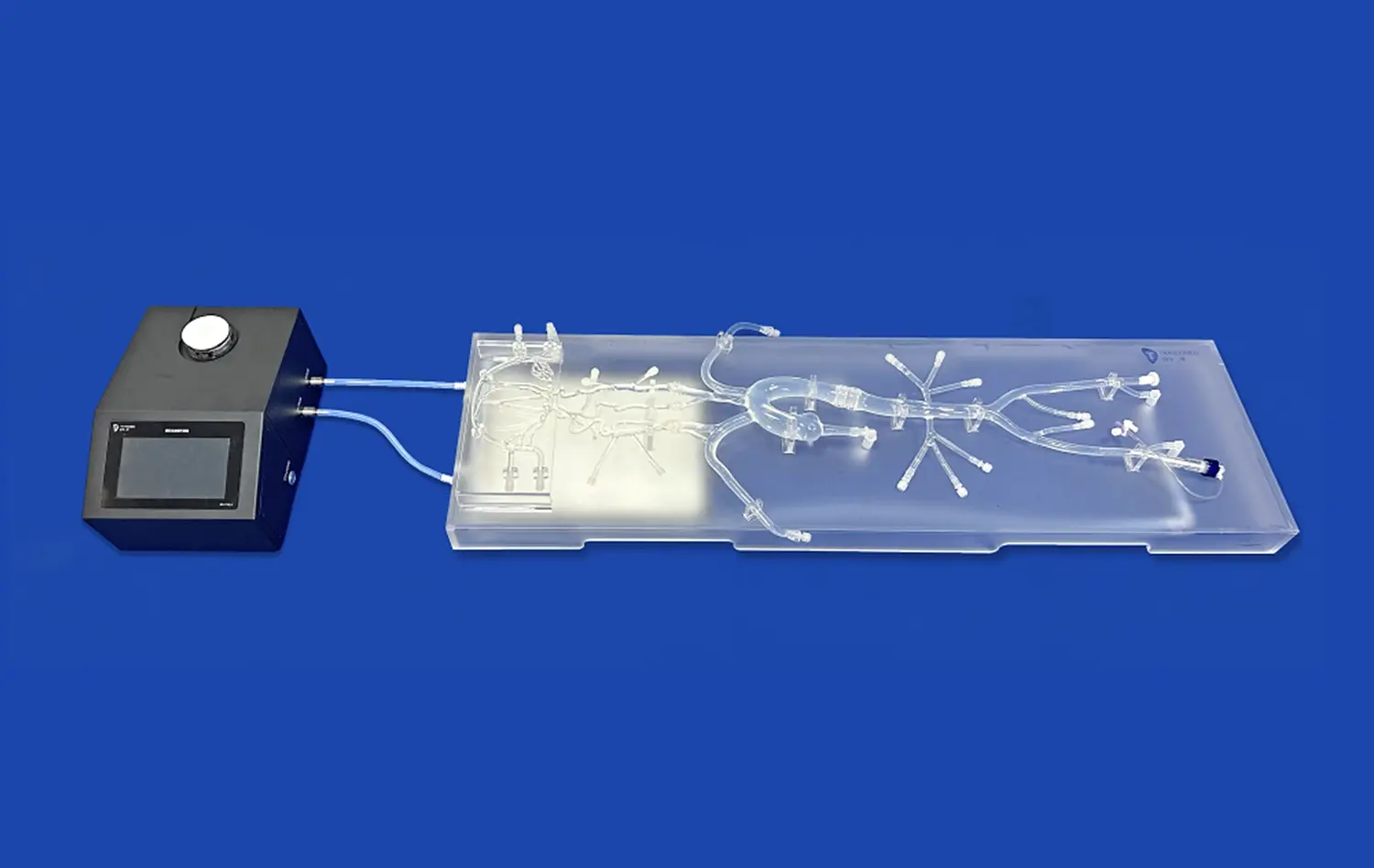
Today's 3D-printed models work perfectly with digital learning tools and simulation systems. This ability to work together makes it possible to mix hands-on VR experiences with a wide range of training programs. These immersive experiences create learning environments that improve student engagement and retention.
Selecting the Right 3D-Printed Human Stomach Model for Medical Training
Essential Evaluation Criteria
When institutions choose anatomical human stomach models for their programs, they need to think about a few important things. It is still very important to be anatomically correct so that students can learn from images that look like real human bodies. Interactive elements like removable parts and layered structures make the teaching experience better because they allow users to fully examine the anatomy of the stomach.
Supplier Assessment and Quality Assurance
It is important to look closely at a manufacturer's knowledge, production skills, and quality control methods in order to choose the right one. With more than 20 years of experience in medical 3D printing, Trandomed makes sure that all of their models meet strict standards for teaching quality. Our thorough quality control methods ensure that all goods work well and can be counted on all the time.
Customization and Scalability Options
Vendors that offer open customization services without extra design fees are helpful for today's schools. Being able to make models from CT or MRI data from an institution or come up with all-new designs is very helpful for specialized training programs. The ability to bulk buy and quick lead times of 7 to 10 days make sure that institutions can scale their programs while staying within budget.
Future Trends and the Growing Impact of 3D-Printed Models in Medical Education
Technological Integration and Innovation
The coming together of 3D printing with augmented and virtual reality will lead to amazing new ways of teaching medicine. These combined systems will offer new ways to learn by combining hands-on work with digital tools. This will create all-around training settings that are better than the old-fashioned ways of doing things.
Personalized Medical Training Solutions
Making anatomy models that are unique to each patient is a big step forward in planning surgeries and teaching medicine. By making models from data on each patient, schools can show students a range of different body types and diseases. This helps students get ready for the difficult work of seeing patients in real life.
Global Accessibility and Standardization
Better manufacturing methods and global shipping networks are making it easier for schools around the world to get their hands on high-quality anatomical models. By opening up educational materials to everyone, this move guarantees that all students can access better training tools, no matter where they are or how big their school is.
Trandomed's Advanced 3D-Printed Stomach Models for Medical Excellence
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. is a leader in new medical 3D printing technologies. They focus on making very accurate models of the human body that change the way that medicine is taught. After twenty years of work on making medical training tools that are both very realistic and can be used for many different purposes, we have now completed our human stomach model. Each model uses information from large sets of CT and MRI scans, which makes sure that they are accurate enough for the needs of today's medical training.
We can do more than just make things; we can also fully customize them. Our factory-direct method makes sure that production is quick and quality is high, whether institutions need models based on certain patient data or one-of-a-kind designs. The eco-friendly and non-toxic materials we use ensure safe frequent use while keeping the structure intact during long training sessions.
Our stomach models can be used in both study and educational settings with complex gastrointestinal device testing systems because they are so adaptable. Because our models can do two things at once, they are very useful for organizations that want a complete answer that can be used in different parts of their program.
Conclusion
The transformation of medical education through 3D-printed stomach models represents a paradigm shift toward more effective, engaging, and comprehensive training methodologies. These advanced tools address the limitations of traditional models while providing unprecedented opportunities for hands-on learning and skill development. The anatomical precision, durability, and customization capabilities of modern 3D-printed models make them indispensable components of contemporary medical curricula. As technology continues to evolve, institutions that embrace these innovations will provide their students with superior educational experiences that better prepare them for successful medical careers.
FAQs
How do 3D-printed stomach models compare to cadaveric specimens in terms of educational value?
3D-printed models offer consistent anatomical representation without the ethical, storage, or safety concerns associated with cadaveric materials. While cadavers provide authentic tissue properties, 3D-printed models deliver reliable, repeatable training experiences with customizable features that can demonstrate various pathological conditions not always available in cadaveric specimens.
Can institutions request models that demonstrate specific gastric pathologies or anatomical variations?
Absolutely. Modern 3D printing technology allows for comprehensive customization, including the representation of ulcers, tumors, anatomical anomalies, and various disease states. These custom features enhance training programs by exposing students to diverse clinical scenarios they will encounter in practice.
What maintenance requirements do 3D-printed stomach models have for long-term institutional use?
High-quality 3D-printed models require minimal maintenance beyond basic cleaning with standard disinfectants. The durable materials and construction ensure longevity through repeated handling, making them cost-effective investments for institutions with active training programs.
Transform Your Medical Training with Premium 3D-Printed Stomach Models
Elevate your institution's medical education program with Trandomed's industry-leading anatomical models designed for excellence in training and research. Our comprehensive range of 3D-printed stomach models delivers unmatched anatomical accuracy, durability, and educational value that transforms student learning experiences. With over 20 years of expertise in medical 3D printing innovation, we provide customized solutions that meet the unique requirements of medical schools, hospitals, and training centers worldwide.
As a trusted human stomach model manufacturer, we offer complete customization services without design costs, rapid 7-10 day lead times, and reliable global shipping through FedEx, DHL, EMS, UPS, and TNT. Our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction ensures that every model meets the highest standards for medical education. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com for detailed product information, customization consultations, or bulk order inquiries.
References
Anderson, M.J., et al. "Advanced 3D Printing Applications in Medical Education: A Comprehensive Analysis of Anatomical Model Effectiveness." Journal of Medical Education Technology, 2023.
Chen, L.K., & Rodriguez, P.M. "Comparative Study of Traditional vs. 3D-Printed Anatomical Models in Gastroenterology Training." Medical Training Innovation Review, 2022.
Thompson, R.A., et al. "Cost-Benefit Analysis of 3D-Printed Medical Models in Healthcare Education Institutions." Healthcare Education Economics Quarterly, 2023.
Williams, S.D., & Kumar, N. "Integration of 3D Printing Technology in Modern Medical Curricula: Best Practices and Implementation Strategies." Educational Technology in Medicine, 2022.
Park, J.H., et al. "Patient-Specific 3D Models for Enhanced Medical Training: A Multi-Institutional Study." Advanced Medical Simulation Journal, 2023.
Morrison, K.L., & Zhang, W. "Future Trends in Medical 3D Printing: Implications for Healthcare Education and Training." Innovation in Medical Education Review, 2023.