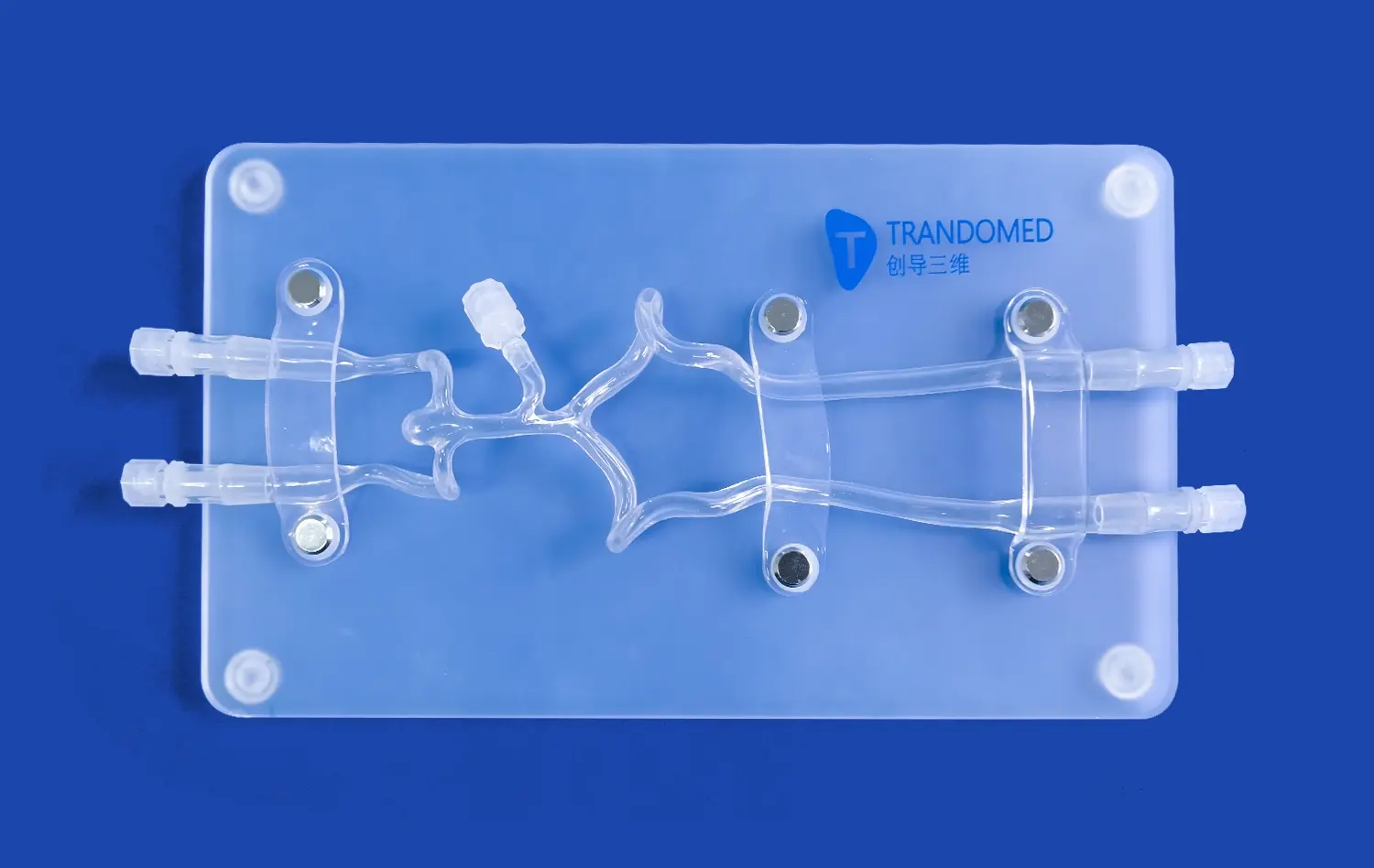
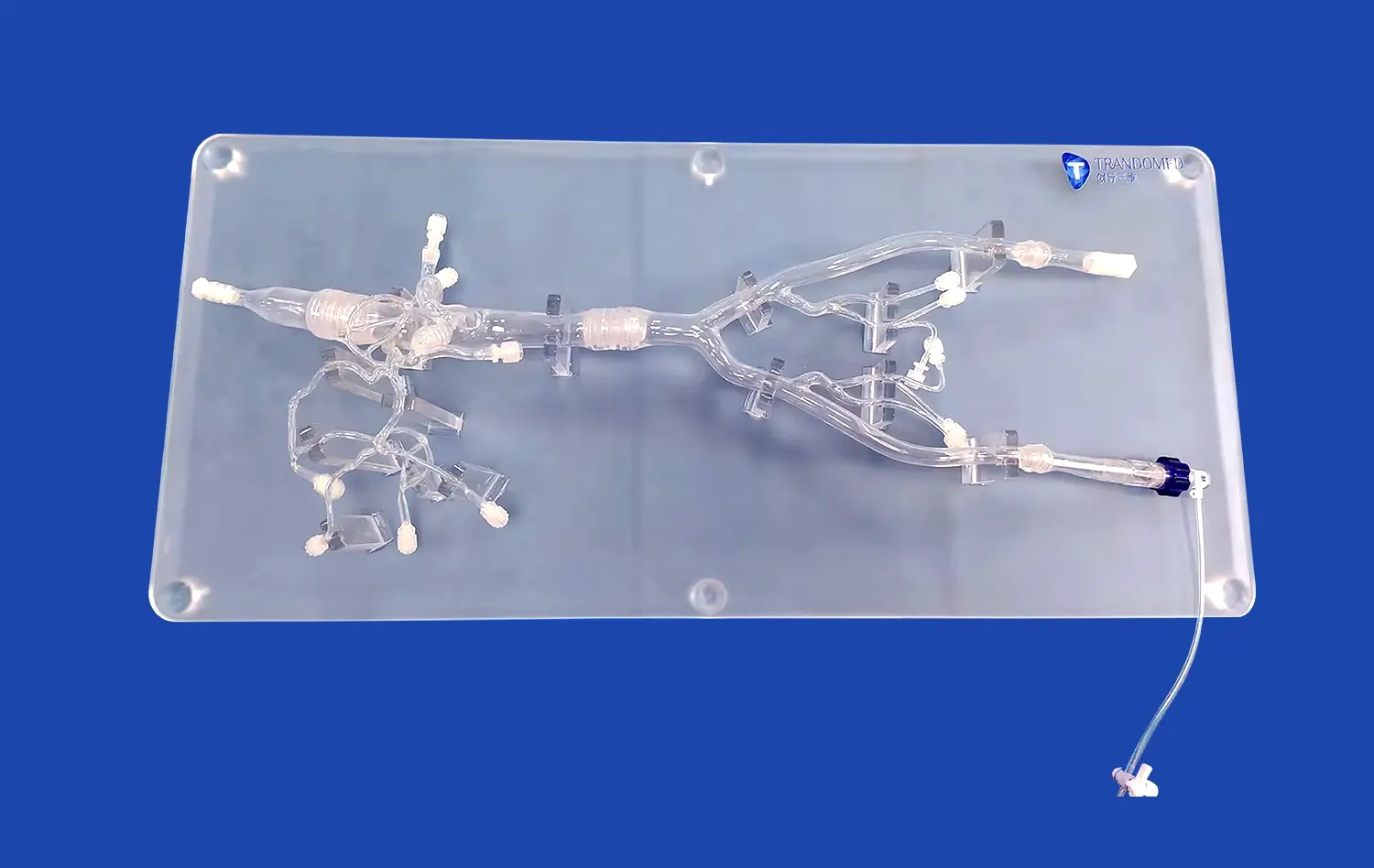
How Anatomical Precision Supports Curriculum Integration in Medical Schools?
Enhancing Visualization of Complex Arterial Networks
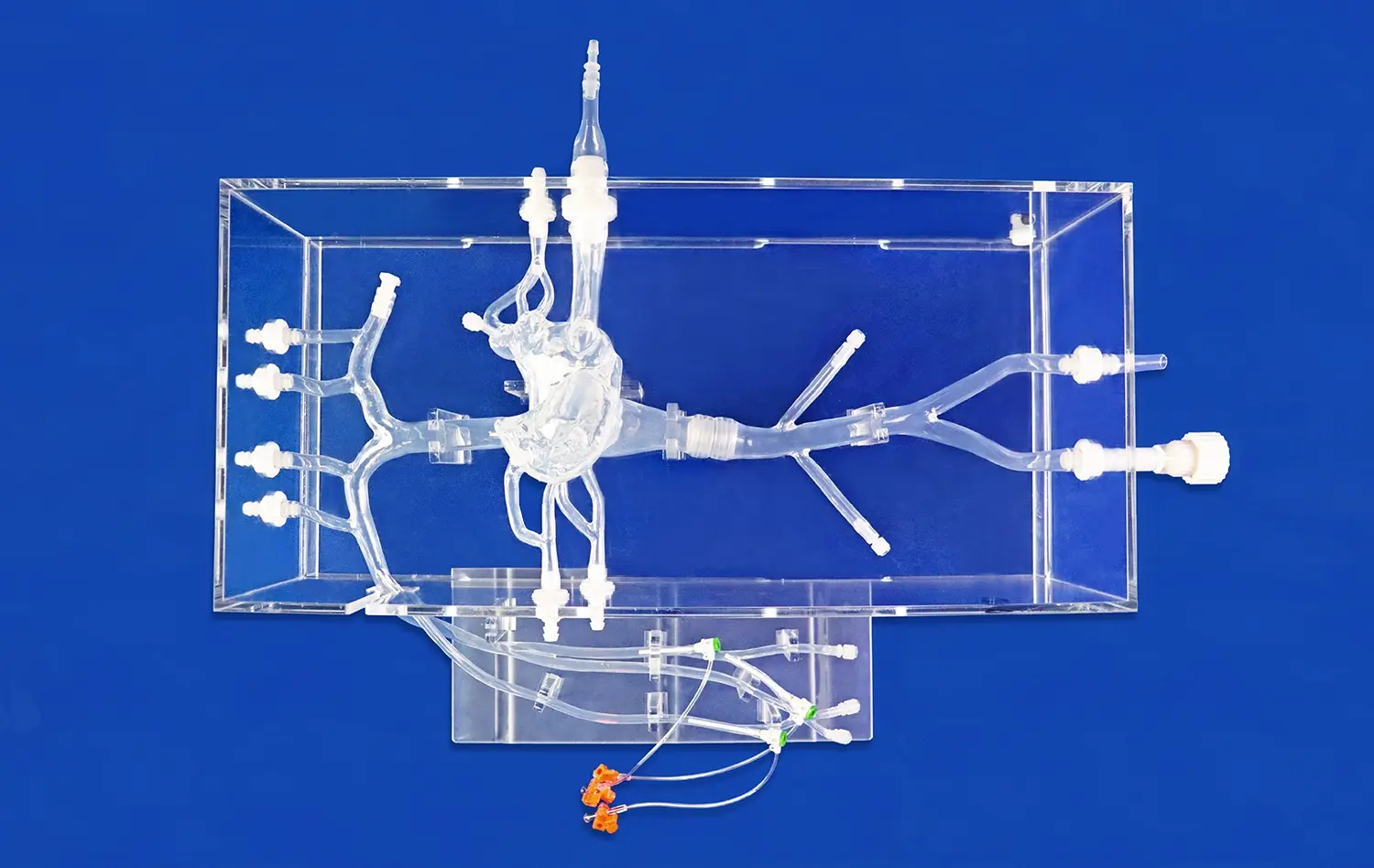
The intricate network of arteries in the lower extremities presents a significant challenge for medical students to comprehend fully. 3D-printed models derived from actual CT data offer unparalleled visualization of these complex structures. Students can observe the precise anatomical relationships between arteries, veins, and surrounding tissues, gaining a deeper understanding of vascular anatomy that textbooks alone cannot provide. This enhanced visualization allows for a more intuitive grasp of arterial pathways, branching patterns, and potential anatomical variations.
Facilitating Multidisciplinary Learning Approaches
Integrating 3D-printed arterial models, such as the lower extremity artery model, into medical curricula supports a multidisciplinary approach to learning. These models serve as valuable tools for various specialties, including vascular surgery, interventional radiology, and anatomy courses. By providing a common reference point, they encourage collaboration between different departments and foster a more holistic understanding of vascular health. This interdisciplinary utility ensures that students develop a well-rounded perspective on lower extremity vascular anatomy and its clinical implications across various medical fields.
Customizing Educational Experiences
The ability to create patient-specific models based on individual CT scans allows for customized educational experiences. Medical schools can develop case-based learning modules featuring unique anatomical variations or pathological conditions. This personalization of learning materials enables students to encounter a diverse range of scenarios they might face in clinical practice. By studying these tailored models, future healthcare professionals can better prepare for the anatomical diversity they will encounter in real patients, enhancing their diagnostic and treatment planning skills.
Hands-On Training with Realistic Vascular Structures
Simulating Endovascular Procedures
3D-printed lower extremity artery models excel in simulating endovascular procedures. These models, constructed from flexible materials like silicone, mimic the tactile feel and mechanical properties of real blood vessels. Trainees can practice catheter navigation, guidewire manipulation, and stent deployment in a risk-free environment. The ability to repeatedly perform these procedures on anatomically accurate models allows for skill refinement and muscle memory development, crucial for mastering complex interventional techniques.
Practicing Surgical Approaches
Beyond endovascular simulations, these models provide an excellent platform for practicing open surgical approaches. Vascular surgery trainees can hone their skills in arterial exposure, bypass grafting, and endarterectomy procedures. The models' realistic tissue properties enable students to experience the nuances of handling delicate vascular structures, tying sutures, and managing potential complications. This hands-on experience builds confidence and competence before trainees encounter real patients in the operating room.
Enhancing Ultrasound Imaging Skills
3D-printed arterial models also serve as valuable tools for developing ultrasound imaging skills. Students can practice identifying and assessing various arterial segments, measuring blood flow velocities, and detecting stenoses or occlusions. The ability to correlate ultrasound images with the physical model enhances understanding of sonographic principles and improves interpretation accuracy. This practical experience is invaluable for developing proficiency in non-invasive vascular diagnostics, a critical skill in modern vascular medicine.
What Educational Benefits Come from Using Advanced Artery Models?
Accelerating the Learning Curve
Advanced 3D-printed lower extremity artery models significantly accelerate the learning curve for medical students and residents. By providing tangible, three-dimensional representations of vascular anatomy, these models bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Learners can quickly grasp complex anatomical concepts that might take considerably longer to understand through traditional teaching methods alone. This accelerated comprehension allows for more efficient use of educational time and resources, enabling students to progress faster in their understanding of vascular medicine.
Improving Procedural Confidence and Competence
Repeated practice on realistic arterial models builds procedural confidence and competence among trainees. The ability to perform simulated interventions in a low-stress environment allows students to develop muscle memory and refine their techniques without the pressure of working on actual patients. This increased confidence translates into better performance in clinical settings, potentially reducing procedural times and improving patient outcomes. Moreover, the opportunity to practice on models representing various pathological conditions prepares trainees for a wide range of clinical scenarios they may encounter in their future practice.
Facilitating Objective Skill Assessment
3D-printed artery models provide an excellent platform for objective skill assessment in medical education. Educators can design standardized tests and performance metrics based on these models, allowing for consistent evaluation of students' procedural skills and anatomical knowledge. This objective assessment helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that graduates meet the required competency levels before entering clinical practice. Furthermore, the use of these models in assessment scenarios can help reduce the subjectivity often associated with evaluating procedural skills, leading to fairer and more accurate assessments of student capabilities.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D-printed lower extremity artery models into medical education represents a significant advancement in preparing future healthcare professionals. These models offer unparalleled anatomical precision, facilitate hands-on training with realistic vascular structures, and provide numerous educational benefits. By accelerating the learning curve, improving procedural confidence, and enabling objective skill assessment, these advanced simulators are transforming the landscape of vascular medicine education. As medical training continues to evolve, the role of 3D-printed arterial models in fostering competent, well-prepared healthcare professionals cannot be overstated.
Contact Us
Elevate your medical education program with Trandomed's cutting-edge 3D-printed lower extremity artery models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of advanced medical simulators, we offer unparalleled anatomical precision and customization options to meet your specific educational needs. Experience the benefits of our innovative technology and expert craftsmanship. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discover how our products can transform your vascular medicine training and prepare the next generation of healthcare professionals for success.
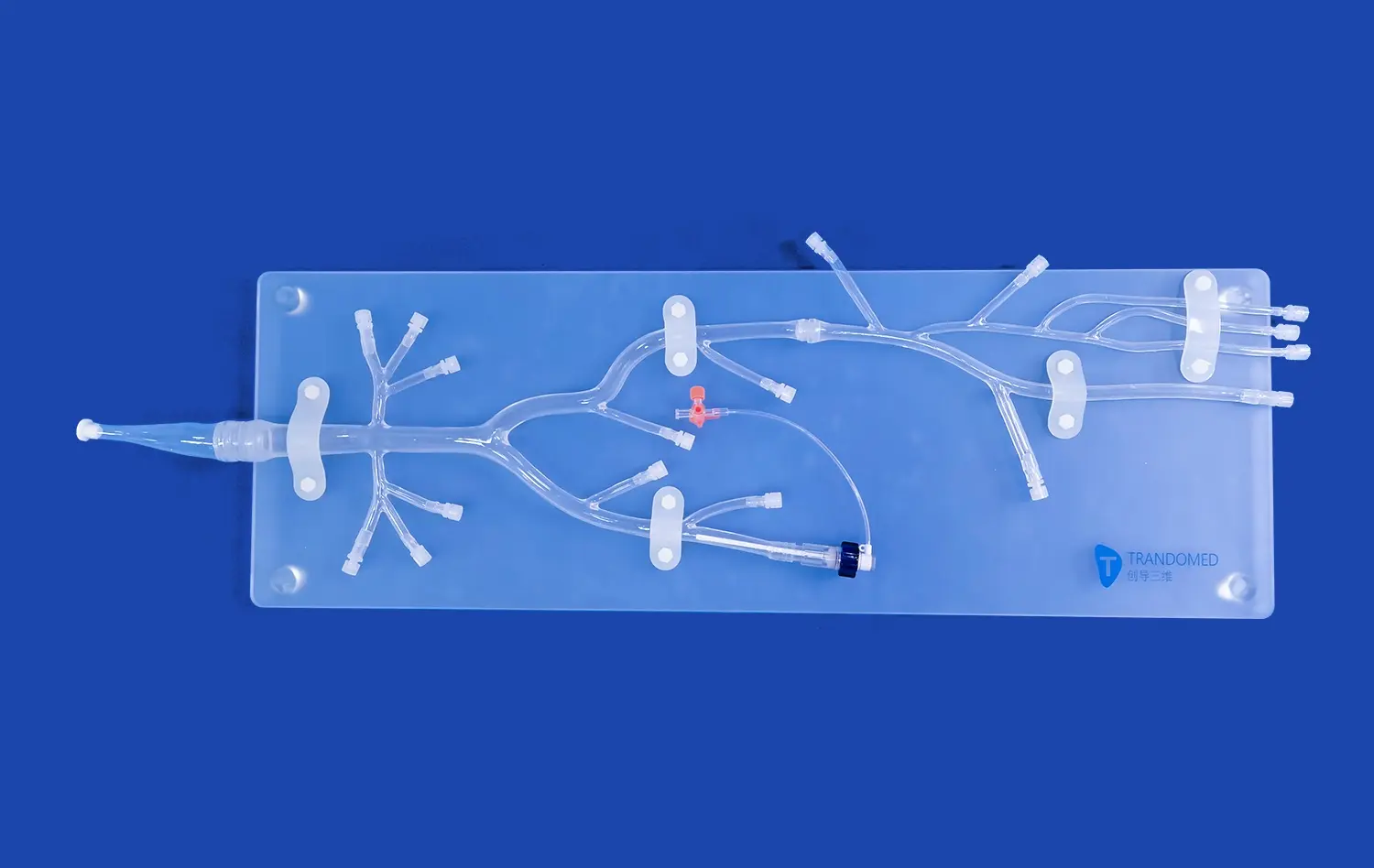
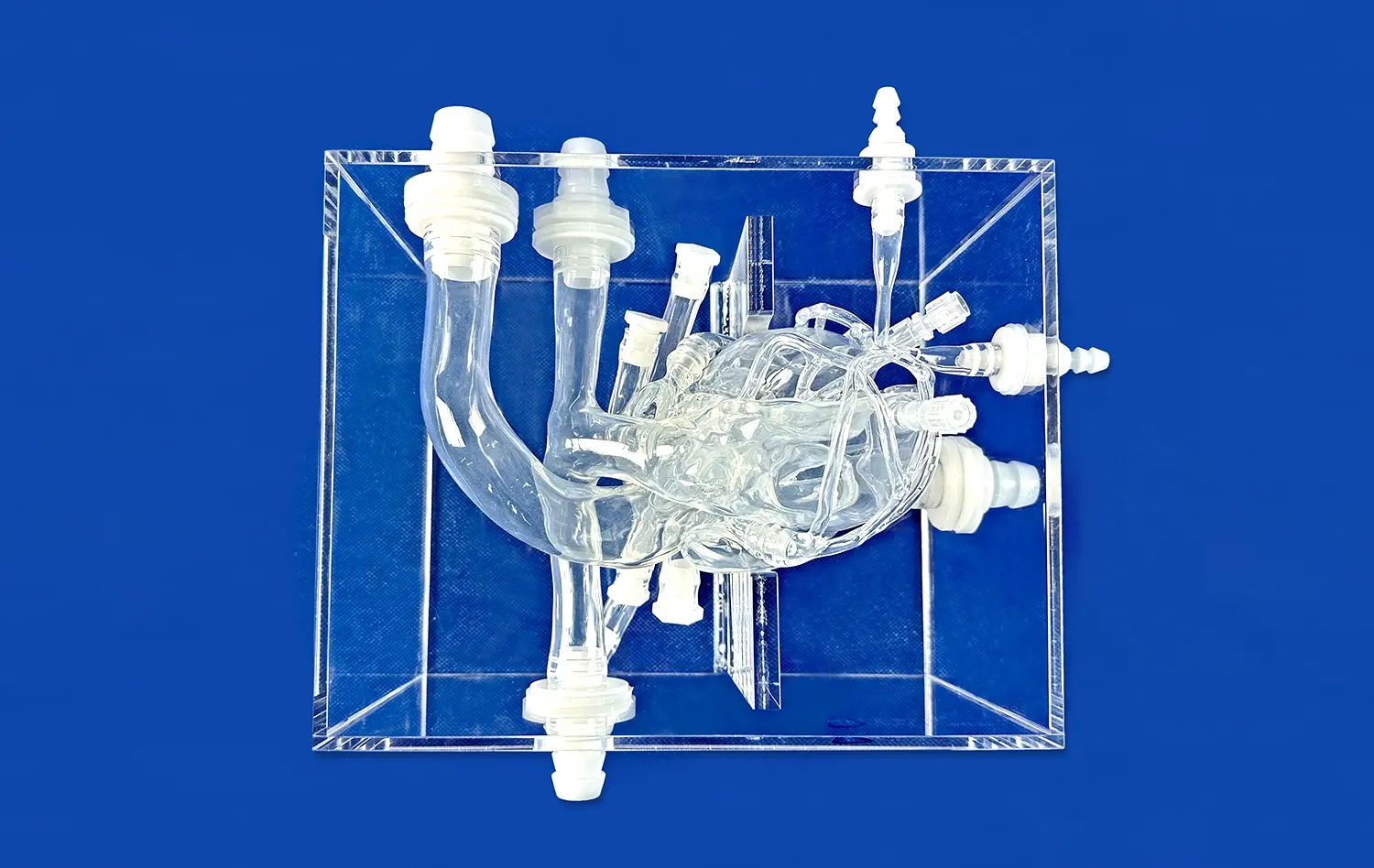
_1735798438356.webp)
1_1732869849284.webp)