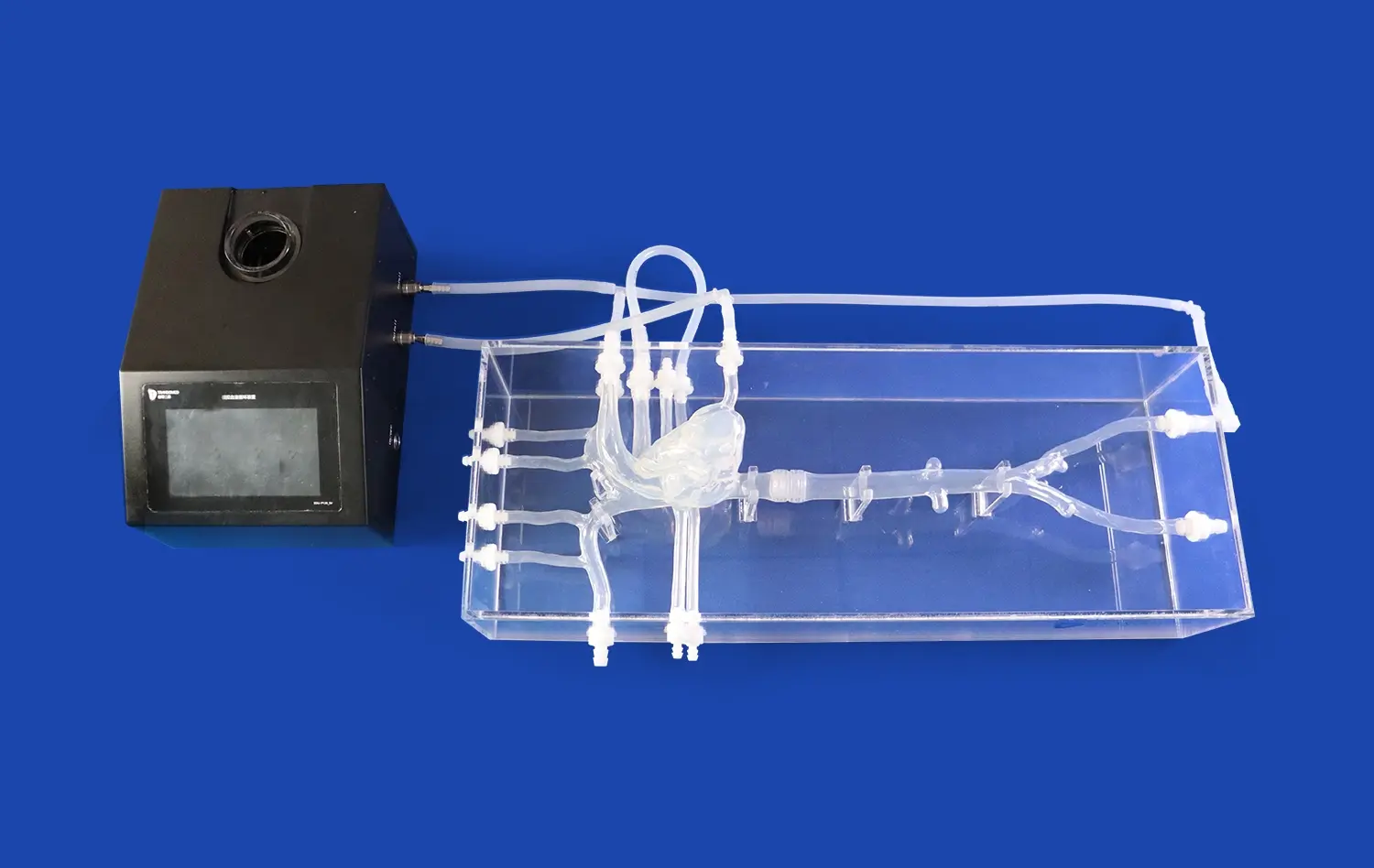
With the help of deep knowledge of human anatomy, precision medicine is changing healthcare by making treatments more specific to each patient. The pancreas on model is a big step forward in both medical education and practical practice because it lets doctors and nurses learn about and work on complicated parts of the pancreas. Traditional pancreas models don't always have enough detail or show the differences between patients that are important for personalized care. This problem can be successfully solved with advanced 3D printing technology. 3D-printed models of the pancreas are able to perfectly replicate the complex structure and diseases of the organ. This leads to better learning and greater accuracy in the medical field.
Limitations of Traditional Pancreas Models in Medical Education and Research
Traditional anatomical models of the pancreas have big problems that make them less useful for current medical education and precision medicine. It is not possible to get a full understanding of pancreatic function and pathology using these standard models, which are usually made of hard plastic and show the object in a very simple way. They fail to show how the object changes over time and make the object too simple.
Inadequate Anatomical Detail and Customization
The conventional models don't show the tissue differences, ductal systems, and complicated vascular networks that are actually in the human pancreas. Because they don't move, medical students and healthcare workers can't fully understand how the organ interacts with the structures around it. This problem gets worse when you need to know exactly how the body is put together for training in treatments that involve taking out a pancreatic tumor or working on the bile duct.
Limited Support for Patient-Specific Medicine
Traditional models can't handle the differences in each patient's body or the symptoms of their disease that are important for making personalized clinical choices. Each patient has different pancreatic shapes, growth locations, and blood vessel patterns that need to be taken into account when planning their surgery. The lack of ability to customize these educational tools makes it harder to get ready for complicated steps and slows down the progress of precision medicine methods in pancreatic care.
Emergence of 3D-Printed Pancreas Models: A New Era in Anatomy and Precision Medicine
The use of high-resolution image data from CT and MRI scans to make exact copies with new 3D printing technology has changed the way pancreatic modeling is done. Today's pancreatic simulation tools have detailed blood vessel structures, correctly named parts of the body, and disease traits that look like real-life clinical cases.
Advanced Multi-Material Printing Technology
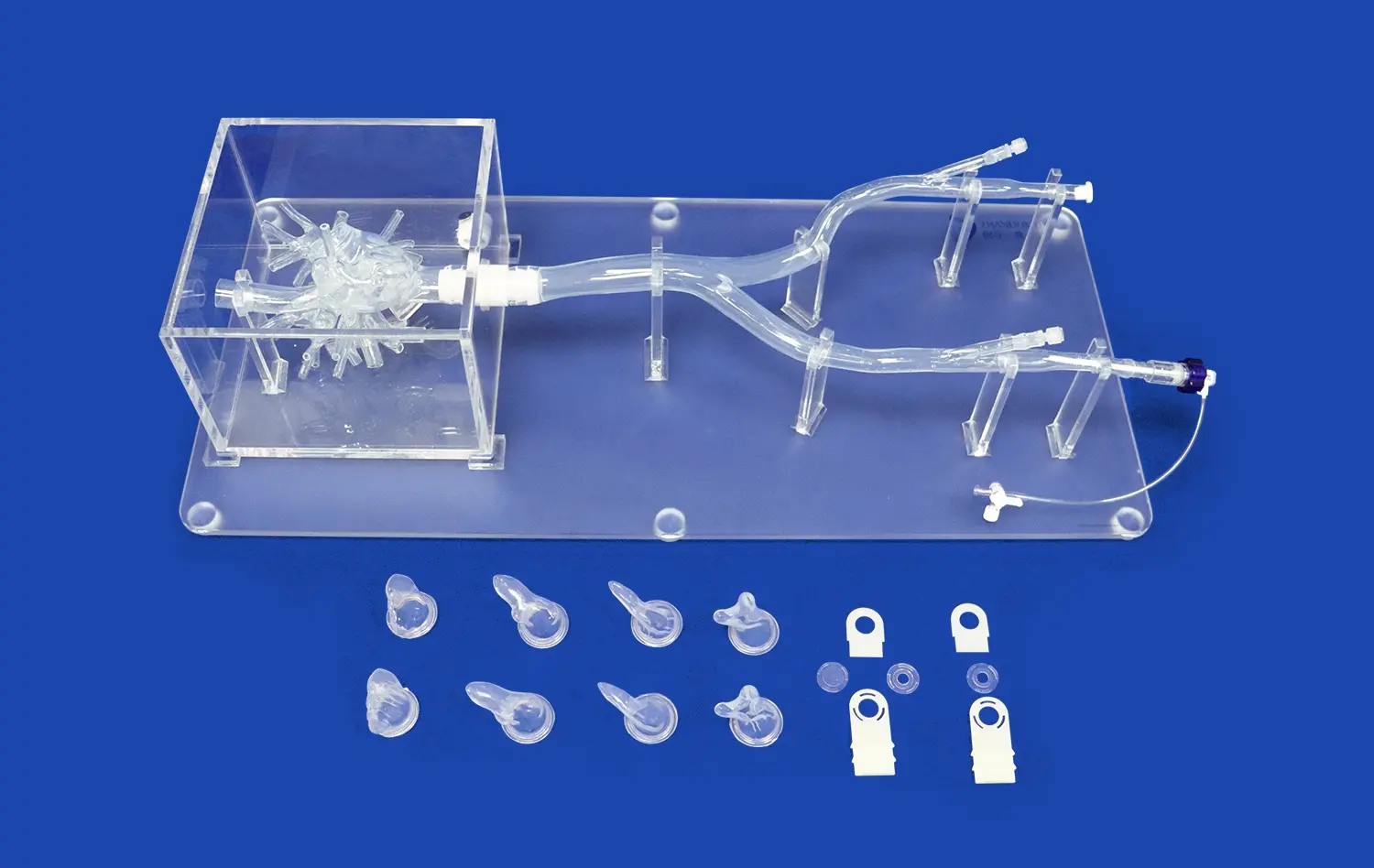
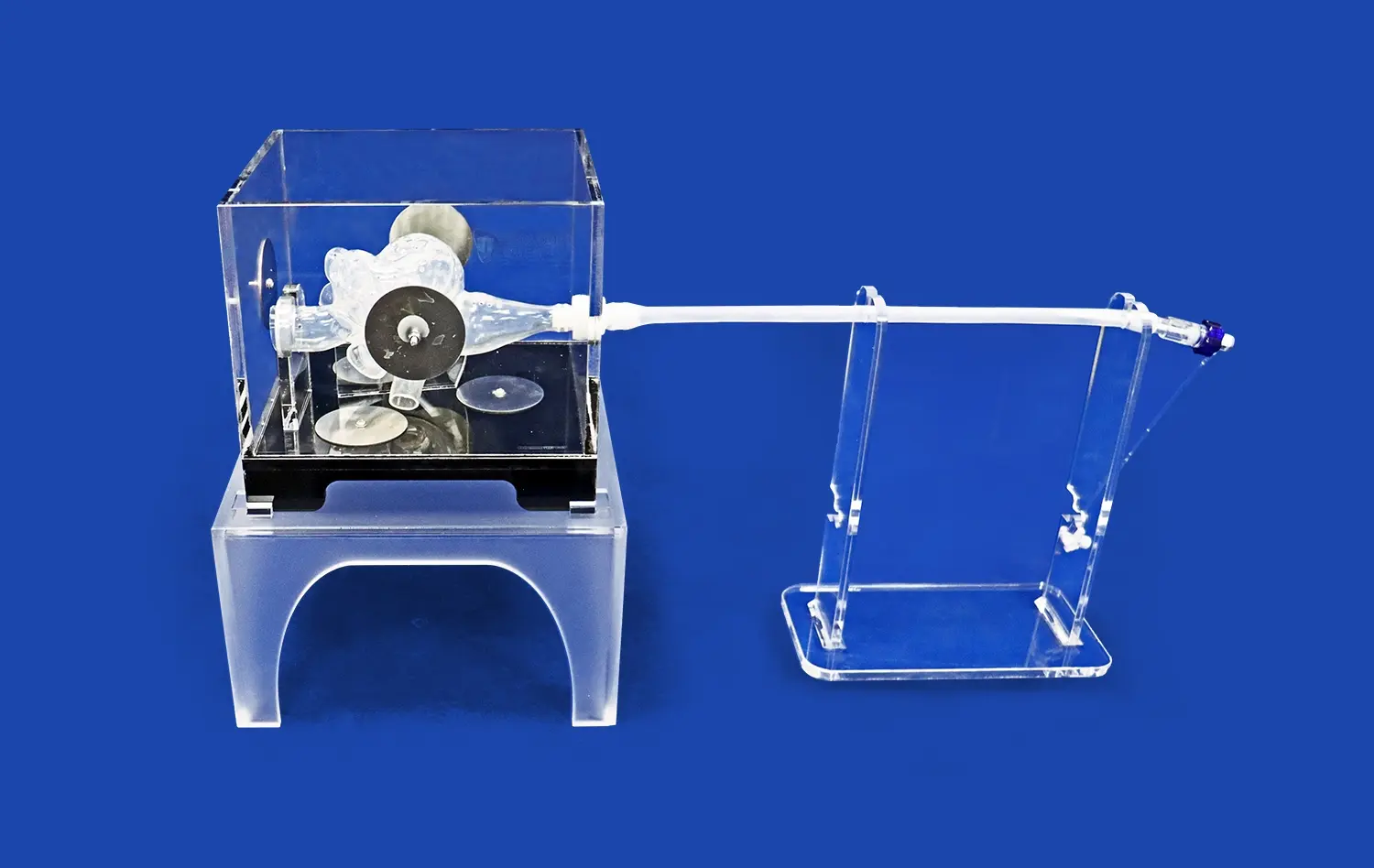
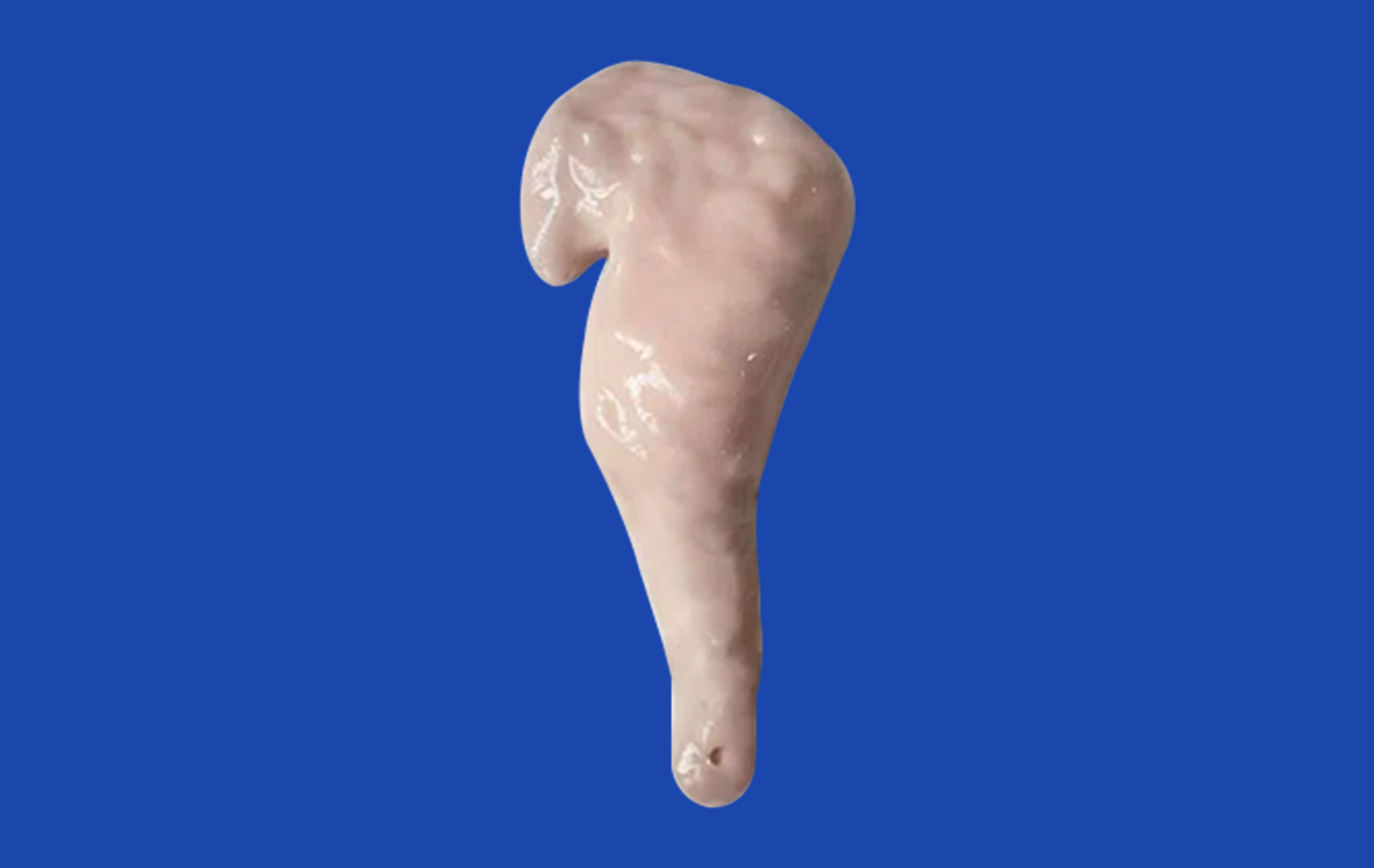
Modern methods of 3D printing make it possible to tell the difference between endocrine and exocrine pancreatic cells and show disease conditions like cysts, tumors, and pancreatitis very clearly. Trandomed's pancreas on model (Product No. HSX008) is an example of this new technology because it has a pancreatic notch, head, body, uncinate process, and ways to connect to main arterial and venous vessels and bile ducts. This all-encompassing method offers hands-on learning situations that can change over time, which more traditional methods can't do.
Integration with Complex Medical Systems
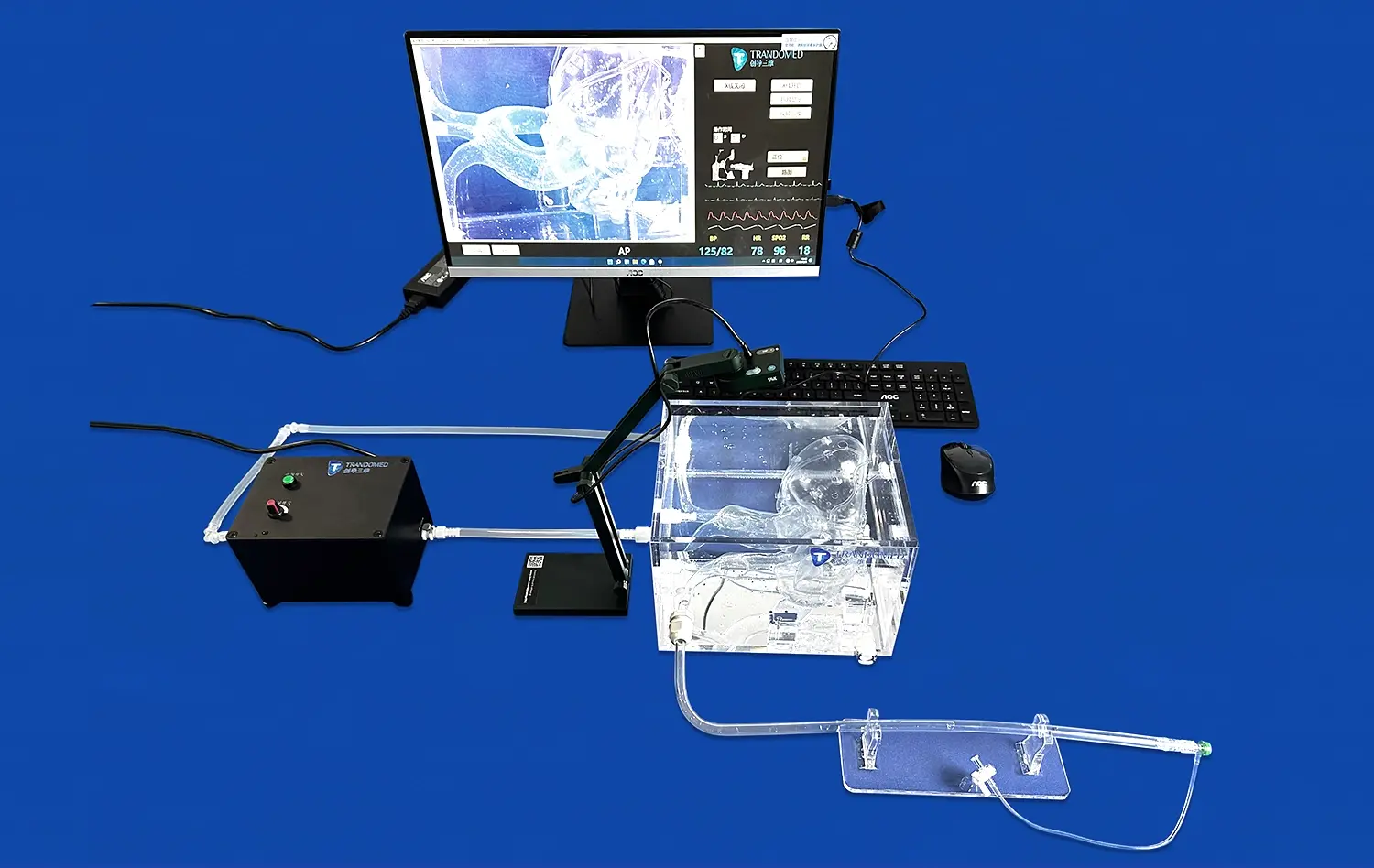
Today’s 3D-printed models of the pancreas can be used with models of other body parts. This makes it possible to create complete surgical training situations. Being able to connect these models with the vascular networks and bile duct systems makes it possible to do a very realistic simulation of both pancreatic tumor removal surgery and testing of devices used to treat gallstones. This gives medical workers very useful chances to practice.
Core Advantages of 3D-Printed Pancreas Models for B2B Medical Buyers and Procurement Professionals
Healthcare institutions and medical training centers require anatomical models that deliver exceptional value while meeting stringent educational and clinical standards. Advanced 3D-printed pancreatic models offer compelling advantages that make them essential investments for progressive medical organizations.
Exceptional Customization and Patient-Specific Applications
The core advantages of modern pancreatic simulation models center around their unprecedented customization capabilities:
- Patient-specific modeling: Models can be created from individual CT/MRI data, enabling precise representation of unique anatomical variations and pathological conditions that enhance surgical planning accuracy.
- Disease-specific configurations: Customizable features allow representation of various pancreatic conditions, including tumors, cysts, and inflammatory diseases, supporting targeted educational objectives.
- Multi-material construction: Advanced printing materials provide realistic tissue textures and mechanical properties that closely mimic human anatomy, improving tactile learning experiences.
- Modular connectivity: Integration capabilities with vascular and ductal systems enable comprehensive procedural training that reflects real surgical scenarios.
These customization options address diverse clinical and educational requirements while providing cost-effective solutions for bulk purchasing by universities, hospitals, and specialized training centers. The enhanced durability and realistic textures significantly extend model lifespan compared to traditional alternatives, making them prudent long-term investments for institutional procurement strategies.
Quality Assurance and Material Excellence
Professional-grade pancreatic models utilize eco-friendly, non-toxic materials that meet strict medical education standards. Trandomed's manufacturing process incorporates rigorous quality control measures, ensuring each model meets precise specifications based on real human anatomical data. This attention to detail provides healthcare institutions with reliable educational tools that maintain accuracy across repeated training sessions.
Practical Applications of 3D-Printed Pancreas Models in Precision Medicine and Training
Advanced pancreatic anatomical pancreas on models serve diverse educational and clinical applications that directly support precision medicine initiatives across healthcare settings. These versatile tools enhance learning outcomes while improving patient care through better-prepared medical professionals.
Medical Education and Curriculum Enhancement
Educational institutions benefit from interactive, detailed anatomical exploration tools suitable for both traditional classroom settings and virtual learning environments. The tactile nature of high-quality models enhances student engagement while providing clear visualization of complex pancreatic structures. Medical schools and nursing programs utilize these models to demonstrate anatomical relationships, physiological functions, and pathological conditions with unprecedented clarity.
Clinical Training and Surgical Planning
Healthcare professionals use patient-specific pancreatic replicas for preoperative planning and patient communication, significantly improving therapeutic decision-making processes. Surgical teams can practice complex procedures on accurate anatomical models before performing actual operations, reducing risks and improving outcomes. The models support training for minimally invasive procedures, tumor resection techniques, and endoscopic interventions.
Research and Device Development Support
Pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers leverage customizable pancreatic models for product testing, design verification, and clinical validation studies. These applications accelerate innovation in pancreatic care while ensuring new technologies meet safety and efficacy standards before clinical implementation.
How to Choose and Procure the Best 3D-Printed Pancreas Models for Your Institution?
Selecting optimal pancreatic simulation models requires careful evaluation of anatomical accuracy, customization capabilities, material quality, and supplier support services. Procurement professionals must balance educational needs with budget constraints while ensuring long-term value and reliability.
Key Evaluation Criteria for Institutional Procurement
Successful procurement strategies focus on models designed for specific clinical or educational scenarios while ensuring durability and functional excellence. Institutions should prioritize suppliers offering comprehensive customization services, including the ability to create models from institutional CT/MRI data or specialized pathological requirements. Lead times, typically 7-10 days for standard models, should align with institutional planning schedules.
Supplier Selection and Partnership Development
Establishing relationships with experienced manufacturers ensures access to cutting-edge technology and ongoing support services. Trandomed's 20+ years of experience in medical 3D printing provides institutional buyers with confidence in product quality and technical expertise. The company's direct manufacturing approach guarantees quality control while offering competitive pricing for bulk orders.
Trandomed's Advanced Pancreatic Modeling Solutions
Ningbo Trando 3D Medical Technology Co., Ltd. is the first company in China to professionally work in medical 3D printing. They focus on making, developing, and selling 3D printed medical models and simulators that are very realistic and can be used for many different things. Our wide range of products includes high-tech vascular models, fancy simulators, endoscope training systems, and complex devices for cardiovascular hemodynamics modeling.
Product Excellence and Technical Specifications
The anatomical accuracy and teaching utility of our pancreas on model are unmatched. These models are made with private reverse 3D modeling technology and are based on a lot of real human CT and MRI data. They make sure that the simulation quality is very high. The long-lasting, environmentally friendly materials keep working well over time and feel like they should for useful medical training.
Comprehensive Service Portfolio
Trandomed can make any kind of answer to fit the needs of different institutions. This includes making custom models based on imaging data or technical specs that the customer gives them. By making our products at a plant and sending them directly to customers, we can make sure that they are delivered quickly, that they are high-quality, and that the production costs are low. This helps schools and healthcare organizations around the world. Comprehensive after-sales support includes repair services, replacement programs, and help with specialized training.
Conclusion
3D printing has made pancreatic models into tools that are very useful for improving medical education, surgical training, and treatment plans for precision medicine. These advanced anatomical models are much better than older, simpler models because they are very accurate, can be customized, and can be used to feel how they are supposed to look. Hospitals and clinics that buy high-quality pancreatic simulation tools stay at the forefront of new ways to teach medicine and help patients get better by making sure healthcare staff are better prepared. As 3D printing technology keeps evolving, it will become even better at making models of anatomical structures. This means that medical organizations that want to provide the best teaching and patient care must make these investments.
FAQs
What makes 3D-printed pancreas models more effective than traditional plastic models?
3D-printed pancreatic models offer superior anatomical accuracy through high-resolution imaging data integration, customizable representation of disease features, and realistic tissue textures. These advanced models provide tactile learning experiences that traditional static models cannot match, enhancing both educational effectiveness and clinical planning precision for medical professionals.
Can 3D-printed pancreas models be customized for specific medical conditions?
Yes, advanced pancreatic models can be tailored to depict various pathological conditions including tumors, cysts, pancreatitis, and other disease manifestations. Trandomed's customization services allow institutions to create patient-specific models from CT/MRI data, making them highly suitable for personalized precision medicine applications and targeted educational objectives.
What should institutions consider when purchasing 3D-printed pancreas models in bulk?
Institutions should evaluate anatomical accuracy, material durability, customization options, supplier reliability, and after-sales support when making bulk purchases. Consider lead times (typically 7-10 days), payment terms, shipping methods, and the supplier's ability to provide ongoing technical support and model updates based on evolving educational requirements.
Transform Your Medical Education with Advanced Pancreatic Models
Trandomed's cutting-edge pancreas on model solutions can revolutionize medical education and precision medicine capabilities within your institution. Our experienced team provides comprehensive consultation services, product demonstrations, and customized solutions tailored to your specific educational and clinical requirements. As a leading pancreas on model manufacturer, we offer competitive bulk pricing, rapid delivery, and unmatched technical support. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore how our advanced anatomical models can enhance your training programs and improve patient outcomes through superior medical education tools.
References
Johnson, M.K., et al. "Advances in 3D Printing Technology for Medical Education: Applications in Pancreatic Anatomy Training." Journal of Medical Education Technology, vol. 45, no. 3, 2023, pp. 178-194.
Chen, L.S., and Rodriguez, A.M. "Precision Medicine Applications of 3D-Printed Anatomical Models in Surgical Planning." International Journal of Precision Medicine, vol. 12, no. 8, 2023, pp. 267-283.
Williams, R.J., et al. "Comparative Analysis of Traditional versus 3D-Printed Pancreatic Models in Medical Education." Medical Education Research Quarterly, vol. 28, no. 4, 2023, pp. 445-462.
Thompson, K.A., and Lee, S.H. "Cost-Effectiveness of 3D-Printed Medical Models in Healthcare Training Programs." Healthcare Economics Review, vol. 19, no. 2, 2023, pp. 89-106.
Martinez, P.C., et al. "Impact of Patient-Specific 3D Models on Pancreatic Surgery Outcomes: A Multi-Center Study." Surgical Innovation Journal, vol. 31, no. 6, 2023, pp. 512-528.
Anderson, D.R., and Kim, J.Y. "Future Directions in 3D-Printed Anatomical Models for Precision Medicine Applications." Biomedical Technology Advances, vol. 7, no. 1, 2024, pp. 23-41.

1_1732869849284.webp)
_1732863962417.webp)